win10下使用mmdet训练自己的数据模型
win10下使用mmdet训练自己的数据模型
- 1.环境配置
- 2.制作自己的coco数据集
- 3.进行训练
- 4.计算测试图像的交并比
- 参考文献
1.环境配置
1.查看自己cuda版本:

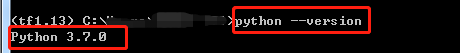
2.查看自己python版本
3.安装pytorch
官方地址,按自己的选择复制粘贴到自己的python虚拟环境中。安装完之后在自己的虚拟环境中打开python,输入import torch,如果没有报错,说明自己的pytorch安装成功。
4.安装mmcv和mmdet
在自己虚拟环境中输入pip install mmcv(或者pip install mmcv-full)和pip install mmdet
。如果自己的电脑报错的话可以先安装pycocotools电脑要有visual C++。不过我的电脑没有报错,应该是新版本的会自己下载吧。其实按照git上的步骤应该就是没有问题的。
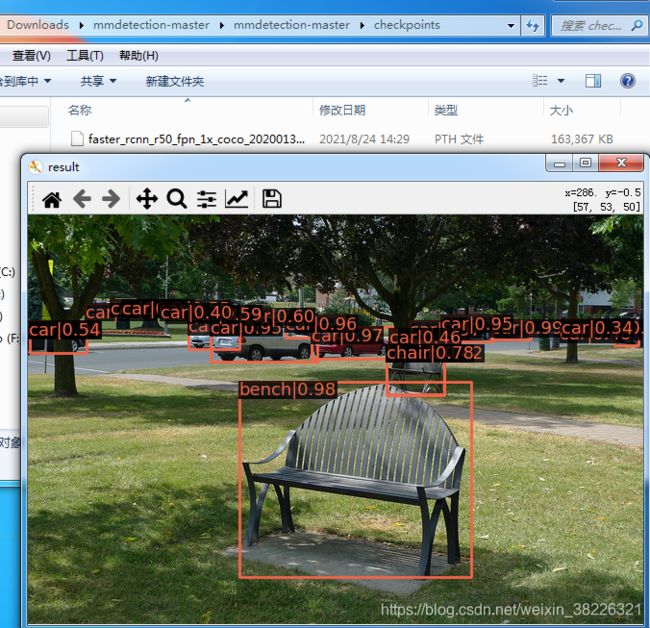
5.测试是否安装成功下载权重文件,我把他放在了新建的文件夹checkoints中,然后修改并运行以下代码
# coding=utf-8
#改三处
import mmcv
from mmdet.apis import init_detector
from mmdet.apis import inference_detector
from mmdet.apis import show_result_pyplot
# from mmdet.models.detectors.base import BaseDetector
# 模型配置文件
config_file = r'C:\Users\ROBOT-773\Desktop\Downloads\mmdetection-master\mmdetection-master\configs\faster_rcnn\faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco.py'#1.改1,这里是你fork的文件夹里面的config文件
# 预训练模型文件
# url: https://download.openmmlab.com/mmdetection/v2.0/faster_rcnn/faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco/faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco_20200130-047c8118.pth
checkpoint_file = r'C:\Users\ROBOT-773\Desktop\Downloads\mmdetection-master\mmdetection-master\checkpoints\faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco_20200130-047c8118.pth'#改2,这里是刚刚下载的权重文件
# 通过模型配置文件与预训练文件构建模型
model = init_detector(config_file, checkpoint_file, device='cuda:0')
# 测试单张图片并进行展示
# img = '/home/cv/mmdetection/my_pictures/cars1.jpeg'
img=r'C:\Users\ROBOT-773\Desktop\Downloads\mmdetection-master\mmdetection-master\demo\demo.jpg'#改3,这里是图片的地址
result = inference_detector(model, img)
show_result_pyplot(model, img, result)
# 测试一个图像列表并保存结果图像
# imgs = ['test1.jpg', 'test2.jpg', 'test3.jpg']
# for i, result in enumerate(inference_detector(model, imgs)):
# show_result_pyplot(model, imgs[i], result)
"""
#
# (3)测试视频和显示测试结果
video = mmcv.VideoReader('demo/Venice-2.mp4')
for frame in video:
result = inference_detector(model, frame)
show_result(frame, result, model.CLASSES, wait_time=1)
"""
2.制作自己的coco数据集
应该是voc和coco数据集都可以,我自己是用了coco数据集。将自己的图片分成训练集和测试集,然后用labelimg分别生成各自的xml文件,然后用下列代码,将xml文件生成json文件
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
import json
coco = dict()
coco['images'] = []
coco['type'] = 'instances'
coco['annotations'] = []
coco['categories'] = []
category_set = dict()
image_set = set()
category_item_id = 0
image_id = 20210000000
annotation_id = 0
def addCatItem(name):
global category_item_id
category_item = dict()
category_item['supercategory'] = 'none'
category_item_id += 1
category_item['id'] = category_item_id
category_item['name'] = name
coco['categories'].append(category_item)
category_set[name] = category_item_id
return category_item_id
def addImgItem(file_name, size):
global image_id
if file_name is None:
raise Exception('Could not find filename tag in xml file.')
if size['width'] is None:
raise Exception('Could not find width tag in xml file.')
if size['height'] is None:
raise Exception('Could not find height tag in xml file.')
image_id += 1
image_item = dict()
image_item['id'] = image_id
image_item['file_name'] = file_name
image_item['width'] = size['width']
image_item['height'] = size['height']
coco['images'].append(image_item)
image_set.add(file_name)
return image_id
def addAnnoItem(object_name, image_id, category_id, bbox):
global annotation_id
annotation_item = dict()
annotation_item['segmentation'] = []
seg = []
# bbox[] is x,y,w,h
# left_top
seg.append(bbox[0])
seg.append(bbox[1])
# left_bottom
seg.append(bbox[0])
seg.append(bbox[1] + bbox[3])
# right_bottom
seg.append(bbox[0] + bbox[2])
seg.append(bbox[1] + bbox[3])
# right_top
seg.append(bbox[0] + bbox[2])
seg.append(bbox[1])
annotation_item['segmentation'].append(seg)
annotation_item['area'] = bbox[2] * bbox[3]
annotation_item['iscrowd'] = 0
annotation_item['ignore'] = 0
annotation_item['image_id'] = image_id
annotation_item['bbox'] = bbox
annotation_item['category_id'] = category_id
annotation_id += 1
annotation_item['id'] = annotation_id
coco['annotations'].append(annotation_item)
def parseXmlFiles(xml_path):
for f in os.listdir(xml_path):
if not f.endswith('.xml'):
continue
bndbox = dict()
size = dict()
current_image_id = None
current_category_id = None
file_name = None
size['width'] = None
size['height'] = None
size['depth'] = None
xml_file = os.path.join(xml_path, f)
print(xml_file)
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
root = tree.getroot()
if root.tag != 'annotation':
raise Exception('pascal voc xml root element should be annotation, rather than {}'.format(root.tag))
# elem is , , ,
for elem in root:
current_parent = elem.tag
current_sub = None
object_name = None
if elem.tag == 'folder':
continue
if elem.tag == 'filename':
file_name = elem.text
if file_name in category_set:
raise Exception('file_name duplicated')
# add img item only after parse tag
elif current_image_id is None and file_name is not None and size['width'] is not None:
if file_name not in image_set:
current_image_id = addImgItem(file_name, size)
print('add image with {} and {}'.format(file_name, size))
else:
raise Exception('duplicated image: {}'.format(file_name))
# subelem is , , , ,
for subelem in elem:
bndbox['xmin'] = None
bndbox['xmax'] = None
bndbox['ymin'] = None
bndbox['ymax'] = None
current_sub = subelem.tag
if current_parent == 'object' and subelem.tag == 'name':
object_name = subelem.text
if object_name not in category_set:
current_category_id = addCatItem(object_name)
else:
current_category_id = category_set[object_name]
elif current_parent == 'size':
if size[subelem.tag] is not None:
raise Exception('xml structure broken at size tag.')
size[subelem.tag] = int(subelem.text)
# option is , , , , when subelem is
for option in subelem:
if current_sub == 'bndbox':
if bndbox[option.tag] is not None:
raise Exception('xml structure corrupted at bndbox tag.')
bndbox[option.tag] = int(option.text)
# only after parse the
if bndbox['xmin'] is not None:
if object_name is None:
raise Exception('xml structure broken at bndbox tag')
if current_image_id is None:
raise Exception('xml structure broken at bndbox tag')
if current_category_id is None:
raise Exception('xml structure broken at bndbox tag')
bbox = []
# x
bbox.append(bndbox['xmin'])
# y
bbox.append(bndbox['ymin'])
# w
bbox.append(bndbox['xmax'] - bndbox['xmin'])
# h
bbox.append(bndbox['ymax'] - bndbox['ymin'])
print('add annotation with {},{},{},{}'.format(object_name, current_image_id, current_category_id,
bbox))
addAnnoItem(object_name, current_image_id, current_category_id, bbox)
if __name__ == '__main__':
xml_path = r'C:\Users\ROBOT-773\Desktop\cs\KM1\XML\test'
json_file = r'C:\Users\ROBOT-773\Desktop\cs\KM1\XML\test.json'
parseXmlFiles(xml_path)
json.dump(coco, open(json_file, 'w'))
3.进行训练
1.先fork商汤的mmdetection,运行python setup.py install。
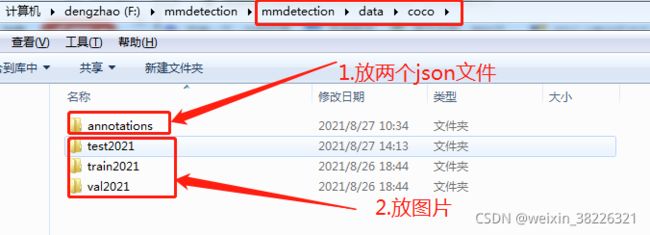
2.在mmdetction文件下新建data/coco文件夹,如图
3.修改文件(这里我用faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco.py文件为例,其实就是修改这个py文件里面的num_classes和classes)
3.1修改mmdetection/mmdet/datasets/coco.py文件里面的CLASSES为自己标签。
3.2修改mmdetection/mmdet/core/evaluation/class_names.py文件里面的coco_classes为自己的标签。
3.3修改F:\mmdetection\mmdetection\configs_base_\models\faster_rcnn_r50_fpn.py的num_classes为自己的类别个数。
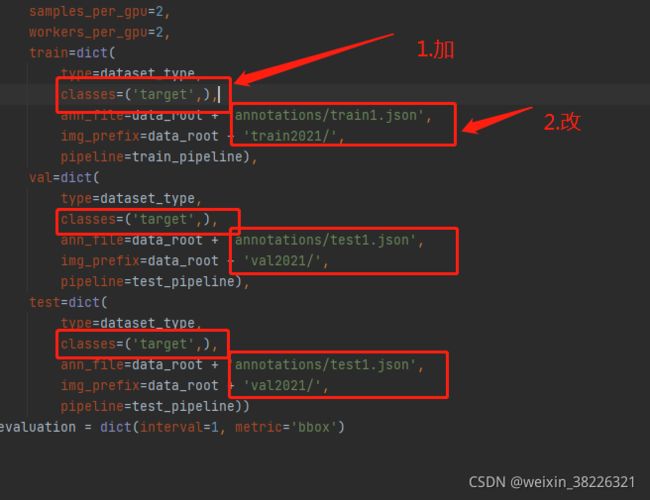
3.4修改F:\mmdetection\mmdetection\configs_base_\datasets\coco_detection.py里面的如图所示,还有data_root最好换成绝对路径。
然后再运行一次python setup.py install,再运行如下进行训练。
python tools/train.py configs/faster_rcnn/faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco.py
测试模型
python tools/test.py configs/faster_rcnn/faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco.py work_dirs/faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco/latest.pth --eval bbox --show
可以查看xml文件画到图片上的效果,用xml_to_jpg.py
import os
import cv2 as cv
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
def xml_to_jpg(imgs_path, xmls_path, out_path):
imgs_list = os.listdir(imgs_path) #读取图片列表
xmls_list = os.listdir(xmls_path) # 读取xml列表
if len(imgs_list) <= len(xmls_list): #若图片个数小于或等于xml个数,从图片里面找与xml匹配的
for imgName in imgs_list:
temp1 = imgName.split('.')[0] #图片名 例如123.jpg 分割之后 temp1 = 123
temp1_ = imgName.split('.')[1] #图片后缀
if temp1_!='jpg':
continue
for xmlName in xmls_list: #遍历xml列表,
temp2 = xmlName.split('.')[0] #xml名
temp2_ = xmlName.split('.')[1]
if temp2_ != 'xml':
continue
if temp2!=temp1: #判断图片名与xml名是否相同,不同的话跳过下面的步骤 继续找
continue
else: #相同的话 开始读取xml坐标信息,并在对应的图片上画框
img_path = os.path.join(imgs_path, imgName)
xml_path = os.path.join(xmls_path, xmlName)
img = cv.imread(img_path)
labelled = img
root = ET.parse(xml_path).getroot()
for obj in root.iter('object'):
bbox = obj.find('bndbox')
xmin = int(bbox.find('xmin').text.strip())
ymin = int(bbox.find('ymin').text.strip())
xmax = int(bbox.find('xmax').text.strip())
ymax = int(bbox.find('ymax').text.strip())
labelled = cv.rectangle(labelled, (xmin, ymin), (xmax, ymax), (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv.imwrite(out_path + '\\' +imgName, labelled)
break
else: # 若xml个数小于图片个数,从xml里面找与图片匹配的。下面操作与上面差不多
for xmlName in xmls_list:
temp1 = xmlName.split('.')[0]
temp1_ = xmlName.split('.')[1]
if temp1_ != 'xml':
continue
for imgName in imgs_list:
temp2 = imgName.split('.')[0]
temp2_ = imgName.split('.')[1] # 图片后缀
if temp2_ != 'jpg':
continue
if temp2 != temp1:
continue
else:
img_path = os.path.join(imgs_path, imgName)
xml_path = os.path.join(xmls_path, xmlName)
img = cv.imread(img_path)
labelled = img
root = ET.parse(xml_path).getroot()
for obj in root.iter('object'):
bbox = obj.find('bndbox')
xmin = int(bbox.find('xmin').text.strip())
ymin = int(bbox.find('ymin').text.strip())
xmax = int(bbox.find('xmax').text.strip())
ymax = int(bbox.find('ymax').text.strip())
labelled = cv.rectangle(labelled, (xmin, ymin), (xmax, ymax), (0, 0, 255), 1)
cv.imwrite(out_path + '\\' +imgName, labelled)
break
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 使用英文路径,中文路径读不进来
imgs_path =r'C:\Users\ROBOT-773\Desktop\cs\KM1\3c_img' #图片路径
xmls_path = r'C:\Users\ROBOT-773\Desktop\cs\KM1\XML\test' #xml路径
retangele_img_path =r'C:\Users\ROBOT-773\Desktop\cs\KM1\XML\test_label' #保存画框后图片的路径
xml_to_jpg(imgs_path, xmls_path, retangele_img_path)
4.计算测试图像的交并比
先测试图片,并保存测试的bbox值
#改6处
from mmdet.apis import inference_detector, init_detector
import cv2
import os
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import csv
from tqdm import tqdm
import time
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "7"
class Model():
def __init__(self, root_config, root_checkpoint, **kwargs):
self.model = init_detector(root_config, root_checkpoint) # 模型初始化
self.thr_ok = kwargs.get('thr_ok', 0.05)
self.classes = kwargs.get('classes', None)
self.color = self.get_color()
self.img_foramt = ['.jpg', '.JPG', '.bmp', '.png']
def get_color(self):
color = dict(red=(0, 0, 255),
green=(0, 255, 0),
blue=(255, 0, 0),
cyan=(255, 255, 0),
yellow=(0, 255, 255),
magenta=(255, 0, 255),
white=(255, 255, 255),
black=(0, 0, 0))
return color
def model_test(self, result, img_name, classes, thr_ok=0.05):
output_bboxes = []
json_dict = []
total_bbox = []
for id, boxes in enumerate(result): # loop for categories
category_id = id + 1
if len(boxes) != 0:
for box in boxes: # loop for bbox
conf = box[4]
if conf > thr_ok:
total_bbox.append(list(box) + [category_id])
bboxes = np.array(total_bbox)
best_bboxes = bboxes
output_bboxes.append(best_bboxes)
for bbox in best_bboxes:
coord = [round(i, 2) for i in bbox[:4]]
conf = bbox[4]
category = classes[int(bbox[5]) - 1] if classes is not None else int(bbox[5])
json_dict.append({'img_name': img_name, 'cats': category, 'bbox': coord, 'score': conf})
det_df = pd.DataFrame(json_dict, columns=['img_name', 'cats', 'bbox', 'score'])
return det_df
def single_test(self, root_img): # 单张图片模型测试
img = cv2.imread(root_img)
model_result = inference_detector(self.model, img)
return model_result
def run(self, img_root):
model_result = self.single_test(img_root)
img_name = self.get_strfile(img_root, pos=-1)
result_df = self.model_test(model_result, img_name, self.classes, thr_ok=self.thr_ok)
img_name_lst, cat_lst, box_lst, score_lst = self.pd2lst(result_df)
return img_name_lst, cat_lst, box_lst, score_lst
def pd2lst(self, result_df):
img_name_lst, cat_lst, box_lst, score_lst = [], [], [], []
if len(result_df) > 0:
for i in range(len(result_df)):
img_name_lst.append(result_df.loc[i]['img_name'])
cat_lst.append(result_df.loc[i]['cats'])
box_lst.append(result_df.loc[i]['bbox'])
score_lst.append(result_df.loc[i]['score'])
return img_name_lst, cat_lst, box_lst, score_lst
def draw_bbox(self, img, cat_lst, box_lst, score_lst,
bbox_color='green',
text_color='green',
thickness=1,
font_scale=0.5
):
for j, cat in enumerate(cat_lst):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = np.array(box_lst[j]).astype(np.int32)
bbox_color_new = self.color[bbox_color]
cv2.rectangle(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), bbox_color_new, thickness=thickness)
score = round(score_lst[j], 4)
text_color_new = self.color[text_color]
label_text = '{}:{}'.format(str(cat), str(score))
cv2.putText(img, label_text, (x1, y1 - 2), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, font_scale, text_color_new)
return img,x1,y1,x2,y2
def get_strfile(self, file_str, pos=-1):
# 得到file_str / or \\ 的最后一个名称
endstr_f_filestr = file_str.split('\\')[pos] if '\\' in file_str else file_str.split('/')[pos]
return endstr_f_filestr
def build_dir(self,out_dir):
# 构建文件
if not os.path.exists(out_dir):
os.makedirs(out_dir)
return out_dir
def show_img(self,img):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
def get_files_root(root):
'''
:return: 寻找root下面有文件夹的路径,输出所有文件夹绝对路径的列表
'''
files_lst = [root]
result_lst = files_lst
if build_files(root) == []:
result_lst = files_lst
else:
is_while = True
files_all_path = [file for file in files_lst]
while is_while:
for file_root in files_lst:
F1 = build_files(file_root)
for F1 in F1:
files_all_path.append(F1)
is_while = False
# 排除主文件夹
record = np.ones((len(files_all_path)))
for i, F3 in enumerate(files_all_path):
F3 = files_all_path[i]
for j, F4 in enumerate(files_all_path):
if F3 + '\\' in F4 or F3 + '/' in F4:
record[i] = 0
break
# 将需要循环聚集
files_lst = []
for i, F3 in enumerate(files_all_path):
if record[i] == 1:
files_lst.append(F3)
# 判断是否有子文件夹
for F4 in files_lst:
file_judge = build_files(F4)
if file_judge != []:
is_while = True
break
result_lst = files_lst
return result_lst
def build_files(root):
'''
:得到该路径下的所有文件
'''
files = [os.path.join(root, file) for file in os.listdir(root)]
files_true = []
for file in files:
if not os.path.isfile(file):
files_true.append(file)
return files_true
def single_main(model,root_img,work_dir,csv_bb):
# 一张图片测试所有集合
img_name_lst, cat_lst, box_lst, score_lst = model.run(root_img) #
img = cv2.imread(root_img)
img,x1,y1,x2,y2 = model.draw_bbox(img, cat_lst, box_lst, score_lst)
file_name = model.get_strfile(root_img, pos=-2)
out_file = model.build_dir(os.path.join(work_dir, file_name))
img_name = model.get_strfile(root_img, pos=-1)
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(out_file, img_name), img)
csv_bb.append([img_name,x1,y1,x2,y2])
return csv_bb
def main(root,model,work_dir):
root_files=get_files_root(root)
csv_bb = []
num=0
for file_path in tqdm(root_files):
for name in tqdm(os.listdir(file_path)):
if name[-4:] in model.img_foramt:
root_img=os.path.join(file_path,name)
csv_bb=single_main(model,root_img,work_dir,csv_bb)
num+=1
print('num of images:',num)
f = open(r'F:\mmdetection\mmdetection\data\coco\test2021_gen.csv', 'w')#改6,生成目标框xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax的csv
writer = csv.writer(f)
for i in csv_bb:
writer.writerow(i)
f.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
root_config = r'F:\mmdetection\mmdetection\configs\faster_rcnn\faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco.py'#改1,配置文件
root_checkpoint = r'F:\mmdetection\mmdetection\work_dirs\faster_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_coco\latest.pth'#改2,模型生成文件
root = r'F:\mmdetection\mmdetection\data\coco\test2021' # 改3,测试文件夹
work_dir=r'F:\mmdetection\mmdetection\data\coco\test2021_gen'#改4,测试生成文件夹
info = {'classes': None}#改5,目标名称
time_start = time.time()
model = Model(root_config, root_checkpoint, **info) # 类实列化,也是初始化
# img_name_lst, cat_lst, box_lst, score_lst = model.run(root_img) #单张图片的预测
main(root, model, work_dir)
time_end=time.time()
time_gap=time_end-time_start
print('time gap:',time_gap)
然后读取测试文件的xml和测试出来的csv文件,计算交并比。
import csv
import pandas as pd
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
import glob
#读xml文件的bbox
os.chdir(r'C:\Users\ROBOT-773\Desktop\cs\KM1\XML\test1')
def xml_bbox(path):
xml_list = []
for xml_file in glob.glob(path + '\\*.xml'):
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
#print(tree)
root = tree.getroot()
#hh=root.findall('object')
#print(hh[0][0].text)
#print(root.find('size')[0])
for member in root.findall('object'):
#print(member,member[0].text)
try:
value = (root.find('filename').text,
int(root.find('size')[0].text),
int(root.find('size')[1].text),
member[0].text,
int(member[4][0].text),
int(member[4][1].text),
int(member[4][2].text),
int(member[4][3].text)
)
except:
pass
#print(value)
xml_list.append(value)
#column_name = ['filename', 'width', 'height', 'class', 'xmin', 'ymin', 'xmax', 'ymax']
#xml_df = pd.DataFrame(xml_list, columns=column_name)
return xml_list
#读csv文件的bbox
def csv_bbox(path,name):
with open(path,'r') as f:
csv.list=[]
reader=csv.reader(f)
for row in reader:
if row == []:
continue
if row[0] == name:
return row
#根据两个bbox计算交并比
def calculate_IoU(predicted_bound, ground_truth_bound):
px1, py1, px2, py2 = map(float,predicted_bound)
print("预测框P的坐标是:({}, {}, {}, {})".format(px1, py1, px2, py2))
gx1, gy1, gx2, gy2 = map(float,ground_truth_bound)
print("原标记框G的坐标是:({}, {}, {}, {})".format(gx1, gy1, gx2, gy2))
parea = (px2 - px1) * (py2 - py1) # 计算P的面积
garea = (gx2 - gx1) * (gy2 - gy1) # 计算G的面积
print("预测框P的面积是:{};原标记框G的面积是:{}".format(parea, garea))
x1 = max(px1, gx1)
y1 = max(py1, gy1)
x2 = min(px2, gx2)
y2 = min(py2, gy2)
w = x2 - x1
h = y2 - y1
if w <=0 or h <= 0:
return 0
area = w * h # G∩P的面积
print("G∩P的面积是:{}".format(area))
# 并集的面积 = 两个矩形面积 - 交集面积
IoU = area / (parea + garea - area)
return IoU
def main():
iou_list=[]
xml_path = r'C:\Users\ROBOT-773\Desktop\cs\KM1\XML\test1'
csv_path=r'F:\mmdetection\mmdetection\data\coco\test2021_gen.csv'
#xmls_list = os.listdir(xml_path) # 读取xml列表
#for xmlname in xmls_list:
# temp2 = xmlname.split('.')[0] # xml名
xml_list = xml_bbox(xml_path)
for xml in xml_list:
csv_df = csv_bbox(csv_path,xml[0])
IoU = calculate_IoU( (xml[4],xml[5],xml[6],xml[7]), (csv_df[1], csv_df[2], csv_df[3], csv_df[4]))
iou_list.append(IoU)
print("IoU是:{}".format(IoU))
print(iou_list)
print(sum(iou_list)/350)
if __name__ =="__main__":
main()
参考文献
【1】https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42341590/article/details/119511297
【2】https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41690533/article/details/115868856
【3】https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33897832/article/details/103995636
【4】https://www.cnblogs.com/tangjunjun/p/14847291.html