【DeepLab系列】 DeepLabV3中的ASPP(Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling)模块搭建
【DeepLab系列】 DeepLabV3中的ASPP模块搭建
1 前言
DeepLab V3 原文:ASPP is inspired by the success of spatial pyramid pooling,which showed that it is effective to resample features at different scales for accurately and efficiently classifying regions of an arbitrary scale.
翻译:ASPP模块的应用是受SPP模块的启发,它能够通过不同尺度的卷积核对特征进行采样,能够准确、高效地对任意尺度的区域进行分类。
2 代码实现
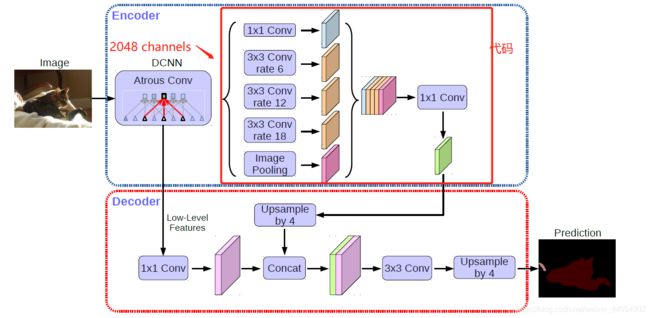
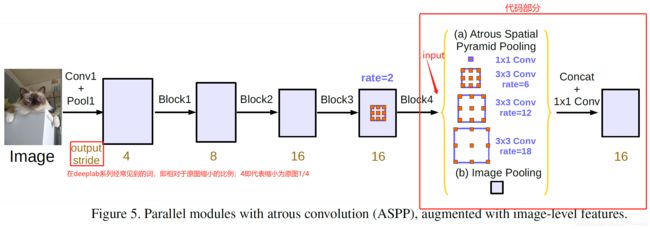
2.1 ASPP模块流程图
说明:图片来自DeepLabV3 Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation
2.1 代码
- 说明:图片来自DeepLabV3+ Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation
- 说明:该代码针对的是DeepLabV3+中,DCNN的Exit Flow输出为2048通道,则该代码输入为2048,使用需要进行微调。
class ASPP_module(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(ASPP_module, self).__init__()
# 定义空洞率,根据图示空洞率为1 6 12 18 ,说明:当空洞率为1时为普通卷积
dilations = [1, 6, 12, 18]
self.Aspp1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=(1,1),padding=0,
dilation=dilations[0], bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU())
self.Aspp2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels = in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=(3,3),
# padding与dilation相同原因:当原始卷积核为3x3时,使输入输出尺寸大小相同,计算见3中说明。
padding=dilations[1],dilation=dilations[1], bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU()
)
self. Aspp3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=(3, 3),
padding=dilations[2], dilation=dilations[2], bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.Aspp4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=(3, 3),
padding=dilations[3], dilation=dilations[3], bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.global_avg_pool = nn.Sequential(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)),
# 输入通道2048,原因:deeplab v3+ 在进去ASPP前为2048
nn.Conv2d(2048, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU()
)
# concat后通道为1280,用1x1卷积改变通道数
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1280, 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
# 初始化卷积核权重
self._init_weight()
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.Aspp1(x); print("X1.shape", x1.size())
x2 = self.Aspp2(x); print("X2.shape", x2.size())
x3 = self.Aspp3(x); print("X3.shape", x3.size())
x4 = self.Aspp4(x); print("X4.shape", x4.size())
x5 = self.global_avg_pool(x); print('x5.shape', x5.size())
# 利用双线性插值恢复x5的尺寸,再进行concat
x5 = F.interpolate(x5, size=x4.size()[2:], mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
cat = torch.cat((x1, x2, x3, x4, x5), dim=1);print('cat.shape', cat.size())
# 此处的output,包含后面1x1卷积进行的通道数调整
output = self.conv1(cat)
output = self.bn1(output);print('output.shape', output.size())
return output
def _init_weight(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n)) # 初始化卷积核方式
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
m.weight.data.fill_(1)
m.bias.data.zero_()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 测试输出尺寸使用
aspp = ASPP_module(2048, 256)
input = torch.randn(2, 2048, 176, 240);print('input_size:', input.size())
out = aspp(input)
- 输出结果:
input_size: torch.Size([2, 2048, 176, 240])
X1.shape torch.Size([2, 256, 176, 240])
X2.shape torch.Size([2, 256, 176, 240])
X3.shape torch.Size([2, 256, 176, 240])
X4.shape torch.Size([2, 256, 176, 240])
x5.shape torch.Size([2, 256, 1, 1])
cat.shape torch.Size([2, 1280, 176, 240])
output.shape torch.Size([2, 256, 176, 240])
3. 常见问题
3.1 为什么在本文aspp子模块中,padding需要与dilation相同?
前提:需要有空洞卷积的基础知识。
self.Aspp2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels = in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=(3,3),
# padding与dilation相同原因:当原始卷积核为3x3时,使输入输出尺寸大小相同,计算见说明。
padding=dilations[1],dilation=dilations[1], bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU()
)
解释: 在Aspp2,3,4中的卷积都是使用空洞卷积(Atrous Convolution)进行的,且原始卷积核为3x3,对于其它大小的原始卷积核大小,请自行计算。