python 强化学习Q-Learning 算法简单应用
Algorithm 3. The SARSA algorithm.
1:Let be a set of states, and (), ∈ , be a set of actions available in the state .
2:Initialize(,),∈,isnotterminal,∈()arbitrarily
3:Initialize and
4:for each game do
5: Initialize a nonterminal state 0 at random
6: Select 0 under the policy 0(|0)
7: ←0
8: for each step of the game until a stopping criterion is reached or until
is a nonterminal state, do
9: Take action , find +1, transition to +1
10: if +1 is a terminal state, then
11: (, ) ← (, ) + (+1 − (, ))
12: else
13: Select +1 under the policy +1(|+1)
14: (, ) ← (, ) + (+1 + (+1, +1) − (, ))
15: end if
16: ← (+1)
17: end if
18:end for
#程序包含以下内容
#使用SARSA方法,进行40000场冰湖游戏
#使用训练完的模型进行游戏
#画出智能体的移动路径
epsilon = 0.1 # Epsilon parameter which is used in epsilon-greedy strategy
gamma = 0.9 # Discount coefficient gamma
random_seed = 2 #Random seed
time_delay = 1 # Time delay when rendering the game process after training (seconds)
lr_rate = 0.9 #Learning rate alpha
import time
# %% md
# %%SARSA
import gym
import numpy as np
import time
from IPython.display import clear_output
def generate_random_map(size, p, sd):
"""Generates a random valid map (one that has a path from start to goal)
:param size: size of each side of the grid
:param p: probability that a tile is frozen
"""
valid = False
np.random.seed(sd)
# DFS to check that it's a valid path.
def is_valid(res):
frontier, discovered = [], set()
frontier.append((0, 0))
while frontier:
r, c = frontier.pop()
if not (r, c) in discovered:
discovered.add((r, c))
directions = [(1, 0), (0, 1), (-1, 0), (0, -1)]
for x, y in directions:
r_new = r + x
c_new = c + y
if r_new < 0 or r_new >= size or c_new < 0 or c_new >= size:
continue
if res[r_new][c_new] == 'G':
return True
if (res[r_new][c_new] not in '#H'):
frontier.append((r_new, c_new))
return False
while not valid:
p = min(1, p)
res = np.random.choice(['F', 'H'], (size, size), p=[p, 1 - p])
res[0][0] = 'S'
res[-1][-1] = 'G'
valid = is_valid(res)
return ["".join(x) for x in res]
# Map generation
random_map = generate_random_map(size=6, p=0.8, sd=random_seed) # Create our map
env = gym.make("FrozenLake-v0", desc=random_map, is_slippery=False) # Initialize environment
print("Your map")
env.render() # Render the map
def choose_action(state):
action = 0
if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < epsilon:
action = np.random.randint(0, env.action_space.n) # ***
else:
action = np.random.choice(np.array(np.argwhere(Q[state, :] == np.amax(Q[state, :])).flatten().tolist()))
return action
def learn(state, state2, reward, action, action2, done):
if done is True:
Q[state, action] = Q[state, action] + lr_rate * (reward - Q[state, action])
else:
Q[state, action] = Q[state, action] + lr_rate * (reward + gamma *Q[state2, action2] - Q[state, action])
# Q[state, action] = #Your code here
from tqdm import tqdm
# Inititalization
np.random.seed(random_seed)
total_games = 40000
max_steps = 100
Q = np.zeros((env.observation_space.n, env.action_space.n))
# Main cycle
game1 = [0] * total_games
for game in tqdm(range(total_games)):
state = env.reset()
t = 0
action = choose_action(state)
while t < max_steps:
# env.render()
t += 1
state2, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
if t == max_steps:
done = True
action2 = choose_action(state2)
learn(state, state2, reward, action, action2, done)
state = state2
action = action2
if done:
if reward == 1:
game1[game] = 1
break
def get_fg_and_v(game):
v = 0
fg = 0
i = 0
l = []
for g in game:
if g == 1:
v = v + 1
if len(l) == 0:
l.append(i)
else:
if len(l) < 5:
if l[-1] - i == -1:
l.append(i)
else:
l = [i]
if len(l) == 5 and fg == 0:
fg = i + 1
i = i + 1
return fg, v
fg, v = get_fg_and_v(game1)
# 1
print("The number of victories in a series of 10,000 games: ", v) # Your code here
# 2
print("Five wins in a row were first won in the game ", fg) # Your code here
import time
# Greedy action selection
def choose_action_one_game(state):
action = np.random.choice(np.array(np.argwhere(Q[state, :] == np.amax(Q[state, :])).flatten().tolist()))
return action
states = [] # Array to save agent states during the game
t = 0
state = env.reset()
wn = 0
while (t < 100):
# env.render()
time.sleep(time_delay)
clear_output(wait=True)
action = choose_action_one_game(state)
state2, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
states.append(state)
state = state2
t += 1
if done and reward == 1:
wn = 1
if done:
break
if wn == 1:
print("!!!WIN!!!")
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def make_maze_pic(maze):
maze_pic = []
for i in range(len(maze)):
row = []
for j in range(len(maze[i])):
if maze[i][j] == 'S':
row.append(0)
if maze[i][j] == 'F':
row.append(0)
if maze[i][j] == 'H':
row.append(1)
if maze[i][j] == 'G':
row.append(0)
maze_pic.append(row)
maze_pic = np.array(maze_pic)
return maze_pic
# Make maze fit to plot
maze_pic = make_maze_pic(random_map)
nrows, ncols = maze_pic.shape
# Arrays of picture elements
rw = np.remainder(states, nrows)
cl = np.floor_divide(states, nrows)
if wn == 1:
rw = np.append(rw, [nrows - 1])
cl = np.append(cl, [ncols - 1])
# Picture plotting
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots(1, 1, tight_layout=True)
ax1.clear()
ax1.set_xticks(np.arange(0.5, nrows, step=1))
ax1.set_xticklabels([])
ax1.set_yticks(np.arange(0.5, ncols, step=1))
ax1.set_yticklabels([])
ax1.grid(True)
ax1.plot([0], [0], "gs", markersize=40) # start is a big green square
ax1.text(0, 0.2, "Start", ha="center", va="center", color="white", fontsize=12) # Start text
ax1.plot([nrows - 1], [ncols - 1], "rs", markersize=40) # exit is a big red square
ax1.text(nrows - 1, ncols - 1 + 0.2, "Finish", ha="center", va="center", color="white", fontsize=12) # Exit text
ax1.plot(rw, cl, ls='-', color='blue') # Blue lines path
ax1.plot(rw, cl, "bo") # Blue dots visited cells
ax1.imshow(maze_pic, cmap="binary")
fig.show()
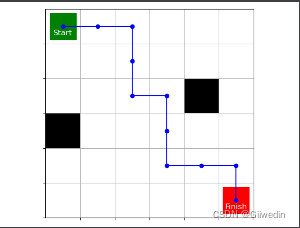
# 3智能体的移动路径如下:
Algorithm 4. Q-learning algorithm
1:Let be a set of states, and (), ∈ , be a set of actions available in the state .
2:Initialize(,),∈,isnotterminal,∈()arbitrarily
3:Initialize and
4:for each game do
5: Initialize a nonterminal state 0 at random
6: ←0
7: for each step of the game until a stopping criterion is reached or until
is a nonterminal state, do
8: Select under the policy (|)
9: Take action , find +1, transition to +1
10: if +1 is a terminal state, then
11: (, ) ← (, ) + (+1 − (, ))
12: else
13: (, ) ← (, ) + (+1 + max((+1, a)) − (, ))
14: end if
15: ← (+1)
16: end if
17:end for
#程序包含以下内容
#使用Q-learning方法,进行10000场冰湖游戏
#使用训练完的模型进行游戏
#画出智能体的移动路径
epsilon = 0.1 # Epsilon parameter which is used in epsilon-greedy strategy
gamma = 0.9 # Discount coefficient gamma
random_seed = 6 #Random seed
time_delay = 1 # Time delay when rendering the game process after training (seconds)
lr_rate = 0.9 #Learning rate alpha
import time
#%% md
#%%Q-Learning
import gym
import numpy as np
import time
from IPython.display import clear_output
def generate_random_map(size, p, sd):
"""Generates a random valid map (one that has a path from start to goal)
:param size: size of each side of the grid
:param p: probability that a tile is frozen
"""
valid = False
np.random.seed(sd)
# DFS to check that it's a valid path.
def is_valid(res):
frontier, discovered = [], set()
frontier.append((0,0))
while frontier:
r, c = frontier.pop()
if not (r,c) in discovered:
discovered.add((r,c))
directions = [(1, 0), (0, 1), (-1, 0), (0, -1)]
for x, y in directions:
r_new = r + x
c_new = c + y
if r_new < 0 or r_new >= size or c_new < 0 or c_new >= size:
continue
if res[r_new][c_new] == 'G':
return True
if (res[r_new][c_new] not in '#H'):
frontier.append((r_new, c_new))
return False
while not valid:
p = min(1, p)
res = np.random.choice(['F', 'H'], (size, size), p=[p, 1-p])
res[0][0] = 'S'
res[-1][-1] = 'G'
valid = is_valid(res)
return ["".join(x) for x in res]
# Map generation
random_map = generate_random_map(size=6, p=0.8, sd = random_seed) #Create our map
env = gym.make("FrozenLake-v0", desc=random_map, is_slippery=False) #Initialize environment
print("Your map")
env.render() #Render the map
def choose_action(state):
action=0
if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < epsilon:
action = np.random.randint(0,env.action_space.n) #***
else:
action = np.random.choice(np.array(np.argwhere(Q[state, :] == np.amax(Q[state, :])).flatten().tolist()))
return action
def learn(state, state2, reward, action, done):
if done is True:
Q[state, action] = Q[state, action] + lr_rate*(reward - Q[state, action])
else:
Q[state, action] = Q[state, action] + lr_rate * (reward + gamma*np.max(Q[state2,:])-Q[state, action])
#Q[state, action] = #Your code here
#Q-learning
from tqdm import tqdm
# Inititalization
np.random.seed(random_seed)
total_games = 10000
max_steps = 100
Q = np.zeros((env.observation_space.n, env.action_space.n))
# Main cycle
game1= [0]*total_games
for game in tqdm(range(total_games)):
state = env.reset()
t = 0
while t < max_steps:
#env.render()
t += 1
action = choose_action(state)
state2, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
if t == max_steps:
done = True
learn(state, state2, reward, action, done)
state = state2
if done:
if reward == 1:
game1[game]=1
break
def get_fg_and_v(game):
v = 0
fg=0
i=0
l=[]
for g in game:
if g ==1:
v=v+1
if len(l) ==0:
l.append(i)
else:
if len(l) <5:
if l[-1] - i == -1:
l.append(i)
else:
l=[i]
if len(l) == 5 and fg==0:
fg = i+1
i=i+1
return fg , v
fg,v=get_fg_and_v(game1)
print("The number of victories in a series of 10,000 games: ",v)#Your code here
print("Five wins in a row were first won in the game ",fg)#Your code here
import time
#Greedy action selection
def choose_action_one_game(state):
action = np.random.choice(np.array(np.argwhere(Q[state, :] == np.amax(Q[state, :])).flatten().tolist()))
return action
states=[]#Array to save agent states during the game
t = 0
state = env.reset()
wn = 0
while(t<100):
#env.render()
time.sleep(time_delay)
clear_output(wait=True)
action = choose_action_one_game(state)
state2, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
states.append(state)
state = state2
t += 1
if done and reward == 1:
wn=1
if done:
break
if wn == 1:
print("!!!WIN!!!")
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def make_maze_pic(maze):
maze_pic = []
for i in range(len(maze)):
row = []
for j in range(len(maze[i])):
if maze[i][j] == 'S':
row.append(0)
if maze[i][j] == 'F':
row.append(0)
if maze[i][j] == 'H':
row.append(1)
if maze[i][j] == 'G':
row.append(0)
maze_pic.append(row)
maze_pic = np.array(maze_pic)
return maze_pic
# Make maze fit to plot
maze_pic = make_maze_pic(random_map)
nrows, ncols = maze_pic.shape
# Arrays of picture elements
rw = np.remainder(states, nrows)
cl = np.floor_divide(states, nrows)
if wn == 1:
rw = np.append(rw, [nrows - 1])
cl = np.append(cl, [ncols - 1])
# Picture plotting
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots(1, 1, tight_layout=True)
ax1.clear()
ax1.set_xticks(np.arange(0.5, nrows, step=1))
ax1.set_xticklabels([])
ax1.set_yticks(np.arange(0.5, ncols, step=1))
ax1.set_yticklabels([])
ax1.grid(True)
ax1.plot([0], [0], "gs", markersize=40) # start is a big green square
ax1.text(0, 0.2, "Start", ha="center", va="center", color="white", fontsize=12) # Start text
ax1.plot([nrows - 1], [ncols - 1], "rs", markersize=40) # exit is a big red square
ax1.text(nrows - 1, ncols - 1 + 0.2, "Finish", ha="center", va="center", color="white", fontsize=12) # Exit text
ax1.plot(rw, cl, ls='-', color='blue') # Blue lines path
ax1.plot(rw, cl, "bo") # Blue dots visited cells
ax1.imshow(maze_pic, cmap="binary")
fig.show()智能体的移动路径如下: