C++基础学习笔记-类与对象
C++基础学习笔记-类与对象
-
- 一、类与对象概述
- 二、结构体和类的区别
- 三、类的封装
-
- 3.1 访问权限
- 3.2 尽量把成员变量的权限设置成私有的权限
- 3.3 课堂小练习
- 四、作业:设计一个类:求圆的周长
- 五、点和圆关系案例
-
- 5.1 点的类设计
- 5.2 圆的类的设计
一、类与对象概述
- 类是自定义数据类型,是C语言的结构体进化而成的
- 对象是类实例化而出的,用数据类型定义一个变量
#include二、结构体和类的区别
结构体的默认权限是公有的,类的默认权限是私有的
三、类的封装
- 封装是把属性(变量)和方法(函数)封装到类内,然后给这些数据赋予权限
- 为什么要有封装
- 防止乱调用函数和变量,出现错误
- 维护代码更加方便
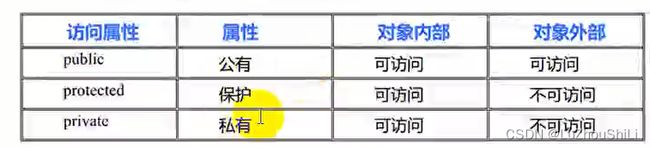
3.1 访问权限
- 在类的内部(作用域范围内),没有访问权限之分,所有成员都可以相互访问
- 在类的外部(作用域范围之外),访问权限才有意义:public,private,protected
- 在类的外部,只有public修饰的成员才能被访问,在没有设计继承与派生时,private和protected是同等级的,外部不允许进行访问
#include//类外不能访问私有权限的成员
//类外可以访问公有权限的成员
//类外不可以访问保护权限的成员
// 子类的类内部可以访问父类的保护权限的成员
// 类内部是没有权限之分
子类访问父类的保护成员,是复制过来的不是同一个值
#include3.2 尽量把成员变量的权限设置成私有的权限
- 可以控制属性的读写权限
- 可以赋予客户端访问数据的一致性
- 可以保护属性的合法性
#include3.3 课堂小练习
请设计一个Maker类,Maker类具有name和age属性,提供初始化函数(Init),并且提供对name和age的读写函数(set,get),但是必须确保age的赋值在有效范围内(0-100),超出有效范围,拒绝赋值,并且提供方法输出姓名和年龄
#include四、作业:设计一个类:求圆的周长
#include五、点和圆关系案例
5.1 点的类设计
class Point
{
void setX();
void setY();
int getX();
int getY();
int x;
int y;
}
5.2 圆的类的设计
class Circle
{
// 圆心
Point mHear;
// 半径
int mR;
// 设置圆心和半径的方法
// 判断点和圆的关系的方法
};
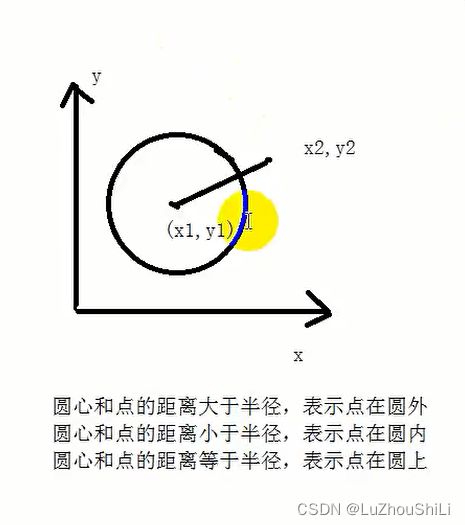
- 圆心和点的距离大于半径,表示点在园外
- 圆心和点的距离小于半径,表示点在园内
- 圆心和点的距离等于半径,表示点在圆上
main.cpp
#includepoint.h
#pragma once
class Point
{
public:
void setX(int x);
void setY(int y);
int getX();
int getY();
private:
int mX;
int mY;
};
point.cpp
#include"point.h"
// 实现函数 加上作用域Point 表示是类Point的成员函数
void Point::setX(int x)
{
mX = x;
}
void Point::setY(int y)
{
mY = y;
}
int Point::getX()
{
return mX;
}
int Point::getY()
{
return mY;
}
Circle.cpp
#include "Circle.h"
void Circle::SetR(int r)
{
mR = r;// 设置半径
}
// 函数重载
void Circle::SetHear(Point& p) {
// 设置圆心
mHear.setX(p.getX());
mHear.setY(p.getY());
}
void Circle::SetHear(int x, int y)
{
// 设置圆心
mHear.setX(x);
mHear.setY(y);
}
int Circle::getR()
{
return mR;
}
Point Circle::getHear()
{
return mHear;
}
void Circle::isPointAndCircle(Point& p)
{
// 获取圆心和点之间的距离
int x2 = p.getX();
int y2 = p.getY();
double distance = pow((x2 - mHear.getX()),2) + pow((y2 - mHear.getY()),2);
double tmp = pow(mR,2);
if (distance > tmp)
{
cout << "点在圆外" << endl;
}
else if (distance == tmp)
{
cout << "点在圆上" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "点在圆内" << endl;
}
}
Circle.h
#pragma once
#include"point.h"
#include