医学影像调窗技术
在年初的时候做过一个dicom格式文件解析,当时只是提了下。看着跟别人的显示出来也差不多 其实是我想太简单了。整理了下思路 这里提供正确的调窗代码。 医学影像 说得挺高科技的 其实在这个过程中本身没太复杂的图像处理技术。窗值处理就算是比较“高深”的了 也就是调窗。
网上都是啥基于 DCMTK的DICOM医学图像显示及其调窗方法研究 说得文绉绉的 没啥鸟用 ,dicom没你想象的那么复杂哈 咱这个全是自主代码 顶多看了点C++的源码 然后改成c#版本的 其实都一样的。
这中间有几个 步骤,
1 字节序转换
2 保留有效位,使用&进行位运算截取有效位
3 根据有无符号进行值转换
4 针对CT影像的窗值偏移处理
5 窗值映射 也就是映射到256级灰度(参考上一篇 )
而我原来的代码啥都没做 直接对两个字节的数据进行toUint16 然后就进行窗值映射,还有就是也没有进行预设窗值读取。那么这样做的后果是什么呢 。
我们先加上预设窗值读取,首先我们加上几个变量 进行影像显示的几个关键数据 图像的长 宽 默认窗值 颜色采样数 1为灰度3为彩色 数据存储位数 有效位数 最高位数,具体查看dicom标准。
变量声明 默认窗值读取代码 (预设窗宽tag 0028 1051 预设窗位tag 0028 1050):
1 if (fileName == string.Empty) 2 return false; 3 4 int dataLen, validLen, hibit;//数据长度 有效位 5 int imgNum;//帧数 6 7 rows = int.Parse(tags["0028,0010"].Substring(5)); 8 cols = int.Parse(tags["0028,0011"].Substring(5)); 9 10 colors = int.Parse(tags["0028,0002"].Substring(5)); 11 dataLen = int.Parse(tags["0028,0100"].Substring(5));//bits allocated 12 validLen = int.Parse(tags["0028,0101"].Substring(5)); 13 bool signed = int.Parse(tags["0028,0103"].Substring(5)) == 0 ? false : true; 14 hibit = int.Parse(tags["0028,0102"].Substring(5)); 15 float rescaleSlop = 1, rescaleinter = 0; 16 if (tags.ContainsKey("0028,1052") && tags.ContainsKey("0028,1053")) 17 { 18 rescaleSlop = float.Parse(tags["0028,1053"].Substring(5)); 19 rescaleinter = float.Parse(tags["0028,1052"].Substring(5)); 20 } 21 //读取预设窗宽窗位 22 //预设窗值读取代码...... 23 #region//读取预设窗宽窗位 24 if (windowWith == 0 && windowCenter == 0) 25 { 26 Regex r = new Regex(@"([0-9]+)+"); 27 if (tags.ContainsKey("0028,1051")) 28 { 29 Match m = r.Match(tags["0028,1051"].Substring(5)); 30 31 if (m.Success) 32 windowWith = int.Parse(m.Value); 33 else 34 windowWith = 1 << validLen; 35 } 36 else 37 { 38 windowWith = 1 << validLen; 39 } 40 41 if (tags.ContainsKey("0028,1050")) 42 { 43 Match m = r.Match(tags["0028,1050"].Substring(5)); 44 if (m.Success) 45 windowCenter = int.Parse(m.Value);//窗位 46 else 47 windowCenter = windowWith / 2; 48 } 49 else 50 { 51 windowCenter = windowWith / 2; 52 } 53 } 54 55 #endregion
虽然原理是正确的 但还是会产生乱七八糟的问题 始终跟别人标准的不一样 :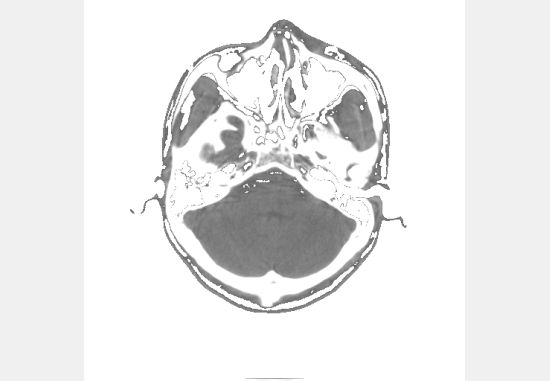
标准的窗值调整请参考这篇论文:医学图像的调窗技术及DI 基本上照着他做就OK ,只是有些地方没讲太明白。
那么我这篇文章基本上就是他经过代码实践后的翻版
参考了过后那么我们就要照标准的流程来处理 ,字节序转换 后截取有效位 然后根据有无符号进行值转换
还是原来的代码 中间加上这几句:
1 if (isLitteEndian == false) 2 Array.Reverse(pixData, 0, 2); 3 4 if (signed == false) 5 gray = BitConverter.ToUInt16(pixData, 0); 6 else 7 gray = BitConverter.ToInt16(pixData, 0);
这么做了后我们发现 1.2.840.113619.2.81.290.23014.2902.1.6.20031230.260236.dcm 那幅图像显示对了: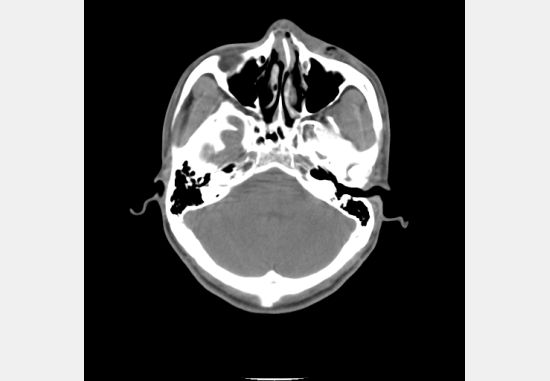
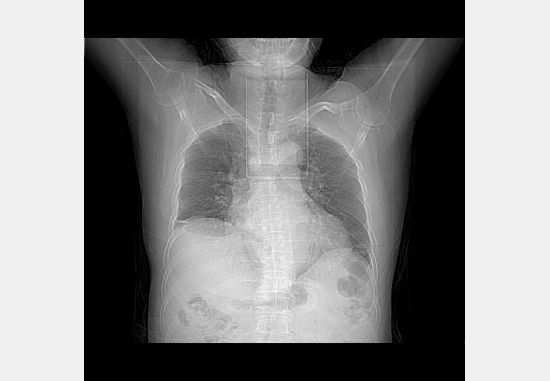
但是测试另一幅 还是不对 CT.dcm:
这幅图像看上去是CR的图,其实是CT序列图像里的一幅 ,因为是CT影像 所以要做值偏移处理 值=值×斜率+截距 这是高中学的,称为HU 至于为什么要这样我也不知道 dicom标准规定的 如果是CT图像需要进行偏移处理则进行偏移处理 然后进行窗值映射。
1 //字节序翻转 2 if (isLitteEndian == false) 3 Array.Reverse(pixData, 0, 2); 4 //取值 5 if (signed == false) 6 gray = BitConverter.ToUInt16(pixData, 0); 7 else 8 gray = BitConverter.ToInt16(pixData, 0); 9 //特别针对CT图像 值=值x斜率+截距 10 if ((rescaleSlop != 1.0f) || (rescaleinter != 0.0f)) 11 { 12 float fValue = (float)gray * rescaleSlop + rescaleinter; 13 gray = (short)fValue; 14 }
所有的数据都读取完成后再setPixel 这种操作效率太低了。所以我们还得优化下代码 先lockbits 然后一边读取一边更新数据。
这是整理后的标准调窗代码,有点多哈 慢慢看,我说得挺简单 中间有各种复杂情况哈 请参考上面说的步骤及论文里的说明来:
1 public unsafe Bitmap convertTo8(BinaryReader streamdata, int colors, bool littleEdition, bool signed, short nHighBit, 2 int dataLen, float rescaleSlope, float rescaleIntercept, float windowCenter, float windowWidth, int width, int height) 3 { 4 Bitmap bmp = new Bitmap(width, height); 5 Graphics gg = Graphics.FromImage(bmp); 6 gg.Clear(Color.Green); 7 BitmapData bmpDatas = bmp.LockBits(new Rectangle(0, 0, bmp.Width, bmp.Height), 8 System.Drawing.Imaging.ImageLockMode.ReadWrite, System.Drawing.Imaging.PixelFormat.Format24bppRgb); 9 long numPixels = width * height; 10 11 if (colors == 3)//color Img 12 { 13 byte* p = (byte*)bmpDatas.Scan0; 14 int indx = 0; 15 for (int i = 0; i < bmp.Height; i++) 16 { 17 for (int j = 0; j < bmp.Width; j++) 18 { 19 p[indx + 2] = streamdata.ReadByte(); 20 p[indx + 1] = streamdata.ReadByte(); 21 p[indx] = streamdata.ReadByte(); 22 indx += 3; 23 } 24 } 25 } 26 else if (colors == 1)//grayscale Img 27 { 28 byte* p = (byte*)bmpDatas.Scan0; 29 int nMin = ~(0xffff << (nHighBit + 1)), nMax = 0; 30 int indx = 0;//byteData index 31 32 for (int n = 0; n < numPixels; n++)//pixNum index 33 { 34 short nMask; nMask = (short)(0xffff << (nHighBit + 1)); 35 short nSignBit; 36 37 byte[] pixData = null; 38 short pixValue = 0; 39 40 pixData = streamdata.ReadBytes(dataLen / 8 * colors); 41 if (nHighBit <= 15 && nHighBit > 7) 42 { 43 if (littleEdition == false) 44 Array.Reverse(pixData, 0, 2); 45 46 // 1. Clip the high bits. 47 if (signed == false)// Unsigned integer 48 { 49 pixValue = (short)((~nMask) & (BitConverter.ToInt16(pixData, 0))); 50 } 51 else 52 { 53 nSignBit = (short)(1 << nHighBit); 54 if (((BitConverter.ToInt16(pixData, 0)) & nSignBit) != 0) 55 pixValue = (short)(BitConverter.ToInt16(pixData, 0) | nMask); 56 else 57 pixValue = (short)((~nMask) & (BitConverter.ToInt16(pixData, 0))); 58 } 59 } 60 else if (nHighBit <= 7) 61 { 62 if (signed == false)// Unsigned integer 63 { 64 nMask = (short)(0xffff << (nHighBit + 1)); 65 pixValue = (short)((~nMask) & (pixData[0])); 66 } 67 else 68 { 69 nMask = (short)(0xffff << (nHighBit + 1)); 70 nSignBit = (short)(1 << nHighBit); 71 if (((pixData[0]) & nSignBit) != 0) 72 pixValue = (short)((short)pixData[0] | nMask); 73 else 74 pixValue = (short)((~nMask) & (pixData[0])); 75 } 76 77 } 78 79 // 2. Rescale if needed (especially for CT) 80 if ((rescaleSlope != 1.0f) || (rescaleIntercept != 0.0f)) 81 { 82 float fValue = pixValue * rescaleSlope + rescaleIntercept; 83 pixValue = (short)fValue; 84 } 85 86 // 3. Window-level or rescale to 8-bit 87 if ((windowCenter != 0) || (windowWidth != 0)) 88 { 89 float fSlope; 90 float fShift; 91 float fValue; 92 93 fShift = windowCenter - windowWidth / 2.0f; 94 fSlope = 255.0f / windowWidth; 95 96 fValue = ((pixValue) - fShift) * fSlope; 97 if (fValue < 0) 98 fValue = 0; 99 else if (fValue > 255) 100 fValue = 255; 101 102 103 p[indx++] = (byte)fValue; 104 p[indx++] = (byte)fValue; 105 p[indx++] = (byte)fValue; 106 } 107 else 108 { 109 // We will map the whole dynamic range. 110 float fSlope; 111 float fValue; 112 113 114 int i = 0; 115 // First compute the min and max. 116 if (n == 0) 117 nMin = nMax = pixValue; 118 else 119 { 120 if (pixValue < nMin) 121 nMin = pixValue; 122 123 if (pixValue > nMask) 124 nMask = pixValue; 125 } 126 127 // Calculate the scaling factor. 128 if (nMax != nMin) 129 fSlope = 255.0f / (nMax - nMin); 130 else 131 fSlope = 1.0f; 132 133 fValue = ((pixValue) - nMin) * fSlope; 134 if (fValue < 0) 135 fValue = 0; 136 else if (fValue > 255) 137 fValue = 255; 138 139 p[indx++] = (byte)fValue; 140 } 141 } 142 } 143 144 bmp.UnlockBits(bmpDatas); 145 //bmp.Dispose(); 146 return bmp; 147 }
完整源码及测试数据下载 猛击此处