数据预处理之数据清洗案例
建议学习文章:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/111499325
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/jNoXHO4qU34gcha4zOGRLA
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ra48vJTsQltydOtfoy5YHQ
参考数据缺失、混乱、重复怎么办?最全数据清洗指南让你所向披靡 (qq.com
数据清洗:从记录集、表或数据库中检测和修正(或删除)受损或不准确记录的过程。它识别出数据中不完善、不准确或不相关的部分,并替换、修改或删除这些脏乱的数据。
为了将数据清洗简单化,本文介绍了一种新型完备分步指南,支持在 Python 中执行数据清洗流程。读者可以学习找出并清洗以下数据的方法:
-
缺失数据;
-
不规则数据(异常值);
-
不必要数据:重复数据(repetitive data)、复制数据(duplicate data)等;
-
不一致数据:大写、地址等;
该指南使用的数据集是 知识追踪数据集你可以换成你要用的数据
数据概况
# import packages
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.mlab as mlab
import matplotlib
plt.style.use('ggplot')
from matplotlib.pyplot import figure
%matplotlib inline
matplotlib.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (12,8)
pd.options.mode.chained_assignment = None
# read the data
df = pd.read_csv(
'F://su//study//知识追踪学习路线//code//Deep-Knowledge-Tracing-master//examples//data//ASSISTments_skill_builder_data.csv')
# shape and data types of the data
print(df.shape)
print(df.dtypes)
# select numeric columns
df_numeric = df.select_dtypes(include=[np.number])
numeric_cols = df_numeric.columns.values
print(numeric_cols)
# select non numeric columns
df_non_numeric = df.select_dtypes(exclude=[np.number])
non_numeric_cols = df_non_numeric.columns.values
print(non_numeric_cols)
(525534, 30)
order_id int64
assignment_id int64
user_id int64
assistment_id int64
problem_id int64
original int64
correct int64
attempt_count int64
ms_first_response int64
tutor_mode object
answer_type object
sequence_id int64
student_class_id int64
position int64
type object
base_sequence_id int64
skill_id float64
skill_name object
teacher_id int64
school_id int64
hint_count int64
hint_total int64
overlap_time int64
template_id int64
answer_id float64
answer_text object
first_action float64
bottom_hint float64
opportunity float64
opportunity_original float64
dtype: object
['order_id' 'assignment_id' 'user_id' 'assistment_id' 'problem_id'
'original' 'correct' 'attempt_count' 'ms_first_response' 'sequence_id'
'student_class_id' 'position' 'base_sequence_id' 'skill_id' 'teacher_id'
'school_id' 'hint_count' 'hint_total' 'overlap_time' 'template_id'
'answer_id' 'first_action' 'bottom_hint' 'opportunity'
'opportunity_original']
['tutor_mode' 'answer_type' 'type' 'skill_name' 'answer_text']
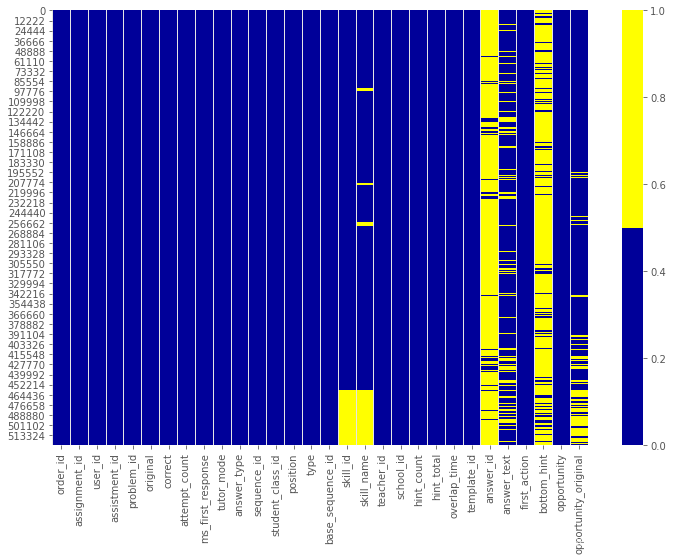
cols = df.columns[:30] # first 30 columns
colours = ['#000099', '#ffff00'] # specify the colours - yellow is missing. blue is not missing.
sns.heatmap(df[cols].isnull(), cmap=sns.color_palette(colours))
下表展示了前 30 个特征的缺失数据模式。横轴表示特征名,纵轴表示观察值/行数,黄色表示缺失数据,蓝色表示非缺失数据。
例如,下图中特征skill——id在多个行中存在缺失值。而特征skillname出现零星缺失值。
方法 2:缺失数据百分比列表
当数据集中存在很多特征时,我们可以为每个特征列出缺失数据的百分比
# if it's a larger dataset and the visualization takes too long can do this.
# % of missing.
for col in df.columns:
pct_missing = np.mean(df[col].isnull())
print('{} - {}%'.format(col, round(pct_missing*100)))order_id - 0% assignment_id - 0% user_id - 0% assistment_id - 0% problem_id - 0% original - 0% correct - 0% attempt_count - 0% ms_first_response - 0% tutor_mode - 0% answer_type - 0% sequence_id - 0% student_class_id - 0% position - 0% type - 0% base_sequence_id - 0% skill_id - 13% skill_name - 15% teacher_id - 0% school_id - 0% hint_count - 0% hint_total - 0% overlap_time - 0% template_id - 0% answer_id - 91% answer_text - 18% first_action - 0% bottom_hint - 85% opportunity - 0% opportunity_original - 15%
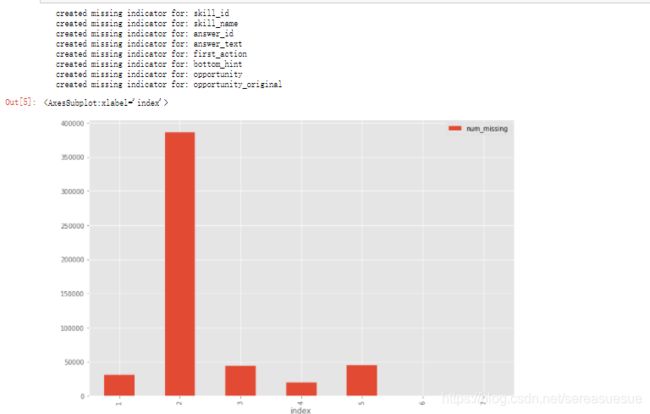
方法 3:缺失数据直方图
在存在很多特征时,缺失数据方图也不失为一种有效方法。
要更深入地了解观察值中的缺失值模式,我们可以用直方图的形式进行可视化。
# first create missing indicator for features with missing data
for col in df.columns:
missing = df[col].isnull()
num_missing = np.sum(missing)
if num_missing > 0:
print('created missing indicator for: {}'.format(col))
df['{}_ismissing'.format(col)] = missing
# then based on the indicator, plot the histogram of missing values
ismissing_cols = [col for col in df.columns if 'ismissing' in col]
df['num_missing'] = df[ismissing_cols].sum(axis=1)
df['num_missing'].value_counts().reset_index().sort_values(by='index').plot.bar(x='index', y='num_missing')如何处理缺失数据?
这方面没有统一的解决方案。我们必须研究特定特征和数据集,据此决定处理缺失数据的最佳方式。
下面介绍了四种最常用的缺失数据处理方法。不过,如果情况较为复杂,我们需要创造性地使用更复杂的方法,如缺失数据建模。
解决方案 1:丢弃观察值
在计学中,该方法叫做成列删除(listwise deletion),需要丢弃包含缺失值的整列观察值。
只有在我们确定缺失数据无法提供信息时,才可以执行该操作。否则,我们应当考虑其他解决方案。
此外,还存在其他标准。
例如,从缺失数据直方图中,我们可以看到只有少量观察值的缺失值数量超过 35。因此,我们可以创建一个新的数据集 df_less_missing_rows,该数据集删除了缺失值数量超过 35 的观察值。
解决方案 2:丢弃特征
与解决方案 1 类似,我们只在确定某个特征无法提供有用信息时才丢弃它。
例如,从缺失数据百分比列表中,我们可以看到 hospital_beds_raion 具备较高的缺失值百分比——47%,因此我们丢弃这一整个特征。
解决方案 3:填充缺失数据
当特征是数值变量时,执行缺失数据填充。对同一特征的其他非缺失数据取平均值或中位数,用这个值来替换缺失值。
当特征是分类变量时,用众数(最频值)来填充缺失值。
不规则数据(异常值)
异常值指与其他观察值具备显著差异的数据,它们可能是真的异常值也可能是错误。
如何找出异常值?
根据特征的属性(数值或分类),使用不同的方法来研究其分布,进而检测异常值。
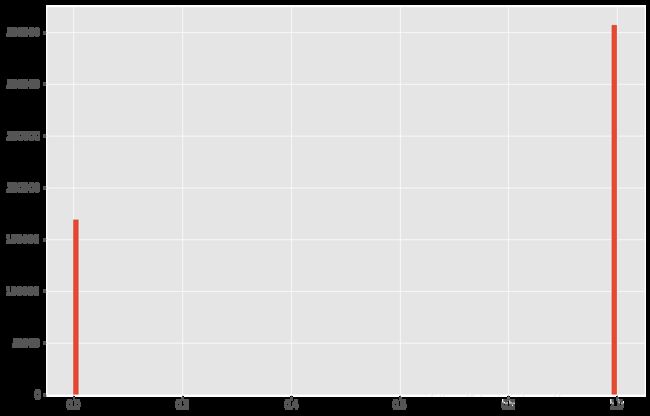
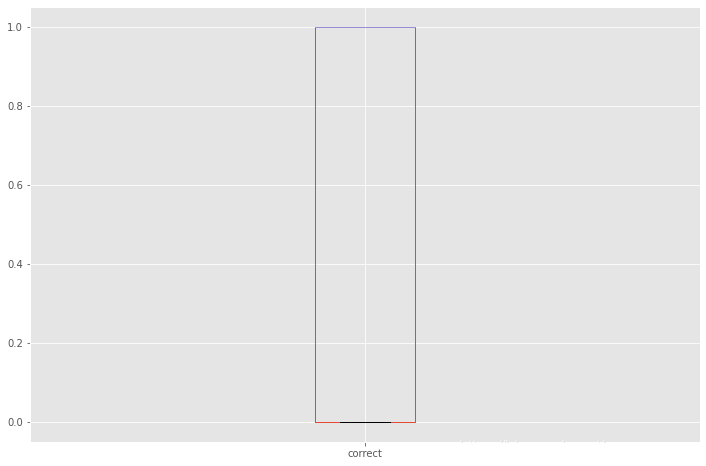
方法 1:直方图/箱形图
当特征是数值变量时,使用直方图和箱形图来检测异常值。
correct是学生回答问题的值只有0 1我们可以检验一下
df['correct'].hist(bins=100)
df.boxplot(column=['correct'])#箱线图
如何处理异常值?
尽管异常值不难检测,但我们必须选择合适的处理办法。而这高度依赖于数据集和项目目标。
处理异常值的方法与处理缺失值有些类似:要么丢弃,要么修改,要么保留。(读者可以返回上一章节处理缺失值的部分查看相关解决方案。)
不必要数据
处理完缺失数据异常值,现在我们来看不必要数据,处理不必要数据的方法更加直接。
输入到模型中的所有数据应服务于项目目标。不必要数据即无法增加价值的数据。
这里将介绍三种主要的不必要数据类型。
不必要数据类型 1:信息不足/重复
有时一个特征不提供信息,是因为它拥有太多具备相同值的行。
如何找出重复数据?
我们可以为具备高比例相同值的特征创建一个列表。
num_rows = len(df.index)
low_information_cols = [] #
for col in df.columns:
cnts = df[col].value_counts(dropna=False)
top_pct = (cnts/num_rows).iloc[0]
if top_pct > 0.95:
low_information_cols.append(col)
print('{0}: {1:.5f}%'.format(col, top_pct*100))
print(cnts)
print()tutor_mode: 99.93664% tutor 525201 test 333 Name: tutor_mode, dtype: int64 type: 100.00000% MasterySection 525534 Name: type, dtype: int64 first_action_ismissing: 99.99391% False 525502 True 32 Name: first_action_ismissing, dtype: int64 opportunity_ismissing: 99.99391% False 525502 True 32 Name: opportunity_ismissing, dtype: int64
缺失值处理