python:numpy.random模块生成随机数
简介
所谓生成随机数,即按照某种概率分布,从给定的区间内随机选取一个数。常用的分布有:均匀分布(uniform distribution),正态分布(normal distribution),泊松分布(poisson distribution)等。
python中的numpy.random模块提供了常用的随机数生成方法,下面简要总结。
按均匀分布生成随机数
rand
功能
按照均匀分布,在[0,1)内生成随机数。
接口
Docstring:
rand(d0, d1, ..., dn)
Random values in a given shape.
Create an array of the given shape and populate it with
random samples from a uniform distribution
over ``[0, 1)``.
实例
In [3]: np.random.rand()
Out[3]: 0.08621180209775481
In [4]: np.random.rand(5)
Out[4]: array([0.85086433, 0.46726857, 0.48144885, 0.36369815, 0.9181539 ])
In [5]: np.random.rand(2,5)
Out[5]:
array([[0.70784333, 0.08966827, 0.50090152, 0.22517888, 0.86735194],
[0.92224362, 0.98468415, 0.19134583, 0.06757754, 0.19330571]])
验证下是按均匀分布生成的随机数
方法:利用直方图可验证其概率密度函数是否与均匀分布一致。
x = np.random.rand(10000)
plt.hist(x,bins=20,density=True)
结果:符合均匀分布的概率密度函数,即P(x)=1, x=[0,1]

uniform
功能
按照均匀分布,在[low,high)内生成随机数。
接口
Docstring:
uniform(low=0.0, high=1.0, size=None)
Draw samples from a uniform distribution.
Samples are uniformly distributed over the half-open interval
``[low, high)`` (includes low, but excludes high). In other words,
any value within the given interval is equally likely to be drawn
by `uniform`.
实例
In [8]: np.random.uniform(-1,1)
Out[8]: -0.34092928027362945
In [9]: np.random.uniform(-1,1,5)
Out[9]: array([ 0.84319637, -0.00449745, -0.21958133, -0.16755161, -0.94383758])
In [10]: np.random.uniform(-1,1,(2,5))
Out[10]:
array([[-0.66176972, 0.71703011, 0.61658043, 0.0373402 , 0.95824383],
[ 0.31743693, 0.48948276, 0.0393428 , 0.64896449, 0.3659116 ]])
验证下是按均匀分布生成的随机数
x = np.random.uniform(-1,1,10000)
plt.hist(x,bins=20,density=True)
randint
功能
按照离散均匀分布,在[low,high)内生成随机整数。
接口
Docstring:
randint(low, high=None, size=None, dtype='l')
Return random integers from `low` (inclusive) to `high` (exclusive).
Return random integers from the "discrete uniform" distribution of
the specified dtype in the "half-open" interval [`low`, `high`). If
`high` is None (the default), then results are from [0, `low`).
实例
In [12]: np.random.randint(0,101)
Out[12]: 27
In [13]: np.random.randint(0,101,5)
Out[13]: array([71, 31, 22, 85, 64])
In [14]: np.random.randint(0,101,(2,5))
Out[14]:
array([[94, 29, 80, 40, 6],
[17, 19, 85, 11, 48]])
验证下是按均匀分布生成的随机数
x = np.random.randint(0,100,10000)
plt.hist(x,bins=20,density=True)
结果:与均匀分布一致。
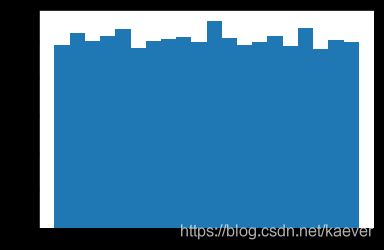
注释:当区间为[0,101),即x = np.random.randint(0,100,10000)时,最后一个区间的概率密度总是会较大些。猜测跟随机数生成机制有关,暂不深入,后续有时间研究下。
按正态分布生成随机数
randn
功能
按照正态分布( μ = 0 , σ = 1 \mu=0,\sigma=1 μ=0,σ=1),生成随机数
接口
Docstring:
randn(d0, d1, ..., dn)
Return a sample (or samples) from the "standard normal" distribution.
If positive, int_like or int-convertible arguments are provided,
`randn` generates an array of shape ``(d0, d1, ..., dn)``, filled
with random floats sampled from a univariate "normal" (Gaussian)
distribution of mean 0 and variance 1 (if any of the :math:`d_i` are
floats, they are first converted to integers by truncation). A single
float randomly sampled from the distribution is returned if no
argument is provided.
This is a convenience function. If you want an interface that takes a
tuple as the first argument, use `numpy.random.standard_normal` instead.
实例
In [15]: np.random.randn()
Out[15]: 0.2594770528010187
In [16]: np.random.randn(5)
Out[16]: array([ 0.51858431, -0.56406054, 0.39934797, 0.87223161, 0.56642685])
In [17]: np.random.randn(2,5)
Out[17]:
array([[-0.09649912, -0.51282169, 0.10047756, 1.03372611, -1.54014928],
[-1.29894642, 0.46580577, 0.77321341, 2.16154836, -0.99208604]])
验证下是按正态分布生成的随机数
x = np.random.randn(10000)
n, bins, patches =plt.hist(x,bins=50,density=True)
y1 = scipy.stats.norm.pdf(bins, loc=0, scale=1)
plt.plot(bins,y1,'r--')
normal
功能
按照正态分布( μ , σ \mu,\sigma μ,σ),生成随机数
接口
Docstring:
normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=None)
Draw random samples from a normal (Gaussian) distribution.
实例
In [22]: np.random.normal(170,10)
Out[22]: 169.24973434084185
In [23]: np.random.normal(170,10,5)
Out[23]:
array([167.0171718 , 169.47192942, 169.61260805, 151.53654937,
172.61541579])
In [24]: np.random.normal(170,10,(2,5))
Out[24]:
array([[187.28916343, 170.30553783, 175.69009811, 171.87050032,
179.26404146],
[171.17078449, 173.25610155, 169.60757285, 178.79427632,
163.25814631]])
验证下是按正态分布生成的随机数
mu,sigma = 170,10
x = np.random.normal(mu,sigma,10000)
n, bins, patches = plt.hist(x,bins=50,density=True)
y1 = scipy.stats.norm.pdf(bins, loc=mu, scale=sigma)
plt.plot(bins,y1,'r--')
给定一个数组,随机排列
permutation
功能
给定一个数组(或list,随机排列
接口
Randomly permute a sequence, or return a permuted range.
If `x` is a multi-dimensional array, it is only shuffled along its
first index.
Parameters
----------
x : int or array_like
If `x` is an integer, randomly permute ``np.arange(x)``.
If `x` is an array, make a copy and shuffle the elements
randomly.
Returns
-------
out : ndarray
Permuted sequence or array range.
实例
In [28]: np.random.permutation(6)
Out[28]: array([2, 1, 3, 4, 0, 5])
In [29]: np.random.permutation(np.arange(1,7))
Out[29]: array([5, 3, 4, 2, 1, 6])
shuffle
功能
给定一个数组或list,打乱顺序(同permutation)
接口
Docstring:
shuffle(x)
Modify a sequence in-place by shuffling its contents.
This function only shuffles the array along the first axis of a
multi-dimensional array. The order of sub-arrays is changed but
their contents remains the same.
Parameters
----------
x : array_like
The array or list to be shuffled.
Returns
-------
None
实例
In [32]: x = np.arange(1,7)
In [33]: x
Out[33]: array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
In [34]: np.random.shuffle(x)
In [35]: x
Out[35]: array([4, 1, 6, 3, 5, 2])
自定义概率分布抽样
choice
功能
给定一个数组或list,从中抽样。可自定义概率分布,即自定义各元素被抽到的概率(默认为均匀分布)
接口
Docstring:
choice(a, size=None, replace=True, p=None)
Generates a random sample from a given 1-D array
注意:replace为True,则抽样出的n个元素可以重复,即每次抽样出一个元素后,还会将其放回样本池,默认可重复;反之。
实例
1、元素为均匀分布
In [107]: x = np.arange(1,7)
In [108]: np.random.choice(x,5)
Out[108]: array([3, 4, 5, 6, 3])
In [109]: np.random.choice(x,5,replace=False)
Out[109]: array([2, 1, 5, 6, 4])
2、自定义元素的概率分布
In [110]: x = ['石头','剪刀','布']
In [111]: np.random.choice(x,5,p=[0.2,0.3,0.5])
Out[111]: array(['布', '布', '布', '布', '剪刀'], dtype='同理,可验证是否按照自定义的概率分布进行抽样。
x = ['石头','剪刀','布']
res = np.random.choice(x,5000,p=[0.2,0.3,0.5])
_, ax = plt.subplots()
n,bins,patches = ax.hist(res,bins=3,density=1)
p = n*(bins[1]-bins[0])
s = [ax.get_xticklabels()[i].get_text() for i in range(3)]
print(list(zip(s,p)))
结果:
[('石头', 0.19440000000000002), ('布', 0.5024), ('剪刀', 0.3031999999999999)]
总结
- 用
uniform(low, high, size)生成[low, high)内均匀分布的随机数(float)
low,high默认为[0,1),即等价于rand() - 用
randint(low, high, size)生成[low, high)内均匀分布的随机整数(int) - 用
normal(loc, scale,size)随机生成正态分布( μ , σ \mu,\sigma μ,σ)的随机数(float)
loc,scale默认为0,1,即等价于randn() - 用
choice生成自定义概率分布的随机数(或其他类型元素)