1、pytorch 张量与运算API
一、初识张量
1、概念
Tensors,与numpy中的ndarray类似,但是在pytorch中,Tensors可以使用GPU进行计算。张量实际上就是一个多维数组,目的是能够创造更高维度的矩阵、向量。
| 张量维度 | 含义 |
| 0维 | 标量 |
| 1维 | 向量 |
| 2维 | 矩阵 |
| 3维 | 时间序列数据 |
| 4维 | 图像 |
2、创建张量
方法一:随机初始化矩阵
import torch
a = torch.rand(2,3)
#创建一个[0,1)均匀取值的2×3张量
b = torch.randn(2,3)
#创建一个以0为均值,1为方差的2×3张量
c = torch.randint(0,5,(5,))
#创建一个[0,5)范围整数随机取值的长度为5的一维张量方法二:构造特殊矩阵
import torch
a = torch.zeros((2,3))
b = torch.ones((2,3))
c = torch.eye(3)
d = torch.zeros_like(torch.rand(2,3))
e = torch.ones_like(torch.rand(2,3))方法三: 直接创建
import torch
t = torch.tensor([[1,2],[3,4]],dtype = torch.float)方法四:tensor与numpy互相转化
import torch
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([1,2,3], dtype=np.float32)
arr2 = np.array([4,5,6])
from_numpy1 = torch.from_numpy(arr1)
from_numpy2 = torch.from_numpy(arr2)
print("from_numpy1:",from_numpy1)
print("from_numpy2:",from_numpy2)二、部分tensor运算常用API
1、torch.arange(start=0, end, step=1)
2、torch.cat(tensors, dim=0, *, out=None) 将张量拼接
3、torch.chunk(input, chunks, dim=0)
dim=0时按行分块,dim=1时按列分块
4、torch.gather(input, dim, index)
解析:dim 0代表按列索引,1代表按行索引
5、torch.numel(input)
计算张量中共有多少元素
6、torch.reshape(input, shape)
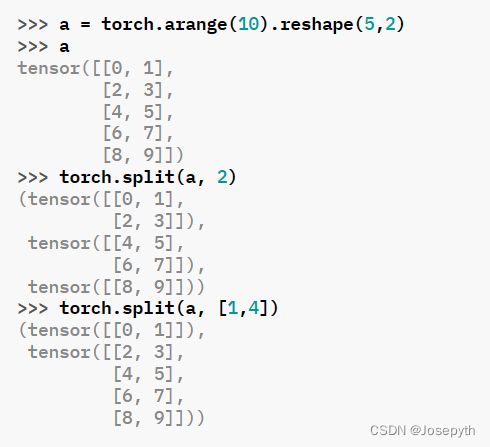
7、 torch.split(tensor, split_size_or_sections, dim=0)
与chunk函数辨析:chunk只能将张量分为等大小的chunk,而split函数可以将张量分为任意大小
8、torch.squeeze(input, dim=None)
压缩维度
9、torch.take(input, index)
将input展开成一维向量并根据索引取数据
10、torch.tile(input, dims)
解释:dims为(2,2)时,即将y的行元素复制两遍,列元素复制两遍,并保持数据维度不变。
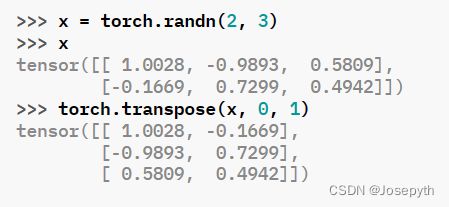
11、 torch.transpose(input, dim0, dim1) 将input在两个维度上转置
12、 torch.unbind(input, dim=0)
按维度进行切片
13、 torch.where(condition, x, y)
解释:若不满足condition,用y的数据替换x的数据
14、torch.normal(mean, std, size)
(1)、mean,std:张量(每个数据均值和标准差一一对应)
(2)、mean:标量 std:张量(共享mean,数据个数与std个数保持一致)
(3)、mean:张量 std:标量(共享std,数据个数与mean个数保持一致)
(4)、mean,std:张量(数据个数由size决定)