string函数
一. string的构造函数的形式:
string str:生成空字符串
string s(str):生成字符串为str的复制品
string s(str, strbegin,strlen):将字符串str中从下标strbegin开始、长度为strlen的部分作为字符串初值
string s(cstr, char_len):以C_string类型cstr的前char_len个字符串作为字符串s的初值
string s(num ,c):生成num个c字符的字符串
string s(str, stridx):将字符串str中从下标stridx开始到字符串结束的位置作为字符串初值
eg:
string str1; //生成空字符串
string str2("123456789"); //生成"1234456789"的复制品
string str3("12345", 0, 3);//结果为"123"
string str4("012345", 5); //结果为"01234"
string str5(5, '1'); //结果为"11111"
string str6(str2, 2); //结果为"3456789"
#include
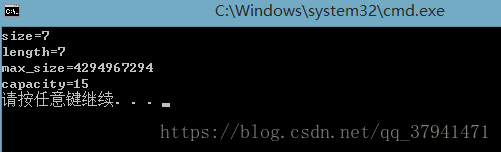
1. size()和length():返回string对象的字符个数,他们执行效果相同。
2. max_size():返回string对象最多包含的字符数,超出会抛出length_error异常
3. capacity():重新分配内存之前,string对象能包含的最大字符数
void test2()
{
string s("1234567");
cout << "size=" << s.size() << endl;
cout << "length=" << s.length() << endl;
cout << "max_size=" << s.max_size() << endl;
cout << "capacity=" << s.capacity() << endl;
}
1. C ++字符串支持常见的比较操作符(>,>=,<,<=,==,!=),甚至支持string与C-string的比较(如 str<”hello”)。
在使用>,>=,<,<=这些操作符的时候是根据“当前字符特性”将字符按字典顺序进行逐一得 比较。字典排序靠前的字符小,
比较的顺序是从前向后比较,遇到不相等的字符就按这个位置上的两个字符的比较结果确定两个字符串的大小(前面减后面)
同时,string (“aaaa”) <string(aaaaa)。
2. 另一个功能强大的比较函数是成员函数compare()。他支持多参数处理,支持用索引值和长度定位子串来进行比较。
他返回一个整数来表示比较结果,返回值意义如下:0:相等 1:大于 -1:小于 (A的ASCII码是65,a的ASCII码是97)
void test3()
{
// (A的ASCII码是65,a的ASCII码是97)
// 前面减去后面的ASCII码,>0返回1,<0返回-1,相同返回0
string A("aBcd");
string B("Abcd");
string C("123456");
string D("123dfg");
// "aBcd" 和 "Abcd"比较------ a > A
cout << "A.compare(B):" << A.compare(B)<< endl; // 结果:1
// "cd" 和 "Abcd"比较------- c > A
cout << "A.compare(2, 3, B):" <<A.compare(2, 3, B)<< endl; // 结果:1
// "cd" 和 "cd"比较
cout << "A.compare(2, 3, B, 2, 3):" << A.compare(2, 3, B, 2, 3) << endl; // 结果:0
// 由结果看出来:0表示下标,3表示长度
// "123" 和 "123"比较
cout << "C.compare(0, 3, D, 0, 3)" <<C.compare(0, 3, D, 0, 3) << endl; // 结果:0
}

四. string的插入:push_back() 和 insert()
void test4()
{
string s1;
// 尾插一个字符
s1.push_back('a');
s1.push_back('b');
s1.push_back('c');
cout<<"s1:"<<s1<<endl; // s1:abc
// insert(pos,char):在制定的位置pos前插入字符char
s1.insert(s1.begin(),'1');
cout<<"s1:"<<s1<<endl; // s1:1abc
}

五、string拼接字符串:append() & + 操作符
void test5()
{
// 方法一:append()
string s1("abc");
s1.append("def");
cout<<"s1:"<<s1<<endl; // s1:abcdef
// 方法二:+ 操作符
string s2 = "abc";
/*s2 += "def";*/
string s3 = "def";
s2 += s3.c_str();
cout<<"s2:"<<s2<<endl; // s2:abcdef
}
void test6()
{
string s1("abcdef"); // 调用一次构造函数
// 方法一: 下标法
for( int i = 0; i < s1.size() ; i++ )
{
cout<<s1[i];
}
cout<<endl;
// 方法二:正向迭代器
string::iterator iter = s1.begin();
for( ; iter < s1.end() ; iter++)
{
cout<<*iter;
}
cout<<endl;
// 方法三:反向迭代器
string::reverse_iterator riter = s1.rbegin();
for( ; riter < s1.rend() ; riter++)
{
cout<<*riter;
}
cout<<endl;
}
1. iterator erase(iterator p);//删除字符串中p所指的字符
2. iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last);//删除字符串中迭代器
区间[first,last)上所有字符
3. string& erase(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);//删除字符串中从索引
位置pos开始的len个字符
4. void clear();//删除字符串中所有字符
void test6()
{
string s1 = "123456789";
// s1.erase(s1.begin()+1); // 结果:13456789
// s1.erase(s1.begin()+1,s1.end()-2); // 结果:189
s1.erase(1,6); // 结果:189
string::iterator iter = s1.begin();
while( iter != s1.end() )
{
cout<<*iter;
*iter++;
}
cout<<endl;
}
八、 string的字符替换:
1. string& replace(size_t pos, size_t n, const char *s);//将当前字符串
从pos索引开始的n个字符,替换成字符串s
2. string& replace(size_t pos, size_t n, size_t n1, char c); //将当前字符串从pos索引开始的n个字符,替换成n1个字符c
3. string& replace(iterator i1, iterator i2, const char* s);//将当前字符串[i1,i2)区间中的字符串替换为字符串s
void test7()
{
string s1("hello,world!");
cout<<s1.size()<<endl; // 结果:12
s1.replace(s1.size()-1,1,1,'.'); // 结果:hello,world.
// 这里的6表示下标 5表示长度
s1.replace(6,5,"girl"); // 结果:hello,girl.
// s1.begin(),s1.begin()+5 是左闭右开区间
s1.replace(s1.begin(),s1.begin()+5,"boy"); // 结果:boy,girl.
cout<<s1<<endl;
}
九、 string的大小写转换:tolower()和toupper()函数 或者 STL中的transform算法
方法一:使用C语言之前的方法,使用函数,进行转换
#include 方法二:通过STL的transform算法配合的toupper和tolower来实现该功能
#include 使用C语言之前的方法,使用函数,进行转换
#include 通过STL的transform算法配合的toupper和tolower来实现该功能
#include 十、 string的查找:find
1. size_t find (constchar* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
//在当前字符串的pos索引位置开始,查找子串s,返回找到的位置索引,
-1表示查找不到子串
2. size_t find (charc, size_t pos = 0) const;
//在当前字符串的pos索引位置开始,查找字符c,返回找到的位置索引,
-1表示查找不到字符
3. size_t rfind (constchar* s, size_t pos = npos) const;
//在当前字符串的pos索引位置开始,反向查找子串s,返回找到的位置索引,
-1表示查找不到子串
4. size_t rfind (charc, size_t pos = npos) const;
//在当前字符串的pos索引位置开始,反向查找字符c,返回找到的位置索引,-1表示查找不到字符
5. size_tfind_first_of (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
//在当前字符串的pos索引位置开始,查找子串s的字符,返回找到的位置索引,-1表示查找不到字符
6. size_tfind_first_not_of (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
//在当前字符串的pos索引位置开始,查找第一个不位于子串s的字符,返回找到的位置索引,-1表示查找不到字符
7. size_t find_last_of(const char* s, size_t pos = npos) const;
//在当前字符串的pos索引位置开始,查找最后一个位于子串s的字符,返回找到的位置索引,-1表示查找不到字符
8. size_tfind_last_not_of (const char* s, size_t pos = npos) const;
//在当前字符串的pos索引位置开始,查找最后一个不位于子串s的字符,返回找到的位置索引,-1表示查找不到子串
void test8()
{
string s("dog bird chicken bird cat");
//字符串查找-----找到后返回首字母在字符串中的下标
// 1. 查找一个字符串
cout << s.find("chicken") << endl; // 结果是:9
// 2. 从下标为6开始找字符'i',返回找到的第一个i的下标
cout << s.find('i',6) << endl; // 结果是:11
// 3. 从字符串的末尾开始查找字符串,返回的还是首字母在字符串中的下标
cout << s.rfind("chicken") << endl; // 结果是:9
// 4. 从字符串的末尾开始查找字符
cout << s.rfind('i') << endl; // 结果是:18-------因为是从末尾开始查找,所以返回第一次找到的字符
// 5. 在该字符串中查找第一个属于字符串s的字符
cout << s.find_first_of("13br98") << endl; // 结果是:4---b
// 6. 在该字符串中查找第一个不属于字符串s的字符------先匹配dog,然后bird匹配不到,所以打印4
cout << s.find_first_not_of("hello dog 2006") << endl; // 结果是:4
cout << s.find_first_not_of("dog bird 2006") << endl; // 结果是:9
// 7. 在该字符串最后中查找第一个属于字符串s的字符
cout << s.find_last_of("13r98") << endl; // 结果是:19
// 8. 在该字符串最后中查找第一个不属于字符串s的字符------先匹配t--a---c,然后空格匹配不到,所以打印21
cout << s.find_last_not_of("teac") << endl; // 结果是:21
}
十一、 string的排序:sort(s.begin(),s.end())
#include 十二、 string的分割/截取字符串:strtok() & substr()
void test10()
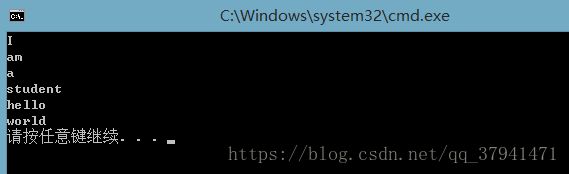
{
char str[] = "I,am,a,student; hello world!";
const char *split = ",; !";
char *p2 = strtok(str,split);
while( p2 != NULL )
{
cout<<p2<<endl;
p2 = strtok(NULL,split);
}
}
void test11()
{
string s1("0123456789");
string s2 = s1.substr(2,5); // 结果:23456-----参数5表示:截取的字符串的长度
cout<<s2<<endl;
}