LeetCode 590. N-ary Tree Postorder Traversal
Given the root of an n-ary tree, return the postorder traversal of its nodes' values.
Nary-Tree input serialization is represented in their level order traversal. Each group of children is separated by the null value (See examples)
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6] Output: [5,6,3,2,4,1]
Example 2:
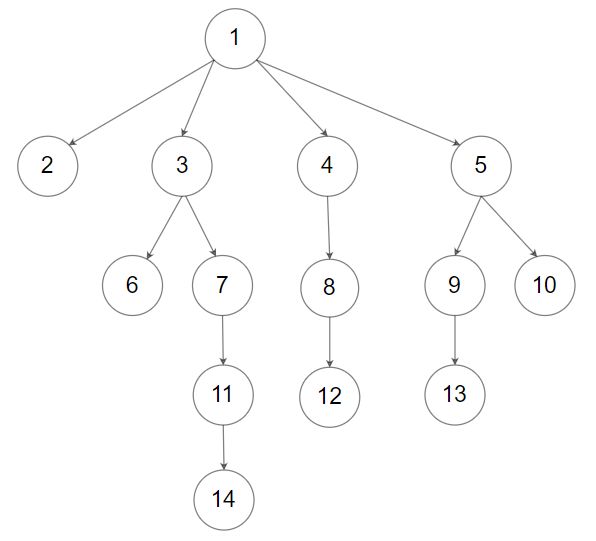
Input: root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14] Output: [2,6,14,11,7,3,12,8,4,13,9,10,5,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 104]. 0 <= Node.val <= 104- The height of the n-ary tree is less than or equal to
1000.
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
递归,也是很简单,只是变成了先遍历children再加root.val。
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public List postorder(Node root) {
List result = new ArrayList<>();
helper(root, result);
return result;
}
public void helper(Node root, List result) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
for (Node node : root.children) {
helper(node, result);
}
result.add(root.val);
}
} 迭代,还是记着Stack + Set的方法呢,但是,debug了巨久都没搞出来,大概是seen set的地方弄错了。想着应该要把所有children都seen了才能pop它,但是刚开始想的是seen表示这个node有没有见过,于是要check所有children都seen了还挺麻烦,也不太确定这个思路对不对,就去看了答案。居然几乎没什么人跟我一个思路,看了一个相似的代码,才确认了确实是只有当node没有chidlren或者children全都seen过了才能pop,于是就把seen的含义变成了这个node的所有children是不是都seen过,调整了seen.add的位置,代码就很简洁也一下就没bug了。也算是加深了对postorder iterative的理解。
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public List postorder(Node root) {
List result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return result;
}
Deque stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
Set seen = new HashSet<>(); // this node's children are all seen
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node node = stack.peek();
int size = node.children.size();
if (size == 0 || seen.contains(node)) {
node = stack.pop();
result.add(node.val);
} else {
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
Node child = node.children.get(i);
if (!seen.contains(child)) {
stack.push(child);
}
}
seen.add(node);
}
}
return result;
}
}