python实现GA求解基于多层编码的柔性作业车间调度问题
参考《matlab智能优化算法30个案例分析》
导入库
import numpy as np
import copy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
数据(可选机器+加工时间)
machine_mat = np.array([[(3,10),(2,),(3,9),(4,),(5,),(2,)],
[(1,),(3,),(4,7),(1,9),(2,7),(4,7)],
[(2,),(5,8),(6,8),(3,7),(3,10),(6,9)],
[(4,7),(6,7),(1,),(2,8),(6,9),(1,)],
[(6,8),(1,),(2,10),(5,),(1,),(5,8)],
[(5,),(4,10),(5,),(6,),(4,8),(3,)]],dtype=object)
process_mat = np.array([[(3,5),(6,),(1,4),(7,),(6,),(2,)],
[(10,),(8,),(5,7),(4,3),(10,12),(4,7)],
[(9,),(1,4),(5,6),(4,6),(7,9),(6,9)],
[(5,4),(5,6),(5,),(3,5),(8,8),(1,)],
[(3,3),(3,),(9,11),(1,),(5,),(5,8)],
[(10,),(3,3),(1,),(3,),(4,7),(3,)]],dtype=object)
相关参数
job_nb = 6 # 作业数
op_nb = 6 # 操作数
machine_nb = 10 # 机器数
maxgen = 200 # 最大迭代次数
pop_size = 50 # 种群规模
cross_rate = 0.8 # 交叉概率
mutate_rate = 0.6 # 变异概率
total_op_nb = job_nb * op_nb # 工序总数
GA
编码

此处编码中机器部分是可选机器集的索引编码。如工件3的工序1可选机器(3,9),机器编码为1,代表工件3的工序1在机器9上加工。工件和工序均从0开始计数
# 编码示例
[4. 2. 4. 5. 5. 2. 4. 2. 1. 0. 1. 2. 5. 5. 1. 1. 4. 5. 1. 0. 0. 3. 5. 2.
0. 4. 2. 0. 3. 4. 3. 3. 1. 0. 3. 3. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 1. 1. 0. 1. 0. 0.
0. 0. 1. 0. 1. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
解码
将染色体还原成三位数表示的工件加工顺序,如302表示工件3的第2道工序,工件和工序均从1开始计数
# 解码示例
[501. 301. 502. 601. 602. 302. 503. 303. 201. 101. 202. 304. 603. 604.
203. 204. 504. 605. 205. 102. 103. 401. 606. 305. 104. 505. 306. 105.
402. 506. 403. 404. 206. 106. 405. 406.]
适应度
[[ 0. 0. 6. 16. 18. 4. 16. 9. 18. 25. 24. 15. 25. 31. 32. 36. 25. 36.
41. 44. 54. 9. 44. 63. 63. 54. 72. 68. 33. 59. 47. 72. 68. 73. 83. 84.]
[ 6. 4. 16. 18. 25. 9. 25. 15. 24. 30. 32. 20. 31. 32. 36. 41. 33. 44.
44. 54. 63. 16. 47. 72. 68. 59. 73. 71. 36. 66. 51. 75. 71. 83. 84. 87.]]
选择
交叉
使用order crossover(OX)交叉算子
示例如下:
(1)父代母代
[5. 0. 0. 5. 3. 5. 4. 3. 3. 0. 4. 5. 5. 0. 0. 3. 3. 0. 4. 2. 3. 2. 5. 4.
2. 2. 4. 1. 2. 2. 4. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 0. 1. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 1. 1. 0. 0. 0.
0. 1. 1. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0.]
[5. 2. 3. 4. 0. 1. 1. 2. 5. 1. 3. 4. 1. 2. 0. 4. 2. 3. 3. 1. 4. 3. 3. 5.
0. 5. 4. 2. 4. 2. 1. 0. 0. 5. 5. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1.
1. 1. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0.]
(2)初始子代
[5. 0. 0. 5. 3. 5. 4. 3. 3. 0. 4. 5. 5. 0. 0. 3. 3. 0. 4. 2. 3. 2. 5. 4.
2. 2. 4. 2. 4. 2. 1. 0. 0. 5. 5. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1.
1. 1. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0.]
(2)子代相比父代缺少的工序和多余工序的位置
[2.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0]
[25, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35]
(3)缺失工序替代多余工序
[5. 0. 0. 5. 3. 5. 4. 3. 3. 0. 4. 5. 5. 0. 0. 3. 3. 0. 4. 2. 3. 2. 5. 4.
2. 2. 4. 2. 4. 2. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1.
1. 1. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0.]
变异
class GA(object):
def __init__(self,chrom_size,cross_rate,mutate_rate,pop_size,job_nb,op_nb):
self.chrom_size = chrom_size # 染色体长度
self.cross_rate = cross_rate # 交叉概率
self.mutate_rate = mutate_rate # 变异概率
self.pop_size = pop_size # 种群大小
self.pop = np.zeros((pop_size,2 * chrom_size)) # 初始种群编码
self.job_nb = job_nb # 作业数
self.op_nb = op_nb # 每个作业的操作数
# 编码
def encode(self):
number = [self.op_nb] * self.job_nb # 每个作业的操作数
for j in range(self.pop_size):
numbertemp = number.copy() # 一定要用copy!否则number也会变化
for i in range(self.chrom_size):
val = np.random.randint(self.job_nb) # 随机选择作业val分配
while numbertemp[val] == 0: # 如果作业val的操作已经安排完,则重新选择作业分配
val = np.random.randint(self.job_nb)
self.pop[j, i] = val # 编码中记录上作业val的序号
numbertemp[val] = numbertemp[val] - 1 # 作业val的操作数减1
temp = machine_mat[self.op_nb - numbertemp[val] - 1, val] # 找到作业val当前操作对应的机器
size_temp = len(temp)
self.pop[j, i + self.chrom_size] = np.random.randint(size_temp)
return self.pop
# 解码
def decode(self,pop_new):
seq = []
for i in range(self.pop_size):
chrom = pop_new[i]
chrom_op = chrom[:self.chrom_size] # 获取操作编码
temp = np.zeros(self.job_nb) # 记录作业出现次数即操作编号
p = np.zeros(self.chrom_size) # 三位数,301表示作业3的第一个操作
for i in range(self.chrom_size):
job = int(chrom_op[i]) # 获取操作编码中的作业编号
temp[job] = temp[job] + 1 # 作业job的操作编号加一
p[i] = (job + 1) * 100 + temp[job] # 单个操作编码成三位数
seq.append(p)
return np.stack(seq)
# 完工时间(适应度函数)
def caltime(self,seq, machine_nb, process_mat, machine_mat,pop_new):
makespan = []
machine_number = []
for i in range(self.pop_size):
chrom = pop_new[i]
chrom_ma = chrom[self.chrom_size:] # 机器编码
TM = np.zeros(machine_nb) # 机器当前时间
TP = np.zeros(job_nb) # 作业当前时间
m_list = np.zeros(self.chrom_size)
Pval = np.zeros((2, self.chrom_size)) # 记录每个工序的开始时间和结束时间
for k in range(self.chrom_size):
job, op = divmod(int(seq[i][k]), 100) # 获取作业和操作编号(job,op)
index = int(chrom_ma[k]) # op对应的机器编码
ma = machine_mat[op-1,job-1][index] # 该操作选择的加工机器ma
m_list[k] = ma
pt = process_mat[op-1, job-1][index] # 该操作的选择机器上的加工时间pt
TMval = TM[ma-1] # 机器ma完成当前op的时间点
TPval = TP[job-1] # 作业job上一道工序完成时间点
if TMval > TPval: # 判断机器先可用还是上一道操作先完成
val = TMval
else:
val = TPval
Pval[0, k] = int(val) # 开始时间点
Pval[1, k] = int(val) + pt # 完工时间点
TM[ma-1] = Pval[1, k] # 更新机器ma的时间
TP[job-1] = Pval[1, k] # 更新作业job的时间
makespan.append(Pval)
machine_number.append(m_list)
return np.stack(makespan),np.stack(machine_number)
# 选择
def select(self,makespan,pop_new):
fitness = np.max(makespan[:,1],axis=1)
max_fitness = np.max(fitness)
for i in range(len(fitness)):
fitness[i] = max_fitness - fitness[i] # 调度方案最大完工时间越小,适应度越大
# 选择保留个体的索引
index = np.random.choice(np.arange(self.pop_size),size=self.pop_size,replace=True,p=fitness/fitness.sum())
return pop_new[index]
# 交叉
def cross(self,cross_rate,father,pop_new):
if np.random.rand() < cross_rate:
mother_index = np.random.randint(self.pop_size)
mother = pop_new[int(mother_index)] # 随机选择另一个个体进行交叉
#print('mother:{}'.format(mother))
pos = int(np.random.default_rng(12345).integers(0, self.chrom_size, 1)) # 交叉位置
global child
child = np.concatenate((father[:pos], mother[pos:])) # 新个体
#print("before:{}".format(child))
child_sub, father_sub = copy.deepcopy(child), copy.deepcopy(father) # 用于调整工序
for i in range(0, total_op_nb): # father_sub和child_sub分别记录了子代相比父代多余和缺少的操作
try:
# index函数找不到索引会报错,因此需要使用try except
inx = list(father_sub).index(child_sub[i])
if inx < total_op_nb:
father_sub[inx] = -1
child_sub[i] = -1
except ValueError as e:
pass
fa_record = [] # 记录缺失的值
ch_record = [] # 记录多余值的位置
for i in range(total_op_nb):
if father_sub[i] != -1:
fa_record.append(father_sub[i])
if child_sub[i] != -1:
ch_record.append(i)
for count in range(len(fa_record)):
child[int(ch_record[count])] = fa_record[count] # 将child中多余的操作更改为缺失的操作
return child
# 变异
def mutate(self, parent,mutate_rate):
for point in range(self.chrom_size):
if np.random.rand() < mutate_rate:
swap_point = np.random.randint(0, self.chrom_size) # 随机变异点
swapA, swapB = parent[point], parent[swap_point]
parent[point], parent[swap_point] = swapB, swapA # 对换作业和机器顺序
swapA_ma, swapB_ma = parent[point + self.chrom_size], parent[swap_point + self.chrom_size]
parent[point + self.chrom_size], parent[swap_point + self.chrom_size] = swapB_ma, swapA_ma
return parent
合法个体
交叉变异后存在机器编码不合理的染色体,需要进行修正
import random
class legal(object):
def __init__(self,chrom_size,job_nb):
self.chrom_size = chrom_size
self.job_nb = job_nb
def random_index(self, rate): # 按照概率返回随机数
start = 0
index = 0
max_time = max(rate)
rate = list(map(lambda x:max_time + 1 -x,rate))
randnum = random.randint(1, sum(rate))
for index, scope in enumerate(rate):
start += scope
if randnum <= start:
break
return index
def legal_solution(self, solution): # 交叉变异后的染色体中机器编码部分可能存在索引超出范围
count = np.zeros(self.job_nb, dtype=int)
for i in range(self.chrom_size):
job_val = int(solution[i])
op_val = count[job_val]
count[job_val] += 1
size = len(machine_mat[op_val, job_val])
if size == 1:
ma = 0
else: # 按照加工时间大小选择机器
ma = self.random_index(list(process_mat[op_val,job_val]))
# if size < solution[i + self.chrom_size] + 1:
# ma = np.random.randint(size)
# solution[i + self.chrom_size] = ma
solution[i + self.chrom_size] = ma # 修改机器编码
return solution
绘图
def plot(mean_ct,best_ct):
plt.figure(figsize=(10,3))
plt.subplot(121)
plt.title('mean')
plt.plot(mean_ct)
plt.subplot(122)
plt.title('best')
plt.plot(best_ct)
plt.show()
主函数
GA_JSP = GA(total_op_nb,cross_rate,mutate_rate,pop_size,job_nb,op_nb)
init_pop = GA_JSP.encode()
pop_new = init_pop
legal = legal(chrom_size=total_op_nb,job_nb=job_nb)
best_ct = 999999
mean_list = []
min_list = []
for gen in range(maxgen):
de_pop = GA_JSP.decode(pop_new)
makespan,machine = GA_JSP.caltime(de_pop,machine_nb,process_mat,machine_mat,pop_new)
fitness = np.max(makespan[:,1],axis=1)
if best_ct > np.min(fitness):
best_ct = np.min(fitness)
best_index = np.argmin(fitness)
best_se = pop_new[best_index]
best_pt = makespan[best_index]
best_ma = machine[best_index]
mean_list.append(np.mean(fitness))
min_list.append(best_ct)
select_pop = GA_JSP.select(makespan,pop_new)
pop_copy = select_pop
for i in range(GA_JSP.pop_size):
new = GA_JSP.cross(cross_rate,pop_copy[i],pop_copy)
new = GA_JSP.mutate(new,mutate_rate)
new = legal.legal_solution(new)
select_pop[i] = new
pop_new = select_pop
plot(mean_list,min_list)
print(best_ct,best_index)
print('best se:{}'.format(best_se))
print('best pt:{}'.format(best_pt))
print('best ma:{}'.format(best_ma))
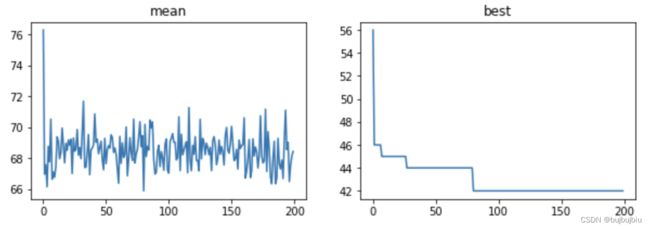
结果
经过200次迭代后找到的最优解如下,完工时间为42(书中最优解为47)
42.0 84
best se:[3. 1. 5. 5. 2. 0. 0. 3. 1. 3. 2. 0. 2. 5. 4. 1. 5. 0. 2. 3. 5. 4. 1. 3.
4. 1. 2. 0. 1. 0. 2. 4. 5. 4. 3. 4. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
best pt:[[ 0. 0. 6. 8. 0. 1. 4. 7. 6. 14. 12. 14. 17. 12. 0. 14. 21. 23.
22. 23. 22. 6. 18. 27. 18. 27. 27. 28. 30. 31. 41. 25. 27. 33. 28. 38.]
[ 7. 6. 8. 12. 1. 4. 14. 10. 14. 18. 17. 23. 22. 21. 6. 15. 22. 28.
27. 26. 27. 18. 24. 28. 25. 30. 36. 31. 33. 41. 42. 33. 30. 38. 31. 42.]]
best ma:[4. 2. 2. 4. 3. 3. 1. 9. 3. 3. 4. 2. 6. 9. 5. 5. 1. 4. 1. 2. 5. 7. 7. 5.
3. 1. 2. 8. 4. 5. 5. 9. 3. 1. 6. 4.]
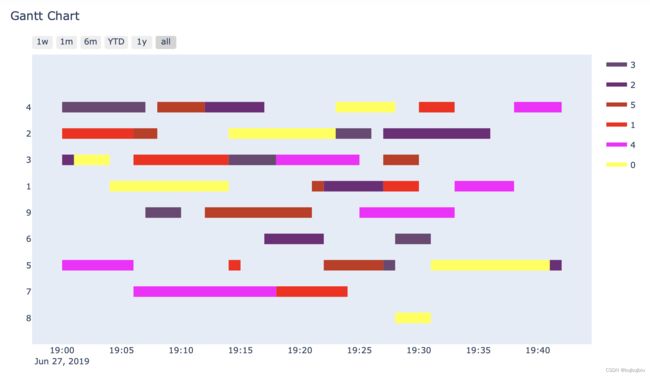
甘特图
create_gantt用法见python绘制作业车间甘特图(plotly库之create_gantt和timeline)
task = list(best_ma.astype(int))
start = list(best_pt[0].astype(int))
finish = list(best_pt[1].astype(int))
resource = list(best_se[:36].astype(int))
import pandas as pd
Resource = pd.Series(resource)
Task = pd.Series(task)
Start = pd.Series(start)
Finish = pd.Series(finish)
df = pd.DataFrame(list(zip(Task,Start,Finish,Resource)))
df.columns = ['Task','Start','Finish','Resource']
datetime = pd.Timestamp('20190627 19:00:00')
for i in range(len(df)):
df['Start'].loc[i] = datetime + pd.Timedelta(minutes = df['Start'].loc[i])
df['Finish'].loc[i] = datetime + pd.Timedelta(minutes = df['Finish'].loc[i])
df['Resource'] = df['Resource'].astype(str)
from plotly.express import timeline
from plotly.figure_factory import create_gantt
colors = ('rgb(46, 137, 205)',
'rgb(114, 44, 121)',
'rgb(198, 47, 105)',
'rgb(58, 149, 136)',
'rgb(107, 127, 135)',
'rgb(46, 180, 50)')
fig = create_gantt(df,colors=['rgb(200,50,25)',(1,0,1),'#6c4774','rgb(114, 44, 121)','rgb(255,0,0)',(1,1,0.2)],
index_col = 'Resource',reverse_colors=True,show_colorbar=True,group_tasks = True)
fig.show()