SMILES Enumeration
将同一个分子用多个 smiles 表示,作为应用 NLP 处理分子的一种数据增强方式,原文:SMILES Enumeration as Data Augmentation for Neural Network Modeling of Molecules,代码:SMILES-enumeration。本文从实例运行开始分析代码即 SmilesEnumerator.py
1.展示
from SmilesEnumerator import SmilesEnumerator
sme = SmilesEnumerator()
for i in range(10):
print(sme.randomize_smiles("CCC(=O)O[C@@]1(CC[NH+](C[C@H]1CC=C)C)c2ccccc2"))
"""
c1cccc([C@@]2(OC(CC)=O)CC[NH+](C)C[C@H]2CC=C)c1
C([C@H]1[C@@](OC(CC)=O)(c2ccccc2)CC[NH+](C)C1)C=C
c1ccc([C@]2(OC(=O)CC)[C@H](CC=C)C[NH+](C)CC2)cc1
c1cccc([C@@]2(OC(=O)CC)CC[NH+](C)C[C@H]2CC=C)c1
C(=O)(CC)O[C@]1(c2ccccc2)CC[NH+](C)C[C@H]1CC=C
C(C)C(O[C@@]1(c2ccccc2)[C@H](CC=C)C[NH+](C)CC1)=O
C1[NH+](C)C[C@@H](CC=C)[C@@](OC(CC)=O)(c2ccccc2)C1
C(C)C(=O)O[C@@]1(c2ccccc2)[C@H](CC=C)C[NH+](C)CC1
CCC(O[C@]1(c2ccccc2)CC[NH+](C)C[C@H]1CC=C)=O
C(C(O[C@]1(c2ccccc2)CC[NH+](C)C[C@H]1CC=C)=O)C
"""
- SmilesEnumerator 对象给定 smiles 表示的分子,产生此分子的其他 smiles 表示,选择产生的第一行 smiles 与原 smiles比较,二者在分子表示方面等价,示例如下:
from rdkit import Chem
from rdkit.Chem.Draw import IPythonConsole
IPythonConsole.ipython_useSVG =True
mol1,mol2=Chem.MolFromSmiles("CCC(=O)O[C@@]1(CC[NH+](C[C@H]1CC=C)C)c2ccccc2"),Chem.MolFromSmiles("c1cccc([C@@]2(OC(CC)=O)CC[NH+](C)C[C@H]2CC=C)c1")
mol1,mol2
1.1.SmilesEnumerator
class SmilesEnumerator(object):
"""SMILES Enumerator, vectorizer and devectorizer
#Arguments
charset: string containing the characters for the vectorization
can also be generated via the .fit() method
pad: Length of the vectorization
leftpad: Add spaces to the left of the SMILES
isomericSmiles: Generate SMILES containing information about stereogenic centers
enum: Enumerate the SMILES during transform
canonical: use canonical SMILES during transform (overrides enum)
"""
def __init__(self, charset = '@C)(=cOn1S2/H[N]\\', pad=120, leftpad=True, isomericSmiles=True, enum=True, canonical=False):
self._charset = None
self.charset = charset
self.pad = pad
self.leftpad = leftpad
self.isomericSmiles = isomericSmiles
self.enumerate = enum
self.canonical = canonical
@property
def charset(self):
return self._charset
@charset.setter
def charset(self, charset):
self._charset = charset
self._charlen = len(charset)
self._char_to_int = dict((c,i) for i,c in enumerate(charset))
self._int_to_char = dict((i,c) for i,c in enumerate(charset))
def fit(self, smiles, extra_chars=[], extra_pad = 5):
"""Performs extraction of the charset and length of a SMILES datasets and sets self.pad and self.charset
#Arguments
smiles: Numpy array or Pandas series containing smiles as strings
extra_chars: List of extra chars to add to the charset (e.g. "\\\\" when "/" is present)
extra_pad: Extra padding to add before or after the SMILES vectorization
"""
charset = set("".join(list(smiles)))
self.charset = "".join(charset.union(set(extra_chars)))
self.pad = max([len(smile) for smile in smiles]) + extra_pad
def randomize_smiles(self, smiles):
"""Perform a randomization of a SMILES string
must be RDKit sanitizable"""
m = Chem.MolFromSmiles(smiles)
ans = list(range(m.GetNumAtoms()))
np.random.shuffle(ans)
nm = Chem.RenumberAtoms(m,ans)
return Chem.MolToSmiles(nm, canonical=self.canonical, isomericSmiles=self.isomericSmiles)
def transform(self, smiles):
"""Perform an enumeration (randomization) and vectorization of a Numpy array of smiles strings
#Arguments
smiles: Numpy array or Pandas series containing smiles as strings
"""
one_hot = np.zeros((smiles.shape[0], self.pad, self._charlen),dtype=np.int8)
if self.leftpad:
for i,ss in enumerate(smiles):
if self.enumerate: ss = self.randomize_smiles(ss)
l = len(ss)
diff = self.pad - l
for j,c in enumerate(ss):
one_hot[i,j+diff,self._char_to_int[c]] = 1
return one_hot
else:
for i,ss in enumerate(smiles):
if self.enumerate: ss = self.randomize_smiles(ss)
for j,c in enumerate(ss):
one_hot[i,j,self._char_to_int[c]] = 1
return one_hot
def reverse_transform(self, vect):
""" Performs a conversion of a vectorized SMILES to a smiles strings
charset must be the same as used for vectorization.
#Arguments
vect: Numpy array of vectorized SMILES.
"""
smiles = []
for v in vect:
#mask v
v=v[v.sum(axis=1)==1]
#Find one hot encoded index with argmax, translate to char and join to string
smile = "".join(self._int_to_char[i] for i in v.argmax(axis=1))
smiles.append(smile)
return np.array(smiles)
- _charset,charset 是 smiles 存储所需的字符组成的字符串,@charset.setter 表示修改 self.charset 时会触发这个方法,更新 self._charset 等属性
- randomize_smiles 先将 smiles 转化为分子,再为原子重新编号,然后转换回 smiles ,示例如下:
from rdkit import Chem
from rdkit.Chem.Draw import IPythonConsole
import numpy as np
m=Chem.MolFromSmiles("CCC(=O)O[C@@]1(CC[NH+](C[C@H]1CC=C)C)c2ccccc2")
ans = list(range(m.GetNumAtoms()))
np.random.shuffle(ans)
print(ans) #[5, 3, 16, 20, 14, 12, 18, 7, 11, 19, 2, 10, 17, 1, 8, 6, 15, 0, 9, 4, 13]
nm = Chem.RenumberAtoms(m,ans) #1.2.Vectorization
import numpy as np
smiles = np.array(["CCC(=O)O[C@@]1(CC[NH+](C[C@H]1CC=C)C)c2ccccc2"])
print(smiles.shape) #(1,)
sme.fit(smiles)
print(sme.charset) #=2@NH+c]OC([1)
print(sme.pad) #50
- fit 先将列表中所有的 smiles 字符串连接在一起,再用 set 去重,拼接可能额外指定的字符后更新charset 属性(这样自动修改 self._charset,self._charlen)和 pad 参数,pad 为 最长 smiles 字符的长度 + extra_pad
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
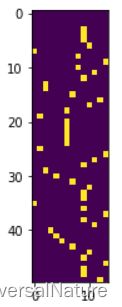
vect = sme.transform(smiles)
plt.imshow(vect[0])
print(sme.enumerate, sme.canonical) #True False
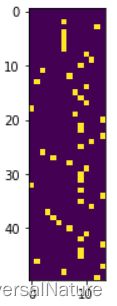
vect = sme.transform(smiles)
plt.imshow(vect[0])
print(sme.reverse_transform(vect)) #['CCC(=O)O[C@@]1(c2ccccc2)[C@H](CC=C)C[NH+](C)CC1']
-
transform 返回 (smiles.shape[0], self.pad, self._charlen) 大小的 one-hot 张量,每个 smiles 用(self.pad, self._charlen) 大小的矩阵表示,smiles 中的每个字符用 self._charlen 大小的 one-hot 表示,每个 smiles 统一为 pad 个字符
-
reverse_transform 将 one-hot 张量转换回 smiles
2.模型测试
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_csv("Example_data/Sutherland_DHFR.csv")
print(data.head())
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
#We ignore the > signs, and use random splitting for simplicity
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data["smiles_parent"],
np.log(data["PC_uM_value"]).values.reshape(-1,1),
random_state=42)
from sklearn.preprocessing import RobustScaler
rbs = RobustScaler(with_centering=True, with_scaling=True, quantile_range=(5.0, 95.0), copy=True)
y_train = rbs.fit_transform((y_train))
y_test = rbs.transform(y_test)
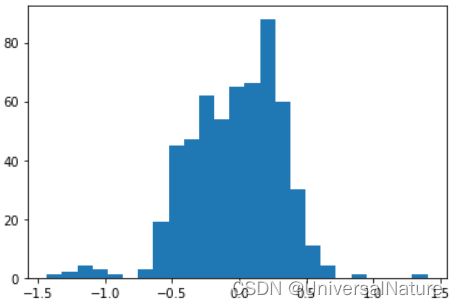
_ = plt.hist(y_train, bins=25)
- 利用 smiles 字符串预测标量数值,RobustScaler 对预测数据进行归一化,从图中可以看出处理后大部分数据分布在 -1~1之间
import tensorflow.keras.backend as K
from SmilesEnumerator import SmilesIterator
#The SmilesEnumerator must be fit to the entire dataset, so that all chars are registered
sme.fit(data["smiles_parent"])
sme.leftpad = True
print(sme.charset) #3o4n+c-(l5N[s1F=SB2IH]#OrC)
print(sme.pad) #75
#The dtype is set for the K.floatx(), which is the numerical type configured for Tensorflow or Theano
generator = SmilesIterator(X_train, y_train, sme, batch_size=200, dtype=K.floatx())
X,y = generator.next()
print(X.shape) #(200, 75, 27)
print(y.shape) #(200, 1)
2.1.Iterator & SmilesIterator
class Iterator(object):
"""Abstract base class for data iterators.
# Arguments
n: Integer, total number of samples in the dataset to loop over.
batch_size: Integer, size of a batch.
shuffle: Boolean, whether to shuffle the data between epochs.
seed: Random seeding for data shuffling.
"""
def __init__(self, n, batch_size, shuffle, seed):
self.n = n
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.shuffle = shuffle
self.batch_index = 0
self.total_batches_seen = 0
self.lock = threading.Lock()
self.index_generator = self._flow_index(n, batch_size, shuffle, seed)
if n < batch_size:
raise ValueError('Input data length is shorter than batch_size\nAdjust batch_size')
def reset(self):
self.batch_index = 0
def _flow_index(self, n, batch_size=32, shuffle=False, seed=None):
# Ensure self.batch_index is 0.
self.reset()
while 1:
if seed is not None:
np.random.seed(seed + self.total_batches_seen)
if self.batch_index == 0:
index_array = np.arange(n)
if shuffle:
index_array = np.random.permutation(n)
current_index = (self.batch_index * batch_size) % n
if n > current_index + batch_size:
current_batch_size = batch_size
self.batch_index += 1
else:
current_batch_size = n - current_index
self.batch_index = 0
self.total_batches_seen += 1
yield (index_array[current_index: current_index + current_batch_size],
current_index, current_batch_size)
def __iter__(self):
# Needed if we want to do something like:
# for x, y in data_gen.flow(...):
return self
def __next__(self, *args, **kwargs):
return self.next(*args, **kwargs)
- 定义 Iterator 基类,index_generator 是一个函数,调用时返回 batch 的索引列表,batch 开始的位置,batch 的大小
- 定义 __iter__ 和 __next__ 是可迭代对象必须的
class SmilesIterator(Iterator):
"""Iterator yielding data from a SMILES array.
# Arguments
x: Numpy array of SMILES input data.
y: Numpy array of targets data.
smiles_data_generator: Instance of `SmilesEnumerator`
to use for random SMILES generation.
batch_size: Integer, size of a batch.
shuffle: Boolean, whether to shuffle the data between epochs.
seed: Random seed for data shuffling.
dtype: dtype to use for returned batch. Set to keras.backend.floatx if using Keras
"""
def __init__(self, x, y, smiles_data_generator,
batch_size=32, shuffle=False, seed=None,
dtype=np.float32
):
if y is not None and len(x) != len(y):
raise ValueError('X (images tensor) and y (labels) '
'should have the same length. '
'Found: X.shape = %s, y.shape = %s' %
(np.asarray(x).shape, np.asarray(y).shape))
self.x = np.asarray(x)
if y is not None:
self.y = np.asarray(y)
else:
self.y = None
self.smiles_data_generator = smiles_data_generator
self.dtype = dtype
super(SmilesIterator, self).__init__(x.shape[0], batch_size, shuffle, seed)
def next(self):
"""For python 2.x.
# Returns
The next batch.
"""
# Keeps under lock only the mechanism which advances
# the indexing of each batch.
with self.lock:
index_array, current_index, current_batch_size = next(self.index_generator)
# The transformation of images is not under thread lock
# so it can be done in parallel
batch_x = np.zeros(tuple([current_batch_size] + [ self.smiles_data_generator.pad, self.smiles_data_generator._charlen]), dtype=self.dtype)
for i, j in enumerate(index_array):
smiles = self.x[j:j+1]
x = self.smiles_data_generator.transform(smiles)
batch_x[i] = x
if self.y is None:
return batch_x
batch_y = self.y[index_array]
return batch_x, batch_y
- batch_x 是 (batch_size,pad,_charlen) 大小的张量,for 循环中,i 是batch 中 smiles 的索引,j 是原始数据中 smiles 的索引,返回 smiles_data_generator 产生的字符串,做到数据增强
2.2.model
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, LSTM
from tensorflow.keras import regularizers
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import RMSprop
input_shape = X.shape[1:]
output_shape = 1
model = Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(64,
input_shape=input_shape,
dropout = 0.19
#unroll= True
))
model.add(Dense(output_shape,
kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l1_l2(0.005,0.01),
activation="linear"))
model.compile(loss="mse", optimizer=RMSprop(lr=0.005))
print(model.summary())
"""
Model: "sequential_4"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
lstm_4 (LSTM) (None, 64) 23552
dense_4 (Dense) (None, 1) 65
=================================================================
Total params: 23,617
Trainable params: 23,617
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
None
"""
- LSTM 第一个参数是隐藏层的大小,经过 LSTM 后,(batch_size,pad,_charlen) 的张量输出 (batch_size,64) 大小的矩阵,batch 中的每个 smiles 被编码为长度为 64 的向量,再经过全连接层输出
- 如果不调用 summary,可以不指定 input_shape 参数,维度能够根据实际输入自动推断
2.3.run & scores
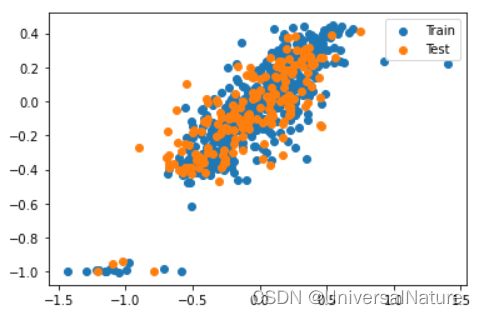
model.fit_generator(generator, steps_per_epoch=100, epochs=25, workers=4)
y_pred_train = model.predict(sme.transform(X_train))
y_pred_test = model.predict(sme.transform(X_test))
plt.scatter(y_train, y_pred_train, label="Train")
plt.scatter(y_test, y_pred_test, label="Test")
plt.legend()
- 从图中可以看出大致是 y = x 的趋势,预测较准确
3.总结
- 将 smiles 字符串等价转换为多个 smiles,做到了数据增强