CSS学习
1 多重样式层叠
一般而言,所有的样式会根据下面的规则层叠于一个新的虚拟样式表中,其中数字 4 拥有最高的优先权。
- 浏览器缺省设置
- 外部样式表
- 内部样式表(位于 <head> 标签内部)
- 内联样式(在 HTML 元素内部)
2 CSS 语法
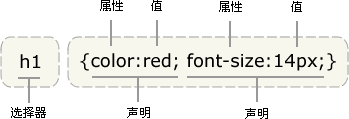
2.1 值的不同写法和单位
p { color: #ff0000; }
CSS 的缩写形式:
p { color: #f00; }
2.2 写引号
提示:如果值为若干单词,则要给值加引号:
p {font-family: "sans serif";}
2.4 继承及其问题
子元素从父元素继承属性。但是它并不总是按此方式工作。
创建一个针对子元素的特殊规则,这样它就会摆脱父元素的规则。
3 选择器
3.1 分组选择器
h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6 {
color: green;
}3.2 派生选择器
定义一个派生选择器:也叫上下文选择器 (contextual selectors)
li strong {
font-style: italic;
font-weight: normal;
}请注意标记为 <strong> 的蓝色代码的上下文关系:
<p><strong>我是粗体字,不是斜体字,因为我不在列表当中,所以这个规则对我不起作用</strong></p> <ol><li><strong>我是斜体字。这是因为 strong 元素位于 li 元素内。</strong></li><li>我是正常的字体。</li> </ol>
在上面的例子中,只有 li 元素中的 strong 元素的样式为斜体字
3.2.1 后代选择器
再看看下面的 CSS 规则(后代选择器):
strong {
color: red;
}
h2 {
color: red;
}
h2 strong {
color: blue;
}
下面是它施加影响的 HTML:
<p>The strongly emphasized word in this paragraph is<strong>red</strong>.</p> <h2>This subhead is also red.</h2><h2>The strongly emphasized word in this subhead is<strong>blue</strong>.</h2>
后代选择器有一个易被忽视的方面,即两个元素之间的层次间隔可以是无限的。
ul em {color:red;}
<ul>
<li>List item 1
<ol>
<li>List item 1-1</li>
<li>List item 1-2</li>
<li>List item 1-3
<ol>
<li>List item 1-3-1</li>
<li>List item <em>1-3-2</em></li>
<li>List item 1-3-3</li>
</ol>
</li>
<li>List item 1-4</li>
</ol>
</li>
<li>List item 2</li>
<li>List item 3</li>
</ul>
3.2.2 子元素选择器(Child selectors)
只能选择作为某元素子元素的元素
h1 > strong {color:red;}
这个规则会把第一个 h1 下面的两个 strong 元素变为红色,但是第二个 h1 中的 strong 不受影响:
<h1>This is <strong>very</strong> <strong>very</strong> important.</h1> <h1>This is <em>really <strong>very</strong></em> important.</h1>
3.2.3 相邻兄弟选择器(Adjacent sibling selector)
可选择紧接在另一元素后的元素,且二者有相同父元素。
如果要增加紧接在 h1 元素后出现的段落的上边距,可以这样写:
h1 + p {margin-top:50px;}
用一个结合符只能选择两个相邻兄弟中的第二个元素。
3.2.4 结合其他选择器
相邻兄弟结合符还可以结合其他结合符:
html > body table + ul {margin-top:20px;}
这个选择器解释为:选择紧接在 table 元素后出现的所有兄弟 ul 元素,该 table 元素包含在一个 body 元素中,body 元素本身是 html 元素的子元素。
3.3 id 选择器
id 选择器以 "#" 来定义,一个html文件中只可出现一次。
下面的两个 id 选择器,第一个可以定义元素的颜色为红色,第二个定义元素的颜色为绿色:
#red{color:red;}#green{color:green;}
下面的 HTML 代码中,id 属性为 red 的 p 元素显示为红色,而 id 属性为 green 的 p 元素显示为绿色。
<pid="red">这个段落是红色。</p> <pid="green">这个段落是绿色。</p>
id选择器和派生选择器
#sidebar p {
font-style: italic;
text-align: right;
margin-top: 0.5em;
}上面的样式只会应用于出现在 id 是 sidebar 的元素内的段落。
3.4 css类选择器
.center {text-align: center}<h1class="center"> This heading will be center-aligned </h1> <pclass="center"> This paragraph will also be center-aligned. </p>
.fancy td {
color: #f60;
background: #666;
}在上面这个例子中,类名为 fancy 的更大的元素内部的表格单元。
td.fancy {
color: #f60;
background: #666;
}在上面的例子中,类名为 fancy 的表格单元将是带有灰色背景的橙色。
3.5 属性选择器
带有 title 属性的所有元素设置样式:
[title]
{
color:red;
}title="W3School" 的所有元素设置样式:
[title=W3School]
{
border:5px solid blue;
}适用于由空格分隔的属性值:
[title~=hello] { color:red; }适用于由连字符分隔的属性值
[lang|=en] { color:red; }
3.6 总结
| 选择器 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| [attribute] | 用于选取带有指定属性的元素。 |
| [attribute=value] | 用于选取带有指定属性和值的元素。 |
| [attribute~=value] | 用于选取属性值中包含指定词汇的元素。以空格分开 |
| [attribute|=value] | 用于选取带有以指定值开头的属性值的元素,该值必须是整个单词。以连接词分开 |
| [attribute^=value] | 匹配属性值以指定值开头的每个元素。 |
| [attribute$=value] | 匹配属性值以指定值结尾的每个元素。 |
| [attribute*=value] | 匹配属性值中包含指定值的每个元素。 |