AppWidgets
App Widgets
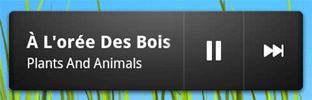
App Widgets是一类视图较小的应用程序,它们可以内嵌在其它应用程序中(比如主屏)并 接收定时更新。在用户接口中,这类widget是以一些view视图呈现的,我们可以使用App Widget provider表述一个这种widget。可以内嵌App Widgets的应用程序组件称作App Widget host。下图是一个Music App Widget的截屏。
本篇介绍如何使用App Widget provider编写一个App Widget。有关创建自己的AppWidgetHost的讨论,参见App Widget Host部分。
Widget Design
更多有关app widget设计的信息,请阅读Widgets设计向导部分。
The Basics
创建一个App Widget,需要如下内容:
AppWidgetProviderInfo对象——描述App Widget的metadata,例如App Widget's的layout,更新频率和AppWidgetProvider类。这需要定义在XML文件中。
AppWidgetProvider类实现——定义了我们和App Widget交互的基于广播事件的接口方法。通过它,接收App Widget更新,enabled,disabled和删除时的广播。
View layout——定义了App Widget的初始layout。定义在XML文件中。
除此之外,我们还可以定义一个App Widget的配置Activity。这是一个可选的Acitivity提供给用户在创建App Widget的时候修改App Widget的设置。
Declaring an App Widget in the Manifest
首先,在AndroidManifest.xml文件中申明一个AppWidgetProvider类。例如:
<receiver android:name="ExampleAppWidgetProvider">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_UPDATE"/>
</intent-filter>
<meta-data android:name="android.appwidget.provider"
android:resource="@xml/example_appwidget_info"/>
</receiver>
<receiver>标签需要android:name属性,指明这个App Widget使用的 AppWidgetProvider。
<intent-filter>标签必须报口一个有android:name属性的<action>标签。这个属性指明AppWidgetProvider接收ACTION_APPWIDGET_UPDATEG广播。这是我们唯一需要明确指明的广播。AppWidgetManager自动在需要的时候向AppWidgetProvider发送App Widget相关广播。
<meta-data>标签指定AppWidgetProviderInfo资源,它要求下列属性:
- android:name-metadata的名字,使用android.appwidget.provider确认AppWidgetProviderInfo描述的数据。
- android:resource-指明AppWidgetProviderInfo资源位置。
<appwidget-provider xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:minWidth="40dp"
android:minHeight="40dp"
android:updatePeroidMillis="86400000"
android:previewImage="@drawable/preview"
android:initialLayout="@layout/example_appwidget"
android:configure="com.example.android.ExampleAppWidgetConfigure"
android:resizeMode="horizontal|vertical"
android:widgetCategory="home_screen|keyguard"
android:initialKeyguardLayout="@layout/example_keyguard">
</appwidget-provider>
<appwidget-provider>属性总结:
- minWidth和minHeight-指定了初始状态下App Widget消费的最小数量空间。主屏定义了网格但愿定义了宽和高,如果App Widget的最小width和height不匹配网格尺寸,那么App Widget的尺寸取舍为最接近的网格尺寸。查看App Widget Design Guidelines获取更多App Widget尺寸相关信息。
- minResizeWidth和minResizeHeight-指定App Widget的绝对最小尺寸。这些值所定义的尺寸的意思是小于它们的时候App Widget将比较模糊或不可使用。这组属性允许用户重定义widget的尺寸,但是这组尺寸必须比minWidth和minHeight定义的缺省尺寸小。Android3.1引入。同样查看App Widget Design Guidelines获取更多App Widget尺寸相关信息。
- updatePeriodMillis-App Widget framework要求AppWidgetProvider调用onUpdate()回调方法更新app Widget。这个定义值不能保证更新即使发生,我们建议更新越少越好——为了省电,可能少于1次/h比较好。还有可能我们允许用户在配置信息中调整更新频率——有些人希望stock ticker15分钟更新一次,有些人可能希望一天只更新四次。
- initialLayout-定义了App Widget的layout资源。
- configure-定义了用户添加App Widget时启动的配置activity。这一项是可选项。
- previewImage-指定了当用户选择了该app widget后的视图。如果未指定,那么只有该应用程序启动器的图标。这一部分与AndroidManifest.xml文件中<receiver>标签下的android:previewImage属性交互。更多使用previewImage的讨论信息,查看Setting a Preview Image部分。
- autoAdvanceViewId-指定了app widget子视图id,它要被widget host主动激发。
- resizeMode-指定该widget尺寸重定义的方式。horizontally,vertically表明在某个方向上可重定义,两个方向都可以的话使用horizontal|vertical。
- minResizeHeight-当这个值比minHeight大或resizeMode中不支持vertical那么它无效。
- minResizeWidth-同上类似
- widgetCategory-申明是否可以显示在home screen上,lock screen上或都可。值为home_screen和keyguard。都可时需要保证它遵循所有widget类的设计规则。更多消息查看Enabling App Widgets on the Lockscreen。缺省值为home_screen。这一属性在Android4.2引入。
- initialKeyguardLayout-它指定义在lock screen上的app widget layout的layout。它工作的方式同android:initialLayout,Android4.2引入。
<FrameLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:padding="@dimen/widget_margin"> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" android:background="@drawable/my_widget_background"> … </LinearLayout></FrameLayout>3.在res/values/文件夹中提供Android4.0之前的自定义margin。res/values-v14文件夹中为Android4.0 widgets定义无额外padding.
<dimen name="widget_margin">8dp</dimen>
res/values-v14/dimens.xml
<dimen name="widget_margin">0dp</dimen>
另一种选择是简单的在nine-patch背景图中构建margin。那么在API level14或更高版本中提供不同的nine-patches背景图。
- onUpdate()——根据updatePeriodMillis属性定义的时间进行调用。同时当用户添加App Widget时也进行调用。所以在这里需要进行必要的设置,例如定义View视图的时间句柄同时如果必要的话启动一个temporary Service。然而如果定义了一个配置Activity,当用户添加App Widget时则不会需要调用这个方法。而配置Activity则有一无在第一次添加时完成配置。详见Creating an App Widget Configuration Activity.
- onAppWidgetOptionsChanged()——用户第一次放置widget和其它任何时候改变widget尺寸的时候调用。可以使用这个回调根据widget的边界范围来显示和隐藏内容。调用getAppWidgetOptions()获取尺寸边界。它返回一个Bundle对象包括下述内容:
- OPTION_APPWIDGET_MIN_WIDTH——当前宽度的下边界
- OPTION_APPWIDGET_MIN_HEIGHT
- OPTION_APPWIDGET_MAX_WIDTH
- OPTION_APPWIDGET_MAX_HEIGHT——当前宽度的上边界
- 这个回调在API Level16引入(Android4.1)更低版本的机器不能使用
- onDeleted(Context, int[])——App Widget从App Widget host中删除时调用这个回调。
- onEnabled(Context)——当一个App Widget实例第一次添加时调用。例如,用户添加了两个App Widget实例,这个回调只在第一次添加时调用。如果你想打开一个新的database或者其它所有App Widget都会使用的设置操作,那么这里是比较好的地方。
- onDisabled(Context)——最后一个App Widget实例被删除时调用。这里是清楚onEnabled(Context)所有操作的地方,例如删除一个临时database。
- onReceive(Context, Intent)——所有广播发生时调用,并且发生于上述所有回调方法之前。通常不需要实现这个方法因为缺省AppWidgetProvider实现过滤了所有App Widget广播并且只在合适的时候调用上述方法。
public class ExampleAppWidgetProvider extends AppWidgetProvider{
public void onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager, int[] appWidgetIds){
final int N = appWidgetIds.length;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
int appWidgetId = appWidgetIds[i];
Intent intent = new Intent(context, ExampleActivity.class);
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(context, 0, intent, 0);
RemoteViews views = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.appwidget_provider_layout);
views.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.button, pendingIntent);
appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetId, views);
}
}
} 这个AppWidgetProvider定义了onUpdate()方法,其中定义了PendingIntent启动一个Activity,并且根据setOnClickPendingIntent(int, PendingIntent)附着于App Widget按钮。注意到它包括一个循环。这个循环处理所有添加AppWidget的ID操作。这样,用户添加了多个App Widget实例同时进行更新。例如一个app widget两小时更新一次。而用户在一个小时之后添加了另外一个实例,那么这两个实例都会在第一个实例的两小时之后更新,而不再是第二个实例的两小时之后。
- ACTION_APPWIDGET_UPDATE
- ACTION_APPWIDGET_DELETED
- ACTION_APPWIDGET_ENABLED
- ACTION_APPWIDGET_DISABLED
- ACTION_APPWIDGET_OPTIONS_CHANGED
<activity android:name=".ExampleAppWidgetConfigure">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_CONFIGURE"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
同时,这个Activity必须在AppWidgetProviderInfo XML文件中声明,相应属性是android:configure。例如:
<appwidget-provider xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
...
android:configure="com.example.android.ExampleAppWidgetConfigure"
... >
</appwidget-provider>
注意到Activity声明使用的是完全名空间。因为它可以在相应的包外指定。
- App Widget host调用配置Activity,配置Activity需要总是返回一个结果,结果里需要包含App Widget ID,它由Intent传递启动配置Activity(作为EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID保存在Intent extras中)。
- 创建App Widget时将不再调用onUpdate()方法(系统在启动配置Activity时将不会发送ACTION_APPWIDGET_UPDATE广播)那么App Widget第一次创建时,配置Activity需要向AppWidgetManager要求更新。然而onUpdate()在后续更新中将会被调用——即只在第一次创建是跳过它。
当App Widget使用配置Activity时。配置完成时更新App Widget的责任就交给了这个Activity。它的做法是向AppWidgetManager要求更新。
- 首先,从启动Activity的Intent中获取App Widget ID。
Intent intent = getIntent();
Bundle extras = intent.getExtras();
if (extras != null) {
mAppWidgetId = extras.getInt(
AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID,
AppWidgetManager.INVALID_APPWIDGET_ID);
}
- 进行App Widget配置。
- 配置完成时,调用getInstance(Context)获取AppWidgetManager实例。
AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager = AppWidgetManager.getInstance(context);
- 调用updateAppWidget(int, RemoteViews)获取RemoteViews layout更新App Widget。
RemoteViews views = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(),
R.layout.example_appwidget);
appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(mAppWidgetId, views);
- 最后,创建返回Intent,设置给Activity返回结果,并且结束Activity。
Intent resultValue = new Intent();
resultValue.putExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, mAppWidgetId);
setResult(RESULT_OK, resultValue);
finish();
Tip:配置Activity第一次打开时,设置Activity result为RESULT_CANCLED。这样,用户在未完成配置设置而退出时,App Widget被告知配置取消,将不会添加App Widget。
<appwidget-provider xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" ... android:previewImage="@drawable/preview"> </appwidget-provider>
Android emulator包含了一个应用程序叫做"Widget Preview"。创建一个preview image,启动这个应用程序,选择一个app widget设置preview image出现的样式,最后放置到应用程序的drawable资源中。
<appwidget-provider xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" ... android:widgetCategory="keyguard|home_screen"> </appwidget-provider>
如果声明的一个widget既可以放置在主屏上,也可以放置在keyguard上,很可能我们希望根据放置的位置定制不同的widget。例如,创建不同的layout文件。那么下一步就是在运行时检测widget category进行响应。调用getAppWidgetOptions()获取widget放置位置的Bundle数据。返回的Bundle将会包括key值OPTION_APPWIDGET_HOST_CATEGORY,它的值为WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN或者WIDGET_CATEGORY_KEYGUARD。然后在AppWidgetProvider中检测widget category。例如:
AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager; int widgetId; Bundle myOptions = appWidgetManager.getAppWidgetOptions(widgetId); int category = myOptions.getInt(AppWidgetManager.OPTION_APPWIDGET_HOST_CATEGORY, -1); boolean isKeyguard = category == AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_KEYGUARD;一旦知道了widget的category,就可以有选择的装载baselayout,设置不同的属性等。例如
int baseLayout = isKeyguard ? R.layout.keyguard_widget_layout :R.layout_widget_layout;
也可以通过android:initialKeyguardLayout属性指定app widget在锁屏界面的初始化layout。它同android:initialLayout工作方式相同。
public class StackWidgetService extends RemoteViewsService {
@Override
public RemoteViewsFactory onGetViewFactory(Intent intent) {
return new StackRemoteViewsFactory(this.getApplicationContext(), intent);
}
}
class StackRemoteViewsFactory implements RemoteViewsService.RemoteViewsFactory {
//... include adapter-like methods here. See the StackView Widget sample.
}
Sample application

- 用户可以纵向滑出顶部的View显示下一个或先前的View。这是一个built-in StackView行为。
- 没有用户交互行为时,app widget自动有序的向前显示Views。这依赖于res/xml/stackwidgetinfo.xml文件中android:autoAdvanceViewId="@id/stack_view"的设置。这个设置应用于view ID,本例中是stack view的ID。
- 用户触摸顶层的view时,app widget显示Toast信息“Touched view n”,更多相关信息,查看Adding behavior to individual items。
- Manifest for app widgets with collections
<service android:name="MyWidgetService" ... android:permission="android.permission.BIND_REMOTEVIEWS" />
android:name="MyWidgetService"指我们继承RemoteViewsService的相关子类。
- Layout for app widgets with collections
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<StackView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/stack_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:loopViews="true" />
<TextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/empty_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:background="@drawable/widget_item_background"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:text="@string/empty_view_text"
android:textSize="20sp" />
</FrameLayout>
注意到上述样例中的empty_view显示的是StackView为空时的状态。
- AppWidgetProvider class for app widgets with collections
public void onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager, int[] appWidgetIds){
for(int i = 0; i < appWidgetIds.length; ++i){
Intent intent = new Intent(context, StackWidgetService.class);
intent.setData(Uri.parse(intent.toUri(Intent.URI_INTENT_SCHEME)));
RemoteViews rv = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.widget_layout);
rv.setRemoteAdapter(appWidgetIds[i], R.id.stack_view, intent);
rv.setEmptyView(R.id.stack_view, R.id.empty_view);
appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetIds[i], rv);
}
super.onUpdate(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetIds);
}
- RemoteViewsService class
如上所述,RemoteViewsService子类提供RemoteViewsFactory用来放置远程容器视图。特别的,需要做以下两步:
- RemoteViewsService子类是远程adapter要求RemoteViews的地方。
- 在RemoteViewsService子类中,包含一个实现了RemoteViewsFactory接口的类。RemoteViewsFactory是为了适配远程容器视图(如ListView, GridView)和提供给该视图的数据所设计的接口。那么这种实现就必须为data set中的每项提供RemoteViews对象。这个接口是Adapter的简单封装。
- RemoteViewsFactory interface
class StackRemoteViewsFactory implements RemoteViewsService.RemoteViewsFactory{
private static final int mCount = 10;
private List<WidgetItem> mWidgetItems = new ArrayList<WidgetItem>();
private Context mContext;
private int mAppWidgetId;
public StackRemoteViewsFactory(Context context, Intent intent){
mContext = context;
mAppWidgetId = intent.getIntExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, AppWidgetManager.INVALID_APPWIDGET_ID);
}
public void onCreate(){
for(int i = 0; i < mCount; i++){
mWidgetItems.add(new WidgetItem(i + "!"));
}
...
}
...
}
public RemoteViews getViewAt(int position){
RemoteViews rv = new RemoteViews(mContext.getPackageName(), R.layout.widget_item);
rv.setTextViewText(R.id.widget_item, mWidgetItems.get(position).text);
...
return rv;
}
Adding behavior to indivual items
- StackWidgetProvider(AppWidgetProvider子类)创建一个pending intent拥有自定义action——TOAST_ACTION。
- 用户触摸视图时,触发该intent并广播TOAST_ACTION。
- 这个广播由StackWidgetProvider的onReceive()函数拦截,由app widget显示这个Toast信息。数据则由RemoteViewsFactory通过RemoteViewsService提供。
public class StackWidgetProvider extends AppWidgetProvider{
public static final String TOAST_ACTION = "com.example.android.stackwidget.TOAST_ACTION";
public static final String EXTRA_ITEM = "com.example.android.stackwidget.EXTRA_ITEM";
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
AppWidgetManager mgr = AppWidgetManager.getInstance(context);
if (intent.getAction().equals(TOAST_ACTION)) {
int appWidgetId = intent.getIntExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID,
AppWidgetManager.INVALID_APPWIDGET_ID);
int viewIndex = intent.getIntExtra(EXTRA_ITEM, 0);
Toast.makeText(context, "Touched view " + viewIndex, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
super.onReceive(context, intent);
}
@Override
public void onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager, int[] appWidgetIds) {
for (int i = 0; i < appWidgetIds.length; ++i) {
Intent intent = new Intent(context, StackWidgetService.class);
intent.putExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, appWidgetIds[i]);
intent.setData(Uri.parse(intent.toUri(Intent.URI_INTENT_SCHEME)));
RemoteViews rv = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.widget_layout);
rv.setRemoteAdapter(appWidgetIds[i], R.id.stack_view, intent);
rv.setEmptyView(R.id.stack_view, R.id.empty_view);
Intent toastIntent = new Intent(context, StackWidgetProvider.class);
toastIntent.setAction(StackWidgetProvider.TOAST_ACTION);
toastIntent.putExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID, appWidgetIds[i]);
intent.setData(Uri.parse(intent.toUri(Intent.URI_INTENT_SCHEME)));
PendingIntent toastPendingIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context, 0, toastIntent,
PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
rv.setPendingIntentTemplate(R.id.stack_view, toastPendingIntent);
appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetIds[i], rv);
}
super.onUpdate(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetIds);
}
}
Setting the fill-in Intent
public class StackWidgetService extends RemoteViewsService {
@Override
public RemoteViewsFactory onGetViewFactory(Intent intent) {
return new StackRemoteViewsFactory(this.getApplicationContext(), intent);
}
}
class StackRemoteViewsFactory implements RemoteViewsService.RemoteViewsFactory {
private static final int mCount = 10;
private List<WidgetItem> mWidgetItems = new ArrayList<WidgetItem>();
private Context mContext;
private int mAppWidgetId;
public StackRemoteViewsFactory(Context context, Intent intent) {
mContext = context;
mAppWidgetId = intent.getIntExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_ID,
AppWidgetManager.INVALID_APPWIDGET_ID);
}
// Initialize the data set.
public void onCreate() {
// In onCreate() you set up any connections / cursors to your data source. Heavy lifting,
// for example downloading or creating content etc, should be deferred to onDataSetChanged()
// or getViewAt(). Taking more than 20 seconds in this call will result in an ANR.
for (int i = 0; i < mCount; i++) {
mWidgetItems.add(new WidgetItem(i + "!"));
}
...
}
...
// Given the position (index) of a WidgetItem in the array, use the item's text value in
// combination with the app widget item XML file to construct a RemoteViews object.
public RemoteViews getViewAt(int position) {
// position will always range from 0 to getCount() - 1.
// Construct a RemoteViews item based on the app widget item XML file, and set the
// text based on the position.
RemoteViews rv = new RemoteViews(mContext.getPackageName(), R.layout.widget_item);
rv.setTextViewText(R.id.widget_item, mWidgetItems.get(position).text);
// Next, set a fill-intent, which will be used to fill in the pending intent template
// that is set on the collection view in StackWidgetProvider.
Bundle extras = new Bundle();
extras.putInt(StackWidgetProvider.EXTRA_ITEM, position);
Intent fillInIntent = new Intent();
fillInIntent.putExtras(extras);
// Make it possible to distinguish the individual on-click
// action of a given item
rv.setOnClickFillInIntent(R.id.widget_item, fillInIntent);
...
// Return the RemoteViews object.
return rv;
}
...
}
Keeping Collection Data Fresh

使用容器的app widget的一个特征是提供给用户即时更新的内容。例如,考虑安卓3.0Gmail app widget,提供了用户对收件箱截屏的功能。实现这样的功能,我们需要触发RemoteViewsFactory和容器视图获取和展示新数据。通过AppWidgetManager调用notifyAppWidgetViewDataChanged()函数获取它。这同时会回调RemoteViewsFactory的onDataSetChanged()方法,获取新数据。注意到在onDataSetChanged()回调中可以同步processing-intensive操作。我们必须保证这一操作必须在从RemoteViewsFactory中获取metadata和视图数据的操作之前完成。除此之外,还可以在getViewAt()方法中进行processing-intensive操作。如果这个回调占用时间较长,加载中的视图(由RemoteViewsFactory的getLoadingView()方法指定)将会在容器视图的响应位置展示知道返回。