Python实现模拟退火算法(SA)在TSP问题中的应用
模拟退火算法
模拟退火算法是一种简单高效的优化算法,它的灵感来源于冶炼金属的降温过程,在这个过程中热运动趋于稳定,在优化过程中就是解的收敛。同时,通过在温度高是较大可能接受劣解和温度低时几乎不接受劣解从而在一定程度上避免了陷入局部最优。因此该算法较爬山算法有了明显的突破,下面我们针对TSP问题进行代码编写。(语言:Python)
代码
导入需要的库
from random import*
import numpy as np
from math import*
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
随机初始化100个城市的坐标
#随机初始化城市坐标
number_of_citys = 100
citys = []
for i in range(number_of_citys):
citys.append([randint(1,100),randint(1,100)])
citys = np.array(citys)
由城市坐标构建距离矩阵
#由城市坐标计算距离矩阵
distance = np.zeros((number_of_citys,number_of_citys))
for i in range(number_of_citys):
for j in range(number_of_citys):
distance[i][j] = sqrt((citys[i][0]-citys[j][0])**2+(citys[i][1]-citys[j][1])**2)
初始化参数
#初始化参数
iteration1 = 2000 #外循环迭代次数
T0 = 100000 #初始温度,取大些
Tf = 1 #截止温度,可以不用
alpha = 0.95 #温度更新因子
iteration2 = 10 #内循环迭代次数
fbest = 0 #最佳距离
初始化解
#初始化初解
x = []
for i in range(100):
x.append(i)
np.random.shuffle(x)
x = np.array(x)
for j in range(len(x) - 1):
fbest = fbest + distance[x[j]][x[j + 1]]
fbest = fbest + distance[x[-1]][x[0]]
xbest = x.copy()
f_now = fbest
x_now = xbest.copy()
这里的x_now和f_now是SA在运行过程中的当前解,但这个解不一定就是历史最优解,因此我们还设置了f_best和x_best用于记录历史最优解。
主循环和内部循环
主循环就是降温过程,内部循环就是在每一个温度下让算法达到平衡点。
for i in range(iteration1):
for k in range(iteration2):
#生成新解
x1 = [0 for q in range(number_of_citys)]
n1,n2 = randint(0,number_of_citys-1),randint(0,number_of_citys-1)
n = [n1,n2]
n.sort()
n1,n2 = n
#n1为0单独写
if n1 > 0:
x1[0:n1] = x_now[0:n1]
x1[n1:n2+1] = x_now[n2:n1-1:-1]
x1[n2+1:number_of_citys] = x_now[n2+1:number_of_citys]
else:
x1[0:n1] = x_now[0:n1]
x1[n1:n2+1] = x_now[n2::-1]
x1[n2+1:number_of_citys] = x_now[n2+1:number_of_citys]
s = 0;
for j in range(len(x1) - 1):
s = s + distance[x1[j]][x1[j + 1]]
s = s + distance[x1[-1]][x1[0]]
#判断是否更新解
if s <= f_now:
f_now = s
x_now = x1.copy()
if s > f_now:
deltaf = s - f_now
if random() < exp(-deltaf/T0):
f_now = s
x_now = x1.copy()
if s < fbest:
fbest = s
xbest = x1.copy()
温度更新
这里采用等比方式更新:
T0 = alpha * T0 #更新温度
如果你想把截止条件设置为最低温度,则有下面语句,不过为了更好的解,不要设置这个,通过该循环次数来调节。
# if T0 < Tf: #停止准则为最低温度时可以取消注释
# break
打印最佳路线和最佳距离
#打印最佳路线和最佳距离
print(xbest)
print(fbest)
[74, 82, 22, 38, 95, 75, 96, 46, 79, 19, 63, 31, 18, 54, 66, 52, 37, 35, 16, 41, 60, 30, 58, 33, 23, 39, 6, 11, 4, 53, 20, 32, 81, 43, 64, 85, 51, 25, 56, 86, 77, 40, 29, 71, 93, 3, 83, 57, 65, 2, 76, 21, 88, 49, 36, 92, 69, 45, 14, 1, 72, 13, 55, 62, 7, 26, 80, 84, 10, 5, 47, 48, 8, 15, 50, 24, 98, 9, 87, 59, 91, 89, 44, 90, 78, 17, 73, 97, 12, 28, 99, 61, 42, 94, 27, 34, 68, 67, 70, 0]
884.7203239019632
Matplotlib绘制结果
#绘制结果
plt.title('SA_TSP')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.plot(citys[...,0],citys[...,1],'ob',ms = 3)
plt.plot(citys[xbest,0],citys[xbest,1])
plt.plot([citys[xbest[-1],0],citys[xbest[0],0]],[citys[xbest[-1],1],citys[xbest[0],1]],ms = 2)
plt.show()
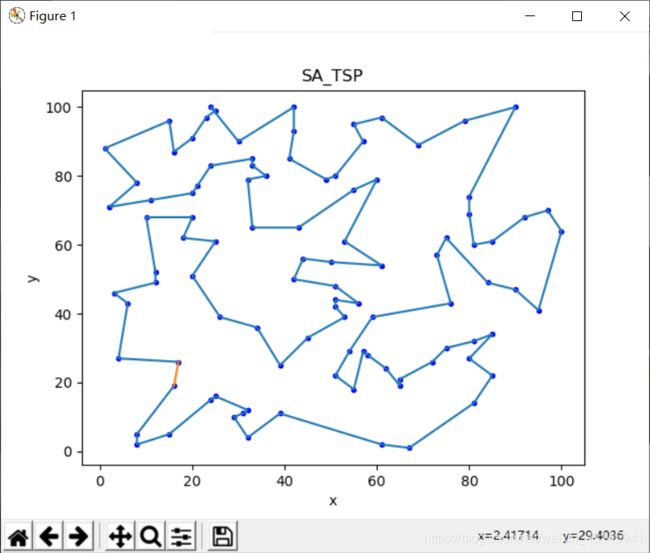
可以直观看出这个结果几乎就是最优解,之前也编写过GA、禁忌搜索解决TSP,现在看来SA不仅运行速度快,效果也不错。
整体代码
from random import*
import numpy as np
from math import*
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
#随机初始化城市坐标
number_of_citys = 100
citys = []
for i in range(number_of_citys):
citys.append([randint(1,100),randint(1,100)])
citys = np.array(citys)
#由城市坐标计算距离矩阵
distance = np.zeros((number_of_citys,number_of_citys))
for i in range(number_of_citys):
for j in range(number_of_citys):
distance[i][j] = sqrt((citys[i][0]-citys[j][0])**2+(citys[i][1]-citys[j][1])**2)
#初始化参数
iteration1 = 2000 #外循环迭代次数
T0 = 100000 #初始温度,取大些
Tf = 1 #截止温度,可以不用
alpha = 0.95 #温度更新因子
iteration2 = 10 #内循环迭代次数
fbest = 0 #最佳距离
#初始化初解
x = []
for i in range(100):
x.append(i)
np.random.shuffle(x)
x = np.array(x)
for j in range(len(x) - 1):
fbest = fbest + distance[x[j]][x[j + 1]]
fbest = fbest + distance[x[-1]][x[0]]
xbest = x.copy()
f_now = fbest
x_now = xbest.copy()
for i in range(iteration1):
for k in range(iteration2):
#生成新解
x1 = [0 for q in range(number_of_citys)]
n1,n2 = randint(0,number_of_citys-1),randint(0,number_of_citys-1)
n = [n1,n2]
n.sort()
n1,n2 = n
#n1为0单独写
if n1 > 0:
x1[0:n1] = x_now[0:n1]
x1[n1:n2+1] = x_now[n2:n1-1:-1]
x1[n2+1:number_of_citys] = x_now[n2+1:number_of_citys]
else:
x1[0:n1] = x_now[0:n1]
x1[n1:n2+1] = x_now[n2::-1]
x1[n2+1:number_of_citys] = x_now[n2+1:number_of_citys]
s = 0;
for j in range(len(x1) - 1):
s = s + distance[x1[j]][x1[j + 1]]
s = s + distance[x1[-1]][x1[0]]
#判断是否更新解
if s <= f_now:
f_now = s
x_now = x1.copy()
if s > f_now:
deltaf = s - f_now
if random() < exp(-deltaf/T0):
f_now = s
x_now = x1.copy()
if s < fbest:
fbest = s
xbest = x1.copy()
T0 = alpha * T0 #更新温度
# if T0 < Tf: #停止准则为最低温度时可以取消注释
# break
#打印最佳路线和最佳距离
print(xbest)
print(fbest)
#绘制结果
plt.title('SA_TSP')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.plot(citys[...,0],citys[...,1],'ob',ms = 3)
plt.plot(citys[xbest,0],citys[xbest,1])
plt.plot([citys[xbest[-1],0],citys[xbest[0],0]],[citys[xbest[-1],1],citys[xbest[0],1]],ms = 2)
plt.show()