《Towards Good Practices for Very Deep Two-Stream ConvNets》阅读笔记
作者信息:Limin Wang, Yuanjun Xiong, Zhe Wang, Yu Qiao,
摘要
深度卷积神经网络在静止图像的目标识别取得了巨大的成功,但是在视频的行为识别领域,深度学习提升的效果并不是很显著,主要的原因有两点:
- 相对于图像识别,视频的行为识别所使用的卷积网络结构深度太浅,因此模型的拟合能力因为深度受到限制。
- 第二点可能更为重要,主要是用于行为识别的视频数据集规模相对于ImageNet太小,因此在训练集上很容易导致严重的过拟合现象发生。
为了解决上述问题,采用了very deep two-stream网络用于行为识别,将当前流行的深度结构应用于视频领域。但是由于视频行为识别的规模较小,这种扩展并不容易。我们设计了多种实践应用于very deep two_stream 的训练,如下:
在时域网络和空间网络预训练
更小的学习速率
- 更多的图像增强技术
- high drop out 系数
与此同时,将Caffe 工具箱延伸到多GPU环境,从而有更高的计算效率,更少的内存消耗。very deep two_stream方法在UCF-101数据集上取得了91.4%的识别精度。
1.引言
近几年视频片段的行为识别取得了巨大的进步,这些方法可以分为两类:
- 人工绘制的局部特征和视觉词袋表示。
- 最成功的方法是提取 提升的轨迹特征,并且使用Fisher vector 表示
- 采用深度卷积神经网络从原始数据中(RGB图像和光流方程)来学习视频表示,以端到端的方式训练识别系统。
然而,不像图像分类,深度卷积神经网络相对于传统方法并没有产生很好的提升效果。我们认为主要的原因有两点:
- 行为的概念比目标更为复杂,并且与其他高层次的视觉概念相关联,例如交互目标,场景内容,人体姿态等。因此,更加复杂的问题需要高复杂性的模型拟合能力。然而,当前two-stream卷积网络的深度相对较浅(5层卷积层,3层全连接层)。
- 相对于图像识别领域的ImageNet数据集,行为识别的视频数据集相对规模较小。例如UCF-101数据集只有13320个视频片段。
2.Very Deep Two-stream ConNets
2.1 网络结构
在过去几年,提出了很多流行的网络结构,例如AlexNet,ClarifaiNet,GoogLeNet,VGGNet等等。这些网络结构特点的趋势主要有:更小的卷积核尺寸,更小的卷积步长,更深的网络结构。这些趋势证明了在提升识别性能上是有效的。
- GoogLeNet
代号为:Inception,其基本的思想是Hebbian 原则和多尺度处理。
每个Inception 模块是由多个不同尺度的卷积滤波器组成,这样可以增强网络的适应能力。
1×1 卷积操作可以进行特征降维,从而加快计算效率。
GoogLeNet由22层的Inception模块堆叠组成,以及可选的max-pooling层将图像对比度减少一半。 - VGGNet
它是一个新的卷积神经网络结构,拥有更小的卷积尺寸( 3×3 ),更小的卷积步长( 1×1 ),更小的下采样窗口( 2×2 ),更深的结构(19层)
VGGNet主要研究网络结构的深度对识别性能的影响。
VGGNet-16:13层卷积层,3层全连接层
VGGNet-19:16层卷积层,3层全连接层 - Very Deep Two-stream ConvNets
单帧图像( 224×224×3 )
时域输入为10帧光流场( 224×224×20 ),因此第一层卷积滤波操作和图像分类模型不一样
2.2网络训练
该部分主要介绍very deep two-stream卷积网络如何在UCF-101数据集进行训练。
UCF-101:13320 视频,提供3中分割方式评价。每一种模式,10000个视频用于训练,3300个视频用于测试。由于数据集规模较小,而且行为的内容相对复杂,所以训练深度two-stream网络比较复杂。 - Pre−trainingforTwo−streamConvNets. 当训练的数据集规模较小,预训练在网络的初始化方面已经被证明很有效果。对于空域网络,采用ImageNet训练的模型来初始化。对于时域网络,虽然它的输入是光流图像,携带的是运动信息,但是使用ImageNet网络模型仍然可以很好工作。
为了使ImageNet预训练模型合理,我们在光流场和ImageNet模型上做了一些修改。
第一步,从每一个视频提取光流场,并且通过线性变换离散化到间隔[0,255]中;
第二步,时域网络的通道数为20(空域是3),在所有通道上,对ImageNet模型滤波器的第一层求平均值,然后将结果复制20次作为时域网络的初始化值。 - 更小的学习速率
- 对于时域网络,学习速率开始为0.005,每10000次迭代下降为它的1/10,迭代30000次结束。
- 对于空域网络,学习速率开始为0.001,每4000次迭代后下降为1/10,迭代10000次结束。
学习速率共下降3次,与此同时我们发现迭代的次数更少,可能的原因在于我们使用了ImageNet模型预训练了网络。
- 更多的增强技术.
研究表明,随机裁剪和水平翻转在防止过拟合的问题上非常有效。我们尝试了两种新的有效的图像增强技术用于训练Two-stream ConvNets. - 设计了角落裁剪策略,我们只裁剪图像的4个角落和1个中间区域。 随机裁剪裁剪的区域容易接近图像中间区域,训练损失下降很快,但是容易导致过拟合问题。如果我们明确地限制裁剪的区域为4个角落和中间区域,网络的输入的变化(图像差异性较大)会增加,这种策略可以减少过拟合的影响。
- 使用多尺度的裁剪方法来训练very deep Two-stream ConvNets.
多尺度的方法在ImageNet数据集上进行目标识别非常有效,我们将其应用到行为识别。将输入图像的尺寸修正为256\times 340.从以下尺寸{256,224,192,168}随机采样裁剪宽和高,之后改变裁剪区域的尺寸为224\times 224.这种裁剪策略不仅引进了多尺度增强,同时增加了长宽比。
- Highdropout系数.
- 对时域网络,在全连接层,设置了较高的随机失活系数,设置的系数为0.9和0.8。
- 对空域网络,在全连接层,设置的系数为0.9和0.9
- 多GPU训练.
深度学习模型应用到视频的行为识别最大的障碍是它的长训练时间,多帧的输入增加了内存消耗来。
解决方法使用多GPU采用并行数据进行训练,使用caffe和OpenMPI实施。
- 4GPU,3.7x faster for VGGNET-16,4x faster for GoogLeNet
- 每个GPU 4x less 内存消耗。
2.3网络测试
测试阶段,采样25帧图像或者光流图像分别测试空域和时域网络。
对每一个选择的帧图像,获取10(4个角落,1个中间区域,以及它们的水平翻转)个输入。
从采样的帧中和裁剪区域获得最后的预测分数。
为了空域网络和时域网络的融合,对它们的预测分数采用加权求和,时域权重为2,空域权重为1.
3.实验
- 数据集实施细节
- 在UCF-101上验证算法,UCF-101包含101个行为类别,每个类别至少100个视频片段,整个数据集包括13320个视频,每个行为类别被分为25组。
- 光流场的提取采用TDD的方法,使用TVL1光流算法。具体地,我们使用OpenCV方案,主要因为它在精度和效率的平衡。
- 结果.
- 比较了三种不同的网络结构,ClarifaiNet,GoogLeNet,VGGNet-16.
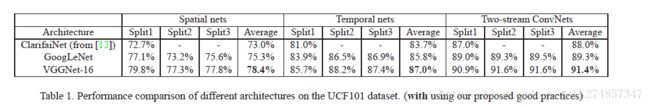
从结果可以看出,更深的网络获得性能更好。
在空域,VGGNet-16的性能相对于浅层网络提升了5%。
在时域,VGGNet-16的性能提升了4%。
Very deep Two-stream ConvNets 相对于原始的Two-Stream ConvNets提升了3.4%。 - 在THUMOS15验证集上,未使用提出好的训练方法,表现结果如下:
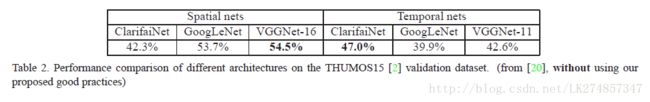
可以发现,在时域上,Very deep Two-stream ConvNets效果不是最好的。我们推测我们提出的方法实 践 (practices) 在避免过拟合的问题上有很好的效果,主要的原因在于
- 使用ImageNet模型预训练时域网络。
- 使用了更多的图像增强技术。
- 比较了三种不同的网络结构,ClarifaiNet,GoogLeNet,VGGNet-16.
Comparison.将我们的方法与最近流行的视频行为识别方法进行了对比,结果如下:

- 首先比较了人工特征和fisher vector表示的方法,如IDT算法; 深度学习特征的方法,比如轨迹池化-深度卷积描述符(TDD).我们的方法比所有的Fisher Vector都要好;
- 其次,比较我们的方法与其他深度网络的方法如DeepNet及基于循环神经网络的Two-stream方法。我们的方法比他们最好的方法提升了2.8%
4.结论
论文中主要提出了Very deep two-stream ConvNets方法,由于数据集规模较小,我们提出了一些好的实践来训练Very deep two-Stream 网络。基于这些训练方法和技巧,Very deep two-stream ConvNets在UCF-101数据集上获得了91.4%的精度。与此同时,我们扩展了Caffe 工具箱到多GPU方案中,从而获得了更高的效率和更少的内存消耗。
Reference.
[1] J. Deng, W. Dong, R. Socher, L. Li, K. Li, and F. Li.
ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database.
In CVPR, pages 248–255, 2009. 1
[2] A. Gorban, H. Idrees, Y.-G. Jiang, A. Roshan Zamir,
I. Laptev, M. Shah, and R. Sukthankar. THUMOS
challenge: Action recognition with a large number of
classes. http://www.thumos.info/, 2015. 3,
4
[3] K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, and J. Sun. Delving deep
into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance
on imagenet classification. CoRR, abs/1502.01852,
2015. 3
[4] Y. Jia, E. Shelhamer, J. Donahue, S. Karayev, J. Long,
R. B. Girshick, S. Guadarrama, and T. Darrell. Caffe:
Convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding.
CoRR, abs/1408.5093. 1, 3
[5] Y.-G. Jiang, J. Liu, A. Roshan Zamir, I. Laptev,
M. Piccardi, M. Shah, and R. Sukthankar. THUMOS
challenge: Action recognition with a large number of
classes, 2013. 3
[6] A. Karpathy, G. Toderici, S. Shetty, T. Leung, R. Sukthankar,
and L. Fei-Fei. Large-scale video classification
with convolutional neural networks. In CVPR,
pages 1725–1732, 2014. 4
[7] A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, and G. E. Hinton. ImageNet
classification with deep convolutional neural
networks. In NIPS, pages 1106–1114, 2012. 1, 2
[8] Z. Lan, M. Lin, X. Li, A. G. Hauptmann, and B. Raj.
Beyond gaussian pyramid: Multi-skip feature stacking
for action recognition. In CVPR, pages 204–212,
2015. 1, 4
[9] J. Y.-H. Ng, M. Hausknecht, S. Vijayanarasimhan,
O. Vinyals, R. Monga, and G. Toderici. Beyond short
snippets: Deep networks for video classification. In
CVPR, pages 4694–4702, 2015. 1, 4
[10] X. Peng, L. Wang, X. Wang, and Y. Qiao. Bag of
visual words and fusion methods for action recognition:
Comprehensive study and good practice. CoRR,
abs/1405.4506, 2014. 4
[11] J. S´anchez, F. Perronnin, T. Mensink, and J. J. Verbeek.
Image classification with the fisher vector: Theory
and practice. International Journal of Computer
Vision, 105(3):222–245, 2013. 1
[12] K. Simonyan and A. Zisserman. Two-stream convolutional
networks for action recognition in videos. In
NIPS, pages 568–576, 2014. 1, 2, 3, 4
[13] K. Simonyan and A. Zisserman. Very deep convolutional
networks for large-scale image recognition.
CoRR, abs/1409.1556, 2014. 1, 2, 3
[14] K. Soomro, A. R. Zamir, and M. Shah. UCF101: A
dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in
the wild. CoRR, abs/1212.0402, 2012. 1, 3
[15] C. Szegedy, W. Liu, Y. Jia, P. Sermanet, S. Reed,
D. Anguelov, D. Erhan, V. Vanhoucke, and A. Rabinovich.
Going deeper with convolutions. CoRR,
abs/1409.4842, 2014. 1, 2
[16] H. Wang and C. Schmid. Action recognition with improved
trajectories. In ICCV, pages 3551–3558, 2013.
1, 4
[17] L. Wang, Y. Qiao, and X. Tang. Mining motion atoms
and phrases for complex action recognition. In ICCV,
pages 2680–2687, 2013. 1
[18] L.Wang, Y. Qiao, and X. Tang. Motionlets: Mid-level
3D parts for human motion recognition. In CVPR,
pages 2674–2681, 2013. 1
[19] L. Wang, Y. Qiao, and X. Tang. Action recognition
with trajectory-pooled deep-convolutional descriptors.
In CVPR, pages 4305–4314, 2015. 1, 3, 4
[20] L. Wang, Z. Wang, Y. Xiong, and Y. Qiao.
CUHK&SIAT submission for THUMOS15 action
recognition challenge. In THUMOS’15 Action Recognition
Challenge, 2015. 3, 4
[21] C. Zach, T. Pock, and H. Bischof. A duality based approach
for realtime tv-L1 optical flow. In 29th DAGM
Symposium on Pattern Recognition, 2007. 3
[22] M. D. Zeiler and R. Fergus. Visualizing and understanding
convolutional networks. In ECCV, pages
818–833, 2014. 2