一、Java框架之Spring配置文件开发
文章目录
- 1. 基础概念
-
- 1.1 Spring Framework
- 1.2 核心概念
-
- 产生背景
- IoC、Bean、DI
- 2. 入门案例
-
- 2.1 普通Maven项目
- 2.2 IoC入门案例
- 2.3 DI入门案例
- 3. bean配置
-
- 3.1 bean基础配置
-
- bean的基础配置
- bean的别名配置
- bean的作用范围
- 3.2 bean实例化
-
- 实例化方法1:构造方法
- 实例化方法2:静态工厂
- 实例化方法3:实例工厂
- 实例化方法4:FactoryBean
- 3.3 bean的生命周期
- 4. 依赖注入
-
- 4.1 四种注入场景
-
- setter注入引用类型
- setter注入简单类型
- 构造器注入引用类型
- 构造器注入简单类型
- 4.2 自动装配
- 4.3 集合注入
- 5. IOC/DI配置管理第三方bean
-
- 5.1 案例:数据源对象管理
-
- druid管理
- c3p0管理
- 5.2 加载Properties文件
- 6. 核心容器
-
- 6.1 容器创建的方式
- 6.2 获取Bean的方式
- 6.3 容器类层次结构
- 7. Spring连接数据库案例
-
- AccountDao接口
- AccountServiceImpl.java
- applicationContext.xml
- Main.java
黑马SSM教程
SSM(Spring+SpringMVC+MyBatis)框架集由Spring、MyBatis两个开源框架整合而成(SpringMVC是Spring中的部分内容),常作为数据源较简单的web项目的框架
使用配置文件开发,涉及核心容器三个部分的内容:
- 1.容器相关;
- 2.bean相关;
- 3.依赖注入相关
1. 基础概念
Spring版本
- Spring1.0是纯配置文件开发
- Spring2.0为了简化开发引入了注解开发,此时是配置文件加注解的开发方式
- Spring3.0已经可以进行纯注解开发,使开发效率大幅提升,我们的课程会以注解开发为主
- Spring4.0根据JDK的版本升级对个别API进行了调整
- Spring5.0已经全面支持JDK8,现在Spring最新的是5系列所以建议大家把JDK安装成1.8版
1.1 Spring Framework
这里所学的Spring其实是Spring家族中的Spring Framework;
Spring Framework是Spring家族中其他框架的底层基础
Spring Framewor架构图如下:
(1)核心层
- Core Container:核心容器,这个模块是Spring最核心的模块,其他的都需要依赖该模块
(2)AOP层
- AOP:面向切面编程,它依赖核心层容器,目的是在不改变原有代码的前提下对其进行功能增强
- Aspects:AOP是思想,Aspects是对AOP思想的具体实现
(3)数据层
- Data Access:数据访问,Spring全家桶中有对数据访问的具体实现技术
- Data Integration:数据集成,Spring支持整合其他的数据层解决方案,比如Mybatis
- Transactions:事务,Spring中事务管理是Spring AOP的一个具体实现,也是后期学习的重点内容
(4)Web层
- 这一层的内容将在SpringMVC框架具体学习
(5)Test层
- Spring主要整合了Junit来完成单元测试和集成测试
1.2 核心概念
产生背景
- 存在的问题:如果在实现类中new了一个对象,那么对象的类需要改变时,就需要重新修改、发布
- 解决方案:IoC(Inversion of Control)控制反转:使用对象时,由主动new产生对象转换为由外部提供对象,此过程中对象创建控制权由程序转移到外部,此思想称为控制反转
private BookDao bookDao = new BookDaoImpl();
//修改为
private BookDao bookDao;//bookDao改为外部提供
IoC、Bean、DI
(1)核心概念
-
IOC(Inversion of Control)控制反转
- 使用对象时,由主动new产生对象转换为由外部提供对象,此过程中对象创建控制权由程序转移到外部,此思想称为控制反转
-
Spring和IoC
- Spring技术对IoC思想进行了实现
- Spring提供了一个容器,称为IoC容器,用来充当IOC思想中的"外部"
- IoC容器负责对象的创建、初始化等一系列工作,被创建或被管理的对象(包括service和dao对象)在IOC容器中统称为Bean
-
DI(Dependency Injection)依赖注入:IoC容器中存放了service和dao对象,并发现service对象依赖于dao对象运行,于是为他们建立依赖
- 在容器中建立bean与bean之间的依赖关系的整个过程,称为依赖注入
(2)这样做的目的是:充分解耦
- 使用IoC容器管理bean(IoC)
- 在IoC容器内将有依赖关系的bean进行关系绑定(DI)
(3)最终效果
- 使用对象时不仅可以直接从IOC容器中获取,并且获取到的bean已经绑定了所有的依赖关系
2. 入门案例
- 管理什么? (Service和Dao)
- 如何将被管理的对象告知IoC容器?(配置文件)
-
被管理的对象交给IoC容器,首先如何获取到IOC容器?(Spring框架提供相应的接口)
-
IoC容器得到后,如何从容器中获取bean? (接口方法)
- 使用Spring导入哪些坐标? (pom.xml)
2.1 普通Maven项目
创建普通的Maven项目,并添加需要的类,结构如下
public interface BookDao {
public void save();
}
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
public void save() {
System.out.println("book dao save ...");
}
}
public interface BookService {
public void save();
}
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
private BookDao bookDao = new BookDaoImpl();
public void save() {
System.out.println("book service save ...");
bookDao.save();
}
}
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BookService bookService = new BookServiceImpl();
bookService.save();
}
}
2.2 IoC入门案例
(1)在pom.xml添加Spring的依赖jar包
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-contextartifactId>
<version>5.2.10.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>4.12version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
(2)添加Spring配置文件
resources - New - XML Configuration File - Spring Config

(3)获取IoC容器和Bean
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//3. 获取IoC容器
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");//ApplicationContext是一个接口
//4. 获取bean - bookDao
BookDao bookDao = (BookDao) ctx.getBean("bookDao");//填写applicationContext.xml里面的id号
bookDao.save();
//获取bean - serviceDao
BookService bookService = (BookService) ctx.getBean("bookService");
bookService.save();
}
}
可以看到在App.java里面已经无需new对象,但此时BookServiceImpl中仍需要new一个对象,下面将通过DI对此进行改进
2.3 DI入门案例
(1)修改业务层需要new对象的部分
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
//5. 删除业务层中使用new的方式创建的dao对象
private BookDao bookDao;
public void save(){
System.out.println("book service save ...");
bookDao.save();
}
//6. 提供对应的set方法
public void setBookDao(BookDao bookDao){
this.bookDao = bookDao;
}
}
(2)修改applicationContext.xml中的配置
3. bean配置
3.1 bean基础配置
bean的基础配置
使用方式已在上一小节演示,重点是id和class属性的使用,此外还要掌握property进行依赖注入
bean的别名配置
bean的作用范围
-
默认情况下为单例模式(singleton),即getBean(“bookDao”)获取的是同一个对象
BookDao bookDao1 = (BookDao) ctx.getBean("bookDao"); BookDao bookDao2 = (BookDao) ctx.getBean("bookDao"); System.out.println(bookDao1); System.out.println(bookDao2); //输出时发现地址一致,都是:org.example.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl@25bbe1b6 -
通过scope属性,可以修改为非单例模式(prototype)
//applicationContext.xml中修改 <bean id="bookDao" class="org.example.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl" scope="prototype"/>注意:使用applicationContext时默认创建了一个bookDao,如果改成prototype,再在程序中创建并调用该bean时,这个过程会执行两次BookDao的构造函数
-
bean默认为单例的原因
为了提升性能,bean基本都是通过反射的方式创建的,反射的效率非常低
可以更快速的获取到bean,涉及到Spring的三级缓存
问题:会带来线程安全问题,因此Spring也提供了其他bean的作用域
3.2 bean实例化
实例化方法1:构造方法
-
私有的构造方法不会影响bean(不安全)
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao { private BookDaoImpl(){ System.out.println("book dao constructor is running ..."); } public void save(){ System.out.println("book dao save ..."); } }要点:(1)构造方法被调用了;(2)将构造方法设置为private不影响调用(因为反射)
-
bean调用的是无参构造
private BookDaoImpl(int i){ System.out.println("book dao constructor is running ..."); } //报错:BeanCreationException
实例化方法2:静态工厂
步骤1:普通静态工厂创建对象使用方法
-
创建OrderDao接口和OrderDaoImpl类
//接口 public interface OrderDao { public void save(); } //实现类 public class OrderDaoImpl implements OrderDao { public void save() { System.out.println("order dao save ..."); } } -
创建一个工厂类OrderDaoFactory并提供一个静态方法
package org.example.factoiry; import org.example.dao.OrderDao; import org.example.dao.impl.OrderDaoImpl; public class OrderDaoFactory { public static OrderDao getOrderDao(){ return new OrderDaoImpl(); } } -
调用静态工厂造对象
OrderDao orderDao = OrderDaoFactory.getOrderDao(); orderDao.save();
步骤2:使用bean管理静态工厂
-
创建bean对象
//在applicationContext.xml中添加 <bean id="orderDao" class="org.example.factory.OrderDaoFactory" factory-method="getOrderDao"/>factory-method指定由哪个方法返回对象
-
获取bean对象(无变化)
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); OrderDao orderDao = (OrderDao) ctx.getBean("orderDao"); orderDao.save();
实例化方法3:实例工厂
步骤1:普通实例工厂创建对象使用方法
-
创建UserDao接口、UserDaoImpl实现类
//接口 public interface UserDao { public void save(); } //实现类 public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao { public void save(){ System.out.println("user dao save ..."); } } -
public class UserDaoFactory { public UserDao getUserDao(){ return new UserDaoImpl(); } } -
调用实例工厂创建对象
UserDaoFactory userDaoFactory = new UserDaoFactory(); UserDao userDao = userDaoFactory.getUserDao(); userDao.save();
步骤2:使用bean管理实例工厂
-
创建bean对象
//在applicationContext.xml中添加 <bean id="userFactory" class="org.example.factory.UserDaoFactory"/> <bean id="userDao" factory-bean="userFactory" factory-method="getUserDao"/>要写2个bean对象,且使用 factory-bean属性
-
获取bean对象(无变化)
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); UserDao userDao = (UserDao) ctx.getBean("userDao"); userDao.save();
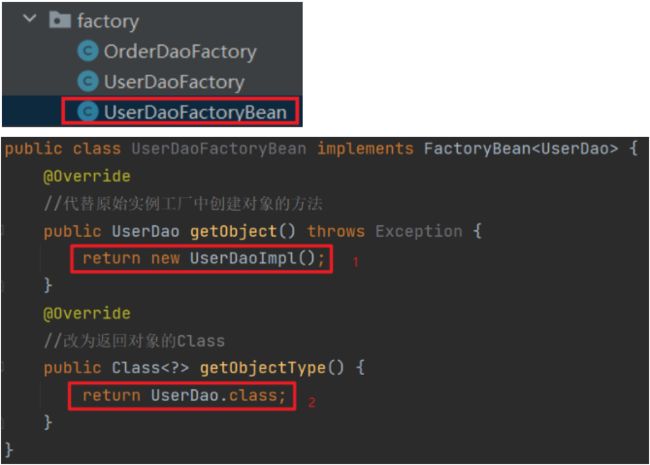
实例化方法4:FactoryBean
基于实例化方法3:实例工厂的改良
-
创建Bean对象
//在applicationContext.xml中添加 <bean id="userDao" class="org.example.factory.UserDaoFactoryBean"/> -
获取bean对象(无变化)
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); UserDao userDao = (UserDao) ctx.getBean("userDao"); userDao.save(); -
由单例修改为非单例(scope方法也可行)
在UserDaoFactoryBean中重写isSingleton()方法
//设置是否为单例 public boolean isSingleton(){ return false;//true为单例,false为非单例 }
3.3 bean的生命周期
-
设置生命周期方法一:init-method 和 destory-method
指定init方法和destory方法
-
BookDaoImpl
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao { public void save(){ System.out.println("book dao save ..."); } //表示bean初始化对应的操作 public void init(){ System.out.println("init..."); } public void destory(){ System.out.println("destory..."); } } -
applicationContext.xml
<bean id="bookDao" class="org.example.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory"/> -
关闭容器的两种方法
Bean的destory尚未执行,虚拟机就退出了,因此不会执行destory()方法。要想执行destory方法可以
(1)关闭容器:ctx.close()ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); ... ctx.close();(2)设置关闭勾子:ctx.registerShutdownHook()
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); ctx.registerShutdownHook();//表示在退出前要先关闭容器,这句话位置只需要在ctx创建之后即可注意:如果scope设置为prototype,那么依然不会执行destory方法
-
-
设置生命周期方法二:InitializingBean 和 DisposableBean
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService, InitializingBean, DisposableBean { private BookDao bookDao; public void save(){ System.out.println("book service save ..."); bookDao.save(); } //属性注入 public void setBookDao(BookDao bookDao){ this.bookDao = bookDao; } //destroy方法 public void destroy() throws Exception{ System.out.println("service destory"); } //init方法 public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception{ System.out.println("service init"); } } -
Bean的生命周期小结
- 初始化容器
- 1.创建对象(内存分配)
- 2.执行构造方法
- 3.执行属性注入(set操作)
- 4.执行bean初始化方法
- 使用bean
- 1.执行业务操作
- 关闭/销毁容器
- 1.执行bean销毁方法
- 初始化容器
4. 依赖注入
思考:
- 向一个类中传递数据的方式有几种?
- 普通方法(set方法)
- 构造方法
- 依赖注入描述了在容器中建立bean与bean之间的依赖关系的过程,如果bean运行需要的是数字或字符串呢?
- 引用类型
- 简单类型(基本数据类型与String)
于是依赖注入方式分为4种:
- setter注入
- 简单类型
- 引用类型(前面使用的方式)
- 构造器注入
- 简单类型
- 引用类型
4.1 四种注入场景
setter注入引用类型
-
提供可访问的set方法
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService { private BookDao bookDao; public void setBookDao(BookDao bookDao) { this.bookDao = bookDao; } } -
配置中使用
property标签ref属性注入引用类型对象<bean id="bookDao" class="org.example.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl"/> <bean id="bookService" class="org.example.service.impl.BookServiceImpl"> <property name="bookDao" ref="bookDao"/> bean>多个注入只需要添加< bean>和< property>即可
setter注入简单类型
-
提供可访问的set方法
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao { private int connectionNum; private String databaseName; public void setConnectionNum(int connectionNum) { this.connectionNum = connectionNum; } public void setDatabaseName(String databaseName) { this.databaseName = databaseName; } public void save(){ System.out.println("book dao save ..."+connectionNum+","+databaseName); } } -
配置中使用
property标签value属性注入简单类型的值<bean id="bookDao" class="org.example.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl"> <property name="databaseName" value="mysql"/> <property name="connectionNum" value="10"/> bean>
构造器注入引用类型
-
提供传参的构造器
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService { private BookDao bookDao; //构造器 public BookServiceImpl(BookDao bookDao){ this.bookDao = bookDao; } public void save(){ System.out.println("book service save ..."); bookDao.save(); } } -
配置中使用
constructor-arg标签name和ref属性注入简单类型的值<bean id="bookService" class="org.example.service.impl.BookServiceImpl"> <constructor-arg name="bookDao" ref="bookDao"/> bean>name指的是形参的名称
构造器注入简单类型
-
提供传参的构造器
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao { private int connectionNum; private String databaseName; public BookDaoImpl(int connectionNum, String databaseName){ this.connectionNum = connectionNum; this.databaseName = databaseName; } public void save(){ System.out.println("book dao save ..."+connectionNum+","+databaseName); } } -
配置中使用
constructor-arg标签name和ref属性注入简单类型的值//标准写法:name <bean id="bookDao" class="org.example.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl"> <constructor-arg name="connectionNum" value="10"/> <constructor-arg name="databaseName" value="mysql"/> </bean>上面的是标准写法,但是这里name标签需要和构造器种的形参名一样,为了降低耦合,还有另一种写法
<bean id="bookDao" class="org.example.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl"> <constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="mysql"/> <constructor-arg type="int" value="10"/> bean>上述无法应对多个相同类型的问题,于是进一步改进
<bean id="bookDao" class="org.example.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl"> <constructor-arg index="1" value="mysql"/> <constructor-arg index="0" value="10"/> bean>
4.2 自动装配
-
自动装配
IoC容器根据bean所依赖的资源在容器中自动查找并注入到bean中的过程称为自动装配(不必再写bean配置) -
自动装配方式
- 按类型(常用)
- 按名称
- 按构造方法
- 不启用自动装配
-
按类型装配
-
在实现类种写好 setter方法
-
在配置中设置自动装配 autowire 及方式 byType
<bean id="bookDao" class="org.example.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl"/> <bean id="bookService" class="org.example.service.impl.BookServiceImpl" autowire="byType"/> -
问题点:(1)要装配的类BookDaoImpl必须先写在配置种;(2)无法解决重复问题
<bean id="bookDao1" class="org.example.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl"/> <bean id="bookDao2" class="org.example.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl"/> <bean id="bookService" class="org.example.service.impl.BookServiceImpl" autowire="byType"/>此时,autowire将不知道装配哪一个bookDao,于是报错NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException
-
-
按名称装配
-
在实现类种写好 setter方法
-
在配置中设置自动装配 autowire 及方式 byName
<bean id="bookDao" class="org.example.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl"/> <bean id="bookService" class="org.example.service.impl.BookServiceImpl" autowire="byName"/>注意,BookDaoImpl的id,即“bookDao”必须要和BookServiceImpl中的setBookDao中的后半部分相对应
-
-
依赖自动装配特征
- 自动装配用于引用类型依赖注入,不能对简单类型进行操作
- 使用按类型装配时(byType)必须保障容器中相同类型的bean唯一,推荐使用
- 使用按名称装配时(byName)必须保障容器中具有指定名称的bean,因变量名与配置耦合,不推荐使用
- 自动装配优先级低于setter注入与构造器注入,同时出现时自动装配配置失效
4.3 集合注入
-
准备 - BookDaoImpl.java
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao { private int[] array; private List<String> list; private Set<String> set; private Map<String,String> map; private Properties properties; public void setArray(int[] array) {this.array = array;} public void setList(List<String> list) {this.list = list;} public void setSet(Set<String> set) {this.set = set;} public void setMap(Map<String, String> map) {this.map = map;} public void setProperties(Properties properties) {this.properties = properties;} public void save() { System.out.println("book dao save ..."); System.out.println("遍历数组:" + Arrays.toString(array)); System.out.println("遍历List" + list); System.out.println("遍历Set" + set); System.out.println("遍历Map" + map); System.out.println("遍历Properties" + properties); } } -
配置Bean
包括Array List Set Map Properties
applicationContext.xml<bean id="bookDao" class="org.example.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl"> <property name="array"> <array> <value>100value> <value>200value> <value>300value> array> property> <property name="list"> <list> <value>firstvalue> <value>secondvalue> <value>thirdvalue> list> property> <property name="set"> <set> <value>firstvalue> <value>secondvalue> <value>thirdvalue> <value>thirdvalue> set> property> <property name="map"> <map> <entry key="country" value="china"/> <entry key="province" value="henan"/> <entry key="city" value="kaifeng"/> map> property> <property name="properties"> <props> <prop key="country">chinaprop> <prop key="province">henanprop> <prop key="city">kaifengprop> props> property> bean> -
运行
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); BookDao bookDao = (BookDao) ctx.getBean("bookDao"); bookDao.save();
5. IOC/DI配置管理第三方bean
5.1 案例:数据源对象管理
druid管理
需求:使用Spring的IOC容器来管理Druid连接池对象
1.使用第三方的技术,需要在pom.xml添加依赖
2.在配置文件中将【第三方的类】制作成一个bean,让IOC容器进行管理
3.数据库连接需要基础的四要素驱动、连接、用户名和密码,【如何注入】到对应的bean中
4.从IOC容器中获取对应的bean对象,将其打印到控制台查看结果
-
准备 - 添加依赖
//pom.xml <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.1.16</version> </dependency> </dependencies> -
配置Bean
由于DruidDataSource是外部数据源,可以点进去查看里面的setter方法,例如setUserName()方法
可以发现构造器不符合条件,只能使用setter注入<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="root"/> bean> -
获取和使用bean
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); DataSource dataSource = (DataSource) ctx.getBean("dataSource"); System.out.println(dataSource);//这里实际上没连接数据库,所以打印一下看下就行
c3p0管理
-
<dependency> <groupId>c3p0</groupId> <artifactId>c3p0</artifactId> <version>0.9.1.2</version> </dependency> -
配置Bean
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_db"/> <property name="user" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="root"/> </bean> -
获取和使用Bean
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); DataSource dataSource = (DataSource) ctx.getBean("dataSource"); System.out.println(dataSource);发现报错:java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
-
添加mysql依赖
<dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.16</version> </dependency>此后再运行可以看到注入的数据
5.2 加载Properties文件
需求:将数据库连接四要素提取到properties配置文件,spring来加载配置信息并使用这些信息来完成属性注入
-
创建jdbc.properties文件
在resource目录下 - New - Resource Bundle

//jdbc.properties jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/spring_db jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=root -
开启一个新的命名空间context
-
使用context空间加载properties配置文件
applicationContext.xml
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"/> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </bean> -
测试 - 将jdbc.username注入到BookDaoImpl中
-
BookDaoImpl
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao { private String name; public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;} public void save(){System.out.println("book dao save ..."+name);} } -
applicationContext.xml
<bean id="bookDao" class="org.example.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl"> <property name="name" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> </bean> -
运行
BookDao bookDao = (BookDao) ctx.getBean("bookDao"); bookDao.save();结果
book dao save ...com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
-
-
系统属性优先级更高
在jdbc.properties中写的是jdbc.username,如果将其改成username=root,运行时将发现该配置失效
这是因为系统自身配置中也有一个username属性,且其优先级更高
可以通过关闭系统配置来解决这个问题,在xml文件中如下修改<!-- 设置不加载系统属性--> <context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties" system-properties-mode="NEVER"/> -
加载多个配置文件
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties,jdbc2.properties" system-properties-mode="NEVER"/>更便利的写法:
<context:property-placeholder location="*.properties" system-properties-mode="NEVER"/>标准写法:
<!-- 提供类路径,读取当前工程里面的配置文件,jar包里面的读取不到--> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:*.properties"/> <!-- 读取所有路径下的配置文件--> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath*:*.properties"/>
6. 核心容器
6.1 容器创建的方式
-
方法1:类路径下的XML配置文件(常用)
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");可以同时加载多个配置文件,以逗号 , 分隔即可
-
方法2:文件系统下的XML配置文件
ApplicationContext ctx = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("D:\\workspace\\spring\\spring_10_container\\src\\main\\resources\\applicationContext.xml");通过文件系统查找时,默认当前路径是项目spring所在路径,此时直接找applicationContext.xml是找不到的
可以通过绝对路径:右击applicationContext.xml - Copy Path - Absolute Path
6.2 获取Bean的方式
-
方法1:强制类型转换
BookDao bookDao = (BookDao) ctx2.getBean("bookDao"); -
方法2:bean名称并指定类型class
BookDao bookDao = ctx.getBean("bookDao", BookDao.class); -
方法3:指定类型class
BookDao bookDao = ctx.getBean(BookDao.class);这种方式就类似我们之前所学习依赖注入中的按类型注入。必须要确保IOC容器中该类型对应的bean对象只能有一个
6.3 容器类层次结构
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory, MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {...}
顺着ListableBeanFactory往上,最终得到IoC顶层接口BeanFactory(已过时)
BeanFactory是最早期的容器接口,后来经过发展被ApplicationContext替代
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml");
BeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(resource);
BookDao bookDao = bf.getBean(BookDao.class);
bookDao.save();
BeanFactory和ApplicationContext的区别:前者是延迟加载,后者是立即加载
使用ApplicationContext会立即执行类的构造方法,而BeanFactory不会,如果希望ApplicationContext能够延迟加载,需要设置:
<bean id="bookDao" class="org.example.dao.impl.BookDaoImpl" lazy-init="true"/>
7. Spring连接数据库案例
AccountDao接口
package org.example.dao;
@Repository("accountDao")
public interface AccountDao {
@Insert("insert into tbl_account(name,money)values(#{name},#{money})")
void save(Account account);
@Delete("delete from tbl_account where id = #{id} ")
void delete(Integer id);
@Update("update tbl_account set name = #{name} , money = #{money} where id = #{id} ")
void update(Account account);
@Select("select * from tbl_account")
List<Account> findAll();
@Select("select * from tbl_account where id = #{id} ")
Account findById(Integer id);
}
AccountServiceImpl.java
package org.example.service;
public interface AccountService {
void save(Account account);
void delete(Integer id);
void update(Account account);
List<Account> findAll();
Account findById(Integer id);
}
package org.example.service.impl;
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public void save(Account account) {
accountDao.save(account);
}
@Override
public void delete(Integer id) {
accountDao.delete(id);
}
@Override
public void update(Account account) {
accountDao.update(account);
}
@Override
public List<Account> findAll() {
return accountDao.findAll();
}
@Override
public Account findById(Integer id) {
return accountDao.findById(id);
}
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
}
applicationContext.xml
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/wt122694/article/details/81227321
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
">
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
bean>
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
bean>
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="org.example.dao" />
bean>
<bean id="accountService" class="org.example.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/>
bean>
beans>
jdbc.properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql:///spring_db?useSSL=false&useServerPrepStmts=true
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=123456
Main.java
package org.example;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
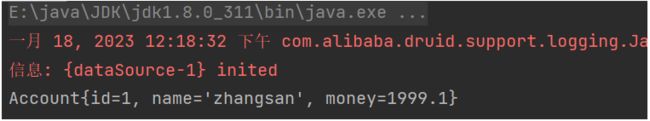
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
AccountService accountService = (AccountService) ctx.getBean("accountService");//@Service标注会自动生成bean
Account account = accountService.findById(1);
System.out.println(account);
}
}