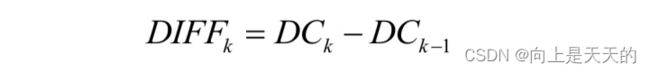数据压缩——JPEG原理分析及JPEG解码器的调试
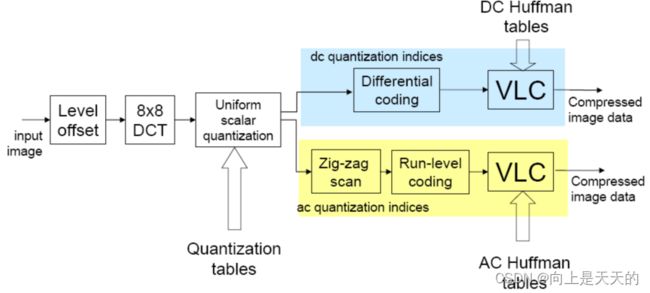
JPEG编解码原理
level off(零偏置)
· 对于灰度级是2n的像素,通过减去2n-1,将无符号的整数值变成有符号数;
· 对于n=8,即将0~ 255的值域,通过减去128,转换为值域在-128~ 127之间的值。
· 目的:使像素的绝对值出现3位10进制的概率大大减少。
8×8 DCT
· 把整个分量图像分成8×8的图像块,再以8×8的图像块为一个单位进行量化和编码处理。
· 目的:去相关,能量集中
图像使用二维DCT变换,其核矩阵为:
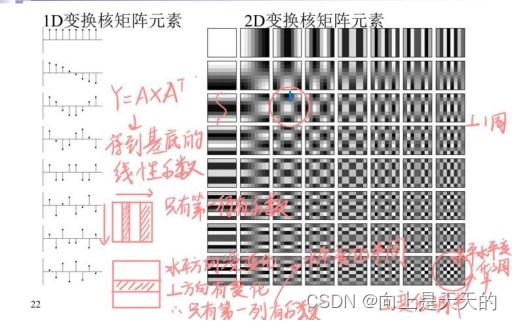
输入图像通过与2D变换核矩阵做矩阵相乘得到DCT系数,系数矩阵反应了输入图像的变化性质
量化
· 采用中平均匀量化器;
· 按照【系数所在位置和颜色分量】来确定量化步距;
· 由人眼对亮度信号比对色度信号更敏感,选择两种量化表:亮度量化表,色度量化表;
· 根据人眼视觉特性:对低频变化敏感于高频变化,采用低频细量化,高频粗量化;
· 真正的量化表=缩放因子×基本量化表
质量因子越大,缩放因子越小,量化表量化步长小,压缩程度小
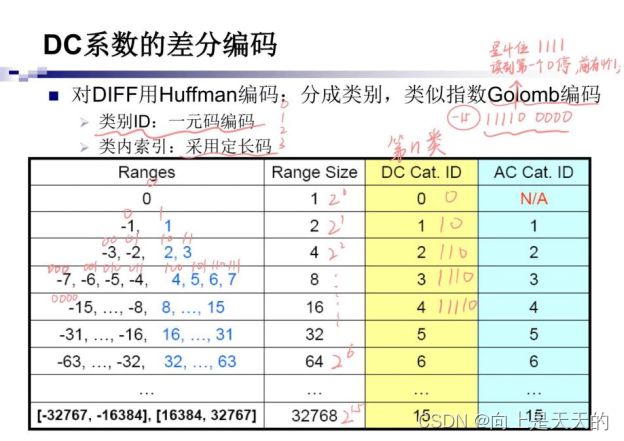
DC系数的差分编码
· 8×8图像块经过DCT变换后得到的DC系数有两个特点:
系数数值比较大;
相邻 8×8 图像块的DC系数值变化不大——冗余
· 根据这个特点,JPEG算法使用了DPCM技术,对相邻图像块之间量化DC系数的差值DIFF进行Huffman编码:
AC系数的zizag(之字扫描)
由于经过DCT变换后,系数大多数集中在左上角,即低频分量区,因此采用z字形按频率由低到高的顺序读出,可以出现很多连零的机会。最后,如果都是0,则给出EOB即可。
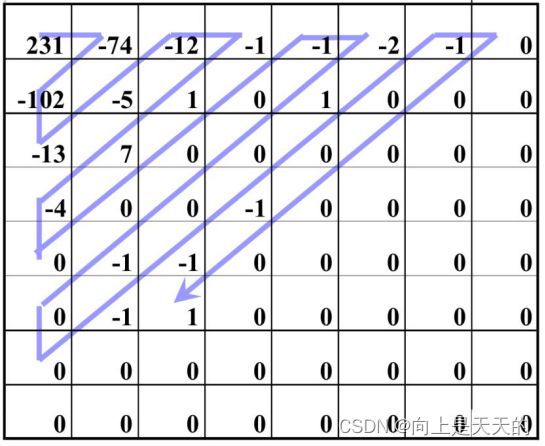
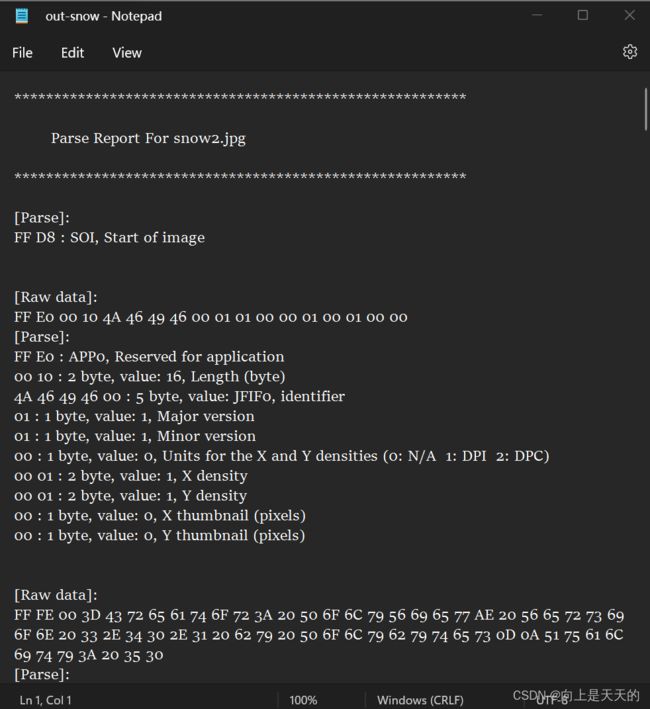
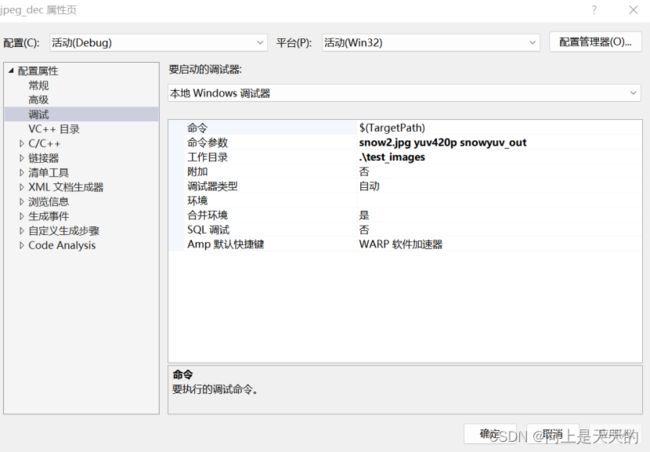
调试 JPEGParser程序
解码JPEG
三个结构体设计目的
- struct huffman_table
快查找和慢查找两种方式,提高编码效率
struct huffman_table
{
/* Fast look up table, using HUFFMAN_HASH_NBITS bits we can have directly the symbol,
* 快查找表,根据HUFFMAN_HASH_NBITS可以快速找到符号
* if the symbol is <0, then we need to look into the tree table
符号<0,使用慢查找表*/
short int lookup[HUFFMAN_HASH_SIZE];//得到权值对应的码字
/* code size: give the number of bits of a symbol is encoded */
unsigned char code_size[HUFFMAN_HASH_SIZE];//得到权值对应的码长
/* some place to store value that is not encoded in the lookup table
* FIXME: Calculate if 256 value is enough to store all values
计算256个值是否足够存储需要存储的所有值*/
uint16_t slowtable[16-HUFFMAN_HASH_NBITS][256];
};
- struct component
保存一个MCU的信息,处理完一个MCU,值更新一次。
struct component
{
unsigned int Hfactor;//水平采样
unsigned int Vfactor;//垂直采样
float *Q_table; /* Pointer to the quantisation table to use指向使用的量化表 */
struct huffman_table *AC_table; //Huffman AC系数表
struct huffman_table *DC_table;//Huffman DC系数表
short int previous_DC; /* Previous DC coefficient 上一个DC系数 */
short int DCT[64]; /* DCT coef *///该块的DCT系数,DCT[0]为该块直流,其他为交流
#if SANITY_CHECK
unsigned int cid;
#endif
};
- struct jdec_private
文件解码信息结构体
struct jdec_private
{
/* Public variables */
uint8_t *components[COMPONENTS];//分别指向YUV分量结构体的指针数组
unsigned int width, height; /* Size of the image 图像宽高*/
unsigned int flags;
/* Private variables */
const unsigned char *stream_begin, *stream_end; //码流开始,结束指针
unsigned int stream_length; //码流长度
const unsigned char *stream; /* Pointer to the current stream 指向当前码流位置*/
unsigned int reservoir, nbits_in_reservoir;
struct component component_infos[COMPONENTS];
float Q_tables[COMPONENTS][64]; /* quantization tables */
struct huffman_table HTDC[HUFFMAN_TABLES]; /* DC huffman tables */
struct huffman_table HTAC[HUFFMAN_TABLES]; /* AC huffman tables */
int default_huffman_table_initialized; //预初始化值
int restart_interval;
int restarts_to_go; /* MCUs left in this restart interval */
int last_rst_marker_seen; /* Rst marker is incremented each time 重新开始的位置每次递增 */
/* Temp space used after the IDCT to store each components */
uint8_t Y[64*4], Cr[64], Cb[64];//反DCT后三个分量的数组
jmp_buf jump_state;
/* Internal Pointer use for colorspace conversion, do not modify it !!! */
uint8_t *plane[COMPONENTS];
};
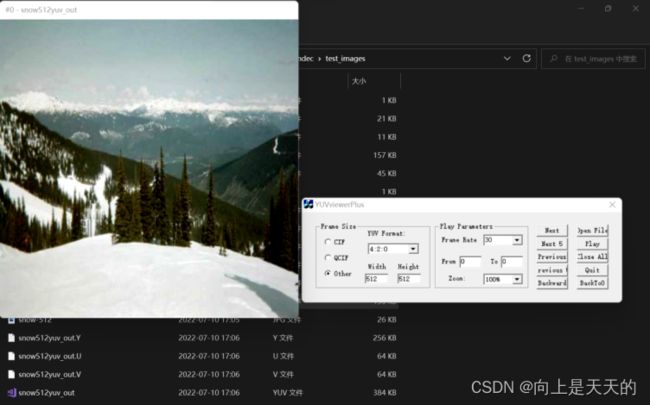
调试程序输出YUV格式
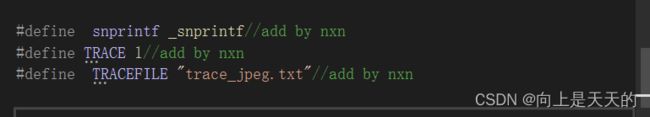
TRACE的作用
打开trace_jpeg.txt
其包含了图像的宽高信息,文件大小,及Huffman码表等信息
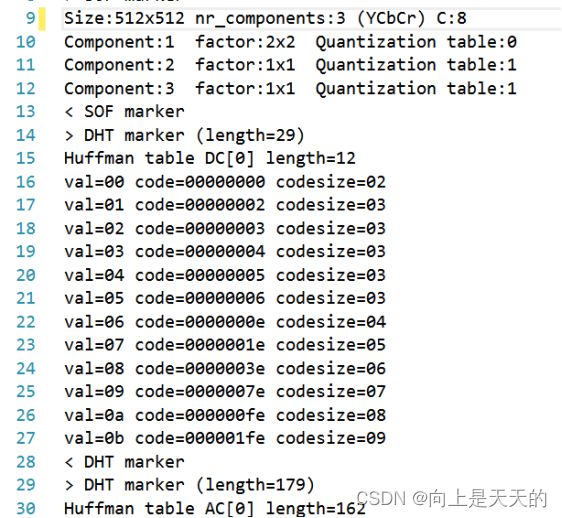
输出量化矩阵
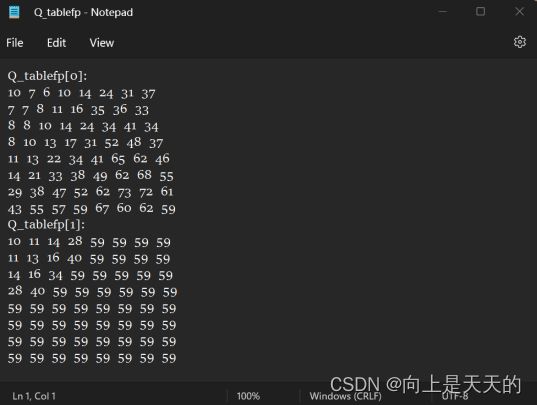
- 类比tracejpeg.txt的代码,在 tinyjpeg.h 中增加文件指针Q_tablefp
- 在结尾加QFILE定义,输出的文件命名为“Q_tablefp.txt”
- 在loadjpeg.c的主函数仿照p_trace,将量化表信息写入txt文件
#if TRACE
p_trace=fopen(TRACEFILE,"w");
//添加一个Q_tablefp量化表的写入
Q_tablefp= fopen(QFILE, "w");
if (p_trace==NULL)
{
printf("trace file open error!");
}
if (Q_tablefp == NULL)
{
printf("Quantization file open error!");
}
#endif
- 在tinyjpeg.c中添加代码:
static void build_quantization_table(float *qtable, const unsigned char *ref_table)
{
int i, j;
static const double aanscalefactor[8] = {
1.0, 1.387039845, 1.306562965, 1.175875602,
1.0, 0.785694958, 0.541196100, 0.275899379
};
const unsigned char *zz = zigzag;
for (i=0; i<8; i++) {
for (j=0; j<8; j++) {
*qtable++ = ref_table[*zz++] * aanscalefactor[i] * aanscalefactor[j];
}
}
//添加部分:
#if TRACE
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
if (j == 7)
{
fprintf(Q_tablefp, "%d\n", (int)ref_table[zigzag[i * 8 + j]]);
//到第八个数时换行,其余空格即可
}
else
{
fprintf(Q_tablefp, "%d ", (int)ref_table[zigzag[i * 8 + j]]);
}
}
}
#endif
}
- 函数 parse_DQT 中添加:
#if SANITY_CHECK
if (qi>>4)
snprintf(error_string, sizeof(error_string),"16 bits quantization table is not supported\n");
if (qi>4)
snprintf(error_string, sizeof(error_string),"No more 4 quantization table is supported (got %d)\n", qi);
#endif
//添加部分:
#if TRACE
fprintf(Q_tablefp, "Q_tablefp[%d]:\n", qi); //码表显示格式
#endif
DC,AC图像及概率分布
图像
#include "tinyjpeg.h"
#include "tinyjpeg-internal.h"
#define snprintf _snprintf
//添加部分:
unsigned char* DC_;
unsigned char* AC_;
unsigned char* UV_;
int i;
int count = 0;
//
DC_ = (unsigned char*)malloc(1);
AC_ = (unsigned char*)malloc(1);
UV_ = (unsigned char*)malloc(1);
*UV_ = 128;
count++;
*DC_ = (unsigned char)((priv->component_infos->DCT[0] + 512.0) / 4 + 0.5);
fwrite(DC_, 1, 1, DC);
*AC_ = (unsigned char)(priv->component_infos->DCT[1] + 128);
fwrite(AC_, 1, 1, AC);
#if TRACE
fprintf(p_trace,"Input file size: %d\n", priv->stream_length+2);
fprintf(p_trace,"Input bytes actually read: %d\n", priv->stream - priv->stream_begin + 2);
fflush(p_trace);
#endif
for (i = 0; i < count / 4 * 2; i++)
{
fwrite(UV_, sizeof(unsigned char), 1, DC);
fwrite(UV_, sizeof(unsigned char), 1, AC);
}
return 0;
- 在loadjpeg.c中写入文件:
DC = fopen(DCFILE, "wb");
AC = fopen(ACFILE, "wb");
- 关闭文件
#if TRACE
fclose(p_trace);
fclose(AC);
fclose(DC);
#endif
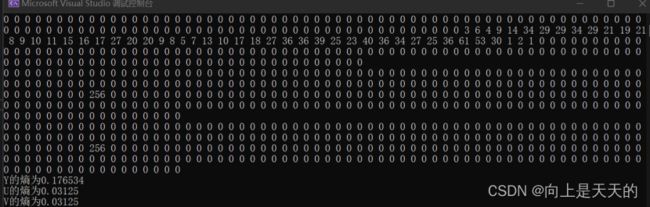
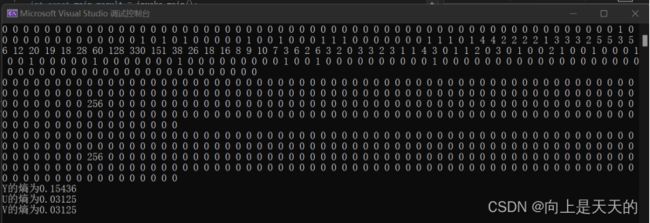
统计DC图像,AC图像的概率分布
修改实验一中求熵的代码:
#includeDC系数统计结果
| Y | U | V |
|---|---|---|
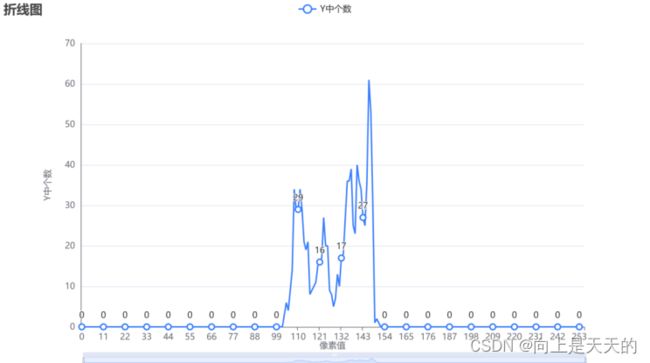 |
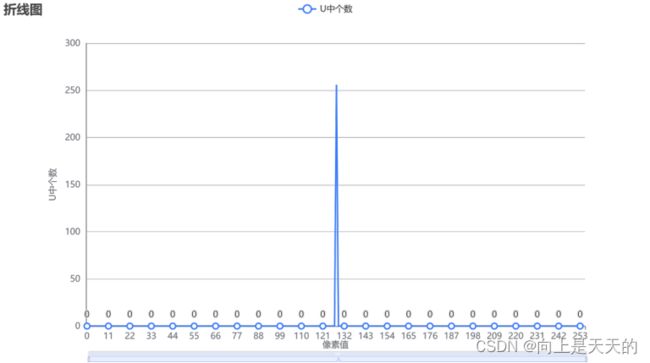 |
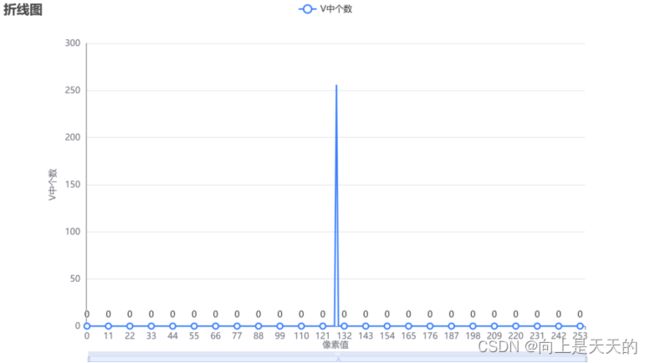 |
AC系数统计结果
| Y | U | V |
|---|---|---|
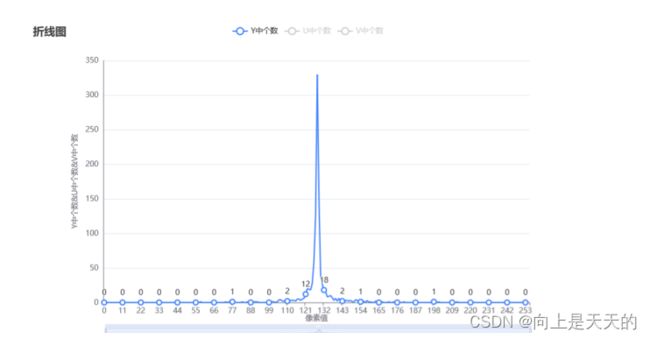 |
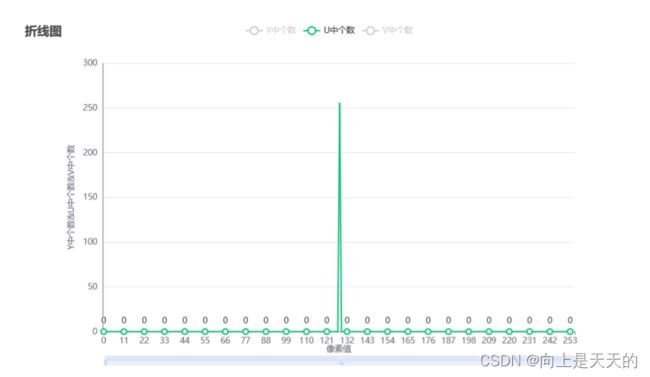 |
 |
参考
- https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_48930495/article/details/117791055
- https://blog.csdn.net/yee_0217/article/details/72846107
- https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_53323848/article/details/117635923