sqlzoo刷题笔记
文章目录
- 前言
- 1 SELECT basics
- 2 SELECT from world
- 3 SELECT from nobel
- 4 SELECT in SELECT
- 5 SUM and COUNT
- 6 JOIN
- 总结
前言
sqlzoo:刷题笔记
在线题库:https://sqlzoo.net/wiki/SELECT_from_WORLD_Tutorial
答案参考:https://blog.csdn.net/zhangzhezhu/article/details/101850325
时间:0104-0110
1 SELECT basics
- Introducing the world table of countries
The example uses a WHERE clause to show the population of ‘France’. Note that strings (pieces of text that are data) should be in ‘single quotes’;
Modify it to show the population of Germany
SELECT population FROM world
WHERE name = 'Germany'
- Scandinavia
Checking a list The word IN allows us to check if an item is in a list. The example shows the name and population for the countries ‘Brazil’, ‘Russia’, ‘India’ and ‘China’.
Show the name and the population for ‘Sweden’, ‘Norway’ and ‘Denmark’.
SELECT name, population FROM world
WHERE name IN ('Sweden', 'Norway', 'Denmark')
- Just the right size
Which countries are not too small and not too big? BETWEEN allows range checking (range specified is inclusive of boundary values). The example below shows countries with an area of 250,000-300,000 sq. km. Modify it to show the country and the area for countries with an area between 200,000 and 250,000.
SELECT name, area FROM world
WHERE area BETWEEN 200000 AND 250000
2 SELECT from world
- Introduction
Read the notes about this table. Observe the result of running this SQL command to show the name, continent and population of all countries.
SELECT name, continent, population FROM world
- Large Countries
How to use WHERE to filter records. Show the name for the countries that have a population of at least 200 million. 200 million is 200000000, there are eight zeros.
SELECT name FROM world
WHERE population > 200000000
- Per capita GDP
Give the name and the per capita GDP for those countries with a population of at least 200 million.
select name, gdp/population from world
where population> 200000000
- South America In millions
Show the name and population in millions for the countries of the continent ‘South America’. Divide the population by 1000000 to get population in millions.
select name,population/1000000 from world
where continent='South America'
- France, Germany, Italy
Show the name and population for France, Germany, Italy
select name,population from world
where name in ('France','Germany','Italy')
- United
Show the countries which have a name that includes the word ‘United’
select name from world where name like '%United%'
- Two ways to be big
Two ways to be big: A country is big if it has an area of more than 3 million sq km or it has a population of more than 250 million.
Show the countries that are big by area or big by population. Show name, population and area.
select name,population,area from world
where area>3000000 or population>250000000
- One or the other (but not both)
Exclusive OR (XOR). Show the countries that are big by area or big by population but not both. Show name, population and area.
Australia has a big area but a small population, it should be included.
Indonesia has a big population but a small area, it should be included.
China has a big population and big area, it should be excluded.
United Kingdom has a small population and a small area, it should be excluded.
select name,population,area from world
where area> 3000000 xor population>250000000
- Rounding
Show the name and population in millions and the GDP in billions for the countries of the continent ‘South America’. Use the ROUND function to show the values to two decimal places.
For South America show population in millions and GDP in billions both to 2 decimal places.
select name,round(population/1000000,2),round(gdp/1000000000,2) from world
where continent='South America'
- Trillion dollar economies
Show the name and per-capita GDP for those countries with a GDP of at least one trillion (1000000000000; that is 12 zeros). Round this value to the nearest 1000.
Show per-capita GDP for the trillion dollar countries to the nearest $1000.
select name,round(gdp/population,-3) from world
where gdp>= 1000000000000
- Name and capital have the same length
Greece has capital Athens.
Each of the strings ‘Greece’, and ‘Athens’ has 6 characters.
Show the name and capital where the name and the capital have the same number of characters.
You can use the LENGTH function to find the number of characters in a string
SELECT name,capital FROM world
WHERE LENGTH(name)=LENGTH(capital)
- Matching name and capital
The capital of Sweden is Stockholm. Both words start with the letter ‘S’.
Show the name and the capital where the first letters of each match. Don’t include countries where the name and the capital are the same word.
You can use the function LEFT to isolate the first character.
You can use <> as the NOT EQUALS operator.
SELECT name, capital FROM world
where LEFT(name,1)=LEFT(capital,1) and name<>capital
- All the vowels
Equatorial Guinea and Dominican Republic have all of the vowels (a e i o u) in the name. They don’t count because they have more than one word in the name.
Find the country that has all the vowels and no spaces in its name.
You can use the phrase name NOT LIKE ‘%a%’ to exclude characters from your results.
The query shown misses countries like Bahamas and Belarus because they contain at least one ‘a’
SELECT name FROM world
WHERE name LIKE '%a%'
and name LIKE '%e%'
and name LIKE '%i%'
and name LIKE '%o%'
and name LIKE '%u%'
AND name NOT LIKE '% %'
掌握SQL知识点总结:
一 、SQL基础教程:
-
<、>、=、<>、
-
and、or、xor、 not
-
between ~ and ~
二 、SQL高级教程:
-
SQL IN / NOT IN 语法
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name IN (value1,value2,…) -
SQL LIKE 操作符语法
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE column_name LIKE pattern -
SQL 通配符
在搜索数据库中的数据时,SQL 通配符可以替代一个或多个字符。
SQL 通配符必须与 LIKE 运算符一起使用。 在 SQL中,可使用以下通配符: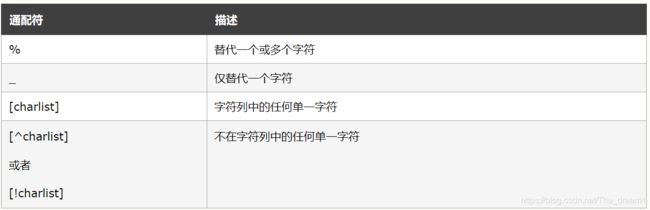
三、SQL函数
-
ROUND() 函数
-
LENGTH() 函数
// LENGTH函数返回文本字段中值的长度。
// SQL LENGTH() 语法
SELECT LENGTH(column_name) FROM table_name -
LEFT 和 RIGHT
// LEFT、RIGHT函数返回ARG最左边、右边的LENGTH个字符串,
// ARG可以是 CHAR或BINARY STRING
LEFT(ARG,LENGTH)、RIGHT(ARG,LENGTH)
3 SELECT from nobel
- Winners from 1950
Change the query shown so that it displays Nobel prizes for 1950.
SELECT yr, subject, winner FROM nobel
WHERE yr = 1950
- 1962 Literature
Show who won the 1962 prize for Literature.
SELECT winner FROM nobel
WHERE yr = 1962 AND subject = 'Literature'
- Albert Einstein
Show the year and subject that won ‘Albert Einstein’ his prize.
select yr,subject from nobel
where winner='Albert Einstein'
- Recent Peace Prizes
Give the name of the ‘Peace’ winners since the year 2000, including 2000.
select winner from nobel
where subject='Peace' and yr>=2000
- Literature in the 1980’s
Show all details (yr, subject, winner) of the Literature prize winners for 1980 to 1989 inclusive.
select*from nobel
where subject='Literature' and yr between 1980 and 1989
- List item
Only Presidents
Show all details of the presidential winners:
Theodore Roosevelt
Woodrow Wilson
Jimmy Carter
Barack Obama
SELECT * FROM nobel
WHERE winner IN ('Theodore Roosevelt',
'Woodrow Wilson',
'Jimmy Carter',
'Barack Obama')
- John
Show the winners with first name John
select winner from nobel
where winner like 'John %'
- Chemistry and Physics from different years
Show the year, subject, and name of Physics winners for 1980 together with the Chemistry winners for 1984.
select*from nobel
where (yr=1980 and subject='Physics')
or (yr=1984 and subject='Chemistry')
- Exclude Chemists and Medics
Show the year, subject, and name of winners for 1980 excluding Chemistry and Medicine
select*from nobel where yr=1980
and subject not in ('Chemistry','Medicine')
- Early Medicine, Late Literature
Show year, subject, and name of people who won a ‘Medicine’ prize in an early year (before 1910, not including 1910) together with winners of a ‘Literature’ prize in a later year (after 2004, including 2004)
select*from nobel
where (subject='Medicine' and yr<1910)
or (subject='Literature' and yr>=2004)
- Umlaut
Find all details of the prize won by PETER GRÜNBERG
select*from nobel
where winner='PETER GRÜNBERG'
- Apostrophe
Find all details of the prize won by EUGENE O’NEILL
select*from nobel
where winner='EUGENE O\'NEILL'
- Knights of the realm
Knights in order
List the winners, year and subject where the winner starts with Sir. Show the the most recent first, then by name order.
select winner,yr,subject from nobel
where winner like 'Sir%' order by yr desc,winner
- Chemistry and Physics last
The expression subject IN (‘Chemistry’,‘Physics’) can be used as a value - it will be 0 or 1.
Show the 1984 winners and subject ordered by subject and winner name; but list Chemistry and Physics last.
SELECT winner, subject FROM nobel
WHERE yr=1984
ORDER BY subject IN ('Physics','Chemistry'),subject,winner
本章总结:
题目14 Chemistry and Physics last
The expression subject IN (‘Chemistry’,‘Physics’) can be used as a value - it will be 0 or 1.
Show the 1984 winners and subject ordered by subject and winner name; but list Chemistry and Physics last.
分析:因为需要将化学和物理排在最后,根据提示“subject IN(‘Chemistry’,‘Physics’)”的结果位0或1,所以可以先利用“subject IN(‘Chemistry’,‘Physics’)”的结果进行升序排序,这样结果位1的化学和物理就会显示在最后。
我的答案:
SELECT winner, subject
FROM nobel
WHERE yr=1984
ORDER BY (subject IN ('Chemistry','Physics')),subject,winner;
掌握SQL知识点总结:
-
ORDER BY 语句
// ORDER BY 语句用于根据指定的列对结果集进行排序。默认按照升(ASC),降序 DESC 关键字。
用法:
SELECT columns FROM talbe
ORDER BY column [ ASC/DWSC] , … -
subject in (‘c’,‘p’)会返回0或1,可以作为排序的依据。
4 SELECT in SELECT
- Bigger than Russia
List each country name where the population is larger than that of ‘Russia’.
SELECT name FROM world
WHERE population >
(SELECT population FROM world
WHERE name='Russia')
- Richer than UK
Show the countries in Europe with a per capita GDP greater than ‘United Kingdom’.
select name from world
where continent='Europe'
and gdp/population > (select gdp/population from world where name ='United Kingdom')
- Neighbours of Argentina and Australia
List the name and continent of countries in the continents containing either Argentina or Australia. Order by name of the country.
select name,continent from world
where continent in (select continent from world where name in ('Argentina','Australia'))
order by name
- Between Canada and Poland
Which country has a population that is more than Canada but less than Poland? Show the name and the population.
select name,population from world
where population>(select population from world where name='Canada')
and population<(select population from world where name='Poland')
- Percentages of Germany
Germany (population 80 million) has the largest population of the countries in Europe. Austria (population 8.5 million) has 11% of the population of Germany.
Show the name and the population of each country in Europe. Show the population as a percentage of the population of Germany.
select name,
concat(round(population*100/(select population from world where name='Germany')),'%') from world
where continent='Europe'
- Bigger than every country in Europe
Which countries have a GDP greater than every country in Europe? [Give the name only.] (Some countries may have NULL gdp values)
select name from world
where gdp>all(select gdp from world where gdp>0 and continent='Europe')
- Largest in each continent
Find the largest country (by area) in each continent, show the continent, the name and the area:
SELECT continent, name, area FROM world x
WHERE area >= ALL(SELECT area FROM world y WHERE y.continent=x.continent AND area>0)
- First country of each continent (alphabetically)
List each continent and the name of the country that comes first alphabetically.
SELECT continent, MIN(name) AS name
FROM world
GROUP BY continent
- Difficult Questions That Utilize Techniques Not Covered In Prior
Sections
Find the continents where all countries have a population <= 25000000. Then find the names of the countries associated with these continents. Show name, continent and population.
select name,continent,population from world x
where 25000000>=all(select population from world y where population>0
and x.continent=y.continent)
- Some countries have populations more than three times that of any of
their neighbours (in the same continent). Give the countries and
continents.
select name,continent from world x
where population/3>=all(select population from world y where y.continent=x.continent
and x.name!=y.name)
本章知识点总结:
(——主要是select嵌套)
(1) concat(数据,‘%’)的使用——给数据加上单位(第5题)
(2) all的使用(使用>all判断时,如果有数据为空null,加个判断 is not null)
5 SUM and COUNT
- Total world population
Show the total population of the world.
SELECT SUM(population) FROM world
- List of continents
List all the continents - just once each.
select distinct continent from world
- GDP of Africa
Give the total GDP of Africa
select sum(gdp) from world
where continent='Africa'
- Count the big countries
How many countries have an area of at least 1000000
select count(name) from world
where area>1000000
- Baltic states population
What is the total population of (‘Estonia’, ‘Latvia’, ‘Lithuania’)
select sum(population) from world
where name in ('Estonia', 'Latvia', 'Lithuania')
- Counting the countries of each continent
For each continent show the continent and number of countries.
select continent,count(name) from world group by continent
- Counting big countries in each continent
For each continent show the continent and number of countries with populations of at least 10 million.
select continent,count(name) from world
where population>10000000 group by continent
- Counting big continents
List the continents that have a total population of at least 100 million.
select continent from world group by continent
having sum(population)>100000000
6 JOIN
- List every match with the goals scored by each team as shown. This will use “CASE WHEN” which has not been explained in any previous exercises.
Notice in the query given every goal is listed. If it was a team1 goal then a 1 appears in score1, otherwise there is a 0. You could SUM this column to get a count of the goals scored by team1. Sort your result by mdate, matchid, team1 and team2.
SELECT game.mdate,team1,
sum(CASE WHEN teamid = team1 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS score1,team2,
sum(CASE WHEN teamid = team2 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS score2
FROM game LEFT JOIN goal ON(game.id = matchid)
GROUP BY mdate, matchid, team1, team2
之所以用做连接是因为goal表记录的是进球的记录,因此如果双方都没有进球,那么则不会记录,所以需要左连接game来显示所有的比赛记录而不仅仅是进球记录.
总结
SQL中默认是跳过null?或者说当列筛选跳过null;联合查询时因为其它列得原因,有时候要补null形成一行。
<、>、=、<>、!=
and、or、xor、 in、 not in、like、not like
between a and b
(边界是否包括得看SQL的引擎)
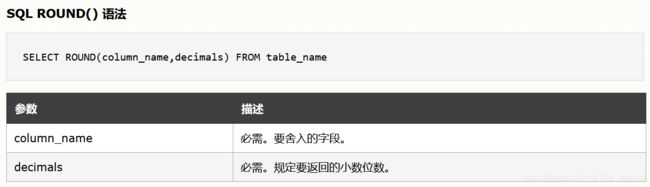
round(column_name,decimals)
函数用于把数值字段舍入为指定的小数位数。
decimals正数表示指定保留位数,为负数表示四舍五入精度
length(column_name)
LENGTH函数返回文本字段中值的长度。
LEFT(ARG,LENGTH)、RIGHT(ARG,LENGTH)
// LEFT、RIGHT函数返回ARG最左边、右边的LENGTH个字符串,
// ARG可以是 CHAR或BINARY STRING
// 强调group by得使用,有时候时双重排序索引——注意其分组得逻辑
ORDER BY column [ ASC/DWSC] , …
ORDER BY 语句用于根据指定的列对结果集进行排序。默认按照升序(ASC),降序 DESC 关键字。
concat(a,b)
将a变为字符串后,添加字符b
eg:concat(10,’%’)——>10%
all的使用
使用>all判断时,如果有数据为空null,加个判断 is not null
sum(column)、count(column)、distinct(column)
注意以下两者的差别:(强调+1)
select * from table
where 条件 --------- (条件限制后,再进行分组)(分组的下面)
group by coulmn
select * from table
group by coulum
having 条件 --------- (分组后,对分的组中进行筛选)(分组这一层)
join得使用
inner join(默认) 内连接(两者的主键意义对应的上的部分)
left join 左连接(以左表为主键为主,作为主表,对不上右表就补null)
right join 右连接(以右表主键为主,作为主表,对不上左表就补null)
full join 完全连接(上面两个主键的综合,每一行对应的列,补不上就null)
CASE WHEN a THEN b ELSE c END
// 使用a的条件进行判断,是就b,不是就c
例如:6-13,例子如下:
“
select teacher.name,
case when dept in (1,2) then ‘Sci’
when dept = 3 then ‘Art’
else ‘None’
end
from teacher
”
null
只能使用is null/ not null —— 为什么不能使用 =,类似java中的数值类型的比较机制!
//这个函数主要用来进行空值处理
COALESCE ( expression,value1,value2……,valuen) 函数
COALESCE()函数的第一个参数expression为待检测的表达式,而其后的参数个数不定。
COALESCE()函数将会返回包括expression在内的所有参数中的第一个非空表达式。
如果expression不为空值则返回expression;否则判断value1是否是空值,
如果value1不为空值则返回value1;否则判断value2是否是空值,
如果value2不为空值则返回value2;……以此类推,
如果所有的表达式都为空值,则返回NULL。
我们将使用COALESCE()函数完成下面的功能,返回人员的“重要日期”:
如果出生日期不为空则将出生日期做为“重要日期”,如果出生日期为空则判断注册日期是否为空,如果注册日期不为空则将注册日期做为“重要日期”,如果注册日期也为空则将“2008年8月8日”做为“重要日期”。实现此功能的SQL语句如下:
SELECT FName,FBirthDay,FRegDay,
COALESCE(FBirthDay,FRegDay,‘2008-08-08’) AS ImportDay
FROM T_Person
临时表的使用
limit的使用
limit a offset b 从b+1开始获取前a个数据