osgEarth示例分析——osgearth_features
前言
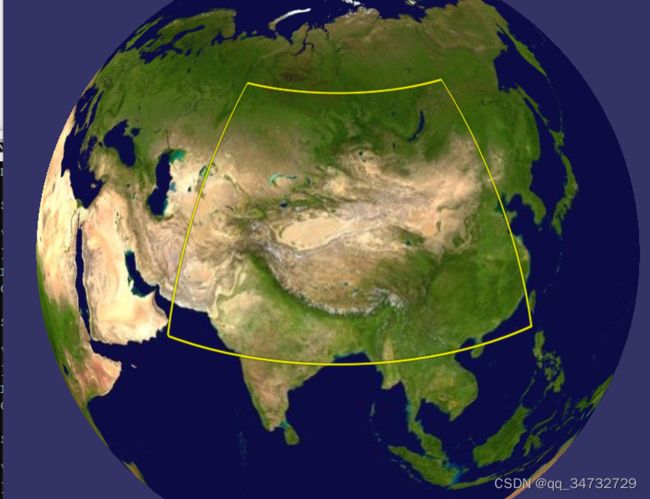
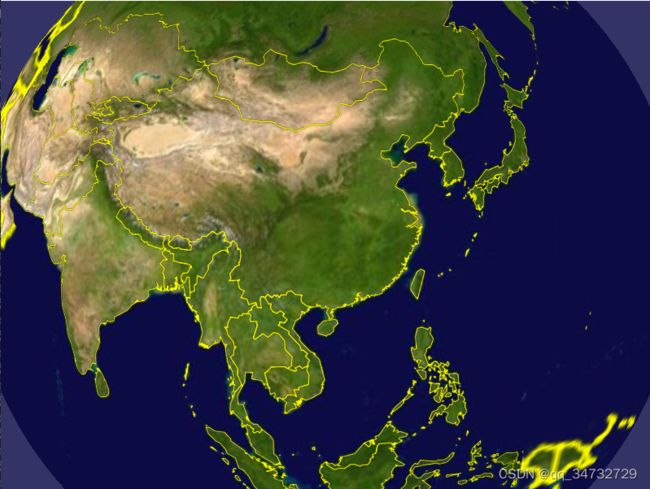
osgearth_features示例,主要演示如何通过代码方式加载shp文件,并设置其样式。在执行时,通过不同 的命令,得到不一样的效果。
cmd执行命令:
// rasterize 光栅化,不输入时,会显示名称
// mem参数输入,加载矩形,否则加载world.shp文件。shp文件路径一定要写全路径,否则无法加载。
// labels 可以不用填写。
// clamp 和 drape 任选其一。
// 采用clamp方式绘制
osgearth_featuresd.exe --rasterize --mem --labels --clamp
// 采用drape方式绘制
osgearth_featuresd.exe --rasterize --mem --labels --drape
// 还有多种组合方式
osgearth_featuresd.exe --labels --drape效果
代码分析
简单流程:
// osgEarth表达矢量的基本思路是:
// 先将shp文件读取到矢量源图层FeatureSourceLayer中,
// 这个图层加载到osgEarth的图层列表中是不显示的,
// 必须得再加载一个专门的符号化图层,将其符号化,才能正常显示。
// 1. 先声明基础地图
osgEarth::Drivers::GDALOptions basemap;
basemap.url() = "world.tif";
// 添加影像图到map节点
map->addLayer( new ImageLayer(ImageLayerOptions("basemap", basemap)));
// 2. 加载特征数据
osgEarth::Drivers::OGRFeatureOptions featureData;
featureData.url() = "world.shp";
// 特征源图层选项设置
osgEarth::Features::FeatureSourceLayerOptions ogrLayer;
ogrLayer.name() = "vector-data";
ogrLayer.featureSource() = featureData;
map->addLayer(new osgEarth::Features::FeatureSourceLayer(ogrLayer));
/*******↑featureData添加到FeatureSourceLayer,*****↓符号化*******/
// 3.初始化线样式
// 对ls alt render 进行设置
Style style;
osgEarth::Symbology::LineSymbol* ls = style.getOrCreateSymbol();
osgEarth::Symbology::AltitudeSymbol* alt = style.getOrCreate();
osgEarth::Symbology::RenderSymbol* render = style.getOrCreate();
// 4.光栅化或矢量化,二选一
// 4.1光栅化
osgEarth::Drivers::AGGLiteOptions rasterOptions;
rasterOptions.featureOptions() = featureData;
rasterOptions.styles()->addStyle( style );
map->addLayer(new ImageLayer("My Features", rasterOptions) );
// 4.2矢量化
osgEarth::Features::FeatureModelLayerOptions fml;
fml.styles()->addStyle(style);
map->addLayer(new FeatureModelLayer(fml));
// 5.如果需要加入label样式,以矢量化为前提
osgEarth::Symbology::Style labelStyle;
osgEarth::Symbology::TextSymbol* text = labelStyle.getOrCreateSymbol();
FeatureModelLayerOptions fml;
fml.styles()->addStyle( labelStyle );
map->addLayer(new FeatureModelLayer(fml)); 完整源码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace osgEarth;
using namespace osgEarth::Features;
using namespace osgEarth::Drivers;
using namespace osgEarth::Symbology;
using namespace osgEarth::Util;
int usage( const std::string& app )
{
OE_NOTICE "\n" << app << "\n" // 绘制特征的方法
<< " --rasterize : draw features as rasterized image tiles \n" // 光栅化平铺瓦片图
<< " --drape : draw features as projected texture \n" // 投影纹理
<< " --clamp : draw features using shader clamping \n" // 使用贴地着色器
<< " --mem : load features from memory \n" // 加载默认线
<< " --labels : add feature labels \n" // 添加文本标签
<< "\n"
<< MapNodeHelper().usage()
<< std::endl;
return 0;
}
//
// NOTE: run this sample from the repo/tests directory.
//
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
osg::ArgumentParser arguments(&argc,argv);
if ( arguments.read("--help") )
return usage( argv[0] );
// cmd执行命令时,输入: osgearth_featuresd.exe --rasterize --mem --labels --drape --clamp (一些参数)
// 当输入了某个参数,则获取到的值为1,否则为0
bool useRaster = arguments.read("--rasterize");
bool useMem = arguments.read("--mem");
bool useLabels = arguments.read("--labels");
bool useDraping = arguments.read("--drape");
bool useClamping = arguments.read("--clamp");
std::cout << useRaster << useMem << useLabels << useDraping << useClamping << std::endl;
osgViewer::Viewer viewer(arguments);
// Start by creating the map:
Map* map = new Map();
// Start with a basemap imagery layer; we'll be using the GDAL driver
// to load a local GeoTIFF file:
// 添加默认地图
GDALOptions basemap;// GDAL选项类,继承自TileSourceOptions
basemap.url() = "../data/world.tif";
map->addLayer( new ImageLayer(ImageLayerOptions("basemap", basemap)));
// Next we add a feature layer.
// 添加shp文件
OGRFeatureOptions featureData;
if ( !useMem )
{
// Configures the feature driver to load the vectors from a shapefile:
// 如果给出相对路径,则国界线总是加载不上
// 此处必须给全路径!!!
featureData.url() = "D:\\osgearth\\data\\world.shp";
std::cout << "add world.shp" << std::endl;
}
else
{
// the --mem options tells us to just make an in-memory geometry:
// 当没有 --mem参数时,采用默认的line绘制
Ring* line = new Ring();
line->push_back( osg::Vec3d(60, 20, 0) );
line->push_back( osg::Vec3d(120, 20, 0) );
line->push_back( osg::Vec3d(120, 60, 0) );
line->push_back( osg::Vec3d(60, 60, 0) );
featureData.geometry() = line;
std::cout << "don't add world.shp" << std::endl;
}
// Make a feature source layer and add it to the Map:
// 制作特征源图层并添加到map
FeatureSourceLayerOptions ogrLayer;
ogrLayer.name() = "vector-data";// 矢量数据
ogrLayer.featureSource() = featureData;// shp 文件或者默认line
map->addLayer(new FeatureSourceLayer(ogrLayer));
// Define a style for the feature data. Since we are going to render the
// vectors as lines, configure the line symbolizer:
// 设置矢量面样式(包括边界线)
Style style;
LineSymbol* ls = style.getOrCreateSymbol();
ls->stroke()->color() = Color::Yellow;
ls->stroke()->width() = 2.0f;// 可以将线宽设置宽一些,更容易看出不同参数useDraping和useClamping产生的区别
ls->tessellationSize()->set(100, Units::KILOMETERS);// 细分程度
if (useDraping)//是否设置drape属性
{
AltitudeSymbol* alt = style.getOrCreate();
alt->clamping() = alt->CLAMP_TO_TERRAIN;
alt->technique() = alt->TECHNIQUE_DRAPE;
std::cout << "drape" << std::endl;
}
else if (useClamping)// 贴地属性
{
AltitudeSymbol* alt = style.getOrCreate();
alt->clamping() = alt->CLAMP_TO_TERRAIN;
alt->technique() = alt->TECHNIQUE_GPU;
// 线的细分程度
ls->tessellationSize()->set(100, Units::KILOMETERS);
RenderSymbol* render = style.getOrCreate();
render->depthOffset()->enabled() = true;
render->depthTest() = false;
std::cout << "no drape,but clamp" << std::endl;
}
if (useRaster)// 光栅化
{
AGGLiteOptions rasterOptions;
rasterOptions.featureOptions() = featureData;
rasterOptions.styles() = new StyleSheet();
rasterOptions.styles()->addStyle( style );
map->addLayer(new ImageLayer("My Features", rasterOptions) );
std::cout << "raster" << std::endl;
}
else //if (useGeom)
{
FeatureModelLayerOptions fml;
fml.name() = "My Features";
fml.featureSourceLayer() = "vector-data";
fml.styles() = new StyleSheet();
fml.styles()->addStyle(style);
// fml.enableLighting() = false;
map->addLayer(new FeatureModelLayer(fml));
std::cout << "no raster" << std::endl;
}
if ( useLabels && !useRaster )// 有标签且非光栅化
{
// set up symbology for drawing labels. We're pulling the label
// text from the name attribute, and its draw priority from the
// population attribute.
// 设置文本样式
Style labelStyle;
TextSymbol* text = labelStyle.getOrCreateSymbol();
text->content() = StringExpression( "[cntry_name]" );//如果需要显示汉字,则需要转换成UTF-8编码
text->priority() = NumericExpression( "[pop_cntry]" );
text->size() = 26.0f;// 字号有些大
text->alignment() = TextSymbol::ALIGN_CENTER_CENTER;
text->fill()->color() = Color::White;
text->halo()->color() = Color::DarkGray;// 文字光环颜色
// and configure a model layer:
FeatureModelLayerOptions fml;
fml.name() = "Labels";
fml.featureSourceLayer() = "vector-data";
fml.styles() = new StyleSheet();
fml.styles()->addStyle( labelStyle );
map->addLayer(new FeatureModelLayer(fml));
std::cout << "no raster, but labels" << std::endl;
}
// That's it, the map is ready; now create a MapNode to render the Map:
MapNode* mapNode = new MapNode(map);
viewer.setSceneData( mapNode );
viewer.setCameraManipulator( new EarthManipulator() );
// add some stock OSG handlers:
MapNodeHelper().configureView(&viewer);
return viewer.run();
}
参考链接:osgEarth使用笔记4——加载矢量数据