import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import math
import cv2
def canny_my(gray):
sigma1=sigma2=0.88
sum=0
gaussian = np.zeros([5, 5])
for i in range(5):
for j in range(5):
gaussian[i, j] = math.exp((-1/(2*sigma1*sigma2))*(np.square(i-3)
+ np.square(j-3)))/(2*math.pi*sigma1*sigma2)
sum = sum + gaussian[i, j]
gaussian = gaussian / sum
W, H = gray.shape
new_gray = np.zeros([W - 5, H - 5])
for i in range(W - 5):
for j in range(H - 5):
new_gray[i, j] = np.sum(gray[i:i + 5, j:j + 5] * gaussian)
W1, H1 = new_gray.shape
dx = np.zeros([W1 - 1, H1 - 1])
dy = np.zeros([W1 - 1, H1 - 1])
d = np.zeros([W1 - 1, H1 - 1])
for i in range(W1 - 1):
for j in range(H1 - 1):
dx[i, j] = new_gray[i, j + 1] - new_gray[i, j]
dy[i, j] = new_gray[i + 1, j] - new_gray[i, j]
d[i, j] = np.sqrt(np.square(dx[i, j]) + np.square(dy[i, j]))
W2, H2 = d.shape
NMS = np.copy(d)
NMS[0, :] = NMS[W2 - 1, :] = NMS[:, 0] = NMS[:, H2 - 1] = 0
for i in range(1, W2 - 1):
for j in range(1, H2 - 1):
if d[i, j] == 0:
NMS[i, j] = 0
else:
gradX = dx[i, j]
gradY = dy[i, j]
gradTemp = d[i, j]
if np.abs(gradY) > np.abs(gradX):
weight = np.abs(gradX) / np.abs(gradY)
grad2 = d[i - 1, j]
grad4 = d[i + 1, j]
if gradX * gradY > 0:
grad1 = d[i - 1, j - 1]
grad3 = d[i + 1, j + 1]
else:
grad1 = d[i - 1, j + 1]
grad3 = d[i + 1, j - 1]
else:
weight = np.abs(gradY) / np.abs(gradX)
grad2 = d[i, j - 1]
grad4 = d[i, j + 1]
if gradX * gradY > 0:
grad1 = d[i + 1, j - 1]
grad3 = d[i - 1, j + 1]
else:
grad1 = d[i - 1, j - 1]
grad3 = d[i + 1, j + 1]
gradTemp1 = weight * grad1 + (1 - weight) * grad2
gradTemp2 = weight * grad3 + (1 - weight) * grad4
if gradTemp >= gradTemp1 and gradTemp >= gradTemp2:
NMS[i, j] = gradTemp
else:
NMS[i, j] = 0
W3, H3 = NMS.shape
DT = np.zeros([W3, H3])
TL = 0.1 * np.max(NMS)
TH = 0.3 * np.max(NMS)
for i in range(1, W3 - 1):
for j in range(1, H3 - 1):
if (NMS[i, j] < TL):
DT[i, j] = 0
elif (NMS[i, j] > TH):
DT[i, j] = 1
elif ((NMS[i - 1, j - 1:j + 1] < TH).any() or NMS[i + 1, j - 1:j + 1].any()
or (NMS[i, [j - 1, j + 1]] < TH).any()):
DT[i, j] = 1
return DT
def sobel_my(img):
W, H = img.shape
new_image = np.zeros((W-3, H-3))
new_imageX = np.zeros((W-3,H-3))
new_imageY = np.zeros((W-3,H-3))
s_suanziX = np.array([[-1,0,1],[-2,0,2],[-1,0,1]])
s_suanziY = np.array([[-1,-2,-1],[0,0,0],[1,2,1]])
for i in range(W-3):
for j in range(H-3):
new_imageX[i, j] = abs(np.sum(img[i:i+3, j:j+3] * s_suanziX))
new_imageY[i, j] = abs(np.sum(img[i:i+3, j:j+3] * s_suanziY))
new_image[i, j] = np.sqrt(np.square(new_imageX[i,j]) + np.square(new_imageY[i, j]))
return new_imageX,new_imageY,new_image
def prewitt(img):
W, H = img.shape
new_image = np.zeros((W-3, H-3))
new_imageX = np.zeros((W-3,H-3))
new_imageY = np.zeros((W-3,H-3))
s_suanziX = np.array([[-1,0,1],[-1,0,1],[-1,0,1]])
s_suanziY = np.array([[-1,-1,-1],[0,0,0],[1,1,1]])
for i in range(W-3):
for j in range(H-3):
new_imageX[i, j] = abs(np.sum(img[i:i+3, j:j+3] * s_suanziX))
new_imageY[i, j] = abs(np.sum(img[i:i+3, j:j+3] * s_suanziY))
new_image[i, j] = max(new_imageX[i,j] , new_imageY[i, j])
return new_image
if __name__ == '__main__':
img=cv2.imread('./lena.jpg')
lena_img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(lena_img, (5, 5), 0)
canny = cv2.Canny(blur, 50, 150)
DT=canny_my(gray)
x = cv2.Sobel(gray, cv2.CV_16S, 1, 0)
y = cv2.Sobel(gray, cv2.CV_16S, 0, 1)
absX = cv2.convertScaleAbs(x)
absY = cv2.convertScaleAbs(y)
Sobel = cv2.addWeighted(absX, 0.5, absY, 0.5, 0)
SX,SY,SM = sobel_my(gray)
kernelx = np.array([[1,1,1],[0,0,0],[-1,-1,-1]],dtype=int)
kernely = np.array([[-1,0,1],[-1,0,1],[-1,0,1]],dtype=int)
Prewitt_x = cv2.filter2D(gray, cv2.CV_16S, kernelx)
Prewitt_y = cv2.filter2D(gray, cv2.CV_16S, kernely)
absPX = cv2.convertScaleAbs(Prewitt_x)
absPY = cv2.convertScaleAbs(Prewitt_y)
Prewitt = cv2.addWeighted(absPX, 0.5, absPY, 0.5, 0)
PW = prewitt(gray)
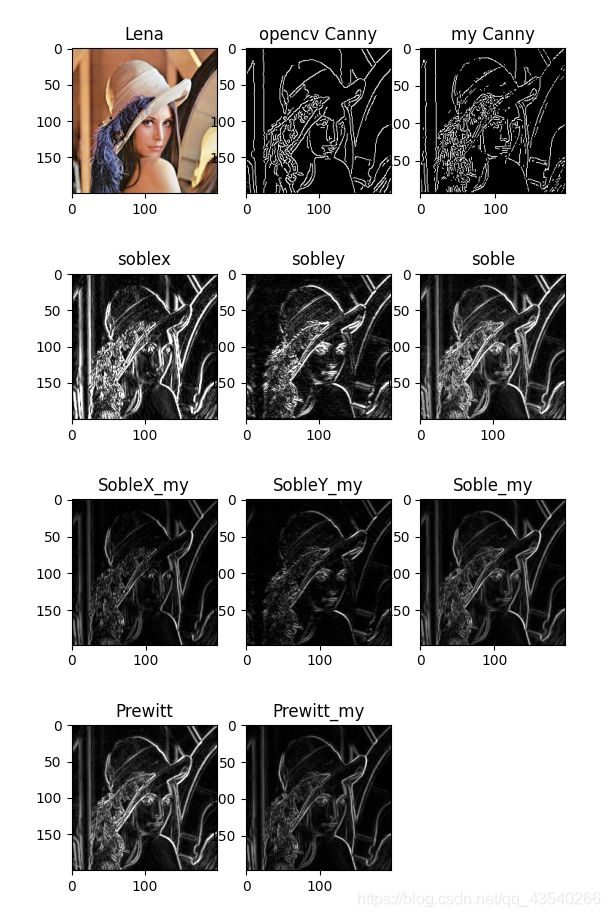
images=[lena_img,canny,DT,absX,absY,Sobel,SX,SY,SM,Prewitt,PW]
titles=["Lena","opencv Canny","my Canny","soblex","sobley","soble","SobleX_my","SobleY_my","Soble_my","Prewitt","Prewitt_my"]
plt.figure(figsize=(20,20))
for i in range(len(images)):
plt.subplot(4,3,i+1)
plt.imshow(images[i],"gray")
plt.title(titles[i])
plt.show()