OpenCV学习(二)Mat对象
Mat对象与IplImage对象
- Mat对象 :OpenCV2.0之后引进的图像数据结构、自动分配内存、不存在内存泄漏的问题,是面向对象的数据结构。分了两个部分,头部与数据部分
- IplImage 是从2001年OpenCV发布之后就一直存在,是C语言风格的数据结构,需要开发者自己分配与管理内存,对大的程序使用它容易导致内存泄漏问题
Mat对象
1. Mat对象的构造函数
| 构造函数(部分) | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Mat(); | 无参构造 |
| Mat(int rows, int cols, int type); | 创建行数为rows,列数为cols,类型为type的图像 |
| Mat(Size size, int type); | 创建大小为size,类型为type的图像 |
| Mat(int rows, int cols, int type, const Scalar& s); | 创建行数为rows,列数为cols,类型为type的图像,并且将所有元素初始化为s |
| Mat(Size size, int type, const Scalar& s); | 创建大小为size,类型为type的图像,并且将所有元素初始化为值s |
| Mat(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type); | ndims是维数。 |
| Mat(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type, const Scalar& s); | |
| Mat(const Mat& m) | 拷贝构造函数,仅复制头和指针,不复制数据部分,即共用数据部分 |
其中:type可以是:CV_8UC1、CV_16SC1、… … 、CV_64FC3 等。C[The channel number]、U(unsigned integer)表示的是无符号整数,S(signed integer)是有符号整数, F(float)是浮点数。
里面的 8U 表示8位无符号整数(0 ~ 255),16S 表示16位有符号整数(-32768 ~ 32767),64F 表示64位浮点 double数据类型,C后面的数表示通道数,例如:C1表示一个通道数的图像,C3表示3通道图像,以此类推。
2.Mat对象的常用方法
| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| rows,cols | 行数,列数 |
| void copyTo(Mat mat) | 完全复制 |
| Mat::zeros,Mat::ones | 返回指定大小和类型的全0或全1数组 |
| void convertTo(Mat dst,int type) | 转换,比如8位的转换为float |
| Mat clone() | 创建一个数组及其基础数据的完整副本 |
| int channels() | 通道数 |
| int depth() | 深度 |
| bool empty() | 是否空,如果数组没有elements,则返回true |
| uchar* ptr(i=0) | 矩阵数据指针 |
| Mat::at | 返回对指定数组元素的引用 |
Mat::at 函数是个模板函数, 需要指明参数类型, img.at,如果这张图是具有红蓝绿三通道的图, 所以它的参数类型可以传递一个 Vec3b, 这是一个存放 3 个 uchar 数据的 Vec(向量). 这里提供了索引重载, [2]表示的是返回第三个通道, 在这里是 Red 通道, 第一个通道(Blue)用[0]返回
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
Mat src;
src = imread("D:/learn_cv/image/xxd.jpg");
if (src.empty()) {
cout << "could not load images...";
return -1;
}
imshow("input", src);
Mat dst;
dst=Mat(src.size(), src.type());
dst = Scalar(127, 25, 45);
dst = src.clone();
imshow("clone",dst);
src.copyTo(dst);
imshow("clone",dst);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
cvtColor(src,dst,COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
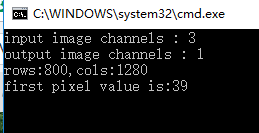
printf("input image channels : %d\n", src.channels());
printf("output image channels : %d\n", dst.channels());
int cols = dst.cols;
int rows = dst.rows;
printf("rows:%d,cols:%d\n", rows, cols);
const uchar* firstRow = dst.ptr(0);
printf("first pixel value is:%d\n", *firstRow);
imshow("gray", dst);
Mat M(3,3,CV_8UC3,Scalar(0,0,127));
cout << "M=" << endl << M << endl;
Mat M2(100, 100, CV_8UC3, Scalar(0, 0, 127));
imshow("output", M2);
Mat对象的使用
- 部分复制:一般情况下只会复制对象的头和指针部分,不会复制数据部分。
Mat A=imread(imgFilePath);
Mat B(A);
-完全复制:如果想把Mat对象的头部和数据部分一起复制,可以通过如下两个API实现
Mat F=A.clone();
Mat G;
A.copeTo(G);
Mat对象的四个使用要点
- 输出图像的内存是自动分配的
- 使用OpenCV的C++接口,不需要考虑内存分配问题
- 赋值操作和拷贝构造函数只会复制头部分
- 使用clone与copyTo两个函数实现数据完全复制
Mat对象创建
- cv::Mat构造函数
Mat M(2,2,CV_8UC3, Scalar(0,0,255))
其中前两个参数分别表示行(row)跟列(column)、第三个CV_8UC3中的8表示每个通道占8位、U表示无符号、C表示Char类型、3表示通道数目是3,第四个参数是向量表示初始化每个像素值是多少,向量长度对应通道数目一致

- 创建多维数组cv::Mat::create
int sz[3] = {2,2,2};
Mat L(3,sz, CV_8UC1, Scalar::all(0));
定义小数组
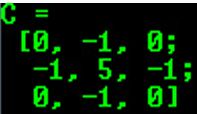
Mat C = (Mat_(3,3) << 0, -1, 0, -1, 5, -1, 0, -1, 0);
cout << "C = " << endl << " " << C << endl << endl;
Mat csrc;
Mat kernel = (Mat_(3,3)<<0,-1,0,-1,5,-1,0,-1,0);
filter2D(src,csrc,-1,kernel);
imshow("output", csrc);