监督学习week 2: Linear Regression using Scikit-Learn
目录
1. Scale/normalize the training data .
2. Create and fit the regression model
3.Plot Results
4.具体的使用方法:
①Load the data set
②Create and fit the model
③ View Parameters
④ Make Predictions
5.another example
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression, SGDRegressor
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScalerScikit-learn has a gradient descent regression model ->sklearn.linear_model.SGDRegressor. Like your previous implementation of gradient descent, this model performs best with normalized inputs. sklearn.preprocessing.StandardScaler will perform z-score normalization as in a previous lab.
1. Scale/normalize the training data .
#先传入训练的数据
X_train, y_train = load_house_data()
X_features = ['size(sqft)','bedrooms','floors','age']
#然后生成对象scaler,调用fit_transform方法
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_norm = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)正则后的结果: Peak to Peak range by column in Raw X:[2.41e+03 4.00e+00 1.00e+00 9.50e+01] Peak to Peak range by column in Normalized X:[5.85 6.14 2.06 3.69]
2. Create and fit the regression model
sgdr = SGDRegressor(max_iter=1000)
sgdr.fit(X_norm, y_train)
print(sgdr)
print(f"number of iterations completed: {sgdr.n_iter_},
number of weight updates: {sgdr.t_}")
#View parameters
b_norm = sgdr.intercept_ #截距项
w_norm = sgdr.coef_
print(f"model parameters: w: {w_norm}, b:{b_norm}")
print(f"model parameters from previous lab: w: [110.56 -21.27 -32.71 -37.97], b: 363.16")
#Make predictions
# make a prediction using sgdr.predict()
y_pred_sgd = sgdr.predict(X_norm)
# make a prediction using w,b.
y_pred = np.dot(X_norm, w_norm) + b_norm
print(f"prediction using np.dot() and sgdr.predict match: {(y_pred == y_pred_sgd).all()}")
print(f"Prediction on training set:\n{y_pred[:4]}" )
print(f"Target values \n{y_train[:4]}")SGDRegressor() number of iterations completed: 148, number of weight updates: 14653.0model parameters: w: [110.29 -21.21 -32.63 -38.02], b:[363.14] model parameters from previous lab: w: [110.56 -21.27 -32.71 -37.97], b: 363.16prediction using np.dot() and sgdr.predict match: True Prediction on training set: [295.19 485.78 389.43 491.94] Target values [300. 509.8 394. 540. ]
各个参数的详解: 随机梯度下降法介绍及其参数讲解_软研院-王新东的博客-CSDN博客_sgdregressor参数详解
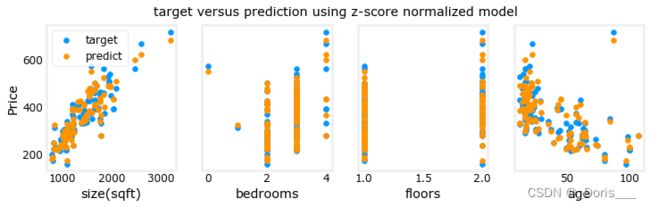
3.Plot Results
# plot predictions and targets vs original features
fig,ax=plt.subplots(1,4,figsize=(12,3),sharey=True)
for i in range(len(ax)):
ax[i].scatter(X_train[:,i],y_train, label = 'target')
ax[i].set_xlabel(X_features[i])
ax[i].scatter(X_train[:,i],y_pred,color=dlorange, label = 'predict')
ax[0].set_ylabel("Price"); ax[0].legend();
fig.suptitle("target versus prediction using z-score normalized model")
plt.show()4.具体的使用方法:
①Load the data set
X_train = np.array([1.0, 2.0]) #features
y_train = np.array([300, 500]) #target value②Create and fit the model
first step:
creates a regression object.
linear_model = LinearRegression()
second step:utilizes one of the methods associated with the object,
fit. This performs regression, fitting the parameters to the input data. The toolkit expects a two-dimensional X matrix.#X must be a 2-D Matrix linear_model.fit(X_train.reshape(-1, 1), y_train)
③ View Parameters
The and parameters are referred to as 'coefficients' and 'intercept' in scikit-learn.
b = linear_model.intercept_ w = linear_model.coef_ print(f"w = {w:}, b = {b:0.2f}") print(f"'manual' prediction: f_wb = wx+b : {1200*w + b}")输出:(intercept->截距 coefficients->系数的意思)
w = [200.], b = 100.00 'manual' prediction: f_wb = wx+b : [240100.]
④ Make Predictions
Calling the predict function generates predictions.
y_pred = linear_model.predict(X_train.reshape(-1, 1))
print("Prediction on training set:", y_pred)
X_test = np.array([[1200]])
print(f"Prediction for 1200 sqft house: ${linear_model.predict(X_test)[0]:0.2f}")输出: Prediction on training set: [300. 500.] Prediction for 1200 sqft house: $240100.00
5.another example
#①load the dataset
X_train, y_train = load_house_data()
X_features = ['size(sqft)','bedrooms','floors','age']
#②create
linear_model = LinearRegression()
linear_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
#③显示参数
b = linear_model.intercept_
w = linear_model.coef_
print(f"w = {w:}, b = {b:0.2f}")
#④make prediction
print(f"Prediction on training set:\n {linear_model.predict(X_train)[:4]}" )
print(f"prediction using w,b:\n {(X_train @ w + b)[:4]}")
print(f"Target values \n {y_train[:4]}")
x_house = np.array([1200, 3,1, 40]).reshape(-1,4)
x_house_predict = linear_model.predict(x_house)[0]
print(f" predicted price of a house with 1200 sqft, 3 bedrooms, 1 floor, 40 years old = ${x_house_predict*1000:0.2f}")w = [ 0.27 -32.62 -67.25 -1.47], b = 220.42Prediction on training set: [295.18 485.98 389.52 492.15] prediction using w,b: [295.18 485.98 389.52 492.15] Target values [300. 509.8 394. 540. ] predicted price of a house with 1200 sqft, 3 bedrooms, 1 floor, 40 years old = $318709.09