YOLO V5源码详解
1.数据读取
首先读取图片以及标签路径,并将标签存入缓存,对单标签情况、特定类别、以及是否保持长方形等情况分别进行处理。
如果需要进行mosaic 数据增强,首先找到中心点,将图片分别放置于四个位置,进行裁剪或者拼接以适应,并对labels进行调整。同时,对进行过mosaic数据增强过的图像,再进行copy_paste数据增强和旋转、平移、缩放数据增强。
同时,还可以进行其他数据增强方式,比如mix up,hsv等
代码如下:
class LoadImagesAndLabels(Dataset):
# YOLOv5 train_loader/val_loader, loads images and labels for training and validation
cache_version = 0.6 # dataset labels *.cache version
rand_interp_methods = [cv2.INTER_NEAREST, cv2.INTER_LINEAR, cv2.INTER_CUBIC, cv2.INTER_AREA, cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4]
def __init__(self,
path,
img_size=640,
batch_size=16,
augment=False,
hyp=None,
rect=False,
image_weights=False,
cache_images=False, # 缓存图片
single_cls=False,
stride=32,
pad=0.0,
prefix=''):
self.img_size = img_size
self.augment = augment
self.hyp = hyp
self.image_weights = image_weights
self.rect = False if image_weights else rect
self.mosaic = self.augment and not self.rect # load 4 images at a time into a mosaic (only during training)
self.mosaic_border = [-img_size // 2, -img_size // 2] # 拼接过程中按照什么中心点进行拼接
self.stride = stride
self.path = path
self.albumentations = Albumentations() if augment else None
try:
f = [] # image files
for p in path if isinstance(path, list) else [path]: # window和linux
p = Path(p) # os-agnostic
if p.is_dir(): # dir
f += glob.glob(str(p / '**' / '*.*'), recursive=True) # 获取指定路径
# f = list(p.rglob('*.*')) # pathlib
elif p.is_file(): # file
with open(p) as t:
t = t.read().strip().splitlines() # 读取图片路径
parent = str(p.parent) + os.sep # 指定系统分隔符
# 相对地址转绝对地址
f += [x.replace('./', parent) if x.startswith('./') else x for x in t] # local to global path
# f += [p.parent / x.lstrip(os.sep) for x in t] # local to global path (pathlib)
else:
raise FileNotFoundError(f'{prefix}{p} does not exist')
self.im_files = sorted(x.replace('/', os.sep) for x in f if x.split('.')[-1].lower() in IMG_FORMATS) # 排序
# self.img_files = sorted([x for x in f if x.suffix[1:].lower() in IMG_FORMATS]) # pathlib
assert self.im_files, f'{prefix}No images found'
except Exception as e:
raise Exception(f'{prefix}Error loading data from {path}: {e}\nSee {HELP_URL}')
# Check cache
self.label_files = img2label_paths(self.im_files) # labels
# 设置缓存
cache_path = (p if p.is_file() else Path(self.label_files[0]).parent).with_suffix('.cache')
try:
cache, exists = np.load(cache_path, allow_pickle=True).item(), True # load dict
assert cache['version'] == self.cache_version # matches current version
assert cache['hash'] == get_hash(self.label_files + self.im_files) # identical hash
except Exception:
cache, exists = self.cache_labels(cache_path, prefix), False # run cache ops
# Display cache
nf, nm, ne, nc, n = cache.pop('results') # found, missing, empty, corrupt, total
if exists and LOCAL_RANK in {-1, 0}:
d = f"Scanning '{cache_path}' images and labels... {nf} found, {nm} missing, {ne} empty, {nc} corrupt"
tqdm(None, desc=prefix + d, total=n, initial=n, bar_format=BAR_FORMAT) # display cache results
if cache['msgs']:
LOGGER.info('\n'.join(cache['msgs'])) # display warnings
assert nf > 0 or not augment, f'{prefix}No labels in {cache_path}. Can not train without labels. See {HELP_URL}'
# Read cache
[cache.pop(k) for k in ('hash', 'version', 'msgs')] # remove items 去除不需要的信息
labels, shapes, self.segments = zip(*cache.values())
self.labels = list(labels) # 标签信息
self.shapes = np.array(shapes, dtype=np.float64) # 图片大小
self.im_files = list(cache.keys()) # update 图片文件名称
self.label_files = img2label_paths(cache.keys()) # update 标签文件名称
n = len(shapes) # number of images
bi = np.floor(np.arange(n) / batch_size).astype(np.int) # batch index
nb = bi[-1] + 1 # number of batches
self.batch = bi # batch index of image
self.n = n
self.indices = range(n) # 索引
# Update labels 筛选标签以仅包括这些类(可选)
include_class = [] # filter labels to include only these classes (optional)
include_class_array = np.array(include_class).reshape(1, -1)
for i, (label, segment) in enumerate(zip(self.labels, self.segments)):
if include_class:
j = (label[:, 0:1] == include_class_array).any(1)
self.labels[i] = label[j]
if segment:
self.segments[i] = segment[j]
if single_cls: # single-class training, merge all classes into 0
self.labels[i][:, 0] = 0
if segment:
self.segments[i][:, 0] = 0
# Rectangular Training
if self.rect:
# Sort by aspect ratio
s = self.shapes # wh
ar = s[:, 1] / s[:, 0] # aspect ratio
irect = ar.argsort()
self.im_files = [self.im_files[i] for i in irect]
self.label_files = [self.label_files[i] for i in irect]
self.labels = [self.labels[i] for i in irect]
self.shapes = s[irect] # wh
ar = ar[irect]
# Set training image shapes
shapes = [[1, 1]] * nb
for i in range(nb):
ari = ar[bi == i]
mini, maxi = ari.min(), ari.max()
if maxi < 1:
shapes[i] = [maxi, 1]
elif mini > 1:
shapes[i] = [1, 1 / mini]
self.batch_shapes = np.ceil(np.array(shapes) * img_size / stride + pad).astype(np.int) * stride
# Cache images into RAM/disk for faster training (WARNING: large datasets may exceed system resources)
# 将图像缓存到RAM/磁盘中以加快训练(警告:大型数据集可能超过系统资源)
self.ims = [None] * n
self.npy_files = [Path(f).with_suffix('.npy') for f in self.im_files]
if cache_images:
gb = 0 # Gigabytes of cached images
self.im_hw0, self.im_hw = [None] * n, [None] * n
fcn = self.cache_images_to_disk if cache_images == 'disk' else self.load_image
results = ThreadPool(NUM_THREADS).imap(fcn, range(n))
pbar = tqdm(enumerate(results), total=n, bar_format=BAR_FORMAT, disable=LOCAL_RANK > 0)
for i, x in pbar:
if cache_images == 'disk':
gb += self.npy_files[i].stat().st_size
else: # 'ram'
self.ims[i], self.im_hw0[i], self.im_hw[i] = x # im, hw_orig, hw_resized = load_image(self, i)
gb += self.ims[i].nbytes
pbar.desc = f'{prefix}Caching images ({gb / 1E9:.1f}GB {cache_images})'
pbar.close()
def cache_labels(self, path=Path('./labels.cache'), prefix=''):
# Cache dataset labels, check images and read shapes
x = {} # dict
nm, nf, ne, nc, msgs = 0, 0, 0, 0, [] # number missing, found, empty, corrupt, messages
desc = f"{prefix}Scanning '{path.parent / path.stem}' images and labels..."
with Pool(NUM_THREADS) as pool:
pbar = tqdm(pool.imap(verify_image_label, zip(self.im_files, self.label_files, repeat(prefix))),
desc=desc,
total=len(self.im_files),
bar_format=BAR_FORMAT)
for im_file, lb, shape, segments, nm_f, nf_f, ne_f, nc_f, msg in pbar:
nm += nm_f
nf += nf_f
ne += ne_f
nc += nc_f
if im_file:
x[im_file] = [lb, shape, segments]
if msg:
msgs.append(msg)
pbar.desc = f"{desc}{nf} found, {nm} missing, {ne} empty, {nc} corrupt"
pbar.close()
if msgs:
LOGGER.info('\n'.join(msgs))
if nf == 0:
LOGGER.warning(f'{prefix}WARNING: No labels found in {path}. See {HELP_URL}')
x['hash'] = get_hash(self.label_files + self.im_files)
x['results'] = nf, nm, ne, nc, len(self.im_files)
x['msgs'] = msgs # warnings
x['version'] = self.cache_version # cache version
try:
np.save(path, x) # save cache for next time
path.with_suffix('.cache.npy').rename(path) # remove .npy suffix
LOGGER.info(f'{prefix}New cache created: {path}')
except Exception as e:
LOGGER.warning(f'{prefix}WARNING: Cache directory {path.parent} is not writeable: {e}') # not writeable
return x
def __len__(self):
return len(self.im_files)
# def __iter__(self):
# self.count = -1
# print('ran dataset iter')
# #self.shuffled_vector = np.random.permutation(self.nF) if self.augment else np.arange(self.nF)
# return self
def __getitem__(self, index):
index = self.indices[index] # linear, shuffled, or image_weights
hyp = self.hyp
mosaic = self.mosaic and random.random() < hyp['mosaic']
if mosaic:
# Load mosaic mosaic数据增强
img, labels = self.load_mosaic(index)
shapes = None
# MixUp augmentation
if random.random() < hyp['mixup']:
img, labels = mixup(img, labels, *self.load_mosaic(random.randint(0, self.n - 1)))
else:
# 不进行mosaic的操作
# Load image
img, (h0, w0), (h, w) = self.load_image(index)
# Letterbox
shape = self.batch_shapes[self.batch[index]] if self.rect else self.img_size # final letterboxed shape
img, ratio, pad = letterbox(img, shape, auto=False, scaleup=self.augment)
shapes = (h0, w0), ((h / h0, w / w0), pad) # for COCO mAP rescaling
labels = self.labels[index].copy()
if labels.size: # normalized xywh to pixel xyxy format
labels[:, 1:] = xywhn2xyxy(labels[:, 1:], ratio[0] * w, ratio[1] * h, padw=pad[0], padh=pad[1])
if self.augment:
img, labels = random_perspective(img,
labels,
degrees=hyp['degrees'],
translate=hyp['translate'],
scale=hyp['scale'],
shear=hyp['shear'],
perspective=hyp['perspective'])
nl = len(labels) # number of labels
if nl:
# x1,y1,x2,y2 转换为x,y,w,h
labels[:, 1:5] = xyxy2xywhn(labels[:, 1:5], w=img.shape[1], h=img.shape[0], clip=True, eps=1E-3)
if self.augment:
# Albumentations 数据增强
img, labels = self.albumentations(img, labels)
nl = len(labels) # update after albumentations
# HSV color-space
augment_hsv(img, hgain=hyp['hsv_h'], sgain=hyp['hsv_s'], vgain=hyp['hsv_v'])
# Flip up-down 翻转操作
if random.random() < hyp['flipud']:
img = np.flipud(img)
if nl:
labels[:, 2] = 1 - labels[:, 2]
# Flip left-right
if random.random() < hyp['fliplr']:
img = np.fliplr(img)
if nl:
labels[:, 1] = 1 - labels[:, 1]
# Cutouts
# labels = cutout(img, labels, p=0.5)
# nl = len(labels) # update after cutout
labels_out = torch.zeros((nl, 6))
if nl:
labels_out[:, 1:] = torch.from_numpy(labels)
# Convert
img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1] # HWC to CHW, BGR to RGB
# ascontiguousarray函数将一个内存不连续存储的数组转换为内存连续存储的数组,使得运行速度更快
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
return torch.from_numpy(img), labels_out, self.im_files[index], shapes
def load_image(self, i):
# Loads 1 image from dataset index 'i', returns (im, original hw, resized hw)
im, f, fn = self.ims[i], self.im_files[i], self.npy_files[i],
if im is None: # not cached in RAM
if fn.exists(): # load npy
im = np.load(fn)
else: # read image
im = cv2.imread(f) # BGR
assert im is not None, f'Image Not Found {f}'
h0, w0 = im.shape[:2] # orig hw
r = self.img_size / max(h0, w0) # ratio
if r != 1: # if sizes are not equal
interp = cv2.INTER_LINEAR if (self.augment or r > 1) else cv2.INTER_AREA # 插值方式
im = cv2.resize(im, (int(w0 * r), int(h0 * r)), interpolation=interp)
return im, (h0, w0), im.shape[:2] # im, hw_original, hw_resized
else:
return self.ims[i], self.im_hw0[i], self.im_hw[i] # im, hw_original, hw_resized
def cache_images_to_disk(self, i):
# Saves an image as an *.npy file for faster loading
f = self.npy_files[i]
if not f.exists():
np.save(f.as_posix(), cv2.imread(self.im_files[i]))
def load_mosaic(self, index):
# YOLOv5 4-mosaic loader. Loads 1 image + 3 random images into a 4-image mosaic
labels4, segments4 = [], []
s = self.img_size
yc, xc = (int(random.uniform(-x, 2 * s + x)) for x in self.mosaic_border) # mosaic center x, y
indices = [index] + random.choices(self.indices, k=3) # 3 additional image indices
random.shuffle(indices)
for i, index in enumerate(indices):
# Load image 加载图片,并将长边resize成(640,640)
img, _, (h, w) = self.load_image(index)
# place img in img4
if i == 0: # top left
img4 = np.full((s * 2, s * 2, img.shape[2]), 114, dtype=np.uint8) # base image with 4 tiles
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), max(yc - h, 0), xc, yc # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (large image)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), h - (y2a - y1a), w, h # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (small image)
elif i == 1: # top right
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, max(yc - h, 0), min(xc + w, s * 2), yc
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, h - (y2a - y1a), min(w, x2a - x1a), h
elif i == 2: # bottom left
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), yc, xc, min(s * 2, yc + h)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), 0, w, min(y2a - y1a, h)
elif i == 3: # bottom right
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, yc, min(xc + w, s * 2), min(s * 2, yc + h)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, 0, min(w, x2a - x1a), min(y2a - y1a, h)
img4[y1a:y2a, x1a:x2a] = img[y1b:y2b, x1b:x2b] # img4[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
padw = x1a - x1b
padh = y1a - y1b
# Labels
labels, segments = self.labels[index].copy(), self.segments[index].copy()
if labels.size:
# 将xywh转换为x1,y1,x2,y2并加上padw,padh
labels[:, 1:] = xywhn2xyxy(labels[:, 1:], w, h, padw, padh) # normalized xywh to pixel xyxy format
segments = [xyn2xy(x, w, h, padw, padh) for x in segments]
labels4.append(labels)
segments4.extend(segments)
# Concat/clip labels 将标签限制在0,2s
labels4 = np.concatenate(labels4, 0)
for x in (labels4[:, 1:], *segments4):
np.clip(x, 0, 2 * s, out=x) # clip when using random_perspective()
# img4, labels4 = replicate(img4, labels4) # replicate
# Augment
# copy_pase数据增强
img4, labels4, segments4 = copy_paste(img4, labels4, segments4, p=self.hyp['copy_paste'])
# 数据增强,旋转、平移、缩放
img4, labels4 = random_perspective(img4,
labels4,
segments4,
degrees=self.hyp['degrees'],
translate=self.hyp['translate'],
scale=self.hyp['scale'],
shear=self.hyp['shear'],
perspective=self.hyp['perspective'],
border=self.mosaic_border) # border to remove
return img4, labels4
def load_mosaic9(self, index):
# YOLOv5 9-mosaic loader. Loads 1 image + 8 random images into a 9-image mosaic
labels9, segments9 = [], []
s = self.img_size
indices = [index] + random.choices(self.indices, k=8) # 8 additional image indices
random.shuffle(indices)
hp, wp = -1, -1 # height, width previous
for i, index in enumerate(indices):
# Load image
img, _, (h, w) = self.load_image(index)
# place img in img9
if i == 0: # center
img9 = np.full((s * 3, s * 3, img.shape[2]), 114, dtype=np.uint8) # base image with 4 tiles
h0, w0 = h, w
c = s, s, s + w, s + h # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (base) coordinates
elif i == 1: # top
c = s, s - h, s + w, s
elif i == 2: # top right
c = s + wp, s - h, s + wp + w, s
elif i == 3: # right
c = s + w0, s, s + w0 + w, s + h
elif i == 4: # bottom right
c = s + w0, s + hp, s + w0 + w, s + hp + h
elif i == 5: # bottom
c = s + w0 - w, s + h0, s + w0, s + h0 + h
elif i == 6: # bottom left
c = s + w0 - wp - w, s + h0, s + w0 - wp, s + h0 + h
elif i == 7: # left
c = s - w, s + h0 - h, s, s + h0
elif i == 8: # top left
c = s - w, s + h0 - hp - h, s, s + h0 - hp
padx, pady = c[:2]
x1, y1, x2, y2 = (max(x, 0) for x in c) # allocate coords
# Labels
labels, segments = self.labels[index].copy(), self.segments[index].copy()
if labels.size:
labels[:, 1:] = xywhn2xyxy(labels[:, 1:], w, h, padx, pady) # normalized xywh to pixel xyxy format
segments = [xyn2xy(x, w, h, padx, pady) for x in segments]
labels9.append(labels)
segments9.extend(segments)
# Image
img9[y1:y2, x1:x2] = img[y1 - pady:, x1 - padx:] # img9[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
hp, wp = h, w # height, width previous
# Offset
yc, xc = (int(random.uniform(0, s)) for _ in self.mosaic_border) # mosaic center x, y
img9 = img9[yc:yc + 2 * s, xc:xc + 2 * s]
# Concat/clip labels
labels9 = np.concatenate(labels9, 0)
labels9[:, [1, 3]] -= xc
labels9[:, [2, 4]] -= yc
c = np.array([xc, yc]) # centers
segments9 = [x - c for x in segments9]
for x in (labels9[:, 1:], *segments9):
np.clip(x, 0, 2 * s, out=x) # clip when using random_perspective()
# img9, labels9 = replicate(img9, labels9) # replicate
# Augment
img9, labels9 = random_perspective(img9,
labels9,
segments9,
degrees=self.hyp['degrees'],
translate=self.hyp['translate'],
scale=self.hyp['scale'],
shear=self.hyp['shear'],
perspective=self.hyp['perspective'],
border=self.mosaic_border) # border to remove
return img9, labels9
@staticmethod
def collate_fn(batch):
im, label, path, shapes = zip(*batch) # transposed
for i, lb in enumerate(label):
lb[:, 0] = i # add target image index for build_targets()
return torch.stack(im, 0), torch.cat(label, 0), path, shapes
@staticmethod
def collate_fn4(batch):
img, label, path, shapes = zip(*batch) # transposed
n = len(shapes) // 4
im4, label4, path4, shapes4 = [], [], path[:n], shapes[:n]
ho = torch.tensor([[0.0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0]])
wo = torch.tensor([[0.0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0]])
s = torch.tensor([[1, 1, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5]]) # scale
for i in range(n): # zidane torch.zeros(16,3,720,1280) # BCHW
i *= 4
if random.random() < 0.5:
im = F.interpolate(img[i].unsqueeze(0).float(), scale_factor=2.0, mode='bilinear',
align_corners=False)[0].type(img[i].type())
lb = label[i]
else:
im = torch.cat((torch.cat((img[i], img[i + 1]), 1), torch.cat((img[i + 2], img[i + 3]), 1)), 2)
lb = torch.cat((label[i], label[i + 1] + ho, label[i + 2] + wo, label[i + 3] + ho + wo), 0) * s
im4.append(im)
label4.append(lb)
for i, lb in enumerate(label4):
lb[:, 0] = i # add target image index for build_targets()
return torch.stack(im4, 0), torch.cat(label4, 0), path4, shapes42.模型配置文件读取
depth_multiple表示网络的深度,表示在网络层的数量,非1的层乘以该系数,width_multiple表示网络的深度,网络最终的输出通道数乘以该系数即可得到网络的最终通道数。YOLO提供了不同版本的模型,对于不同版本的模型,最大的不同的在于以上两个系数。
anchor表示网络的先验框
对于网络参数,from表示输入来自于哪一层的输出,number表示网络层的层数,module表示网络层的名称。args表示网络的超参数。
# YOLOv5 by Ultralytics, GPL-3.0 license
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.50 # layer channel multiple
anchors:
- [10,13, 16,30, 33,23] # P3/8
- [30,61, 62,45, 59,119] # P4/16
- [116,90, 156,198, 373,326] # P5/32
# YOLOv5 v6.0 backbone
backbone:
# [from, number, module, args]
[[-1, 1, Conv, [64, 6, 2, 2]], # 0-P1/2
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
[-1, 3, C3, [128]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
[-1, 6, C3, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
[-1, 9, C3, [512]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
[-1, 3, C3, [1024]],
[-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]], # 9
]
# YOLOv5 v6.0 head
head:
[[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 13
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
[-1, 3, C3, [256, False]], # 17 (P3/8-small)
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 20 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
[-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]], # 23 (P5/32-large)
[[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
]
读取代码:
def parse_model(d, ch): # model_dict, input_channels(3)
# ch (list):表示各层输出通道数
LOGGER.info(f"\n{'':>3}{'from':>18}{'n':>3}{'params':>10} {'module':<40}{'arguments':<30}") # 打印表头
# 读取相应数据 anchors:锚框,nc:类别 gd:深度系数 gw 宽度系数
anchors, nc, gd, gw = d['anchors'], d['nc'], d['depth_multiple'], d['width_multiple']
na = (len(anchors[0]) // 2) if isinstance(anchors, list) else anchors # number of anchors
no = na * (nc + 5) # number of outputs = anchors * (classes + 5)
layers, save, c2 = [], [], ch[-1] # layers, savelist, ch out
for i, (f, n, m, args) in enumerate(d['backbone'] + d['head']): # from, number, module, args
m = eval(m) if isinstance(m, str) else m # eval strings
for j, a in enumerate(args):
try:
args[j] = eval(a) if isinstance(a, str) else a # eval strings
except NameError:
pass
n = n_ = max(round(n * gd), 1) if n > 1 else n # depth gain
if m in (Conv, GhostConv, Bottleneck, GhostBottleneck, SPP, SPPF, DWConv, MixConv2d, Focus, CrossConv,
BottleneckCSP, C3, C3TR, C3SPP, C3Ghost, nn.ConvTranspose2d, DWConvTranspose2d, C3x):
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != no: # if not output
c2 = make_divisible(c2 * gw, 8) # 输出通道
args = [c1, c2, *args[1:]] # 更新配置参数
# 对应层需要重复
if m in [BottleneckCSP, C3, C3TR, C3Ghost, C3x]:
args.insert(2, n) # number of repeats
n = 1
elif m is nn.BatchNorm2d:
args = [ch[f]] # batch_normal层,上一层的输出维度
elif m is Concat:
c2 = sum(ch[x] for x in f) # concat层:通道数之和
elif m is Detect:
args.append([ch[x] for x in f]) # detect:通道数之和
if isinstance(args[1], int): # 整数表示number of anchors
args[1] = [list(range(args[1] * 2))] * len(f) # 初始化一个anchors矩阵
elif m is Contract:
c2 = ch[f] * args[0] ** 2
elif m is Expand:
c2 = ch[f] // args[0] ** 2
else:
c2 = ch[f]
# 构建对应层的模型
m_ = nn.Sequential(*(m(*args) for _ in range(n))) if n > 1 else m(*args) # module
t = str(m)[8:-2].replace('__main__.', '') # module type
np = sum(x.numel() for x in m_.parameters()) # number params
m_.i, m_.f, m_.type, m_.np = i, f, t, np # attach index, 'from' index, type, number params
LOGGER.info(f'{i:>3}{str(f):>18}{n_:>3}{np:10.0f} {t:<40}{str(args):<30}') # print
# 保存不等于-1的x的x%i
save.extend(x % i for x in ([f] if isinstance(f, int) else f) if x != -1) # append to savelist
layers.append(m_)
if i == 0:
ch = []
ch.append(c2)
return nn.Sequential(*layers), sorted(save)3.网络结构(yolox.pt)
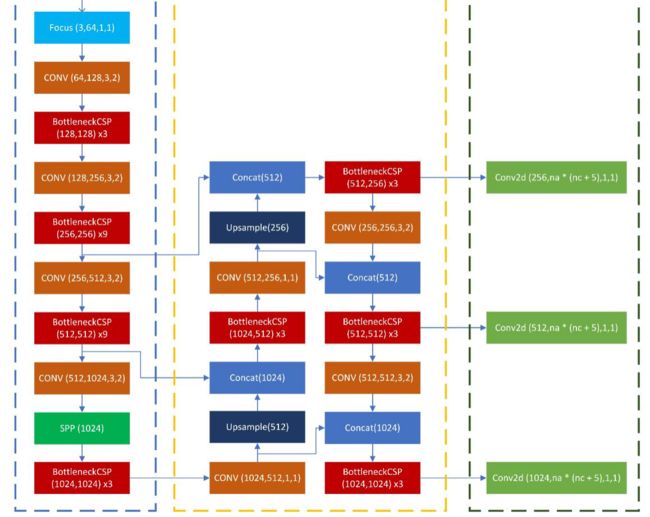
(1)前两层
网络前两层一层为6*6的卷积,strides为2,padding为(2,2),第二层为3*3的卷积,strides为2,padding为2,特征维度变换为3*640*640-->80*320*320-->160*160*160
(2) C3模块
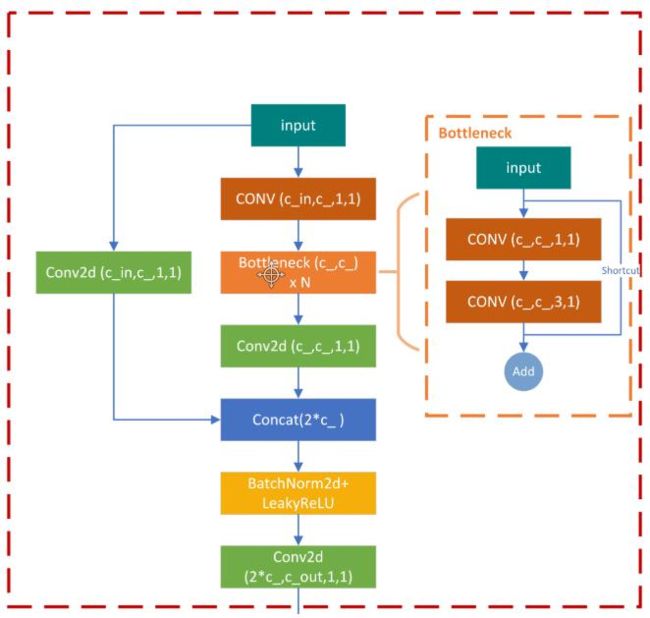
C3层有两个路径,第一个短路径, 只有一个1*1的卷积,将特征图从c1降维成c1*e,第二条路径是n个bottleneck模块,每个bottomneck包含两个卷积,第一个卷积为1*1的卷积,将通道数降维成c1-->c1*e,第二层为3*3的卷积,将通道数由c1*e-->c2,最后再做一层3*3的卷积,调整通道数。其中,bottleneck都采用残差连接。经过c3模块,特征图大小不变,通道数由c1变成c2,最后,再经过3*3的卷积,将特征图大小减半。
(3)SPPF模块
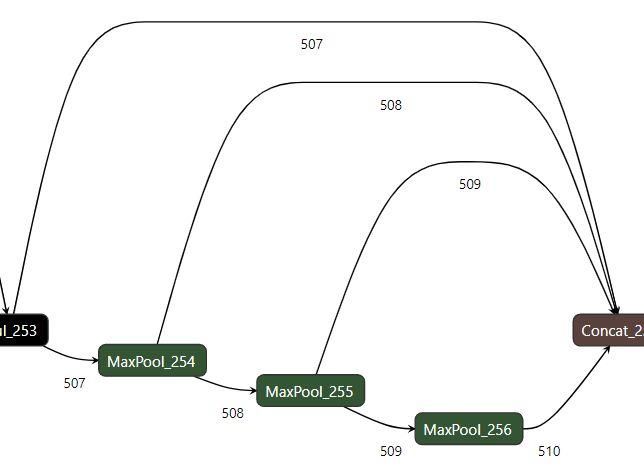
SPPF是SPP的快速版本,有四条路径,第一条路径,1*1的卷积,将特征图通道数由c1变成c1//2【1】,第二条路径,对【1】的结果经过5*5的最大池化,pading为2【2】,第三条路径,对【2】的结果,经过5*5的最大池化,pading为2【3】,第四条路径,经过 5*5的最大池化,pad为2【4】。将四条路径的结果融合,再做一层1*1的卷积。
4.PAN流程
PAN实现了双向通信,将高维特征与低维特征进行融合,三个特征图大小分别下采样8倍,16倍和32倍。首先,将高维特征进行上采样,与低维特征融合,然后再通过卷积实现从低维特征到高维特征的融合
假设网络输入为256*256,网络各层输出如下:对于上采样部分,
对于缩小32倍的特征图:将第10层输出进行上采样后,与第6层输出concat,输出大小为1,1280,16,16【1】
对于缩小8倍的特征图,将【1】的结果,经过一层C3层,此时维度变为:将通道数由1280变为640,再经过一层卷积层,将通道数变为320,再经过上采样,与第四层的结果相连接,输出维度为1,640,32,32【2】
下采样部分:
对于【2】,首先,经过一层C3层,将维度变为1,320,32,32,然后经过一层3*3的卷积,与第14层的结果相连,即【1】经过C3和1*1的卷积后的结果相连,维度为1,640,16,16。【3】
对于【3】,经过一层C3层和1*1的卷积,通道数保持不变,与第10层的结果相连,即为32层特征图上采样之前的结果。此时特征图为1,1280,8,8,再经过一层C3模块。【4】
对于【2】【3】【4】层结果,分别做预测
models.common.Conv 网络层数 0 输出: torch.Size([1, 80, 128, 128])
models.common.Conv 网络层数 1 输出: torch.Size([1, 160, 64, 64])
models.common.C3 网络层数 2 输出: torch.Size([1, 160, 64, 64])
models.common.Conv 网络层数 3 输出: torch.Size([1, 320, 32, 32])
models.common.C3 网络层数 4 输出: torch.Size([1, 320, 32, 32])
models.common.Conv 网络层数 5 输出: torch.Size([1, 640, 16, 16])
models.common.C3 网络层数 6 输出: torch.Size([1, 640, 16, 16])
models.common.Conv 网络层数 7 输出: torch.Size([1, 1280, 8, 8])
models.common.C3 网络层数 8 输出: torch.Size([1, 1280, 8, 8])
models.common.SPPF 网络层数 9 输出: torch.Size([1, 1280, 8, 8])
models.common.Conv 网络层数 10 输出: torch.Size([1, 640, 8, 8])
torch.nn.modules.upsampling.Upsample 网络层数 11 输出: torch.Size([1, 640, 16, 16])
models.common.Concat 网络层数 12 输出: torch.Size([1, 1280, 16, 16])
models.common.C3 网络层数 13 输出: torch.Size([1, 640, 16, 16])
models.common.Conv 网络层数 14 输出: torch.Size([1, 320, 16, 16])
torch.nn.modules.upsampling.Upsample 网络层数 15 输出: torch.Size([1, 320, 32, 32])
models.common.Concat 网络层数 16 输出: torch.Size([1, 640, 32, 32])
models.common.C3 网络层数 17 输出: torch.Size([1, 320, 32, 32])
models.common.Conv 网络层数 18 输出: torch.Size([1, 320, 16, 16])
models.common.Concat 网络层数 19 输出: torch.Size([1, 640, 16, 16])
models.common.C3 网络层数 20 输出: torch.Size([1, 640, 16, 16])
models.common.Conv 网络层数 21 输出: torch.Size([1, 640, 8, 8])
models.common.Concat 网络层数 22 输出: torch.Size([1, 1280, 8, 8])
models.common.C3 网络层数 23 输出: torch.Size([1, 1280, 8, 8])
代码如下:
class Model(nn.Module):
# YOLOv5 model
def __init__(self, cfg='yolov5s.yaml', ch=3, nc=None, anchors=None): # model, input channels, number of classes
super().__init__()
if isinstance(cfg, dict):
self.yaml = cfg # model dict
else: # is *.yaml
import yaml # for torch hub
self.yaml_file = Path(cfg).name
with open(cfg, encoding='ascii', errors='ignore') as f:
self.yaml = yaml.safe_load(f) # model dict
# Define model
ch = self.yaml['ch'] = self.yaml.get('ch', ch) # input channels
if nc and nc != self.yaml['nc']:
LOGGER.info(f"Overriding model.yaml nc={self.yaml['nc']} with nc={nc}")
self.yaml['nc'] = nc # override yaml value
if anchors:
LOGGER.info(f'Overriding model.yaml anchors with anchors={anchors}')
self.yaml['anchors'] = round(anchors) # override yaml value
# 根据参数、构建模型 self.save:保留需要连接的层
self.model, self.save = parse_model(deepcopy(self.yaml), ch=[ch]) # model, savelist
self.names = [str(i) for i in range(self.yaml['nc'])] # default names
self.inplace = self.yaml.get('inplace', True)
# Build strides, anchors
m = self.model[-1] # Detect()
if isinstance(m, Detect):
s = 256 # 2x min stride
m.inplace = self.inplace
# ch:input channels s:
m.stride = torch.tensor([s / x.shape[-2] for x in self.forward(torch.zeros(1, ch, s, s))]) # forward
check_anchor_order(m) # must be in pixel-space (not grid-space) 检查顺序是否正确
m.anchors /= m.stride.view(-1, 1, 1) # 各特征层的anchors
self.stride = m.stride # [8,16,32]
self._initialize_biases() # only run once
# Init weights, biases
initialize_weights(self)
self.info()
LOGGER.info('')
def forward(self, x, augment=False, profile=False, visualize=False):
if augment:
return self._forward_augment(x) # augmented inference, None
return self._forward_once(x, profile, visualize) # single-scale inference, train
def _forward_augment(self, x):
img_size = x.shape[-2:] # height, width
s = [1, 0.83, 0.67] # scales
f = [None, 3, None] # flips (2-ud, 3-lr)
y = [] # outputs
for si, fi in zip(s, f):
xi = scale_img(x.flip(fi) if fi else x, si, gs=int(self.stride.max()))
yi = self._forward_once(xi)[0] # forward
# cv2.imwrite(f'img_{si}.jpg', 255 * xi[0].cpu().numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0))[:, :, ::-1]) # save
yi = self._descale_pred(yi, fi, si, img_size)
y.append(yi)
y = self._clip_augmented(y) # clip augmented tails
return torch.cat(y, 1), None # augmented inference, train
def _forward_once(self, x, profile=False, visualize=False):
y, dt = [], [] # outputs
for m in self.model:
if m.f != -1: # if not from previous layer
x = y[m.f] if isinstance(m.f, int) else [x if j == -1 else y[j] for j in m.f] # from earlier layers
if profile:
self._profile_one_layer(m, x, dt)
x = m(x) # run
print(m.type,"网络层数 ",m.i,"输出:",x.shape)
y.append(x if m.i in self.save else None) # save output
if visualize:
feature_visualization(x, m.type, m.i, save_dir=visualize)
return x
def _descale_pred(self, p, flips, scale, img_size):
# de-scale predictions following augmented inference (inverse operation)
if self.inplace:
p[..., :4] /= scale # de-scale
if flips == 2:
p[..., 1] = img_size[0] - p[..., 1] # de-flip ud
elif flips == 3:
p[..., 0] = img_size[1] - p[..., 0] # de-flip lr
else:
x, y, wh = p[..., 0:1] / scale, p[..., 1:2] / scale, p[..., 2:4] / scale # de-scale
if flips == 2:
y = img_size[0] - y # de-flip ud
elif flips == 3:
x = img_size[1] - x # de-flip lr
p = torch.cat((x, y, wh, p[..., 4:]), -1)
return p
def _clip_augmented(self, y):
# Clip YOLOv5 augmented inference tails
nl = self.model[-1].nl # number of detection layers (P3-P5)
g = sum(4 ** x for x in range(nl)) # grid points
e = 1 # exclude layer count
i = (y[0].shape[1] // g) * sum(4 ** x for x in range(e)) # indices
y[0] = y[0][:, :-i] # large
i = (y[-1].shape[1] // g) * sum(4 ** (nl - 1 - x) for x in range(e)) # indices
y[-1] = y[-1][:, i:] # small
return y
def _profile_one_layer(self, m, x, dt):
c = isinstance(m, Detect) # is final layer, copy input as inplace fix
o = thop.profile(m, inputs=(x.copy() if c else x,), verbose=False)[0] / 1E9 * 2 if thop else 0 # FLOPs
t = time_sync()
for _ in range(10):
m(x.copy() if c else x)
dt.append((time_sync() - t) * 100)
if m == self.model[0]:
LOGGER.info(f"{'time (ms)':>10s} {'GFLOPs':>10s} {'params':>10s} module")
LOGGER.info(f'{dt[-1]:10.2f} {o:10.2f} {m.np:10.0f} {m.type}')
if c:
LOGGER.info(f"{sum(dt):10.2f} {'-':>10s} {'-':>10s} Total")
def _initialize_biases(self, cf=None): # initialize biases into Detect(), cf is class frequency
# https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.02002 section 3.3
# cf = torch.bincount(torch.tensor(np.concatenate(dataset.labels, 0)[:, 0]).long(), minlength=nc) + 1.
m = self.model[-1] # Detect() module
for mi, s in zip(m.m, m.stride): # from
b = mi.bias.view(m.na, -1).detach() # conv.bias(255) to (3,85)
b[:, 4] += math.log(8 / (640 / s) ** 2) # obj (8 objects per 640 image)
b[:, 5:] += math.log(0.6 / (m.nc - 0.999999)) if cf is None else torch.log(cf / cf.sum()) # cls
mi.bias = torch.nn.Parameter(b.view(-1), requires_grad=True)
def _print_biases(self):
m = self.model[-1] # Detect() module
for mi in m.m: # from
b = mi.bias.detach().view(m.na, -1).T # conv.bias(255) to (3,85)
LOGGER.info(
('%6g Conv2d.bias:' + '%10.3g' * 6) % (mi.weight.shape[1], *b[:5].mean(1).tolist(), b[5:].mean()))
# def _print_weights(self):
# for m in self.model.modules():
# if type(m) is Bottleneck:
# LOGGER.info('%10.3g' % (m.w.detach().sigmoid() * 2)) # shortcut weights
def fuse(self): # fuse model Conv2d() + BatchNorm2d() layers
LOGGER.info('Fusing layers... ')
for m in self.model.modules():
if isinstance(m, (Conv, DWConv)) and hasattr(m, 'bn'):
m.conv = fuse_conv_and_bn(m.conv, m.bn) # update conv
delattr(m, 'bn') # remove batchnorm
m.forward = m.forward_fuse # update forward
self.info()
return self
def info(self, verbose=False, img_size=640): # print model information
model_info(self, verbose, img_size)
def _apply(self, fn):
# Apply to(), cpu(), cuda(), half() to model tensors that are not parameters or registered buffers
self = super()._apply(fn)
m = self.model[-1] # Detect()
if isinstance(m, Detect):
m.stride = fn(m.stride)
m.grid = list(map(fn, m.grid))
if isinstance(m.anchor_grid, list):
m.anchor_grid = list(map(fn, m.anchor_grid))
return self4.训练参数解释
--weights:初始权重 --cfg:模型配置文件 --data:数据配置文件 --hyp:学习率等超参数文件 --epochs:迭代次数 -imgsz:图像大小 --rect:长方形训练策略,不resize成正方形 --resume:恢复最近的培训,从last.pt开始 --nosave:只保存最后的检查点 --noval:仅在最后一次epochs进行验证 --noautoanchor:禁用AutoAnchor --noplots:不保存打印文件 --evolve:为x个epochs进化超参数 --bucket:上传操作 --cache:在ram或硬盘中缓存数据 --image-weights:使用加权图像选择进行训练(类别加权) --single-cls:单类别标签置0 --device:gpu设置 --multi-scale:改变img大小+/-50%,能够被32整除 --optimizer:学习率优化器 --sync-bn:使用SyncBatchNorm,仅在DDP模式中支持,跨gpu时使用 --workers:最大 dataloader 的线程数 (per RANK in DDP mode) --project:保存文件的地址 --name:保存日志文件的名称 ----exist-ok:现有项目/名称确定,不递增 --quad --cos-lr:余弦学习率调度 --label-smoothing: --patience:经过多少个epoch损失不再下降,就停止迭代 --freeze:迁移学习,冻结训练 --save-period:每x个周期保存一个检查点(如果<1,则禁用) --seed: --local_rank:gpu编号