RepVGG模型——pytorch实现
论文传送门:RepVGG: Making VGG-style ConvNets Great Again
RepVGG的出发点:
RepVGG的特点:
为保证模型的性能,以及加快模型推理速度(Fast),减少模型内存需求(Memory-economical),使模型更加灵活(Flexible),作者提出了模型重参数化(Model Re-parameterization)。
训练时,采用并行多分支结构;推理时,采用等效的单路结构。
RepVGG的分支结构:
Block中包含3(或2)个分支,分别是3x3ConvBN、1x1ConvBN、(BN),其计算结果相加,再经过ReLU激活函数输出。
整体结构与VGG相似,每个Stage堆叠N个Block,其中第一个Block实现下采样2倍(stride=2),剩余Block保持特征图尺寸不变(stride=1),网络共5个Stage。
每个Stage的第一个Block为下采样层,仅包含3x3ConvBN和1x1ConvBN分支,不包含BN分支。

模型重参数化:
分支结构可以转化为等效的单路结构:
①ConvBN结构可以用一个等效的Conv(带偏置Bias)来表示;
②1x1Conv可以用一个等效的3x3Conv来表示(权重padding0);
③可以创建恒等映射的3x3Conv(卷积前后张量不变),将BN转化为等价的ConvBN,再根据①转化为等效的Conv(实际上可以直接将BN转化为等效的Conv);
④多个Conv分支结构,可以将多个Conv的weight和bias分别相加,获得一个等效的Conv,将分支结构转化为单路结构。

分支结构转化为等效的单路结构,计算公式如下:

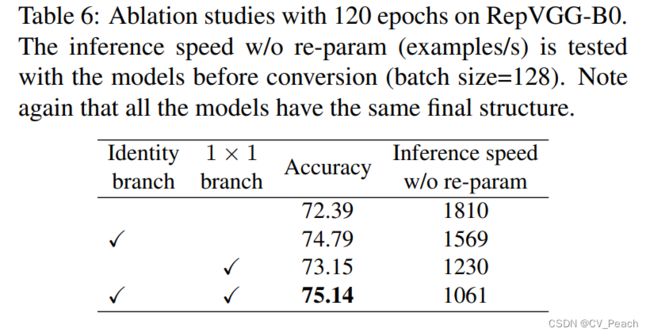
不同规模的RepVGG模型:

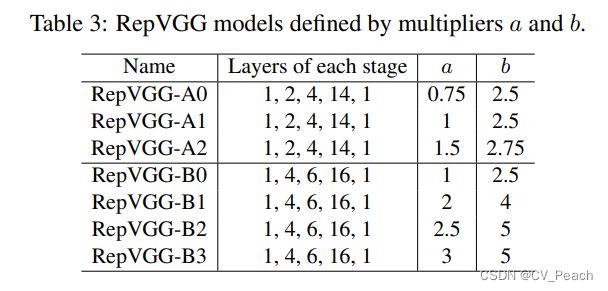
作者还采用了group convolution搭建了其他规模的RepVGG模型。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
def convbn(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding): # ConvBN
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
)
class RepVGGBlock(nn.Module): # RepVGG Block
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride, deploy=False):
super(RepVGGBlock, self).__init__()
self.deploy = deploy # 是否为测试部署模式
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.re_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 3, stride, 1, bias=True) # 结构重参数化的等效Conv
self.conv3x3 = convbn(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1) # 3x3ConvBN分支
self.conv1x1 = convbn(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, padding=0) # 1x1ConvBN分支
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels) if stride == 1 else None # BN分支(下采样层没有BN分支)
def forward(self, x):
if self.deploy: # 如果为测试部署模式
return self.relu(self.re_conv(x)) # 采用等效Conv
else:
if self.bn is not None:
return self.relu(self.conv3x3(x) + self.conv1x1(x) + self.bn(x))
else:
return self.relu(self.conv3x3(x) + self.conv1x1(x))
def _pad1x1conv(self, conv: nn.Conv2d): # 将1x1Conv填充至等效的3x3Conv(对weight进行padding0)
return F.pad(conv.weight, [1, 1, 1, 1], value=0.)
def _createconv(self, channels): # 创建一个恒等映射卷积(卷积前后张量不发生变化)
conv_w = torch.zeros(channels, channels, 3, 3, device=self.bn.weight.device)
for i in range(channels):
conv_w[i, i, 1, 1] = 1.
return conv_w
def _convbn2conv(self, conv_w, bn: nn.BatchNorm2d): # 将ConvBN转化为等价的Conv(带有偏置B)
mean = bn.running_mean
var = bn.running_var
bn_w = bn.weight
bn_b = bn.bias
eps = bn.eps
std = (var + eps).sqrt()
new_conv_w = conv_w * (bn_w / std).view(-1, 1, 1, 1)
new_conv_b = bn_b - mean * bn_w / std
return new_conv_w, new_conv_b
def convert(self): # 计算与(3x3ConvBn + 1x1ConvBN + BN)等价的3x3Conv
w3, b3 = self._convbn2conv(self.conv3x3[0].weight, self.conv3x3[1])
w1, b1 = self._convbn2conv(self._pad1x1conv(self.conv1x1[0]), self.conv1x1[1])
if self.bn is not None:
w0, b0 = self._convbn2conv(self._createconv(self.out_channels), self.bn)
else:
w0, b0 = 0, 0
w = w3 + w1 + w0
b = b3 + b1 + b0
self.re_conv.weight.data = w
self.re_conv.bias.data = b
self.deploy = True
class RepVGG(nn.Module): # RepVGG
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000, stage_layers=[1, 2, 4, 14, 1], a=0.75, b=2.5):
super(RepVGG, self).__init__()
self.stage0 = self._make_stage(3, min(64, 64 * a), stage_layers[0])
self.stage1 = self._make_stage(min(64, 64 * a), 64 * a, stage_layers[1])
self.stage2 = self._make_stage(64 * a, 128 * a, stage_layers[2])
self.stage3 = self._make_stage(128 * a, 256 * a, stage_layers[3])
self.stage4 = self._make_stage(256 * a, 512 * b, stage_layers[4])
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1),
nn.Conv2d(int(512 * b), num_classes, 1, 1, 0),
)
def _make_stage(self, in_channels, out_channels, num_layers):
layers = []
for i in range(num_layers):
# 每个Stage的第一层为下采样层,剩余各层特征图尺寸不变
layers.append(RepVGGBlock(int(in_channels), int(out_channels), stride=2 if i == 0 else 1))
in_channels = out_channels
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.stage0(x)
x = self.stage1(x)
x = self.stage2(x)
x = self.stage3(x)
x = self.stage4(x)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x.squeeze()
def convert_model(model: nn.Module): # 结构重参数化
for module in model.modules():
if hasattr(module, "convert"):
module.convert()
return model
def RepVGG_A0(num_classes=1000):
return RepVGG(num_classes=num_classes, stage_layers=[1, 2, 4, 14, 1], a=0.75, b=2.5)
def RepVGG_A1(num_classes=1000):
return RepVGG(num_classes=num_classes, stage_layers=[1, 2, 4, 14, 1], a=1., b=2.5)
def RepVGG_A2(num_classes=1000):
return RepVGG(num_classes=num_classes, stage_layers=[1, 2, 4, 14, 1], a=1.5, b=2.75)
def RepVGG_B0(num_classes=1000):
return RepVGG(num_classes=num_classes, stage_layers=[1, 4, 6, 16, 1], a=1, b=2.5)
def RepVGG_B1(num_classes=1000):
return RepVGG(num_classes=num_classes, stage_layers=[1, 4, 6, 16, 1], a=2., b=4.)
def RepVGG_B2(num_classes=1000):
return RepVGG(num_classes=num_classes, stage_layers=[1, 4, 6, 16, 1], a=2.5, b=5.)
def RepVGG_B3(num_classes=1000):
return RepVGG(num_classes=num_classes, stage_layers=[1, 4, 6, 16, 1], a=3., b=5.)
if __name__ == "__main__":
cuda = True if torch.cuda.is_available() else False
images = torch.randn(8, 3, 224, 224)
repvgg = RepVGG_A0()
if cuda:
images = images.cuda()
repvgg.cuda()
repvgg.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
output1 = repvgg(images)
repvgg = convert_model(repvgg)
output2 = repvgg(images)
print(torch.allclose(output1, output2, rtol=1e-02, atol=1e-05))