【ROS】URDF集成Gazebo
【ROS】URDF集成Gazebo
- 一、ubuntu16.04中下载gazebo_models
-
- 1 下载压缩包
- 2 解压到本地
- 3 复制到指定目录
- 二、在gazebo中显示简单模型
-
- 1 创建功能包,导入依赖
- 2 编写URDF文件
- 3 编写launch文件
- 4 在gazebo中显示机器人模型
- 三、URDF集成Gazebo相关设置
-
- 1 collision
- 2 inertial
-
- 2.1 球体惯性矩阵
- 2.2 圆柱惯性矩阵
- 2.3 立方体惯性矩阵
- 3 颜色设置
- 四、在gazebo中导入小车模型
-
- 1 编写xacro文件
- 2 编写launch文件
- 3 运行结果
一、ubuntu16.04中下载gazebo_models
博主的ubuntu系统是ros-kinetic版本,但是在第一次打开gazebo时,打开的速度比较缓慢,而且加载场景特别慢。博主在这里解决的办法,是将官方的模型库下载到本地,这样,再一次打开gazebo时,速度就会快很多。博主在这里使用的是手动导入的方法,因为这种方式更加快速一些。
1 下载压缩包
博主这里下载的是github中上传的gazebo_models文件,里面包含了绝大部分官方的模型文件,对于我们打开或者使用gazebo是完全足够的,链接如下。
链接: https://github.com/osrf/gazebo_models.
2 解压到本地
下载完后,你会在Downloads文件夹中找到这个解压包,解压包的名称是gazebo_models-master.zip,选中解压包,点击右键,选择提取到此处,并将解压后的文件命名为models。
3 复制到指定目录
在Downloads文件夹中打开终端,输入以下指令,将其将其复制到指定目录下,这样,当我们再次打开gazebo时加载的速度会变快很多,并可以在gazebo中添加官方的一些模型文件,如图所示,这样我们就完成了gazebo_models文件的下载。
sudo mv models/ /usr/share/gazebo-7/
二、在gazebo中显示简单模型
1 创建功能包,导入依赖
打开vs code,在vs code的终端中输入以下命令
cd ~/fjy_xm //这是自定义的文件夹
mkdir catkin_urdf_gazebo
cd catkin_urdf_gazebo
mkdir src
carkin_make
source devel/setup.bash
cd src
catkin_create_pkg urdf_gazebo urdf xacro gazebo_ros gazebo_ros_control gazebo_plugins
cd urdf_gazebo
mkdir launch //存储launch文件
mkdir urdf //存储urdf文件的目录
cd urdf
mkdir urdf
mkdir xacro
cd urdf
touch urdf_gazebo.urdf
2 编写URDF文件
在urdf_gazebo.urdf文件中编写以下程序,生成一个长度为0.5,宽度为0.2,高度为0.1的长方体。
<robot name="mycar">
<link name="base_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<box size="0.5 0.2 0.1" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0.0 0.0 0.0" />
<material name="yellow">
<color rgba="0.5 0.3 0.0 1" />
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<box size="0.5 0.2 0.1" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0.0 0.0 0.0" />
</collision>
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" />
<mass value="6" />
<inertia ixx="1" ixy="0" ixz="0" iyy="1" iyz="0" izz="1" />
</inertial>
</link>
<gazebo reference="base_link">
<material>Gazebo/Black</material>
</gazebo>
</robot>
3 编写launch文件
在launch文件夹下创建一个文件,文件名为urdf_gazebo.launch,在urdf_gazebo.launch文件中编写以下程序:
<launch>
<!-- 将 Urdf 文件的内容加载到参数服务器 -->
<param name="robot_description" textfile="$(find urdf_gazebo)/urdf/urdf/urdf_gazebo.urdf" />
<!-- 启动 gazebo -->
<include file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch" />
<!-- 在 gazebo 中显示机器人模型 -->
<node pkg="gazebo_ros" type="spawn_model" name="model" args="-urdf -model mycar -param robot_description" />
</launch>
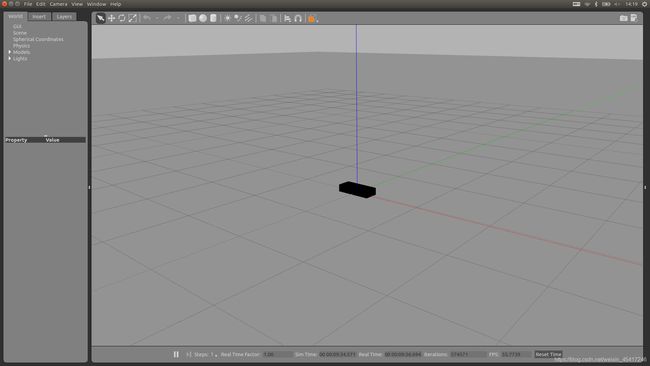
4 在gazebo中显示机器人模型
编译并设置环境变量后,在终端输入以下指令,运行urdf_gazebo.launch文件,启动界面如下:
roslaunch urdf_gazebo urdf_gazebo.launch
三、URDF集成Gazebo相关设置
在URDF建模篇中,我们已经学习了相关的标签,由于在gazebo中要考虑碰撞属性和和惯性矩阵,在这里,特别对碰撞属性和惯性矩阵的设置进行说明。
关于URDF建模的相关链接在这里给出,有需要的,可以去学习一下。
链接: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45417246/article/details/116029389.
1 collision
如果机器人link是标准的几何体形状,和link的 visual 属性设置一致即可。
2 inertial
惯性矩阵的设置需要结合link的质量与外形参数动态生成,标准的球体、圆柱与立方体的惯性矩阵公式如下(已经封装为 xacro 实现):
2.1 球体惯性矩阵
<!-- Macro for inertia matrix -->
<xacro:macro name="sphere_inertial_matrix" params="m r">
<inertial>
<mass value="${m}" />
<inertia ixx="${2*m*r*r/5}" ixy="0" ixz="0"
iyy="${2*m*r*r/5}" iyz="0"
izz="${2*m*r*r/5}" />
</inertial>
</xacro:macro>
2.2 圆柱惯性矩阵
<xacro:macro name="cylinder_inertial_matrix" params="m r h">
<inertial>
<mass value="${m}" />
<inertia ixx="${m*(3*r*r+h*h)/12}" ixy = "0" ixz = "0"
iyy="${m*(3*r*r+h*h)/12}" iyz = "0"
izz="${m*r*r/2}" />
</inertial>
</xacro:macro>
2.3 立方体惯性矩阵
<xacro:macro name="Box_inertial_matrix" params="m l w h">
<inertial>
<mass value="${m}" />
<inertia ixx="${m*(h*h + l*l)/12}" ixy = "0" ixz = "0"
iyy="${m*(w*w + l*l)/12}" iyz= "0"
izz="${m*(w*w + h*h)/12}" />
</inertial>
</xacro:macro>
但是需要注意的是,原则上,除了 base_footprint 外,机器人的每个刚体部分都需要设置惯性矩阵,且惯性矩阵必须经计算得出,如果随意定义刚体部分的惯性矩阵,那么可能会导致机器人在 Gazebo 中出现抖动,移动等现象。
3 颜色设置
在 gazebo 中显示 link 的颜色,必须要使用指定的标签,material 标签中,设置的值区分大小写,颜色可以设置为Red、Blue、Green、Black等等
<gazebo reference="link节点名称">
<material>Gazebo/Blue</material>
</gazebo>
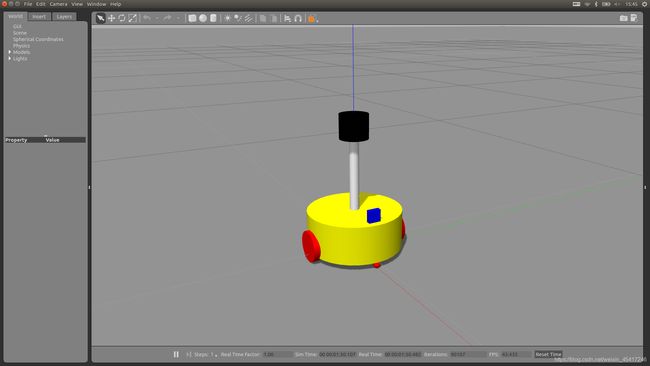
四、在gazebo中导入小车模型
1 编写xacro文件
在URDF建模和xacro建模中我们已经完成了关于如何创建一个小车模型,这里以在xacro建模篇中构建的小车模型为例,修改其对应的碰撞属性和惯性矩阵,将其导入gazebo中显示。
在xacro文件夹下创建文件,gazebo_car.xacro,gazebo_camera.xacro,gazebo_laser.xacro,gazebo_head.xarco,gazebo_car_union.xacro四个文件。
在gazebo_head.xacro文件中编写以下程序:
<robot name="base" xmlns:xacro="http://wiki.ros.org/xacro">
<xacro:macro name="sphere_inertial_matrix" params="m r">
<inertial>
<mass value="${m}" />
<inertia ixx="${2*m*r*r/5}" ixy="0" ixz="0"
iyy="${2*m*r*r/5}" iyz="0"
izz="${2*m*r*r/5}" />
</inertial>
</xacro:macro>
<xacro:macro name="cylinder_inertial_matrix" params="m r h">
<inertial>
<mass value="${m}" />
<inertia ixx="${m*(3*r*r+h*h)/12}" ixy = "0" ixz = "0"
iyy="${m*(3*r*r+h*h)/12}" iyz = "0"
izz="${m*r*r/2}" />
</inertial>
</xacro:macro>
<xacro:macro name="Box_inertial_matrix" params="m l w h">
<inertial>
<mass value="${m}" />
<inertia ixx="${m*(h*h + l*l)/12}" ixy = "0" ixz = "0"
iyy="${m*(w*w + l*l)/12}" iyz= "0"
izz="${m*(w*w + h*h)/12}" />
</inertial>
</xacro:macro>
</robot>
在gazebo_camera.xacro文件中编写以下程序:
<robot name="my_camera" xmlns:xacro="http://wiki.ros.org/xacro">
<xacro:property name="camera_length" value="0.01" />
<xacro:property name="camera_width" value="0.025" />
<xacro:property name="camera_height" value="0.025" />
<xacro:property name="camera_x" value="0.08" />
<xacro:property name="camera_y" value="0.0" />
<xacro:property name="camera_z" value="${base_link_length / 2 + camera_height / 2}" />
<xacro:property name="camera_m" value="0.01" />
<link name="camera">
<visual>
<geometry>
<box size="${camera_length} ${camera_width} ${camera_height}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0.0 0.0 0.0" />
<material name="black" />
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<box size="${camera_length} ${camera_width} ${camera_height}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0.0 0.0 0.0" />
</collision>
<xacro:Box_inertial_matrix m="${camera_m}" l="${camera_length}" w="${camera_width}" h="${camera_height}" />
</link>
<joint name="camera2base_link" type="fixed">
<parent link="base_link" />
<child link="camera" />
<origin xyz="${camera_x} ${camera_y} ${camera_z}" />
</joint>
<gazebo reference="camera">
<material>Gazebo/Blue</material>
</gazebo>
</robot>
在gazebo_laser.xacro文件中编写以下程序:
<robot name="my_laser" xmlns:xacro="http://wiki.ros.org/xacro">
<xacro:property name="support_length" value="0.15" />
<xacro:property name="support_radius" value="0.01" />
<xacro:property name="support_x" value="0.0" />
<xacro:property name="support_y" value="0.0" />
<xacro:property name="support_z" value="${base_link_length / 2 + support_length / 2}" />
<xacro:property name="support_m" value="0.02" />
<link name="support">
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${support_radius}" length="${support_length}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0.0 0.0 0.0" />
<material name="red">
<color rgba="0.8 0.2 0.0 0.8" />
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${support_radius}" length="${support_length}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0.0 0.0 0.0" />
</collision>
<xacro:cylinder_inertial_matrix m="${support_m}" r="${support_radius}" h="${support_length}" />
</link>
<joint name="support2base_link" type="fixed">
<parent link="base_link" />
<child link="support" />
<origin xyz="${support_x} ${support_y} ${support_z}" />
</joint>
<gazebo reference="support">
<material>Gazebo/White</material>
</gazebo>
<xacro:property name="laser_length" value="0.05" />
<xacro:property name="laser_radius" value="0.03" />
<xacro:property name="laser_x" value="0.0" />
<xacro:property name="laser_y" value="0.0" />
<xacro:property name="laser_z" value="${support_length / 2 + laser_length / 2}" />
<xacro:property name="laser_m" value="0.1" />
<link name="laser">
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${laser_radius}" length="${laser_length}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0.0 0.0 0.0" />
<material name="black" />
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${laser_radius}" length="${laser_length}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0.0 0.0 0.0" />
</collision>
<xacro:cylinder_inertial_matrix m="${laser_m}" r="${laser_radius}" h="${laser_length}" />
</link>
<joint name="laser2support" type="fixed">
<parent link="support" />
<child link="laser" />
<origin xyz="${laser_x} ${laser_y} ${laser_z}" />
</joint>
<gazebo reference="laser">
<material>Gazebo/Black</material>
</gazebo>
</robot>
在gazebo_car.xacro文件中编写以下程序:
<robot name="my_base" xmlns:xacro="http://www.ros.org/wiki/xacro">
<xacro:property name="PI" value="3.1415926"/>
<material name="black">
<color rgba="0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0" />
</material>
<xacro:property name="base_footprint_radius" value="0.001" />
<xacro:property name="base_link_radius" value="0.1" />
<xacro:property name="base_link_length" value="0.08" />
<xacro:property name="earth_space" value="0.015" />
<xacro:property name="base_link_m" value="0.5" />
<link name="base_footprint">
<visual>
<geometry>
<sphere radius="${base_footprint_radius}" />
</geometry>
</visual>
</link>
<link name="base_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${base_link_radius}" length="${base_link_length}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<material name="yellow">
<color rgba="0.5 0.3 0.0 0.5" />
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${base_link_radius}" length="${base_link_length}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
</collision>
<xacro:cylinder_inertial_matrix m="${base_link_m}" r="${base_link_radius}" h="${base_link_length}" />
</link>
<joint name="base_link2base_footprint" type="fixed">
<parent link="base_footprint" />
<child link="base_link" />
<origin xyz="0 0 ${earth_space + base_link_length / 2 }" />
</joint>
<gazebo reference="base_link">
<material>Gazebo/Yellow</material>
</gazebo>
<xacro:property name="wheel_radius" value="0.0325" />
<xacro:property name="wheel_length" value="0.015" />
<xacro:property name="wheel_m" value="0.05" />
<xacro:macro name="add_wheels" params="name flag">
<link name="${name}_wheel">
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${wheel_radius}" length="${wheel_length}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="${PI / 2} 0.0 0.0" />
<material name="black" />
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${wheel_radius}" length="${wheel_length}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="${PI / 2} 0.0 0.0" />
</collision>
<xacro:cylinder_inertial_matrix m="${wheel_m}" r="${wheel_radius}" h="${wheel_length}" />
</link>
<joint name="${name}_wheel2base_link" type="continuous">
<parent link="base_link" />
<child link="${name}_wheel" />
<origin xyz="0 ${flag * base_link_radius} ${-(earth_space + base_link_length / 2 - wheel_radius) }" />
<axis xyz="0 1 0" />
</joint>
<gazebo reference="${name}_wheel">
<material>Gazebo/Red</material>
</gazebo>
</xacro:macro>
<xacro:add_wheels name="left" flag="1" />
<xacro:add_wheels name="right" flag="-1" />
<xacro:property name="support_wheel_radius" value="0.0075" />
<xacro:property name="support_wheel_m" value="0.03" />
<xacro:macro name="add_support_wheel" params="name flag" >
<link name="${name}_wheel">
<visual>
<geometry>
<sphere radius="${support_wheel_radius}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<material name="black" />
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<sphere radius="${support_wheel_radius}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
</collision>
<xacro:sphere_inertial_matrix m="${support_wheel_m}" r="${support_wheel_radius}" />
</link>
<joint name="${name}_wheel2base_link" type="continuous">
<parent link="base_link" />
<child link="${name}_wheel" />
<origin xyz="${flag * (base_link_radius - support_wheel_radius)} 0 ${-(base_link_length / 2 + earth_space / 2)}" />
<axis xyz="1 1 1" />
</joint>
<gazebo reference="${name}_wheel">
<material>Gazebo/Red</material>
</gazebo>
</xacro:macro>
<xacro:add_support_wheel name="front" flag="1" />
<xacro:add_support_wheel name="back" flag="-1" />
</robot>
在gazebo_car_union.xacro文件中编写以下程序:
<robot name="my_car_camera" xmlns:xacro="http://wiki.ros.org/xacro">
<xacro:include filename="gazebo_head.xacro" />
<xacro:include filename="gazebo_car.xacro" />
<xacro:include filename="gazebo_laser.xacro" />
<xacro:include filename="gazebo_camera.xacro" />
</robot>
2 编写launch文件
在launch文件夹下创建一个文件,文件名为gazebo_car.launch,在gazebo_car.launch文件中编写以下程序:
<launch>
<!-- 将 Urdf 文件的内容加载到参数服务器 -->
<param name="robot_description" command="$(find xacro)/xacro $(find urdf_gazebo)/urdf/xacro/gazebo_car_union.xacro" />
<!-- 启动 gazebo -->
<include file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch" />
<!-- 在 gazebo 中显示机器人模型 -->
<node pkg="gazebo_ros" type="spawn_model" name="model" args="-urdf -model mycar -param robot_description" />
</launch>