实训总结报告
实训总结报告
阶段 1 :项目启动
学习使用 vi, JAVA, Ant, Junit ,配置 SonarQube ,并熟悉 GridWorld 的使用。
详见GridWorld 阶段一学习报告
vi/vim 编辑器
vi 编辑器是所有 Unix 及 Linux 系统下标准的编辑器, vim 编辑器是 vi 的升级版,增加了一些功能,同时完全兼容 vi 命令。
vi/vim 编辑器有三种模式:
(1) 一般模式
打开 vi/vim 编辑器后的默认模式。
在一般模式中可以进行删除、复制、粘贴,但是无法编辑文件内容。
(2) 编辑模式
在编辑模式中可以编辑文件内容。
(3) 命令行模式
在命令行模式下可以进行查找数据、读取、保存、大量替换字符、离开编辑器、显示行号等操作。
JAVA 语言
java是一门面向对象编程语言,吸收了C/C++的优点,摒弃了C/C++复杂的指针等内容,也不需要用户手动释放内存空间。java本身还具备了很强的可移植性,通过将源代码编译成二进制字节码,然后通过不同平台的java虚拟机来解释执行字节码,从而实行了“一次编译,到处执行”的跨平台特性。
Java的应用领域非常广泛。可以做应用系统、互联网网站、以及移动端的安卓等。
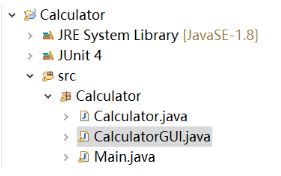
Java 编写计算器小程序
实现加减乘除运算,调用 swing 库实现 GUI ,并在 Eclipse 集成环境下编译运行。
项目结构如下:
运行结果如下:
Ant 环境
Ant 是 JAVA 的生成工具,是 Apache 的核心项目。
Ant 类似于与 Unix 中的 Make 工具,都是用来编译、生成。
可以在 Eclipse 中集成 Ant 环境。
Junit
Junit 是一个 Java 单元测试的工具,可以用来检验程序中的方法是否符合预期。
可以在 Eclipse 中简单地导入 Junit。
Junit 的一个测试类形如:
import org.junit.Test;
public class Test {
@Test
public void test1() {
assertEquals(expected_result, new test_class().test_method(args));
}
}
SonarQube
Sonar 是一个用于代码质量管理的开源平台,用于管理源代码的质量,可以从七个维度检测代码质量。
GridWorld 的使用
编译运行第一个 GridWorld 应用 BugRunner。
命令行进入到项目跟文件夹下 $Gridworld_Project/GridWorldCode/projects/firstProject,通过以下指令引用预先打包好的 gridworld.jar 包,编译运行 BugRunner。
## 编译:
javac -classpath .:./../../gridworld.jar BugRunner.java
## 执行:
java -classpath .:./../../gridworld.jar BugRunner
运行结果如下:
阶段 2 :基本任务
学习和使用 GridWorld 中的重要类。
Part 2:Bug Variations
Bug 类的方法有:
// tests whether the bug can move forward into a location that is empty or contains aflower
public boolean canMove()
// moves the bug forward, putting a flower into the location it previously occupied
public void move()
// turns the bug 45 degrees to the right without changing its location
public void turn()
These methods are used in the bug’s act method.
public void act()
{
if (canMove())
move();
else
turn();
}
拓展 Bug 类:
BoxBug
最大行动轨迹为边长为 sideLength 的正方形的 Bug。
SpiralBug
每次旋转 90 度后 sideLength++ 的 Bug。
ZBug
行走轨迹为各边长 sideLength 的 Z 字的 Bug。
DancingBug
一个数组记录 Bug 的舞步,数组的元素的值表示 Bug 在本次移动前要顺时针旋转 45 度多少次。
Part 3:GridWorld Classes and Interfaces
Location 类
Location 类帮助定位一个 actor 在 grid 中的坐标,并且定义了每个 actor 的方向。
Location 类宏定义了指南针方向以及角度。
/**
* The turn angle for turning 90 degrees to the left.
*/
public static final int LEFT = -90;
/**
* The turn angle for turning 90 degrees to the right.
*/
public static final int RIGHT = 90;
...
/**
* The compass direction for north.
*/
public static final int NORTH = 0;
/**
* The compass direction for northeast.
*/
public static final int NORTHEAST = 45;
...
Location 类有以下方法。
/**
* Gets the row coordinate.
* @return the row of this location
*/
public int getRow();
/**
* Gets the column coordinate.
* @return the column of this location
*/
public int getCol();
/**
* Gets the adjacent location in any one of the eight compass directions.
* @param direction the direction in which to find a neighbor location
* @return the adjacent location in the direction that is closest to
* direction
*/
public Location getAdjacentLocation(int direction);
/**
* Returns the direction from this location toward another location. The
* direction is rounded to the nearest compass direction.
* @param target a location that is different from this location
* @return the closest compass direction from this location toward
* target
*/
public int getDirectionToward(Location target);
/**
* Indicates whether some other Location object is "equal to"
* this one.
* @param other the other location to test
* @return true if other is a
* Location with the same row and column as this location;
* false otherwise
*/
public boolean equals(Object other);
/**
* Generates a hash code.
* @return a hash code for this location
*/
public int hashCode();
/**
* Compares this location to other for ordering. Returns a
* negative integer, zero, or a positive integer as this location is less
* than, equal to, or greater than other. Locations are
* ordered in row-major order.
* (Precondition: other is a Location object.)
* @param other the other location to test
* @return a negative integer if this location is less than
* other, zero if the two locations are equal, or a positive
* integer if this location is greater than other
*/
public int compareTo(Object other);
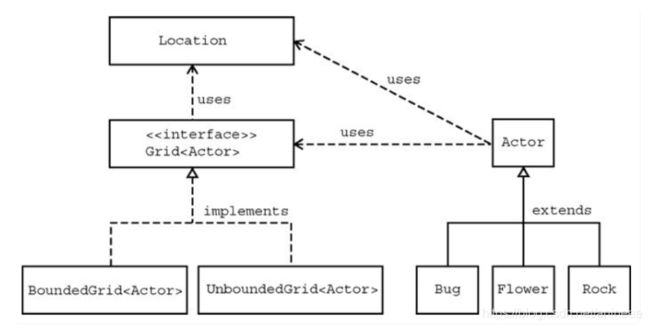
Grid 接口
Grid 接口定义了所有包含对象的 grid 的方法,BoundedGrid 和 UnboundedGrid 实现了这个接口。
Grid 接口的方法有:
/**
* Returns the number of rows in this grid.
* @return the number of rows, or -1 if this grid is unbounded
*/
int getNumRows();
/**
* Returns the number of columns in this grid.
* @return the number of columns, or -1 if this grid is unbounded
*/
int getNumCols();
/**
* Checks whether a location is valid in this grid.
* Precondition: loc is not null
* @param loc the location to check
* @return true if loc is valid in this grid,
* false otherwise
*/
boolean isValid(Location loc);
/**
* Puts an object at a given location in this grid.
* Precondition: (1) loc is valid in this grid (2)
* obj is not null
* @param loc the location at which to put the object
* @param obj the new object to be added
* @return the object previously at loc (or null
* if the location was previously unoccupied)
*/
E put(Location loc, E obj);
/**
* Removes the object at a given location from this grid.
* Precondition: loc is valid in this grid
* @param loc the location of the object that is to be removed
* @return the object that was removed (or null if the location
* is unoccupied)
*/
E remove(Location loc);
/**
* Returns the object at a given location in this grid.
* Precondition: loc is valid in this grid
* @param loc a location in this grid
* @return the object at location loc (or null
* if the location is unoccupied)
*/
E get(Location loc);
/**
* Gets the locations in this grid that contain objects.
* @return an array list of all occupied locations in this grid
*/
ArrayList<Location> getOccupiedLocations();
/**
* Gets the valid locations adjacent to a given location in all eight
* compass directions (north, northeast, east, southeast, south, southwest,
* west, and northwest).
* Precondition: loc is valid in this grid
* @param loc a location in this grid
* @return an array list of the valid locations adjacent to loc
* in this grid
*/
ArrayList<Location> getValidAdjacentLocations(Location loc);
/**
* Gets the valid empty locations adjacent to a given location in all eight
* compass directions (north, northeast, east, southeast, south, southwest,
* west, and northwest).
* Precondition: loc is valid in this grid
* @param loc a location in this grid
* @return an array list of the valid empty locations adjacent to
* loc in this grid
*/
ArrayList<Location> getEmptyAdjacentLocations(Location loc);
/**
* Gets the valid occupied locations adjacent to a given location in all
* eight compass directions (north, northeast, east, southeast, south,
* southwest, west, and northwest).
* Precondition: loc is valid in this grid
* @param loc a location in this grid
* @return an array list of the valid occupied locations adjacent to
* loc in this grid
*/
ArrayList<Location> getOccupiedAdjacentLocations(Location loc);
/**
* Gets the neighboring occupants in all eight compass directions (north,
* northeast, east, southeast, south, southwest, west, and northwest).
*
* Precondition: loc is valid in this grid
* @param loc a location in this grid
* @return returns an array list of the objects in the occupied locations
* adjacent to loc in this grid
*/
ArrayList<E> getNeighbors(Location loc);
Actor 类
Actor 类定义有 Getter 方法取得该 actor 对象的属性。
public Color getColor();
public int getDirection();
public Grid<Actor> getGrid();
public Location getLocation();
Actor 类定义有将对象放入 grid 、将对象从 grid 中移除的方法。
public void putSelfInGrid(Grid<Actor> gr, Location loc);
public void removeSelfFromGrid();
Actor 类定义有 Setter 方法设置该 actor 对象的属性。
public void moveTo(Location loc);
public void setColor(Color newColor);
public void setDirection(int newDirection);
Actor 类定义有 act 方法,决定给对象的行动模式,所有 Actor 的子类都可以通过重载 act 方法定义自己的行为,如 Rock 类、Flower 类和 Bug 类。
public void act();
Jumper 类
实现一个 Actor 的子类 Jumper ,在正常情况下 Jumper 每次移动两个,设计特殊情况下的行为,并通过 Junit 测试。
详见 设计文档、测试文档
Part 4:Interacting Objects
Critter 是有许多相似行为,但是行为的细节有所不同的一些 actor。
Critter 类的方法有:
ArrayList<Actor> getActors();
void processActors(ArrayList<Actor> actors);
ArrayList<Location> getMoveLocations();
Location selectMoveLocation(ArrayList<Location> locs);
void makeMove(Location loc);
Critter 的 act 方法都相同,流程为:
(1) 调用 getActor 获取一个 Actor 的列表;
(2) 调用 processActors 对列表中的 Actor 作操作;
(3) 调用 getMoveLocations 获取可以移动的位置的列表;
(4) 调用 selectMoveLocation 从列表中选择一个可以移动的位置;
(5) 调用 makeMove 移动到下一位置。
扩展 Critter 类
通过重载 Critter 类的 getActor 、processActors 、getMoveLocations、 selectMoveLocation 、makeMove 方法中的一个或多个,实现有特定行为的 Critter。
Part 5:Grid Data Structures
AbstractGrid 类
GridWorld 中提供了 BoundedGrid 和 UnboundedGrid 这两种对 Grid 接口的实现,为了不重复相同的代码,定义一个 AbstractGrid 类实现两种具体 Grid 相同的方法。
AbstractGrid 类实现的方法有:
public ArrayList<E> getNeighbors(Location loc);
public ArrayList<Location> getValidAdjacentLocations(Location loc);
public ArrayList<Location> getEmptyAdjacentLocations(Location loc);
public ArrayList<Location> getOccupiedAdjacentLocations(Location loc);
public String toString();
BoundedGrid 类
有界 Grid 有确定的行数和列数,只能访问界限内的位置。
BoundedGrid 类使用一个二维数组存储各个位置上的对象,若位置空闲,数组元素为 null。
private Object[][] occupantArray;
UnboundedGrid 类
在无界 Grid 中,所有位置都是有效的。
UnboundedGrid 类使用 Map 数据结构存储位置以及位置上的对象,不存储空闲的位置。
private Map<Location, E> occupantMap;
SparseGrid 类
使用不同的数据结构实现对象稀疏的 Grid。
Sparse Array 数据结构
Sparse Array 是一个链表的数组,链表的每个元素存储有一个对象和对象所在的列索引,数组的每个元素存储一个链表,若该行为空,对应链表为 null。
Sparse Array 有两种实现方式:
(1) 可以使用链节点
public class SparseGridNode
{
private Object occupant;
private int col;
private SparseGridNode next;
... ...
}
(2) 可以使用链表和辅助类
public class OccupantInCol
{
private Object occupant;
private int col;
... ...
}
HashMap 和 TreeMap 数据结构
存储 (Location,Actor) 的键值对。
private HashMap<Location,E> occupant = new HashMap<Location,E>();
private TreeMap<Location,E> occupant = new TreeMap<Location,E>();
阶段 3:扩展任务
ImageProcessing
图像的本质就是一个存放着每个像素颜色值信息的矩阵。本实验要求利用本实验软装置,实现一个利用二进制流读取 Bitmap 图像,并且能够进行简单地处理和保存的软件。
Bitmap 文件结构
典型的位图文件格式通常包含下面几个数据块:
- 位图头: 保存位图文件的总体信息。
- 位图信息: 保存位图图像的详细信息。
- 调色板: 保存所用颜色的定义。
- 位图数据: 保存一个又一个像素的实际图像。
ImageReader
实现 IImageIO 接口。
myRead 方法以二进制形式读 Bitmap 图像;myWrite 方法调用 Java API 写 Bitmap 图像。
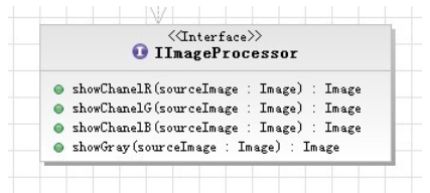
ImageProcessor
实现 IImageProcessor 接口。
showChanelR、showChanelG、showChanelB方法提取图像的颜色通道;showGray 方法将图像转换为灰度图。
MazeBug
学习、理解和应用深度优先搜索算法。本实验要求在改进的Grid World软件装置中实现深度优先搜索算法,从而使虫子走出迷宫。
深度优先搜索算法
基本步骤:
-
先将树的所有节点标记为”未访问”状态。
-
输出起始节点,将起始节点标记为”已访问”状态。
-
将起始节点入栈。
-
当栈非空时重复执行以下步骤:
a. 取当前栈顶节点。
b. 如果当前栈顶节点是结束节点(迷宫出口),输出该节点,结束搜索。
c. 如果当前栈顶节点存在”未访问”状态的邻接节点,则选择一个未访问节点,置为”已访问”状态,并将它入栈,继续步骤a。
d. 如果当前栈顶节点不存在”未访问”状态的邻接节点,则将栈顶节点出栈,继续步骤a。
改进搜索算法
增加方向的概率估计。在行走正确路径时,对四个方向的选择次数进行统计,从而控制随机选择时选择某个方向的概率。增加方向的概率估计后能有效地提高走有方向偏向性的迷宫的效率。
N-Puzzle
重排拼图游戏也叫N-数码问题(N-puzzle,N=MxM-1),以3x3拼图(8-数码问题)为例,在3x3的方格棋盘上,放置8个标有1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8数字的方块和1个空白格,空白格可以上下左右移动。要求通过反复移动空白格,寻找一条从某初始状态到目标状态的移动路径。
盲目搜索策略
使用广度优先算法求解 N-数码问题。
广度优先算法基本步骤:
-
将起始节点放入一个open列表中。
-
如果open列表为空,则搜索失败,问题无解;否则重复以下步骤:
a. 访问open列表中的第一个节点v,若v为目标节点,则搜索成功,退出。
b. 从open列表中删除节点v,放入close列表中。
c. 将所有与v邻接且未曾被访问的节点放入open列表中。
启发式搜索
与盲目搜索不同,启发式搜索(如A*算法)利用问题拥有的启发信息来引导搜索,动态地确定搜索节点的排序,以达到减少搜索范围,降低问题复杂度的目的。
算法基本步骤:
-
将起始节点放入一个列表中。
-
如果列表为空,则搜索失败,问题无解;否则重复以下步骤:
a. 访问列表中的第一个节点v,若v为目标节点,则搜索成功,退出。
b. 从列表中删除节点v。
c. 利用估价函数,对所有与v邻接且未曾被发现的节点进行估价,按照估价大小(小的在前)插入列表中。
重点在于设计合理有效的估价函数,用于估计下一节点到达目的节点的代价。
在实验中,使用了后续节点不正确的数码个数、曼哈顿距离、欧几里得距离三种估价方法,以 1:2:1 的权重加权求和。在解 5x5 的数码问题时,平均需要搜索 5000 个节点。