目标跟踪-------卡尔曼滤波
在MOT中需要利用卡尔曼滤波预测bbox的位置,下面记录一些个人理解
卡尔曼滤波的讲解:
国外大神写的教程:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/39912633
云羽落分享的教学视频:https://www.zhihu.com/question/23971601/answer/839664224
卡尔曼滤波器是一种优化估计算法
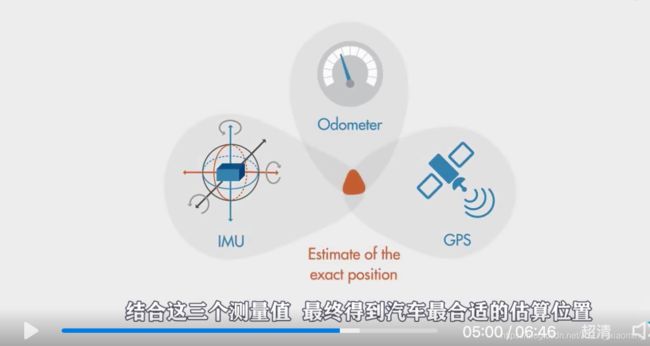
数据源在噪声的影响下,使用卡尔曼滤波估计系统的状态
卡尔曼滤波器可以用于优化估算一些无法直接测量但是可以间接测量的量
还可用于从受误差影响的传感器测量值中估算出系统的状态
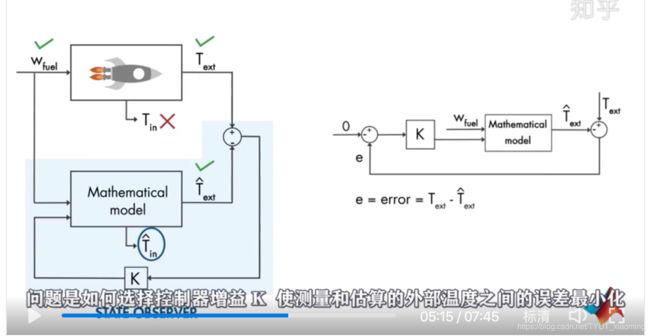
最佳状态估计器
这个过程中存在测量误差Vk 是一个随机变量, 也会存在过程误差Wk(代表风的影响或汽车速度的变化)
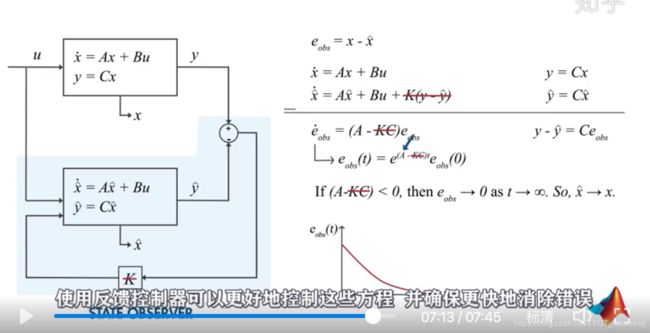
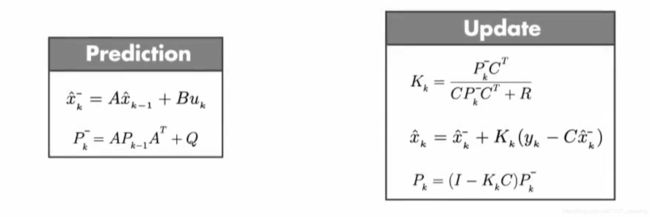
卡尔曼滤波的预测和更新过程
卡尔曼滤波的公式如下所示
卡尔曼滤波的递归循环过程
要估计当前的状态,算法不需要所有过去的信息,只需要上一帧的信息
卡尔曼滤波也叫 多传感器融合算法
协方差:用于描述两个变量的相关性 cov(x,y)
协方差矩阵:是一个对称矩阵 从数值来看,协方差的数值越大,两个变量同向程度也就越大(矩阵中的每个值都是协方差)
deep sort 算法中的卡尔曼滤波
A simple Kalman filter for tracking bounding boxes in image space.
使用8个参数来描述bbox的运动状态 (x, y, a, h, vx, vy, va, vh)
分别代表bbox的中心点坐标,纵横比,以及它们在图像坐标中的速度
物体运动遵循恒定速度模型。 边界框位置(x,y,a,h)被视为状态空间的直接观察(线性观察模型)
1. Kalman filter 类的初始化
1. 创建卡尔曼滤波器模型矩阵
2.相对于当前状态估计值选择运动和观察不确定性。这些权重控制模型中的不确定性量
def __init__(self):
ndim, dt = 4, 1.
# Create Kalman filter model matrices.
self._motion_mat = np.eye(2 * ndim, 2 * ndim)
for i in range(ndim):
self._motion_mat[i, ndim + i] = dt
self._update_mat = np.eye(ndim, 2 * ndim)
# Motion and observation uncertainty are chosen relative to the current
# state estimate. These weights control the amount of uncertainty in
# the model. This is a bit hacky.
self._std_weight_position = 1. / 20
# 可调整参数
self._std_weight_velocity = 1. / 160_motion_mat
2. Create track from unassociated measurement
def _initiate_track(self, detection):
mean, covariance = self.kf.initiate(detection.to_xyah())Kalman filter 对象的 initiate( ) 函数
传入的参数: bbox的xyah坐标
返回值 : mean, covariance
Returns the mean vector (8 dimensional) and covariance matrix (8x8 dimensional) of the new track. 未观察到的速度初始化为0均值
def initiate(self, measurement):
mean_pos = measurement
mean_vel = np.zeros_like(mean_pos)
mean = np.r_[mean_pos, mean_vel]
std = [
2 * self._std_weight_position * measurement[3],
2 * self._std_weight_position * measurement[3],
1e-2,
2 * self._std_weight_position * measurement[3],
10 * self._std_weight_velocity * measurement[3],
10 * self._std_weight_velocity * measurement[3],
1e-5,
10 * self._std_weight_velocity * measurement[3]]
covariance = np.diag(np.square(std))
return mean, covariance
3. Run Kalman filter prediction step
def predict(self):
for track in self.tracks:
track.predict(self.kf)def predict(self, kf):
self.mean, self.covariance = kf.predict(self.mean, self.covariance)
self.age += 1
self.time_since_update += 1
函数predict( )
Parameters:
mean : ndarray The 8 dimensional mean vector of the object state at the previous time step.
covariance : ndarray The 8x8 dimensional covariance matrix of the object state at the previous time step.
Returns:
the mean vector and covariance matrix of the predicted state. Unobserved velocities are initialized to 0 mean.
predict( )
def predict(self, mean, covariance):
std_pos = [
self._std_weight_position * mean[3],
self._std_weight_position * mean[3],
1e-2,
self._std_weight_position * mean[3]]
std_vel = [
self._std_weight_velocity * mean[3],
self._std_weight_velocity * mean[3],
1e-5,
self._std_weight_velocity * mean[3]]
motion_cov = np.diag(np.square(np.r_[std_pos, std_vel]))
mean = np.dot(self._motion_mat, mean)
covariance = np.linalg.multi_dot((
self._motion_mat, covariance, self._motion_mat.T)) + motion_cov
return mean, covariance
4. Run Kalman filter correction step. (校正步骤)
def update(self, detections):
"""Perform measurement update and track management.
Parameters
----------
detections : List[deep_sort.detection.Detection]
A list of detections at the current time step.
"""
# Run matching cascade.
matches, unmatched_tracks, unmatched_detections = \
self._match(detections)
# Update track set.
for track_idx, detection_idx in matches:
self.tracks[track_idx].update(
self.kf, detections[detection_idx])
.......def update(self, kf, detection):
"""Perform Kalman filter measurement update step and update the feature
cache.
Parameters
----------
kf : kalman_filter.KalmanFilter
The Kalman filter.
detection : Detection
The associated detection.
"""
self.mean, self.covariance = kf.update(
self.mean, self.covariance, detection.to_xyah())
self.features.append(detection.feature)
self.hit_streak += 1
self.hits += 1
self.time_since_update = 0
if self.state == TrackState.Tentative and self.hits >= self._n_init:
self.state = TrackState.Confirmedkf.update( )函数
Parameters:
mean : ndarray The predicted state's mean vector (8 dimensional).covariance : ndarray The state's covariance matrix (8x8 dimensional).
measurement : ndarray The 4 dimensional measurement vector (x, y, a, h)
Returns (ndarray, ndarray)
Returns the measurement-corrected state distribution 返回测量校正的状态分布
def update(self, mean, covariance, measurement):
projected_mean, projected_cov = self.project(mean, covariance)
chol_factor, lower = scipy.linalg.cho_factor(
projected_cov, lower=True, check_finite=False)
kalman_gain = scipy.linalg.cho_solve(
(chol_factor, lower), np.dot(covariance, self._update_mat.T).T,
check_finite=False).T
innovation = measurement - projected_mean
new_mean = mean + np.dot(innovation, kalman_gain.T)
new_covariance = covariance - np.linalg.multi_dot((
kalman_gain, projected_cov, kalman_gain.T))
return new_mean, new_covariance