激光雷达障碍物检测与追踪实战——基于欧几里德聚类的激光雷达障碍物检测
文章目录
- 欧几里德聚类
- 分割点云
- bounding box
- 实验效果
激光雷达是实现无人驾驶环境感知的重要传感器,激光雷达以其稳定可靠、精度高并且能同时应用于定位和环境感知而被广泛采用
激光雷达传统的障碍物检测与跟踪的流程:
- 提取感兴趣ROI区域
- 滤波:一般采用体素滤波(体素滤波即将空间按照一定尺寸的立方体格进行划分,每个立方格内仅保留一个点),降低点云密度,减少后续计算量
- 地面分割:常见的方法RANSAC,地面平面拟合(Ground Plane Fitting),linefit_ground_segmentation等。
- 点云聚类:采用欧几里得聚类,设置不同半径阈值进行聚类获取获得目标轮廓的点云簇,由于采用不同半径阈值聚类,可能会把一个物体分割成多个,需要对不同的点云簇进行merge。
- 在完成聚类后,可得到障碍物的轮廓,接下来计算bounding box,采用凸多边形拟合,根据凸多边形的顶点计算斜矩形,得到bounding box的中心,优化bounding box的长宽高和中心和朝向。
- 目标追踪:对检测出的障碍物进行追踪,最经典采用卡尔曼滤波方法,如EKF。另一种跟踪算法就是基于cnn-kcf系列,利用online kernal learning可以与检测的网络做到一起。
现今,点云上的深度学习变得越来越流行,涌现许多基于深度神经网络的点云端到端检测算法,该方法依赖密集点云,通常采用高线的激光雷达,对于低速,简单场景下,低线激光雷达采用聚类方法也可以取得较好的障碍物感知效果。
欧几里德聚类
欧式聚类是一种基于欧氏距离度量的聚类算法。采用基于KD-Tree的近邻查询算法是加速欧式聚类。
KD-Tree最近邻搜索
KD-Tree是对数据点在k维空间中划分的一种数据结构;KD-Tree是一种平衡二叉树
KD-Tree采用分而治之的思想,即将整个空间划分为几个小部分。KD-Tree算法的应用可以分为两方面,一方面是有关KD-Tree树建立的算法,另一方面是在KD-Tree树基础上进行最邻近查找。
KD-Tree是每个节点均为k维数值点的二叉树,其上的每个节点代表一个超平面,该超平面垂直于当前划分维度的坐标轴,并在该维度上将空间划分为两部分,一部分在其左子树,另一部分在其右子树。即若当前节点的划分维度为d,其左子树上所有点在d维的坐标值均小于当前值,右子树上所有点在d维的坐标值均大于等于当前值,递归处理其子树,直至所有数据点挂载完毕。
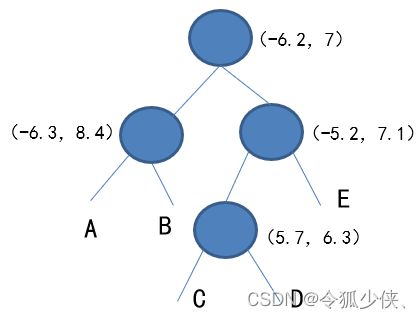
下面以二维空间为例:
- KD-Tree树构建:在KD-Tree中插入点
首先我们得确定一个根点(-6.2, 7), 第0层为x轴, 需要插入的点为(-6.3, 8.4), (-5.2, 7.1), 因为-6.3<-6.2,(-6.3, 8.4)划分为左子节点, 而-5.2>-6.2, (-5.2, 7.1)划分为右子节点. (-5.7, 6.3)中x轴-5.7>-6.2,所以放在(-5.2, 7.1)节点下, 接下来第1层使用y轴, 6.3<7.1, 因此放在(-5.2, 7.1)的左子节点. 同理, 如果我们想插入第五个点(7.2, 6.1), 你可以交替对比x,y轴数值, (7.2>-6.2)->(6.1<7.1)->(7.2>-5.7), 第五点应插入到(-5.7, 6.3)的右子节点C
分割点云
为了达到更好的聚类效果,我们在不同距离的区域使用不同的聚类半径阈值
- 首先将扫描的点云按距离划分为5块,对每块分别采用一个线程聚类,提高聚类速度
void EuclideanCluster::segmentByDistance(const pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr in,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr &outCloudPtr, std::vector<pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr> &points_vector)
{
// cluster the pointcloud according to the distance of the points using different thresholds (not only one for the entire pc)
// in this way, the points farther in the pc will also be clustered
std::vector<pcl::PointIndices> clusterIndices;
if (!use_multiple_thres_)
{
cluster_vector(in, clusterIndices);
for (auto it = clusterIndices.begin(); it != clusterIndices.end(); ++it)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr temp_cluster(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>);
pcl::copyPointCloud(*in, it->indices, *temp_cluster);
*outCloudPtr += *temp_cluster;
points_vector.push_back(temp_cluster);
}
}
else
{
std::vector<pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr> cloud_segments_array(7);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < cloud_segments_array.size(); i++)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr tmp_cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>);
cloud_segments_array[i] = tmp_cloud;
}
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < in->points.size(); i++)
{
pcl::PointXYZI current_point;
current_point.x = in->points[i].x;
current_point.y = in->points[i].y;
current_point.z = in->points[i].z;
current_point.intensity = in->points[i].intensity;
float origin_distance = sqrt(pow(current_point.x, 2) + pow(current_point.y, 2));
if (origin_distance < clustering_ranges_[0])
{
cloud_segments_array[0]->points.push_back(current_point);
}
else if (origin_distance < clustering_ranges_[1])
{
cloud_segments_array[1]->points.push_back(current_point);
}
else if (origin_distance < clustering_ranges_[2])
{
cloud_segments_array[2]->points.push_back(current_point);
}
else if (origin_distance < clustering_ranges_[3])
{
cloud_segments_array[3]->points.push_back(current_point);
}
else
{
cloud_segments_array[4]->points.push_back(current_point);
}
}
std::vector<std::thread> thread_vec(cloud_segments_array.size());
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < cloud_segments_array.size(); i++)
{
std::promise<std::vector<pcl::PointIndices>> promiseObj;
std::shared_future<std::vector<pcl::PointIndices>> futureObj = promiseObj.get_future();
thread_vec[i] = std::thread(&EuclideanCluster::clusterIndicesMultiThread, this, cloud_segments_array[i], std::ref(clustering_distances_[i]), std::ref(promiseObj));
clusterIndices = futureObj.get();
for (int j = 0; j < clusterIndices.size(); j++)
{
//每次聚类得出的indices为输入点云对应的索引
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr temp_cluster(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>);
pcl::copyPointCloud(*cloud_segments_array[i], clusterIndices[j], *temp_cluster);
*outCloudPtr += *temp_cluster;
points_vector.push_back(temp_cluster);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < thread_vec.size(); i++)
{
thread_vec[i].join();
}
}
}
bounding box
-
聚类并计算障碍物中心,和Bounding Box
五个点云分别使用不同的半径阈值进行欧几里德聚类,对聚类完以后的一个个点云簇,我们计算其形心作为该障碍物的中心,同时计算点云簇的长宽高,从而确定一个能够将点云簇包裹的三维Bounding Box -
凸多边形拟合,优化bounding box的中心和长宽
-
计算bounding box朝向
采用拟合出的凸多边型的顶点计算点云轮廓最小外界矩形,是一个Box2D结构,包含最小外接矩形的中心、宽高、旋转角度(水平轴(x轴)逆时针旋转,与碰到的矩形的第一条边的夹角)
void BoundingBox::SetCloud(std_msgs::Header header, const pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr in, bool in_estimate_pose)
{
// extract pointcloud using the indices
// calculate min and max points
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr currentCluster(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>);
float min_x = std::numeric_limits<float>::max();
float max_x = -std::numeric_limits<float>::max();
float min_y = std::numeric_limits<float>::max();
float max_y = -std::numeric_limits<float>::max();
float min_z = std::numeric_limits<float>::max();
float max_z = -std::numeric_limits<float>::max();
float average_x = 0, average_y = 0, average_z = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < in->points.size(); i++)
{
// fill new colored cluster point by point
pcl::PointXYZRGB p;
p.x = in->points[i].x;
p.y = in->points[i].y;
p.z = in->points[i].z;
average_x += p.x;
average_y += p.y;
average_z += p.z;
centroid_.x += p.x;
centroid_.y += p.y;
centroid_.z += p.z;
currentCluster->points.push_back(p);
if (p.x < min_x)
min_x = p.x;
if (p.y < min_y)
min_y = p.y;
if (p.z < min_z)
min_z = p.z;
if (p.x > max_x)
max_x = p.x;
if (p.y > max_y)
max_y = p.y;
if (p.z > max_z)
max_z = p.z;
}
// min, max points
minPoint_.x = min_x;
minPoint_.y = min_y;
minPoint_.z = min_z;
maxPoint_.x = max_x;
maxPoint_.y = max_y;
maxPoint_.z = max_z;
// calculate centroid, average
if (in->points.size() > 0)
{
centroid_.x /= in->points.size();
centroid_.y /= in->points.size();
centroid_.z /= in->points.size();
average_x /= in->points.size();
average_y /= in->points.size();
average_z /= in->points.size();
}
averagePoint_.x = average_x;
averagePoint_.y = average_y;
averagePoint_.z = average_z;
// calculate bounding box
float length_ = maxPoint_.x - minPoint_.x;
float width_ = maxPoint_.y - minPoint_.y;
float height_ = maxPoint_.z - minPoint_.z;
boundingBox_.header = header;
boundingBox_.pose.position.x = minPoint_.x + length_ / 2;
boundingBox_.pose.position.y = minPoint_.y + width_ / 2;
boundingBox_.pose.position.z = minPoint_.z + height_ / 2;
boundingBox_.dimensions.x = ((length_ < 0) ? -1 * length_ : length_);
boundingBox_.dimensions.y = ((width_ < 0) ? -1 * width_ : width_);
boundingBox_.dimensions.z = ((height_ < 0) ? -1 * height_ : height_);
// pose estimation
double rz = 0;
std::vector<cv::Point2f> points;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < currentCluster->points.size(); i++)
{
cv::Point2f pt;
pt.x = currentCluster->points[i].x;
pt.y = currentCluster->points[i].y;
points.push_back(pt);
}
std::vector<cv::Point2f> hull;
cv::convexHull(points, hull);
polygon_.header = header;
for (size_t i = 0; i < hull.size() + 1; i++)
{
geometry_msgs::Point32 point;
point.x = hull[i % hull.size()].x;
point.y = hull[i % hull.size()].y;
point.z = minPoint_.z;
polygon_.polygon.points.push_back(point);
}
if (in_estimate_pose)
{
cv::RotatedRect box = minAreaRect(hull);
rz = box.angle * 3.14 / 180;
boundingBox_.pose.position.x = box.center.x;
boundingBox_.pose.position.y = box.center.y;
boundingBox_.dimensions.x = box.size.width;
boundingBox_.dimensions.y = box.size.height;
}
// set bounding box direction
tf::Quaternion quat = tf::createQuaternionFromRPY(0.0, 0.0, rz);
/** \brief convert Quaternion to Quaternion msg*/
tf::quaternionTFToMsg(quat, boundingBox_.pose.orientation);
currentCluster->width = currentCluster->points.size();
currentCluster->height = 1;
currentCluster->is_dense = true;
// Get EigenValues, eigenvectors
if (currentCluster->points.size() > 3)
{
pcl::PCA<pcl::PointXYZ> currentClusterPca;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr current_cluster_mono(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::copyPointCloud(*currentCluster, *current_cluster_mono);
currentClusterPca.setInputCloud(current_cluster_mono);
eigenVectors_ = currentClusterPca.getEigenVectors();
eigenValues_ = currentClusterPca.getEigenValues();
}
validCluster_ = true;
pointCloud_ = currentCluster;
}
4.对可能的bounding_box进行合并
void BoundingBox::getBoundingBox(std_msgs::Header header,
std::vector<pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr> &points_vector,
autoware_msgs::CloudClusterArray &inOutClusters)
{
std::vector<BoundingBoxPtr> Clusters;
for (int i = 0; i < points_vector.size(); i++)
{
// pcl::PointCloud::Ptr temp_cluster(new pcl::PointCloud);
// pcl::copyPointCloud(*in, it->indices, *temp_cluster);
// *outCloudPtr += *temp_cluster;
BoundingBoxPtr cluster(new BoundingBox());
cluster->SetCloud(header, points_vector[i], inEstimatePose_);
Clusters.push_back(cluster);
}
// Clusters can be merged or checked in here
// check for mergable clusters
std::vector<BoundingBoxPtr> midClusters;
std::vector<BoundingBoxPtr> finalClusters;
if (Clusters.size() > 0)
checkAllForMerge(header, Clusters, midClusters, clusterMergeThreshold_, inEstimatePose_);
else
midClusters = Clusters;
if (midClusters.size() > 0)
checkAllForMerge(header, midClusters, finalClusters, clusterMergeThreshold_, inEstimatePose_);
else
finalClusters = midClusters;
// Get final PointCloud to be published
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < Clusters.size(); i++)
{
if (Clusters[i]->validCluster_)
{
autoware_msgs::CloudCluster cloudCluster;
Clusters[i]->ToROSMessage(header, cloudCluster);
inOutClusters.clusters.push_back(cloudCluster);
}
}
inOutClusters.header = header;
}
实验效果
我这里采用了基于同心区域的区域地面分割和地面似然估计方法,地面过滤效果比我上面列举的RANSAC,地面平面拟合(Ground Plane Fitting),linefit_ground_segmentation效果都要好
1.安装相应的 ros 依赖包
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-jsk-rviz-plugins
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-jsk-recognition-msgs
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-autoware-msgs
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-visualization-msgs
2.启动
rosbag play -l kitti_2011_09_30_drive_0016_synced.bag /kitti/velo/pointcloud:=/velodyne_points
roslaunch lidar_obstacle_detection lidar_obstacle_detection.launch
launch有两个节点,运行launch直接会打开rviz可视化
<launch>
<node pkg="lidar_obstacle_detection" type="lidar_obstacle_detection_node" name="lidar_obstacle_detection_node" output="screen" />
<rosparam file="$(find lidar_obstacle_detection)/config/lidar_obstacle_detection.yaml" command="load" />
<!-- Start lidar_obstacle_detection.rviz -->
<node pkg="rviz" type="rviz" name="rviz" output = "screen" args="-d $(find lidar_obstacle_detection)/rviz/lidar_obstacle_detection.rviz" required="true" />
</launch>
用kitti数据集,效果如下,大家可以自行根改config下的launch文件里的参数进行调试

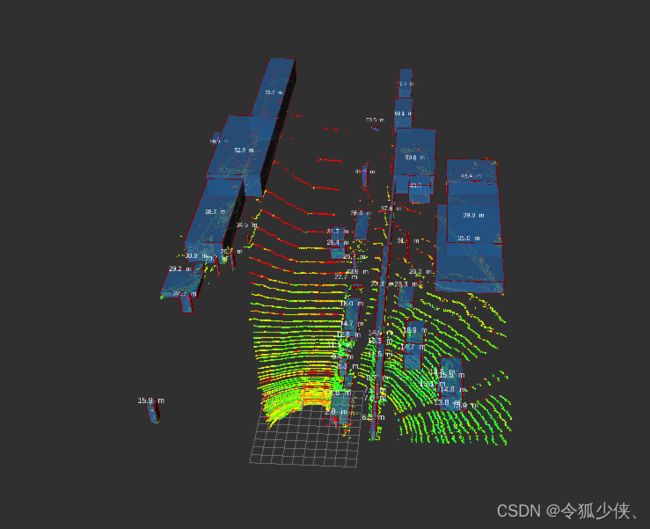
可视化MarkerArray输出包括5个信息:
- label:显示距离信息
- hull:凸多边形拟合,绿色线
- cube:蓝色的实心box
- box:红色线条围成的box
- centroid:bounding_box中心
上图为bounding_box未加方向,加方向后,效果不太好,对于道路两边的区域的姿态估计显然会不准确,可以将isEstimatePose字段设置为true,观测添加姿态估计后的效果
这是我业余写的一个粗版demo,有地方是可以改进的,比如多线程获取返回值速度不快,大家自行修改吧
..