如何在keras版本的YOLOv3上训练自己的数据集?
0. 项目背景
论文地址:
You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection
作者:Joseph Redmon, Santosh Divvala, Ross Girshick, Ali Farhadi.
C和CUDA原始实现:Darknet
1. 项目指引
这里以keras版本的YOLOv3版本为例,首先找到相应的github仓库,以下提供两个比较靠谱的链接:
1.1 https://github.com/qqwweee/keras-yolo3
1.2 https://github.com/experiencor/keras-yolo3
2. 项目准备
这里以qqwweee大神的仓库为例进行讲解
2.1 环境搭配
我搭配的环境为:
Ubuntu18.04+Cuda10.1+Cudnn7.6+Tensorflow1.14.0+Keras2.1.5
查看Cuda版本指令:
cat /usr/local/cuda/version.txt
查看Cudnn版本指令:
cat /usr/local/cuda/include/cudnn.h | grep CUDNN_MAJOR -A 2
2.2 标注及整理数据
Ubuntu的LableImg直接参考这里。
2.2.1 下载标注工具(Wins版本)LabelImg
提取码:wo8e
2.2.2 对数据进行标注
1- 打开labelImg.exe,选择图片所在的目录;
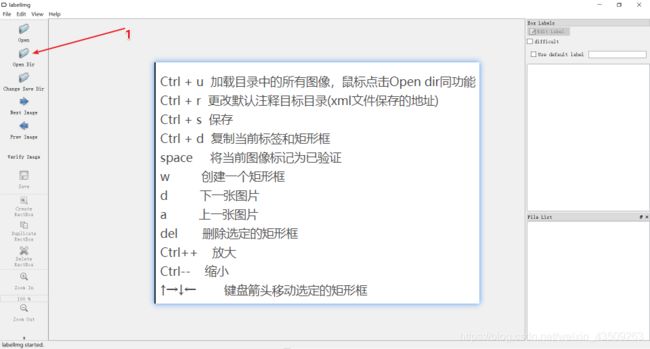
2- 每标注完一张图片就保存一次
2.2.3 对数据进行分类
1- 创建一个如下的文件夹目录结构,根目录为VOC2007,该文件下放置三个子文件夹[Annotations, ImageSets, JPEGImages],在ImageSets文件夹下新建一个Main文件夹,总体目录结构图如下:

2- 将所有的图片放置到JPEGImages文件下;
3- 将所有的xml文件放置到Annotations文件夹下;
4- 将以下的脚本文件放置到VOC2007目录下并运行,生成相应的序号文件:
import os
import random
trainval_percent = 0.1
train_percent = 0.9
xmlfilepath = 'Annotations'
txtsavepath = 'ImageSets\Main'
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
ftrainval = open('ImageSets/Main/trainval.txt', 'w')
ftest = open('ImageSets/Main/test.txt', 'w')
ftrain = open('ImageSets/Main/train.txt', 'w')
fval = open('ImageSets/Main/val.txt', 'w')
for i in list:
name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'
if i in trainval:
ftrainval.write(name)
if i in train:
ftest.write(name)
else:
fval.write(name)
else:
ftrain.write(name)
ftrainval.close()
ftrain.close()
fval.close()
ftest.close()
2.2.4 数据清洗
1- 过滤掉图片像素值太小的图片(默认是低于416的,可自行修改参数):
import os
import random
from PIL import Image
import shutil
#获取文件夹中的文件路径
def getFilePathList(dirPath, partOfFileName=''):
allFileName_list = list(os.walk(dirPath))[0][2]
fileName_list = [k for k in allFileName_list if partOfFileName in k]
filePath_list = [os.path.join(dirPath, k) for k in fileName_list]
return filePath_list
#获取一部分像素足够,即长,宽都大于416的图片
def generate_qualified_images(dirPath, sample_number, new_dirPath):
jpgFilePath_list = getFilePathList(dirPath, '.JPEG') # ====》可修改
random.shuffle(jpgFilePath_list)
if not os.path.isdir(new_dirPath):
os.makedirs(new_dirPath)
i = 0
for jpgFilePath in jpgFilePath_list:
image = Image.open(jpgFilePath)
width, height = image.size
if width >= 416 and height >= 416: # ====》可修改
i += 1
new_jpgFilePath = os.path.join(new_dirPath, '%03d.jpg' %i)
shutil.copy(jpgFilePath, new_jpgFilePath)
if i == sample_number:
break
#获取数量为1000的合格样本存放到selected_images文件夹中
# 图片路径,所需图片数量,筛选后所存放的路径
generate_qualified_images('.', 1000, 'train_images') # ====》可修改
2- 检查标记好的文件夹是否有图片漏标记的以及xml文件中是否有物体标记类别拼写错误的:
#获取文件夹中的文件路径
import os
def getFilePathList(dirPath, partOfFileName=''):
allFileName_list = list(os.walk(dirPath))[0][2]
fileName_list = [k for k in allFileName_list if partOfFileName in k]
filePath_list = [os.path.join(dirPath, k) for k in fileName_list]
return filePath_list
#此段代码检查标记好的文件夹是否有图片漏标
def check_1(dirPath):
jpgFilePath_list = getFilePathList(dirPath, '.jpg')
allFileMarked = True
for jpgFilePath in jpgFilePath_list:
xmlFilePath = jpgFilePath[:-4] + '.xml'
if not os.path.exists(xmlFilePath):
print('%s this picture is not marked.' %jpgFilePath)
allFileMarked = False
if allFileMarked:
print('congratulation! it is been verified that all jpg file are marked.')
#此段代码检查标记的xml文件中是否有物体标记类别拼写错误
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
def check_2(dirPath, className_list):
className_set = set(className_list)
xmlFilePath_list = getFilePathList(dirPath, '.xml')
allFileCorrect = True
for xmlFilePath in xmlFilePath_list:
with open(xmlFilePath) as file:
fileContent = file.read()
root = ET.XML(fileContent)
object_list = root.findall('object')
for object_item in object_list:
name = object_item.find('name')
className = name.text
if className not in className_set:
print('%s this xml file has wrong class name "%s" ' %(xmlFilePath, className))
allFileCorrect = False
if allFileCorrect:
print('congratulation! it is been verified that all xml file are correct.')
if __name__ == '__main__':
dirPath = 'train_image' # ====》可修改
className_list = ['class1', 'class2'] # ====》可修改
check_1(dirPath)
check_2(dirPath, className_list)
2.3 下载github仓库及修改相应参数
1- 使用git clone指令将keras-yolo3下载到本地上;
2- 将步骤2.2.3中生成的VOC2007整个文件夹放置到keras-yolo3目录下

3- 打开voc_annotation.py文件修改并运行
(1)第6行左右的classes里面的类别替换成你自己的类别;
(2)第10行in_file里面的路径稍微改下,如下所示:
in_file = open('VOC%s/Annotations/%s.xml' % (year, image_id))
(3)第27行改为:
image_ids = open('VOC%s/ImageSets/Main/%s.txt' % (year, image_set)).read().strip().split()
(4)第28行改为:
list_file = open('%s.txt' % image_set, 'w')
(5)第30行改为(这里默认你的图片都是jpg格式,可做相应更改):
list_file.write('%s/VOC%s/JPEGImages/%s.jpg' % (wd, year, image_id))
(6)运行这个脚本,在根目录下会自动生成3个txt文件 [train.txt, val.txt, test.txt]
4- 打开kmeans.py文件修改并运行
(1)第8行改为:
self.filename = filename
(2)第61行改为:
f = open("./model_data/yolo_anchors.txt", 'w')
(3)第99行改为:
filename = "train.txt"
注意:聚类基于原始图片,大小会在特征图上做变换.
5- 进入到keras-yolo3/model_data目录下的voc_classes.txt文件,定义为你自己的类别;
6- 在keras-yolo3目录下新建一个文件:logs,并再其子目录下新建一个子目录:000,用于存放相应的模型文件,这里后期可以自定义,只需要修改train.py这个脚本文件即可;
3. 项目开始
3.1 训练数据
0- [options] 如果你自己所需要训练的目标不包含在coco训练过的80个类别里,那么这里不建议预训练权重,即这一步可直接忽略掉跳到 1- 开始;
(1)下载权重文件:百度云,提取码:l2yr
将权重文件放置到根目录keras-yolo3下;
(2)打开yolov3.cfg,按Ctrl+f搜索关键词yolo,总共需要搜索3下,每一遍改动下面这三个参数:

filters定义为:3 * (5 + len(classes)),其中classes为你自己数据集的类别数;
classes:类别数;
random=1表示多尺寸训练,random=0表示常规训练;
(3)在根目录下运行以下指令:
python convert.py -w yolov3.cfg yolov3.weights model_data/yolo_weights.h5
1- 打开train.py文件,将整个文件的内容替换为以下内容:
"""
Retrain the YOLO model for your own dataset.
"""
import numpy as np
import keras.backend as K
from keras.layers import Input, Lambda
from keras.models import Model
from keras.callbacks import TensorBoard, ModelCheckpoint, EarlyStopping
from yolo3.model import preprocess_true_boxes, yolo_body, tiny_yolo_body, yolo_loss
from yolo3.utils import get_random_data
def _main():
annotation_path = 'train.txt'
log_dir = 'logs/000/' # 这里可自由替换
classes_path = 'model_data/voc_classes.txt'
anchors_path = 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt'
class_names = get_classes(classes_path)
anchors = get_anchors(anchors_path)
input_shape = (416, 416) # multiple of 32, hw
model = create_model(input_shape, anchors, len(class_names))
train(model, annotation_path, input_shape, anchors, len(class_names), log_dir=log_dir)
def train(model, annotation_path, input_shape, anchors, num_classes, log_dir='logs/'):
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss={'yolo_loss': lambda y_true, y_pred: y_pred})
logging = TensorBoard(log_dir=log_dir)
checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(log_dir + "ep{epoch:03d}-loss{loss:.3f}-val_loss{val_loss:.3f}.h5",
monitor='val_loss', save_weights_only=True, save_best_only=True, period=1)
batch_size = 8 # 显存允许的话可适当加大
val_split = 0.1 # 数据量大的可设置为0.2
with open(annotation_path) as f:
lines = f.readlines()
np.random.shuffle(lines)
num_val = int(len(lines)*val_split)
num_train = len(lines) - num_val
print('Train on {} samples, val on {} samples, with batch size {}.'.format(num_train, num_val, batch_size))
# 训练精度不太行的可适当增大epochs个数
model.fit_generator(data_generator_wrap(lines[:num_train], batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes),
steps_per_epoch=max(1, num_train//batch_size),
validation_data=data_generator_wrap(lines[num_train:], batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes),
validation_steps=max(1, num_val//batch_size),
epochs=500,
initial_epoch=0)
model.save_weights(log_dir + 'trained_weights.h5')
def get_classes(classes_path):
with open(classes_path) as f:
class_names = f.readlines()
class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names]
return class_names
def get_anchors(anchors_path):
with open(anchors_path) as f:
anchors = f.readline()
anchors = [float(x) for x in anchors.split(',')]
return np.array(anchors).reshape(-1, 2)
def create_model(input_shape, anchors, num_classes, load_pretrained=False, freeze_body=False,
weights_path='model_data/yolo_weights.h5'):
K.clear_session() # get a new session
image_input = Input(shape=(None, None, 3))
h, w = input_shape
num_anchors = len(anchors)
y_true = [Input(shape=(h//{0: 32, 1: 16, 2: 8}[l], w//{0: 32, 1: 16, 2: 8}[l],
num_anchors//3, num_classes+5)) for l in range(3)]
model_body = yolo_body(image_input, num_anchors//3, num_classes)
print('Create YOLOv3 model with {} anchors and {} classes.'.format(num_anchors, num_classes))
if load_pretrained:
model_body.load_weights(weights_path, by_name=True, skip_mismatch=True)
print('Load weights {}.'.format(weights_path))
if freeze_body:
# Do not freeze 3 output layers.
num = len(model_body.layers)-7
for i in range(num): model_body.layers[i].trainable = False
print('Freeze the first {} layers of total {} layers.'.format(num, len(model_body.layers)))
model_loss = Lambda(yolo_loss, output_shape=(1,), name='yolo_loss',
arguments={'anchors': anchors, 'num_classes': num_classes, 'ignore_thresh': 0.5})(
[*model_body.output, *y_true])
model = Model([model_body.input, *y_true], model_loss)
return model
def data_generator(annotation_lines, batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes):
n = len(annotation_lines)
np.random.shuffle(annotation_lines)
i = 0
while True:
image_data = []
box_data = []
for b in range(batch_size):
i %= n
image, box = get_random_data(annotation_lines[i], input_shape, random=True)
image_data.append(image)
box_data.append(box)
i += 1
image_data = np.array(image_data)
box_data = np.array(box_data)
y_true = preprocess_true_boxes(box_data, input_shape, anchors, num_classes)
yield [image_data, *y_true], np.zeros(batch_size)
def data_generator_wrap(annotation_lines, batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes):
n = len(annotation_lines)
if n == 0 or batch_size <= 0: return None
return data_generator(annotation_lines, batch_size, input_shape, anchors, num_classes)
if __name__ == '__main__':
_main()
2- 如果显存过大过小可适当调节batch_size大小,设置好之后可直接运行train.py文件进行训练,keras版本的yolov3作者在复现的时候加入了l2正则化,所以loss如果能收敛到10左右效果就算还ok,这个可以作为一个基准去衡量;
3- 如果要在之前训练基础上,追加训练,一般要把batch_size设置小一些,然后加载之前的权重;
3.2 测试数据
3.2.1 单张图片测试
1- 打开yolo.py文件,修改给定的参数:
在YOLO类里面修改_defults字典里的几个参数,根据实际情况自行调节;(model_path就是你最终要用来预测的模型,gpu_num代表是否加载多GPU进行测试,score和iou设置太低会造成很多框出来)
2- 运行测试文档:
直接运行 python yolo_detect.py --image即可对单张图片进行测试;
3.2.2 批量图片测试
1- 在根目录下新建一个yolo_test.py文件:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
功能:keras-yolov3 进行批量测试并保存结果
项目来源:https://github.com/qqwweee/keras-yolo3
"""
import colorsys
import os
from timeit import default_timer as timer
import time
import numpy as np
from keras import backend as K
from keras.models import load_model
from keras.layers import Input
from PIL import Image, ImageFont, ImageDraw
from yolo3.model import yolo_eval, yolo_body, tiny_yolo_body
from yolo3.utils import letterbox_image
from keras.utils import multi_gpu_model
path = './test/' # 待检测图片的位置
# 创建创建一个存储检测结果的dir
result_path = './result'
if not os.path.exists(result_path):
os.makedirs(result_path)
# result如果之前存放的有文件,全部清除
for i in os.listdir(result_path):
path_file = os.path.join(result_path, i)
if os.path.isfile(path_file):
os.remove(path_file)
# 创建一个记录检测结果的文件
txt_path = result_path + '/result.txt'
file = open(txt_path, 'w')
class YOLO(object):
_defaults = {
"model_path": './logs/001/ep1478-loss5.401-val_loss4.683.h5',
"anchors_path": 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt',
"classes_path": 'model_data/coco_classes.txt',
"score": 0.9,
"iou": 0.1,
"model_image_size": (416, 416),
"gpu_num": 1,
}
@classmethod
def get_defaults(cls, n):
if n in cls._defaults:
return cls._defaults[n]
else:
return "Unrecognized attribute name '" + n + "'"
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.__dict__.update(self._defaults) # set up default values
self.__dict__.update(kwargs) # and update with user overrides
self.class_names = self._get_class()
self.anchors = self._get_anchors()
self.sess = K.get_session()
self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes = self.generate()
def _get_class(self):
classes_path = os.path.expanduser(self.classes_path)
with open(classes_path) as f:
class_names = f.readlines()
class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names]
return class_names
def _get_anchors(self):
anchors_path = os.path.expanduser(self.anchors_path)
with open(anchors_path) as f:
anchors = f.readline()
anchors = [float(x) for x in anchors.split(',')]
return np.array(anchors).reshape(-1, 2)
def generate(self):
model_path = os.path.expanduser(self.model_path)
assert model_path.endswith('.h5'), 'Keras model or weights must be a .h5 file.'
# Load model, or construct model and load weights.
num_anchors = len(self.anchors)
num_classes = len(self.class_names)
is_tiny_version = num_anchors == 6 # default setting
try:
self.yolo_model = load_model(model_path, compile=False)
except:
self.yolo_model = tiny_yolo_body(Input(shape=(None, None, 3)), num_anchors // 2, num_classes) \
if is_tiny_version else yolo_body(Input(shape=(None, None, 3)), num_anchors // 3, num_classes)
self.yolo_model.load_weights(self.model_path) # make sure model, anchors and classes match
else:
assert self.yolo_model.layers[-1].output_shape[-1] == \
num_anchors / len(self.yolo_model.output) * (num_classes + 5), \
'Mismatch between model and given anchor and class sizes'
print('{} model, anchors, and classes loaded.'.format(model_path))
# Generate colors for drawing bounding boxes.
hsv_tuples = [(x / len(self.class_names), 1., 1.)
for x in range(len(self.class_names))]
self.colors = list(map(lambda x: colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(*x), hsv_tuples))
self.colors = list(
map(lambda x: (int(x[0] * 255), int(x[1] * 255), int(x[2] * 255)),
self.colors))
np.random.seed(10101) # Fixed seed for consistent colors across runs.
np.random.shuffle(self.colors) # Shuffle colors to decorrelate adjacent classes.
np.random.seed(None) # Reset seed to default.
# Generate output tensor targets for filtered bounding boxes.
self.input_image_shape = K.placeholder(shape=(2,))
if self.gpu_num >= 2:
self.yolo_model = multi_gpu_model(self.yolo_model, gpus=self.gpu_num)
boxes, scores, classes = yolo_eval(self.yolo_model.output, self.anchors,
len(self.class_names), self.input_image_shape,
score_threshold=self.score, iou_threshold=self.iou)
return boxes, scores, classes
def detect_image(self, image):
start = timer() # 开始计时
if self.model_image_size != (None, None):
assert self.model_image_size[0] % 32 == 0, 'Multiples of 32 required'
assert self.model_image_size[1] % 32 == 0, 'Multiples of 32 required'
boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, tuple(reversed(self.model_image_size)))
else:
new_image_size = (image.width - (image.width % 32),
image.height - (image.height % 32))
boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, new_image_size)
image_data = np.array(boxed_image, dtype='float32')
print(image_data.shape) # 打印图片的尺寸
image_data /= 255.
image_data = np.expand_dims(image_data, 0) # Add batch dimension.
out_boxes, out_scores, out_classes = self.sess.run(
[self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes],
feed_dict={
self.yolo_model.input: image_data,
self.input_image_shape: [image.size[1], image.size[0]],
K.learning_phase(): 0
})
print('Found {} boxes for {}'.format(len(out_boxes), 'img')) # 提示用于找到几个bbox
font = ImageFont.truetype(font='font/FiraMono-Medium.otf',
size=np.floor(2e-2 * image.size[1] + 0.2).astype('int32'))
thickness = (image.size[0] + image.size[1]) // 500
# 保存框检测出的框的个数
file.write('find ' + str(len(out_boxes)) + ' target(s) \n')
for i, c in reversed(list(enumerate(out_classes))):
predicted_class = self.class_names[c]
box = out_boxes[i]
score = out_scores[i]
label = '{} {:.2f}'.format(predicted_class, score)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
label_size = draw.textsize(label, font)
top, left, bottom, right = box
top = max(0, np.floor(top + 0.5).astype('int32'))
left = max(0, np.floor(left + 0.5).astype('int32'))
bottom = min(image.size[1], np.floor(bottom + 0.5).astype('int32'))
right = min(image.size[0], np.floor(right + 0.5).astype('int32'))
# 写入检测位置
file.write(
predicted_class + ' score: ' + str(score) + ' \nlocation: top: ' + str(top) + '、 bottom: ' + str(
bottom) + '、 left: ' + str(left) + '、 right: ' + str(right) + '\n')
print(label, (left, top), (right, bottom))
if top - label_size[1] >= 0:
text_origin = np.array([left, top - label_size[1]])
else:
text_origin = np.array([left, top + 1])
# My kingdom for a good redistributable image drawing library.
for i in range(thickness):
draw.rectangle(
[left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i],
outline=self.colors[c])
draw.rectangle(
[tuple(text_origin), tuple(text_origin + label_size)],
fill=self.colors[c])
draw.text(text_origin, label, fill=(0, 0, 0), font=font)
del draw
end = timer()
print('time consume:%.3f s ' % (end - start))
return image
def close_session(self):
self.sess.close()
# 图片检测
if __name__ == '__main__':
t1 = time.time()
yolo = YOLO()
for filename in os.listdir(path):
image_path = path + '/' + filename
portion = os.path.split(image_path)
file.write(portion[1] + ' detect_result:\n')
image = Image.open(image_path)
r_image = yolo.detect_image(image)
file.write('\n')
# r_image.show() 显示检测结果
image_save_path = './result1/result_' + portion[1]
print('detect result1 save to....:' + image_save_path)
r_image.save(image_save_path)
time_sum = time.time() - t1
file.write('time sum: ' + str(time_sum) + 's')
print('time sum:', time_sum)
file.close()
yolo.close_session()
2- 修改文件相关参数,并运行即可
3.2.3 对预测结果进一步优化:
import sys
import argparse
from yolo_matt import YOLO, detect_video
from PIL import Image
yolo_test_args = {
"model_path": 'logs/003/ep077-loss19.318-val_loss19.682.h5',
"anchors_path": 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt',
"classes_path": 'model_data/class_file_en.txt',
"score" : 0.2,# 0.2
"iou" : 0.1,# 0.45
"model_image_size" : (416, 416),
"gpu_num" : 1,
}
yolo_test = YOLO(**yolo_test_args)
# 输出内容整理
def _get_class(classes_path):
classes_path = os.path.expanduser(classes_path)
with open(classes_path) as f:
class_names = f.readlines()
class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names]
return class_names
def yolov3_output(image,out_boxes,out_scores,out_classes):
output = []
yolo_classes = _get_class(yolo_test_args['classes_path'])
for n,box in enumerate(out_boxes):
y_min, x_min, y_max, x_max = box
y_min = max(0, np.floor(y_min + 0.5).astype('int32'))
x_min = max(0, np.floor(x_min + 0.5).astype('int32'))
y_max = min(image.size[1], np.floor(y_max + 0.5).astype('int32'))
x_max = min(image.size[0], np.floor(x_max + 0.5).astype('int32'))
score = out_scores[n]
yo_class = yolo_classes[out_classes[n]]
output.append({ 'y_min':y_min, 'x_min':x_min, 'y_max':y_max, 'x_max':x_max,\
'width':image.size[0],'height':image.size[1],\
'score':score,'yo_class':yo_class})
return output
image = Image.open('images/images_all/path1.jpg')
r_image,out_boxes, out_scores, out_classes = yolo_test.detect_image(image)
output = yolov3_output(r_image,out_boxes,out_scores,out_classes)
4. 项目总结
4.1 文件目录:
1- font文件夹存放的是字体目录,可忽略;
2- coco_annotation.py和voc_annotation.py就是用来生成模型训练验证和测试的最终txt文件;
3- logs文件用于保存模型权重;
4- results文件用于保存测试结果;
5- VOC2007文件用于保存原始训练数据;
6- test文件用于保存待测试数据的图片;
7- kmeans文件用于生成model_data/yolo_anchor所需要的锚点,共9个;
8- model_data文件夹重点关注voc_classes.txt(定义你自己的类别的)和yolo_anchor.txt(定义锚点的大小);
9- convert.py 把原始权重转换为kares的能读取的原始h5文件;
10- yolo_video.py 使用yolo.py文件中的yolo检测模型,并且对视频中的物体进行检测;
11- coco_annoataion.py 把json文件转换为txt文件
12- voc_annoataion.py 把xml文件转换为txt
4.2 train.py
1- 输入图片的宽高大小必须为32的倍数,默认是(416,416),一般经常用到的数值还有(320,320),(608,608);
2- epochs_stage_1 = 10 和 stage_1_train = False,用于判断否进行迁移学习,要学习的话,学习几个epoch;
3- epochs_finally = 100 和 finally_train = True ,用于判断是否进行后面开放所有层的学习,以及确定学习多少个epoch;
[如果要接着上次训练过的模型进行训练,一般要把batch_size设置小一些,然后再加载之前的权重]
4-
参考资料:
1- 基础设置:
(1) https://www.jianshu.com/p/3fddf7c08a58
(2) https://github.com/SpikeKing/keras-yolo3-detection
(3) https://blog.csdn.net/plSong_CSDN/article/details/89502117
(4) https://github.com/mattzheng/keras-yolo3-improved
(5) https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1418308
2- 评价指标的计算:
(1) https://github.com/Cartucho/mAP
(2) https://blog.csdn.net/leviopku/article/details/82660381
(3) https://github.com/KUASWoodyLIN/keras-yolo3/blob/master/train_v2.py#L254
3- 模型之间的转换:
(1)https://github.com/ysh329/deep-learning-model-convertor