UVM实战(张强)--- UART实例代码详细注解
目录
-
- 一、整体的设计结构图
- 二、各个组件代码详解
-
- 2.1 DUT
- 2.2 my_driver
- 2.3 my_transaction
- 2.4 my_env
- 2.5 my_monitor
- 2.6 my_agent
- 2.7 my_model
- 2.8 my_scoreboard
- 2.9 my_sequencer
- 2.10 base_test
- 2.11 my_case0
- 2.12 my_case1
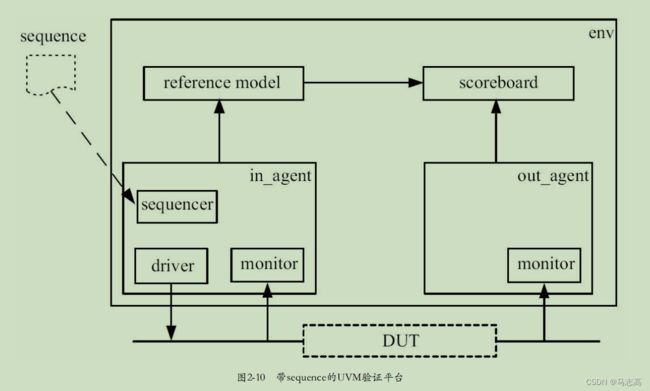
一、整体的设计结构图
各个模块的基础介绍:
(1)DUT:待测平台,这里为uart串口功能
(2)sequence:创建一个my_straction的实例m_trans,将其随机化,最终将其送给sequencer
(3)sequencer:uvm_sequencer就如同一个管道,从这个管道中产生连续的激励事务,并最终通过TLM端口送至driver一侧
(4)driver:该类会从uvm_sequencer中获取事务(transaction),经过转化进而在接口中对DUT进行时序激励
(5)monitor:负责把transaction级别的数据转变为DUT的端口级别,并驱动给DUT,mointor的行为与其相对,用于收集DUT的端口数据并将其转化成transaction交给后续的组件如reference model,scoreboard等处理
(6)reference model:reference model用于完成和DUT相同的功能
(7)scoreboard:uvm_scoreboard担任和SV中的check一样的功能,即进行数据的对比和报告,这里要比较的一源于reference model,二源于o_agent的monitor
(8)env:从环境层次结构而言,uvm_env包含多个uvm_agent和其他component,这些不同的组件共同构成一个完整的验证环境。
uvm_env的角色就是一个结构化的容器,它可以容纳其它组件的同时它也可以作为子环境在更高层次集中被嵌入
二、各个组件代码详解
2.1 DUT
module dut(clk,rst_n,rxd,rx_dv,txd,tx_en);
input clk;
input rst_n;
input[7:0] rxd; //rxd接收数据
input rx_dv; //发送数据有效指示
output [7:0] txd; //txd发送数据
output tx_en; //接收数据有效指示
reg[7:0] txd; //always赋值用reg
reg tx_en; //always赋值用reg
always @(posedge clk) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
txd <= 8'b0;
tx_en <= 1'b0;
end
else begin
txd <= rxd; //输出数据txd会打一拍
tx_en <= rx_dv;
end
end
endmodule
2.2 my_driver
//(1)`ifndef的使用方法
`ifndef MY_DRIVER__SV
`define MY_DRIVER__SV
class my_driver extends uvm_driver#(my_transaction); //类的定义
virtual my_if vif; //(2)virtual的作用
//(3)工厂机制
`uvm_component_utils(my_driver) //工厂的注册
function new(string name = "my_driver", uvm_component parent = null); //函数的创建
// 所有派生自uvm_driver的类的new函数有两个参数,一个是string类型的name,一个是uvm_component类型的parent。
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
//(4)build_phase和main_phase
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
//(8)uvm_config_db的用法
if(!uvm_config_db#(virtual my_if)::get(this, "", "vif", vif))
//(5)uvm_fatal宏
`uvm_fatal("my_driver", "virtual interface must be set for vif!!!")
endfunction
//(7)extern的用法
extern task main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern task drive_one_pkt(my_transaction tr);
endclass
task my_driver::main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
vif.data <= 8'b0;
vif.valid <= 1'b0;
while(!vif.rst_n)
@(posedge vif.clk);
while(1) begin
seq_item_port.get_next_item(req);
drive_one_pkt(req);
seq_item_port.item_done();
end
endtask
task my_driver::drive_one_pkt(my_transaction tr);
byte unsigned data_q[];
int data_size;
data_size = tr.pack_bytes(data_q) / 8;
`uvm_info("my_driver", "begin to drive one pkt", UVM_LOW);
repeat(3) @(posedge vif.clk);
for ( int i = 0; i < data_size; i++ ) begin
@(posedge vif.clk);
vif.valid <= 1'b1;
vif.data <= data_q[i];
end
// (6)uvm_info宏。
@(posedge vif.clk);
vif.valid <= 1'b0;
`uvm_info("my_driver", "end drive one pkt", UVM_LOW);
endtask
`endif
(1)如何理解ifndef和define的使用
目的:为了防止同一个文件在编译的时候被重复编译,引起多重定义的问题
即 “if not defined”,也就是说,当文件编译到这一行,如果这个文件还没有被编译过,也就是首次编译,就会执行后续的 `define xxx这句话,把后续的代码定义一次。反之,则不会再重复编译。
详细解释链接
(2)virtual的作用
1)不使用virtual,父类句柄虽指向子类对象,但调用的仍是父类本身的函数
2)使用virtual,父类句柄指向子类对象,调用的是子类的函数
详细解释链接
(3)工厂机制
factory机制的实现被集成在了一个宏中:uvm_component_utils。这个宏所做的事情非常多,其中之一就是将my_driver登记在UVM内部的一张表中,这张表是factory功能实现的基础。只要在定义一个新的类时使用这个宏,就相当于把这个类注册到了这张表中。
(4)build_phase和main_phase
理解build_phase和main_phase build_phase在new函数之后main_phase之前执行 build_phase是一个函数phase,而main_phase是一个任务phase,build_phase是不消耗仿真时间的。build_phase总是在仿真时间($time函数打印出的时间)为0时执行。
(5)uvm_fatal宏
在build_phase中出现了uvm_fatal宏,uvm_fatal宏是一个类似于uvm_info的宏,但是它只有两个参数,这两个参数与uvm_info宏的前两个参数的意义完全一样。与uvm_info宏不同的是,当它打印第二个参数所示的信息后,会直接调用Verilog的finish函数来结束仿真。
(6)uvm_info宏
这个宏的功能与Verilog中display语句的功能类似,但是它比display语句更加强大。它有三个参数,第一个参数是字符串,用于把打印的信息归类;第二个参数也是字符串,是具体需要打印的信息;第三个参数则是冗余级别。在验证平台中,某些信息是非常关键的,这样的信息可以设置为UVM_LOW,而有些信息可有可无,就可以设置为UVM_HIGH,介于两者之间的就是UVM_MEDIUM。UVM默认只显示UVM_MEDIUM或者UVM_LOW的信息。
(7)extern的用法
extern可以在使得function和task书写在class的外部,避免class过大难以阅读
(8)uvm_config_db的用法
uvm_config_db有set和get两种方法,一般成对出现
set:自顶层向下set,如从top_tb向driver设置参数
- uvm_config_db#(int)::set(this, “env.agt.drv”, “vif”, 100);
第一个参数this与第二个参数“env.agt.drv”——构成目标路径;因此也可以为(this.env, “agt.drv”, “num”, 100)
第三个参数是传给该路径的哪个成员;
第四个参数是要设置的值。
get:从底层向顶层get,如从driver中的build_phase使用get。 - uvm_config_db#(int)::get(this, “”,“vif”, vif);
第一个参数必须是uvm_component实例的指针,第二个参数是相对此实例的路径。一般的,如果第一个参数被设置成this,第二个参数可以是一个空的字符串。
第三个参数要与set中的第三个参数严格一致。
第四个参数是要设置的值。
详细解释链接
//打印结果
UVM_INFO my_driver.sv
(20)//指明此条打印信息的来源,其中括号里的数字表示原始的uvm_info打印语句在my_driver.sv中的行号。
@48500000 //表明此条信息的打印时间
:drv[my_driver]data is drived //这是driver在UVM树中的路径索引。UVM采用树形结构,对于树中任何一个结点,都有一个与其相应的字符串类型的
//路径索引。路径索引可以通过get_full_name函数来获取,把下列代码加入任何UVM树的结点中就可以得知当前结点的路径索引:
2.3 my_transaction
`ifndef MY_TRANSACTION__SV
`define MY_TRANSACTION__SV
//(1)uvm_sequence_item
class my_transaction extends uvm_sequence_item;
rand bit[47:0] dmac;//48bit的以太网目的地址
rand bit[47:0] smac;//48bit的以太网源地址
rand bit[15:0] ether_type;//以太网类型
rand byte pload[];//携带数据的大小
rand bit[31:0] crc;//面所有数据的校验值
constraint pload_cons{
pload.size >= 46;
pload.size <= 1500;
}
function bit[31:0] calc_crc();
return 32'h0;
endfunction
//(2)post_randomize()
function void post_randomize();
crc = calc_crc;
endfunction
//(3)uvm_object_utils
`uvm_object_utils_begin(my_transaction)
//(4)uvm_field_int
`uvm_field_int(dmac, UVM_ALL_ON)
`uvm_field_int(smac, UVM_ALL_ON)
`uvm_field_int(ether_type, UVM_ALL_ON)
`uvm_field_array_int(pload, UVM_ALL_ON)
`uvm_field_int(crc, UVM_ALL_ON)
`uvm_object_utils_end
function new(string name = "my_transaction");
super.new();
endfunction
endclass
`endif
(1)uvm_sequence_item
一是my_transaction的基类是uvm_sequence_item。在UVM中,所有的transaction都要从uvm_sequence_item派生,只有从uvm_sequence_item派生的transaction才可以使用后文讲述的UVM中强大的sequence机制。
(2)post_randomize()
post_randomize是SystemVerilog中提供的一个函数,当某个类的实例的randomize函数被调用后,post_randomize会紧随其后无条件
地被调用。
(3)uvm_object_utils
二是这里没有使用uvm_component_utils宏来实现factory机制,而是使用了uvm_object_utils。从本质上来说,my_transaction与my_driver是有区别的,在整个仿真期间,my_driver是一直存在的,my_transaction不同,它有生命周期。它在仿真的某一时间产生,经过driver驱动,再经过reference model处理,最终由scoreboard比较完成后,其生命周期就结束了。一般来说,这种类都是派生自uvm_object或者uvm_object的派生类,uvm_sequence_item的祖先就是uvm_object。UVM中具有这种特征的类都要使用uvm_object_utils宏来实现。
(4)uvm_field_int
uvm中的宏方法。
2.4 my_env
`ifndef MY_ENV__SV
`define MY_ENV__SV
//(1)为什么要使用my_env
class my_env extends uvm_env;
my_agent i_agt;
my_agent o_agt;
my_model mdl;
my_scoreboard scb;
//(4)uvm_tlm_analysis_fifo的用法
uvm_tlm_analysis_fifo #(my_transaction) agt_scb_fifo;
uvm_tlm_analysis_fifo #(my_transaction) agt_mdl_fifo;
uvm_tlm_analysis_fifo #(my_transaction) mdl_scb_fifo;
function new(string name = "my_env", uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
//(2)工厂创建对象的方式
i_agt = my_agent::type_id::create("i_agt", this);
o_agt = my_agent::type_id::create("o_agt", this);
i_agt.is_active = UVM_ACTIVE;
o_agt.is_active = UVM_PASSIVE;
mdl = my_model::type_id::create("mdl", this);
scb = my_scoreboard::type_id::create("scb", this);
agt_scb_fifo = new("agt_scb_fifo", this);
agt_mdl_fifo = new("agt_mdl_fifo", this);
mdl_scb_fifo = new("mdl_scb_fifo", this);
endfunction
extern virtual function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
//(3)uvm_component_utils的位置
`uvm_component_utils(my_env)
endclass
function void my_env::connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.connect_phase(phase);
i_agt.ap.connect(agt_mdl_fifo.analysis_export);
mdl.port.connect(agt_mdl_fifo.blocking_get_export);
mdl.ap.connect(mdl_scb_fifo.analysis_export);
scb.exp_port.connect(mdl_scb_fifo.blocking_get_export);
o_agt.ap.connect(agt_scb_fifo.analysis_export);
scb.act_port.connect(agt_scb_fifo.blocking_get_export);
endfunction
`endif
(1)为什么使用my_env
在验证平台中加入reference model、scoreboard等之前,思考一个问题:假设这些组件已经定义好了,那么在验证平台的什么位置对它们进行实例化呢?在top_tb中使用run_test进行实例化显然是不行的,因为run_test函数虽然强大,但也只能实例化一个实例;如果在top_tb中使用2.2.1节中实例化driver的方式显然也不可行,因为run_test相当于在top_tb结构层次之外建立一个新的结构层次,而2.2.1节的方式则是基于top_tb的层次结构,如果基于此进行实例化,那么run_test的引用也就没有太大的意义了;如果在driver中进行实例化则更加不合理。
(2)工厂创建对象的方式
这里没有直接调用my_driver的new函数,而是使用了一种古怪的方式。这种方式就是factory机制带来的独特的实例化方式。只有使用factory机制注册过的类才能使用这种方式实例化;只有使用这种方式实例化的实例,才能使用后文要讲述的factory机制中最为强大的重载功能。验证平台中的组件在实例化时都应该使用type_name::type_id::create的方式。
(3)uvm_component_utils的位置
uvm_componnet_utils常定义在class的最前方,这里放在class的最后不影响结果。
2.5 my_monitor
`ifndef MY_MONITOR__SV
`define MY_MONITOR__SV
class my_monitor extends uvm_monitor;//所有的monitor都应该派生自uvm_monitor
virtual my_if vif;
uvm_analysis_port #(my_transaction) ap;
`uvm_component_utils(my_monitor)
function new(string name = "my_monitor", uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
if(!uvm_config_db#(virtual my_if)::get(this, "", "vif", vif))
`uvm_fatal("my_monitor", "virtual interface must be set for vif!!!")
ap = new("ap", this);
endfunction
extern task main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern task collect_one_pkt(my_transaction tr);
endclass
task my_monitor::main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
my_transaction tr;
while(1) begin
tr = new("tr");
collect_one_pkt(tr);
ap.write(tr);
end
endtask
task my_monitor::collect_one_pkt(my_transaction tr);
byte unsigned data_q[$];
byte unsigned data_array[];
logic [7:0] data;
logic valid = 0;
int data_size;
while(1) begin
@(posedge vif.clk);
if(vif.valid) break;
end
`uvm_info("my_monitor", "begin to collect one pkt", UVM_LOW);
while(vif.valid) begin
data_q.push_back(vif.data);
@(posedge vif.clk);
end
data_size = data_q.size();
data_array = new[data_size];
for ( int i = 0; i < data_size; i++ ) begin
data_array[i] = data_q[i];
end
tr.pload = new[data_size - 18]; //da sa, e_type, crc
data_size = tr.unpack_bytes(data_array) / 8;
`uvm_info("my_monitor", "end collect one pkt", UVM_LOW);
endtask
`endif
有几点需要注意的是:
第一,所有的monitor类应该派生自uvm_monitor;
第二,与driver类似,在my_monitor中也需要有一个virtual my_if;
第三,uvm_monitor在整个仿真中是一直存在的,所以它是一个component,要使用uvm_component_utils宏注册;
第四,由于monitor需要时刻收集数据,永不停歇,所以在main_phase中使用while(1)循环来实现这一目的。
2.6 my_agent
`ifndef MY_AGENT__SV
`define MY_AGENT__SV
//(1)为什么会有agent这个模块
class my_agent extends uvm_agent ;
my_sequencer sqr;
my_driver drv;
my_monitor mon;
uvm_analysis_port #(my_transaction) ap;
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
extern virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern virtual function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
`uvm_component_utils(my_agent)
endclass
function void my_agent::build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
//(2)如何理解is_active变量
if (is_active == UVM_ACTIVE) begin
sqr = my_sequencer::type_id::create("sqr", this);
drv = my_driver::type_id::create("drv", this);
end
mon = my_monitor::type_id::create("mon", this);
endfunction
function void my_agent::connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.connect_phase(phase);
if (is_active == UVM_ACTIVE) begin
drv.seq_item_port.connect(sqr.seq_item_export);
end
ap = mon.ap;
endfunction
`endif
(1)为什么会有agent这个模块?
driver和monitor两者之间的代码高度相似。其本质是因为二者处理的是同一种协议,在同样一套既定的规则下做着不同的事情。由于二者的这种相似性,UVM中通常将二者封装在一起,成为一个agent。因此,不同的agent就代表了不同的协议。
(2)如何理解is_active变量
is_active有两种模式,分别为UVM_PASSIVE和UVM_ACTIVE,is_active默认值为UVM_ACTIVE,这种模式下,是需要例化driver的。那么什么情况下需要UVM_PASSIVE模式呢?下图中,在输出端口上不需要驱动任何信号,只需要监测信号。在这种情况下,端口上是只需要monitor的,所以driver可以不用实例化。

2.7 my_model
`ifndef MY_MODEL__SV
`define MY_MODEL__SV
class my_model extends uvm_component;
uvm_blocking_get_port #(my_transaction) port;
(1)uvm_analysis_port的使用方法
uvm_analysis_port #(my_transaction) ap;
extern function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
extern function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern virtual task main_phase(uvm_phase phase);//extern外部定义写了virtual,下面不需要再写virtual
`uvm_component_utils(my_model)
endclass
function my_model::new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void my_model::build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
port = new("port", this);
ap = new("ap", this);
endfunction
task my_model::main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
my_transaction tr;
my_transaction new_tr;
super.main_phase(phase);
while(1) begin
port.get(tr);
new_tr = new("new_tr");
new_tr.copy(tr);
`uvm_info("my_model", "get one transaction, copy and print it:", UVM_LOW)
new_tr.print();
ap.write(new_tr);
end
endtask
`endif
(1)uvm_analysis_port的使用方法
在UVM中,通常使用TLM(Transaction Level Modeling)实现component之间transaction级别的通信。要实现通信,有两点是值得考虑的:第一,数据是如何发送的?第二,数据是如何接收的?在UVM的transaction级别的通信中,数据的发送有多种方式,其中一种是使用uvm_analysis_port。uvm_analysis_port是一个参数化的类,其参数就是这个analysis_port需要传递的数据的类型,也就是uvm_analysis_port #(my_transaction) ap;里面括号的内容my_transaction。
2.8 my_scoreboard
`ifndef MY_SCOREBOARD__SV
`define MY_SCOREBOARD__SV
class my_scoreboard extends uvm_scoreboard;
my_transaction expect_queue[$];
//(1)exp_port和act_port
uvm_blocking_get_port #(my_transaction) exp_port;
uvm_blocking_get_port #(my_transaction) act_port;
`uvm_component_utils(my_scoreboard) //不加封号
extern function new(string name, uvm_component parent = null);
extern virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern virtual task main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
endclass
function my_scoreboard::new(string name, uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
//(2)build_phase
function void my_scoreboard::build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
exp_port = new("exp_port", this);
act_port = new("act_port", this);
endfunction
task my_scoreboard::main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
my_transaction get_expect, get_actual, tmp_tran;
bit result;
super.main_phase(phase);
fork
while (1) begin
exp_port.get(get_expect);
//(3)expect_queue
expect_queue.push_back(get_expect);
end
while (1) begin
act_port.get(get_actual);
if(expect_queue.size() > 0) begin
//(3)expect_queue
tmp_tran = expect_queue.pop_front();
//(4)compare
result = get_actual.compare(tmp_tran);
if(result) begin
`uvm_info("my_scoreboard", "Compare SUCCESSFULLY", UVM_LOW);//这里uvm_info后面加了封号,但是有些书上没加封号,应该是都可以,不影响。
end
else begin
`uvm_error("my_scoreboard", "Compare FAILED");
$display("the expect pkt is");
tmp_tran.print();
$display("the actual pkt is");
get_actual.print();
end
end
else begin
//(5)uvm_error
`uvm_error("my_scoreboard", "Received from DUT, while Expect Queue is empty");
$display("the unexpected pkt is");
get_actual.print();
end
end
join
endtask
`endif
(1)exp_port和act_port
scoreboard的两个比较值一个来自于reference model,用exp_port获取,另外一个来自于o_agt,用act_port获取。
(2)main_phase
在main_phase中通过fork建立起了两个进程,一个进程处理exp_port的数据,;另外一个进程处理act_port的数据,这是DUT的输出数据。
(3)expect_queue
当收到数据后,把数据放入expect_queue中,当收集到这些数据后,从expect_queue中弹出之前从exp_port收到的数据,并调用my_transaction的my_compare函数。
(4)compare
my_compare逐字比较两个my_transaction。
(5)uvm_error
UVM_ERROR的默认处理方式为UVM_DISPLAY|UVM_COUNT,将消息输出到标准出口端,增加退出计划变量quit_count,当quit_count达到一定数量时,停止仿真。
2.9 my_sequencer
`ifndef MY_SEQUENCER__SV
`define MY_SEQUENCER__SV
class my_sequencer extends uvm_sequencer #(my_transaction);
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
`uvm_component_utils(my_sequencer)
endclass
`endif
sequencer的定义非常简单,派生自uvm_sequencer,并且使用uvm_component_utils宏来注册到factory中。uvm_sequencer是一个
参数化的类,其参数是my_transaction,即此sequencer产生的transaction的类型。
2.10 base_test
`ifndef BASE_TEST__SV
`define BASE_TEST__SV
class base_test extends uvm_test;
my_env env;//?
function new(string name = "base_test", uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name,parent);
endfunction
extern virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern virtual function void report_phase(uvm_phase phase);
`uvm_component_utils(base_test)
endclass
function void base_test::build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
env = my_env::type_id::create("env", this);
endfunction
function void base_test::report_phase(uvm_phase phase);
uvm_report_server server;
int err_num;
super.report_phase(phase);
server = get_report_server();
err_num = server.get_severity_count(UVM_ERROR);
if (err_num != 0) begin
$display("TEST CASE FAILED");
end
else begin
$display("TEST CASE PASSED");
end
endfunction
`endif
base_test派生自uvm_test,使用uvm_component_utils宏来注册到factory中
2.11 my_case0
`ifndef MY_CASE0__SV
`define MY_CASE0__SV
class case0_sequence extends uvm_sequence #(my_transaction);
my_transaction m_trans;
function new(string name= "case0_sequence");
super.new(name);
endfunction
virtual task body();
if(starting_phase != null)
starting_phase.raise_objection(this);
repeat (10) begin
`uvm_do(m_trans)
end
#100;
if(starting_phase != null)
starting_phase.drop_objection(this);
endtask
`uvm_object_utils(case0_sequence)
endclass
class my_case0 extends base_test;
function new(string name = "my_case0", uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name,parent);
endfunction
extern virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
`uvm_component_utils(my_case0)
endclass
function void my_case0::build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
uvm_config_db#(uvm_object_wrapper)::set(this,
"env.i_agt.sqr.main_phase",
"default_sequence",
case0_sequence::type_id::get());
endfunction
`endif
2.12 my_case1
`ifndef MY_CASE1__SV
`define MY_CASE1__SV
class case1_sequence extends uvm_sequence #(my_transaction);
my_transaction m_trans;
function new(string name= "case1_sequence");
super.new(name);
endfunction
virtual task body();
if(starting_phase != null)
starting_phase.raise_objection(this);
repeat (10) begin
`uvm_do_with(m_trans, { m_trans.pload.size() == 60;})
end
#100;
if(starting_phase != null)
starting_phase.drop_objection(this);
endtask
`uvm_object_utils(case1_sequence)
endclass
class my_case1 extends base_test;
function new(string name = "my_case1", uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name,parent);
endfunction
extern virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
`uvm_component_utils(my_case1)
endclass
function void my_case1::build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
uvm_config_db#(uvm_object_wrapper)::set(this,
"env.i_agt.sqr.main_phase",
"default_sequence",
case1_sequence::type_id::get());
endfunction
`endif