大家好!今天为大家带来的是一篇经验帖文。本次分享的主人公是黑客松比赛参赛者郑必城,他将为大家带来比赛项目“No.80瑞芯微RK3588:通过Paddle2ONNX打通5个飞桨模型的部署中如何为FastDeploy”任务中的一些心得体会,快来看看他是如何为FastDeploy贡献代码的吧!
RKNPU2是瑞芯微Rockchip推出的针对RK356X/RK3588/RV1103/RV1106的C++推理工具。在参加黑客松比赛时,FastDeploy仓库[1]还没有集成RKNPU2的引擎。开发者需要使用RKNPU2从头编写代码。在参加完黑客松之后,我为FastDeploy仓库贡献了RKNPU2的后端推理引擎的代码,现在能直接使用FastDeploy快速开发基于RKNPU2的代码。本次教程将以贡献SCRFD模型[2]为例,教你如何给FastDeploy贡献代码。
Zheng_Bicheng主页
No.80瑞芯微RK3588:通过Paddle2ONNX打通5个飞桨模型的部署链接
FastDeploy简介
FastDeploy是一款全场景、易用灵活、极致高效的AI推理部署工具,提供开箱即用的云边端部署体验,支持超过150+文本、计算机视觉、语音和跨模态模型,并实现端到端的推理性能优化。其应用于图像分类、物体检测、图像分割、人脸检测、人脸识别、关键点检测、抠图、OCR、NLP、TTS等任务,满足开发者多场景、多硬件、多平台的产业部署需求。同时,FastDeploy集成了多种后端推理引擎,其中就包括RKNPU2。开发者能够快速基于现有的模型以及后端来进行开发。
很多开发者可能会有疑惑,为什么Rockchip提供了RKNPU2和rknn-toolkit2这两个分别面向C++和Python的推理引擎,我们还要使用FastDeploy进行开发呢?简单来说,RKNPU2和rknn-toolkit2是推理引擎,它们侧重于推理;FastDeploy是推理部署工具侧重于部署。给RKNPU2输入一张图片,会得到一串数字。给FastDeploy输入一张图片,会直接得到经过后处理后的图片。这样就能大大减少开发者在项目落地过程中的一些困难。
RKNPU2
rknn-toolkit2
贡献步骤
给FastDeploy贡献代码,我一般按以下步骤进行,当然你可以根据自己的能力制定自己的开发步骤。
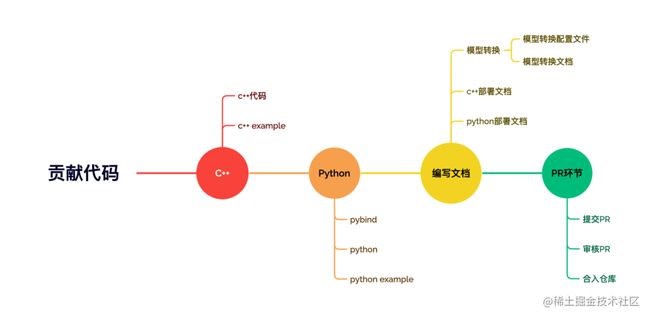
由上图所示,给FastDeploy贡献代码的步骤一般为编写C++代码、编写C++ example、编写Python代码、编写Python example代码、编写文档、提交PR。
贡献代码指南
下面我以贡献SCRFD模型为例子,给大家详细介绍每个贡献环节中的注意事项。
转换模型
不管你是在FastDeploy上开发C++还是Python的代码,转换模型都是你首先需要完成的任务。通常情况下,转换模型的工具一般使用rknn-toolkit2,但是这个工具API比较多,用起来较为复杂。为了让大家能够更快速的转换模型,在FastDeploy中,我已经编写了转换模型的代码并且提供了详细的文档。详情请查看FastDeploy RKNPU2模型转换文档。这里为了缩短篇幅,直接给出模型转换的配置文件以及模型转换的文档。大家可以参考这几个文档转换自己的模型。
FastDeploy RKNPU2模型转换文档
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/blob/develop/docs/cn/faq/rknpu2/export.md
编写C++代码
上文提到,SCRFD的C++代码需要在fastdeploy/vision/facedet/contrib这个目录下编写,因此我创建了scrfd.h和scrfd.cc这两个文件,实现模型具体代码。这里要注意与常见的文件命名形式不同,scrfd.cc这个C++代码文件的后缀不是 .cpp而是 .cc ,如果scrfd.cc改为scrfd.cpp将无法成功编译!
- 编写scrfd.h
scrfd.h里定义了SCRFD模型的一些基本参数以及需要重定义的函数。其中定义的SCRFD模型需要继承FastDeployModel这个公共的模型类,为的是继承FastDeploy的一些公共特性。如下面的代码所示,在头文件中,我们需要重写FastDeployModel中的以下几个函数,包括Initialize、Preprocess、Postprocess、Predict、ModelName。分别对应初始化、预处理、后处理、预测、模型名称。如果你需要完整详细的代码,请访问下方链接。
scrfd.h
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/blob/develop/fastdeploy/vision/facedet/contrib/scrfd.h
#pragma once
#include
#include "fastdeploy/fastdeploy_model.h"
#include "fastdeploy/vision/common/processors/transform.h"
#include "fastdeploy/vision/common/result.h"
namespace fastdeploy {
namespace vision {
namespace facedet {
class FASTDEPLOY_DECL SCRFD : public FastDeployModel {
public:
SCRFD(const std::string& model_file, const std::string& params_file = "",
const RuntimeOption& custom_option = RuntimeOption(), const ModelFormat& model_format = ModelFormat::ONNX);
std::string ModelName() const { return "scrfd"; }
virtual bool Predict(cv::Mat* im, FaceDetectionResult* result, float conf_threshold = 0.25f, float nms_iou_threshold = 0.4f);
private:
bool Initialize();
bool Preprocess(Mat* mat, FDTensor* output, std::map>* im_info);
bool Postprocess(std::vector& infer_result, FaceDetectionResult* result, const std::map>& im_info, float conf_threshold, float nms_iou_threshold);
};
} // namespace facedet
} // namespace vision
} // namespace fastdeploy - 编写scrfd.cc
scrfd.cc负责对在scrfd.h中声明的函数进行了实现。在编写预处理的过程中要注意,RKNPU2目前仅支持NHWC格式的输入数据,因此必须屏蔽Permute操作。我这里使用disable_permute_ 变量控制Permute操作。此外由于FastDeploy采用的是RKNPU2的零拷贝流程来实现后端的处理和运算,因此可以考虑将Normalize操作放在NPU上来做,提升速度,我这里使用disable_normalize_ 变量控制Normalize的开关。如果需要详细的代码,请访问以下链接。
代码链接
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/blob/develop/fastdeploy/vision/facedet/contrib/scrfd.cc
#include "fastdeploy/vision/facedet/contrib/scrfd.h"
#include "fastdeploy/utils/perf.h"
#include "fastdeploy/vision/utils/utils.h"
namespace fastdeploy {
namespace vision {
namespace facedet {
bool SCRFD::Preprocess(Mat* mat, FDTensor* output, std::map>* im_info) {
return true;
}
bool SCRFD::Postprocess(std::vector& infer_result, FaceDetectionResult* result, const std::map>& im_info, float conf_threshold, float nms_iou_threshold) {
return true;
}
bool SCRFD::Predict(cv::Mat* im, FaceDetectionResult* result, float conf_threshold, float nms_iou_threshold) {
return true;
}
} // namespace facedet
} // namespace vision
} // namespace fastdeploy - 在vision.h中添加我们的模型
我们编写完scrfd的代码之后,我们还需要让FastDeploy知道我们已经编写了scrfd代码,因此我们需要在fastdeploy/vision.h文件中补充scrfd.h头文件的路径。
编译FastDeploy C++ SDK
编写完C++代码后,我们需要编译C++版本的FastDeploy。一是为了测试我们编写的代码是否有程序上的漏洞,二是为了后续编写example可以链接FastDeploy编译出来的动态库。编译的细节详情请参考FastDeploy C++代码编译指南。
FastDeploy C++代码编译指南
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/blob/develop/docs/cn/faq/rknpu2/build.md
这里直接给出编译时的命令:
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy.git
cd FastDeploy
mkdir build && cd build
cmake .. -DENABLE_ORT_BACKEND=ON \
-DENABLE_RKNPU2_BACKEND=ON \
-DENABLE_VISION=ON \
-DRKNN2_TARGET_SOC=RK3588 \
-DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=${PWD}/fastdeploy-0.0.3
make -j8
make install编写C++ example代码
为了调试我们已经完成的C++代码,以及方便用户使用,在编写完上述代码之后,我们需要编写对应example的代码来验证我们的想法是否正确。在编写C++ example时,目录下的文件一般由infer_model_name.cc以及CMakeLists.txt组成。在CMakeLists.txt中需要对不同的infer_model_name.cc生成不同的infer_model_name程序。
- 编写infer.cc
infer.cc主要负责调用FastDeploy的C++代码来对SCRFD进行测试。在上文中,我们提到vision.h可以让fastdeploy知道我们已经编写了SCRFD模型。因此在编写example时,我们只需要包含vision.h,即可让程序知道,我们已经声明了FastDeploy所有已经实现的视觉模型。针对RKNPU的测试,其流程一般为初始化模型,然后根据转换模型时的配置决定是否需要disable_normalize和disable_permute,随后输入测试图片,调用Predict函数进行处理,最后使用对应的可视化函数进行可视化。
#include
#include
#include "fastdeploy/vision.h"
void RKNPU2Infer(const std::string& model_dir, const std::string& image_file) {
auto model = fastdeploy::vision::facedet::SCRFD(model_file, params_file, option, format);
model.Initialized();
model.DisableNormalize();
model.DisablePermute();
auto im = cv::imread(image_file);
fastdeploy::vision::FaceDetectionResult res;
model.Predict(&im, &res)
auto vis_im = fastdeploy::vision::VisFaceDetection(im, res);
cv::imwrite("infer_rknn.jpg", vis_im);
std::cout << "Visualized result saved in ./infer_rknn.jpg" << std::endl;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
if (argc < 3) {
std::cout
<< "Usage: infer_demo path/to/model_dir path/to/image run_option, "
"e.g ./infer_model ./picodet_model_dir ./test.jpeg"
<< std::endl;
return -1;
}
RKNPU2Infer(argv[1], argv[2]);
return 0;
} - 编写CMakeLists.txt
编写完C++ example的代码后,我们还需要编写CMakeLists.txt。CMakeLists.txt相当于编译时的配置文件,负责链接infer_model_name.cc和FastDeploy的动态库,并且把模型推理需要用到的东西集成在install目录下。
CMAKE_MINIMUM_REQUIRED(VERSION 3.10)
project(rknpu_test)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
# 指定下载解压后的fastdeploy库路径
set(FASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR "thirdpartys/fastdeploy-0.7.0")
include(${FASTDEPLOY_INSTALL_DIR}/FastDeployConfig.cmake)
include_directories(${FastDeploy_INCLUDE_DIRS})
add_executable(rknpu_test infer.cc)
target_link_libraries(rknpu_test ${FastDeploy_LIBS})编写Python代码
Python代码的编写主要包括pybind文件的编写以及py本体文件的编写。上文提到,在FastDeploy中,python代码通过调用pybind暴露出的C++ API来进行工作,因此我们首先需要编写pybind.cc。
- 编写scrfd_pybind.cc
pybind.cc主要负责提供可用的API给Python调用。scrfd_pybind.cc中对SCRFD C++的代码进行了暴露,代码如下:
#include "fastdeploy/pybind/main.h"
namespace fastdeploy {
void BindSCRFD(pybind11::module& m) {
// Bind SCRFD
pybind11::class_(m, "SCRFD")
.def(pybind11::init())
.def("predict",
[](vision::facedet::SCRFD& self, pybind11::array& data,
float conf_threshold, float nms_iou_threshold) {
auto mat = PyArrayToCvMat(data);
vision::FaceDetectionResult res;
self.Predict(&mat, &res, conf_threshold, nms_iou_threshold);
return res;
})
.def("disable_normalize",&vision::facedet::SCRFD::DisableNormalize)
.def("disable_permute",&vision::facedet::SCRFD::DisablePermute);
}
} // namespace fastdeploy - 在facedet_pybind.cc中添加声明
和在vision.h文件中添加声明一样,在编写完pybind代码之后,我们还需要在fastdeploy/vision/facedet/facedet_pybind.cc中添加声明。目的是告诉编译器我们已经编写了pybind的代码,并且在编译Python时请把我们的代码加上。核心代码如下:
#include "fastdeploy/pybind/main.h"
namespace fastdeploy {
void BindSCRFD(pybind11::module& m);
void BindFaceDet(pybind11::module& m) {
auto facedet_module = m.def_submodule("facedet", "Face detection models.");
BindSCRFD(facedet_module);
}
}- 编写scrfd.py
编写完pybind.cc后,我们还需要编写对应的py文件调用pybind暴露出来的C++ API。代码如下
from __future__ import absolute_import
import logging
from .... import FastDeployModel, ModelFormat
from .... import c_lib_wrap as C
class SCRFD(FastDeployModel):
def __init__(self,
model_file,
params_file="",
runtime_option=None,
model_format=ModelFormat.ONNX):
super(SCRFD, self).__init__(runtime_option)
self._model = C.vision.facedet.SCRFD(model_file, params_file, self._runtime_option, model_format)
assert self.initialized, "SCRFD initialize failed."
def predict(self, input_image, conf_threshold=0.7, nms_iou_threshold=0.3):
return self._model.predict(input_image, conf_threshold, nms_iou_threshold)编译FastDeploy Python SDK
编写example之前我们肯定需要编译Python版本的FastDeploy代码,请参考FastDeploy RKNPU2编译指南编译Python版本的FastDeploy。
FastDeploy RKNPU2编译指南
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/blob/develop/docs/cn/faq/rknpu2/build.md
这里给出我经常使用的编译命令:
cd FastDeploy
cd python
export ENABLE_ORT_BACKEND=ON
export ENABLE_RKNPU2_BACKEND=ON
export ENABLE_VISION=ON
export RKNN2_TARGET_SOC=RK3588
python3 setup.py build
python3 setup.py bdist_wheel
cd dist
pip3 install fastdeploy_python-0.0.0-cp39-cp39-linux_aarch64.whl编写Python example代码
为了调试我们已经完成的Python代码,以及方便用户使用,在编写完上述scrfd代码之后,我们需要编写对应example的代码来验证我们的想法是否正确。在编写Python example时,目录下的文件一般由infer_model_name.py组成。
- 编写infer.py
infer.py 主要负责调用FastDeploy的Python代码来对SCRFD的测试。与C++ example相似,针对RKNPU的测试,其流程一般为初始化模型,然后根据转换模型时的配置决定是否需要disable_normalize和disable_permute,随后输入测试图片,调用Predict函数进行处理,最后使用对应的可视化函数进行可视化。
import fastdeploy as fd
import cv2
import os
def parse_arguments():
import argparse
import ast
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--model_file", required=True, help="Path of FaceDet model.")
parser.add_argument("--image", type=str, required=True, help="Path of test image file.")
return parser.parse_args()
def build_option(args):
option = fd.RuntimeOption()
option.use_rknpu2()
return option
args = parse_arguments()
# 配置runtime,加载模型
runtime_option = build_option(args)
model_file = args.model_file
params_file = ""
model = fd.vision.facedet.SCRFD(model_file, params_file, runtime_option=runtime_option, model_format=fd.ModelFormat.RKNN)
model.disable_normalize()
model.disable_permute()
# 预测图片分割结果
im = cv2.imread(args.image)
result = model.predict(im)
print(result)
# 可视化结果
vis_im = fd.vision.vis_face_detection(im, result)
cv2.imwrite("visualized_result.jpg", vis_im)
print("Visualized result save in ./visualized_result.jpg")编写文档以及提交pr
请参考SCRFD example编写模型的转换文档、模型的cpp example运行文档、模型的python运行文档共三份文档,然后向FastDeploy的Github仓库提交PR。待审核过后,你的贡献就会被记录啦。
SCRFD example
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/FastDeploy/tree/develop/examples/vision/facedet/scrfd/rknpu2
总结
在飞桨做开源贡献的体验是无与伦比的,首先能够快速实现编程能力提升,在贡献代码的过程中,你会更加深刻的理解书本上的内容,掌握行业前沿的代码逻辑和编程规范。同时在开发过程中,你还会认识飞桨研发团队的同学以及很多志同道合的好友,与他们共同创造一些有趣的成果,在修复bug的过程中体验成就感。欢迎和我一起加入贡献代码的行列。
参考文献
[1]https://github.com/PaddlePadd...
[2]Guo J , Deng J , Lattas A , et al. Sample and Computation Redistribution for Efficient Face Detection[J]. 2021.