02- pandas 数据库 (数据库)
pandas 数据库重点:
-
pandas 的主要数据结构: Series (一维数据)与 DataFrame (二维数据)。
-
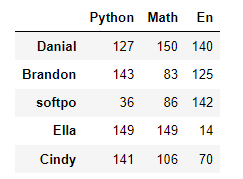
pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,151,size = (5,3)), # 生成pandas数据
index = ['Danial','Brandon','softpo','Ella','Cindy'], # 行索引
columns=['Python','Math','En']) # 列索引 -
data.shape # (150, 3) # 查看形状
-
data.head(10) # 查看前10列数据
-
存储数据常用格式: .csv, .xls, .h5
-
df.loc[['A','C','D','F']] # 选取指定行标签数据
-
df[ df.Python > 100 ] # 判断Python分数是否大于100,返回值是boolean类型的Series
-
pd.concat([df1,df2],axis = 0) # df1和df2行串联,df2的行追加df2行后面
-
df.insert(loc = 1,column='Pytorch',value=1024) # 插入列
-
空数据筛选: df.isnull()
-
df.rename(index = {'A':'AA','B':'BB'},columns = {'Python':'人工智能'}) # 重命名轴索引
-
df.replace([0,7],2048) # 将0和7替换为2048
-
去重: df['Keras'].unique()
- 基础数据处理:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,100,size = (20,3)),
index = list('ABCDEFHIJKLMNOPQRSTU'),
columns=['Python','Tensorflow','Keras'])
# 1、简单统计指标
df.count() # 非NA值的数量
df.max(axis = 0) #轴0最大值,即每一列最大值
df.min() #默认计算轴0最小值
df.median() # 中位数
df.sum() # 求和
df.mean(axis = 1) #轴1平均值,即每一行的平均值
df.quantile(q = [0.2,0.4,0.8]) # 分位数
df.describe() # 查看数值型列的汇总统计,计数、平均值、标准差、最小值、四分位数、最大值
第一部分 pandas数据库
- Python在数据处理和准备方面一直做得很好,但在数据分析和建模方面就差一些。需要pandas的补充。
- pandas与出色的 jupyter工具包和其他库相结合的比较好
- pandas的主要数据结构是 Series (一维数据)与 DataFrame (二维数据),这两种数据结构足以处理金融、统计、社会科学、工程等领域里的大多数案例
- 处理数据一般分为几个阶段:数据整理与清洗、数据分析与建模、数据可视化与制表,Pandas 是处理数据的理想工具。
第二部分 数据结构
第一节 Series
用列表生成 Series时,Pandas 默认自动生成整数索引,也可以指定索引。
l = [0,1,7,9,np.NAN,None,1024,512]
# 无论是numpy中的NAN还是Python中的None在pandas中都以缺失数据NaN对待
s1 = pd.Series(data = l) # pandas自动添加索引
s2 = pd.Series(data = l,index = list('abcdefhi'),dtype='float32') # 指定行索引
# 传入字典创建,key行索引
s3 = pd.Series(data = {'a':99,'b':137,'c':149},name = 'Python_score')
display(s1,s2,s3)
''' s1数组:
0 0.0
1 1.0
2 7.0
3 9.0
4 NaN
5 NaN
6 1024.0
7 512.0
dtype: float64
s3数组:
a 99
b 137
c 149
Name: Python_score, dtype: int64'''第二节 DataFrame
DataFrame是由多种类型的列构成的二维标签数据结构,类似于 Excel 、SQL 表,或 Series 对象构成的字典。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# index 作为行索引,字典中的key作为列索引,创建了3*3的DataFrame表格二维数组
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data = {'Python':[99,107,122],'Math':[111,137,88],
'En':[68,108,43]}, # key作为列索引
index = ['张三','李四','Michael']) # 行索引
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,151,size = (5,3)),
index = ['Danial','Brandon','softpo','Ella','Cindy'], # 行索引
columns=['Python','Math','En']) # 列索引第三部分 数据查看
查看DataFrame的常用属性和DataFrame的概览和统计信息:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# 创建 shape(150,3)的二维标签数组结构DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,151,size = (150,3)),
index = None,# 行索引默认
columns=['Python','Math','En'])# 列索引
# 查看其属性、概览和统计信息
df.head(10) # 显示头部10行,默认5个
df.tail(10) # 显示末尾10行,默认5个
df.shape # (150, 3) # 查看形状,行数和列数
df.dtypes # Python: int32 Math: int32 En: int32 dtype: object # 查看数据类型
df.index # RangeIndex(start=0, stop=150, step=1) # 行索引
df.columns # Index(['Python', 'Math', 'En'], dtype='object') # 列索引
df.values # 对象值,二维ndarray数组
df.describe() # 查看数值型列的汇总统计,计数、平均值、标准差、最小值、四分位数、最大值
df.info() # 查看列索引、数据类型、非空计数和内存信息第四部分 数据输入与输出
第一节 csv文件
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,50,size = [50,5]), # 薪资情况
columns=['IT','化工','生物','教师','士兵'])
# 保存到当前路径下,文件命名是:salary.csv。csv逗号分割值文件格式
df.to_csv('./salary.csv',
sep = ';', # 文本分隔符,默认是逗号
header = True, # 是否保存列索引
index = True) # 是否保存行索引,保存行索引,文件被加载时,默认行索引会作为一列
# 加载
pd.read_csv('./salary.csv',
sep = ';', # 默认是逗号
header = [0], # 指定列索引
index_col=0) # 指定行索引
pd.read_table('./salary.csv', # 和read_csv类似,读取限定分隔符的文本文件
sep = ';',
header = [0], #指定列索引
index_col=1) # 指定行索引,IT作为行索引第二节 Excel文件
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,50,size = [50,5]), # 薪资情况
columns=['IT','化工','生物','教师','士兵'])
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,50,size = [150,3]), # 计算机考试成绩
columns=['Python','Tensorflow','Keras'])
# 保存到当前路径下,文件命名是:salary.xls
df1.to_excel('./salary.xls',
sheet_name = 'salary', # Excel中工作表的名字
header = True, # 是否保存列索引
index = False) # 是否保存行索引,保存行索引
pd.read_excel('./salary.xls',
sheet_name=0, # 读取哪一个Excel中工作表,默认第一个
header = 0, # 使用第一行数据作为列索引
names = list('ABCDE'), # 替换行索引
index_col=1) # 指定行索引,B作为行索引
# 一个Excel文件中保存多个工作表
with pd.ExcelWriter('./data.xlsx') as writer:
df1.to_excel(writer,sheet_name='salary',index = False)
df2.to_excel(writer,sheet_name='score',index = False)
pd.read_excel('./data.xlsx',
sheet_name='salary') # 读取Excel中指定名字的工作表
第三节 SQL
import pandas as pd
# SQLAlchemy是Python编程语言下的一款开源软件。提供了SQL工具包及对象关系映射(ORM)工具
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
df = pd.DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0,50,size = [150,3]),# 计算机科目的考试成绩
columns=['Python','Tensorflow','Keras'])
# 数据库连接
cn=create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:12345678@localhost/pandas?charset=UTF8MB4')
# 保存到数据库
df.to_sql('score',#数据库中表名
cn,# 数据库连接
if_exists='append') # 如果表名存在,追加数据
# 从数据库中加载
pd.read_sql('select * from score limit 10', # sql查询语句
cn, # 数据库连接
index_col='Python') # 指定行索引名第四节 HDF5
HDF5,可以存储不同类型数据的文件格式,后缀通常是.h5,它的结构是层次性的。一个HDF5文件可以被看作是一个组包含了各类不同的数据集。
对于HDF5文件中的数据存储,有两个核心概念:(group 和 dataset)
- dataset 代表数据集,一个文件当中可以存放不同种类的数据集,这些数据集如何管理,就用到了group, 最直观的理解,可以参考我们的文件管理系统,不同的文件位于不同的目录下。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,50,size = [50,5]), # 薪资情况
columns=['IT','化工','生物','教师','士兵'])
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,50,size = [150,3]), # 计算机科目成绩
columns=['Python','Tensorflow','Keras'])
# 保存到当前路径下,文件命名是:data.h5
df1.to_hdf('./data.h5',key='salary') # 保存数据的key,标记
df2.to_hdf('./data.h5',key = 'score')
pd.read_hdf('./data.h5', key = 'salary') # 获取指定的标记、key的数据第五部分 数据选取
第一节 字段数据
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,150,size = [150,3]),# 计算机科目成绩
columns=['Python','Tensorflow','Keras'])
df['Python'] # Name: Python, Length: 150, dtype: int32 # 获取单列,Series
df.Python # Name: Python, Length: 150, dtype: int32 # 获取单列,Series
df[['Python','Keras']] # 150 rows × 2 columns # 获取多列,DataFrame
df[3:15] # 行切片第二节 标签选择
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,150,size = [10,3]),# 计算机科目成绩
index = list('ABCDEFGHIJ'),# 行标签
columns=['Python','Tensorflow','Keras'])
df.loc[['A','C','D','F']] # 选取指定行标签数据
df.loc['A':'E',['Python','Keras']] # 根据行标签切片,选取指定列标签的数据
df.loc[:,['Keras','Tensorflow']] # :默认保留所有行
df.loc['E'::2,'Python':'Tensorflow'] # 行切片从标签E开始每2个中取一个,列标签进行切片
df.loc['A','Python'] # 12 # 选取标量值第三节 位置选择
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,150,size = [10,3]), # 计算机科目成绩
index = list('ABCDEFGHIJ'),# 行标签
columns=['Python','Tensorflow','Keras']) # 列标签
df.iloc[4] # 用整数位置选择。
df.iloc[2:8,0:2] # 用整数切片,类似NumPy
df.iloc[[1,3,5],[0,2,1]] # 整数列表按位置切片
df.iloc[1:3,:] # 行切片
df.iloc[:,:2] # 列切片
df.iloc[0,2] # 选取标量值
第四节 boolean索引
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,150,size = [10,3]), # 计算机科目成绩
index = list('ABCDEFGHIJ'),# 行标签,用户
columns=['Python','Tensorflow','Keras']) # 考试科目
cond1 = df.Python > 100 # 判断Python分数是否大于100,返回值是boolean类型的Series
df[cond1] # 返回Python分数大于100分的用户所有考试科目数据
cond2 = (df.Python > 50) & (df['Keras'] > 50) # &与运算
df[cond2] # 返回Python和Keras同时大于50分的用户的所有考试科目数据
df[df > 50] # 选择DataFrame中满足条件的值,如果满足返回值,不然返回空数据NaN
df[df.index.isin(['A','C','F'])] # isin判断是否在数组中,返回也是boolean类型值
第五节 赋值操作
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,150,size = [10,3]),# 计算机科目成绩
index = list('ABCDEFGHIJ'),# 行标签,用户
columns=['Python','Tensorflow','Keras']) # 考试科目
s = pd.Series(data = np.random.randint(0,150,size = 9),
index=list('BCDEFGHIJ'), name = 'PyTorch')
df['PyTorch'] = s # 增加一列,DataFrame行索引自动对齐
df.loc['A','Python'] = 256 # 按标签赋值
df.iloc[3,2] = 512 # 按位置赋值
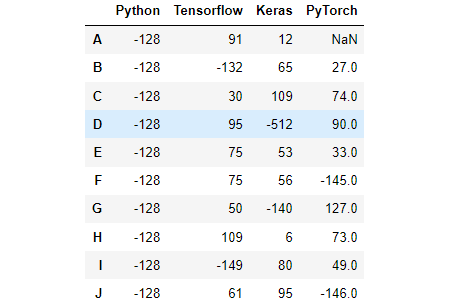
df.loc[:,'Python'] = np.array([128]*10) # 按NumPy数组进行赋值
df[df >= 128] = -df # 按照where条件进行赋值,大于等于128变成原来的负数,否则不变效果:
第六部分 数据集成
pandas 提供了多种将 Series、DataFrame 对象组合在一起的功能.
第一节 concat数据串联
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,150,size = [10,3]), # 计算机科目成绩
index = list('ABCDEFGHIJ'), # 行标签,用户
columns=['Python','Tensorflow','Keras']) # 考试科目
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,150,size = [10,3]), # 计算机科目成绩
index = list('KLMNOPQRST'), # 行标签,用户
columns=['Python','Tensorflow','Keras']) # 考试科目
df3 = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,150,size = (10,2)),
index = list('ABCDEFGHIJ'),
columns=['PyTorch','Paddle'])
pd.concat([df1,df2],axis = 0) # df1和df2行串联,df2的行追加df2行后面
df1.append(df2) # 在df1后面追加df2
pd.concat([df1,df3],axis = 1) # df1和df2列串联,df2的列追加到df1列后面
第二节 插入
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,151,size = (10,3)),
index = list('ABCDEFGHIJ'),
columns = ['Python','Keras','Tensorflow'])
df.insert(loc = 1,column='Pytorch',value=1024) # 插入列
# 对行的操作,使用追加append,默认在最后面,无法指定位置
# 如果想要在指定位置插入行:切割-添加-合并
第三节 Join SQL风格合并
数据集的 合并(merge)或连接(join) 运算是通过一个或者多个键将数据链接起来的。这些运算是关系型数据库的核心操作。pandas的merge函数是数据集进行join运算的主要切入点。
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# 表一中记录的是name和体重信息
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data = {'name':['softpo','Daniel','Brandon','Ella'],
'weight':[70,55,75,65]})
# 表二中记录的是name和身高信息
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data = {'name':['softpo','Daniel','Brandon','Cindy'],
'height':[172,170,170,166]})
df3 = pd.DataFrame(data = {'名字':['softpo','Daniel','Brandon','Cindy'],
'height':[172,170,170,166]})
# 根据共同的name将俩表的数据,进行合并
pd.merge(df1,df2, # 结果为交集, 6数据
how = 'inner', # 内合并代表两对象交集
on = 'name')
pd.merge(df1,df3, # 数据量较大
how = 'outer', # 全外连接,两对象并集
left_on = 'name', # 左边DataFrame使用列标签 name进行合并
right_on = '名字') # 右边DataFrame使用列标签 名字进行合并
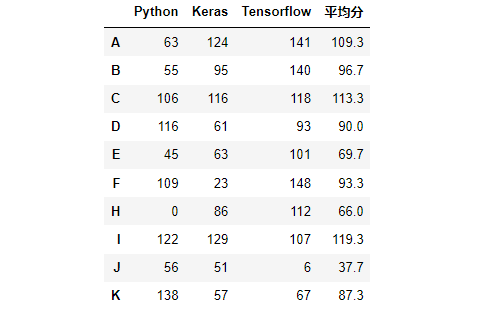
# 创建10名学生的考试成绩
df4 = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,151,size = (10,3)),
index = list('ABCDEFHIJK'),
columns=['Python','Keras','Tensorflow'])
# 计算每位学生各科平均分,转换成DataFrame
score_mean = pd.DataFrame(df4.mean(axis = 1).round(1),columns=['平均分'])
# 将平均分和df4使用merge进行合并,它俩有共同的行索引
pd.merge(left = df4,right = score_mean,
left_index=True,# 左边DataFrame使用行索引进行合并
right_index=True)# 右边的DataFrame使用行索引进行合并效果:
第七部分 数据清洗
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data = {'color':['red','blue','red','green','blue',None,'red'],
'price':[10,20,10,15,20,0,np.NaN]})
# 1、重复数据过滤
df.duplicated() # 判断是否存在重复数据
df.drop_duplicates() # 删除重复数据
# 2、空数据过滤
df.isnull() # 判断是否存在空数据,存在返回True,否则返回False
df.dropna(how = 'any') # 删除空数据
df.fillna(value=1111) # 填充空数据
# 3、指定行或者列过滤
del df['color'] # 直接删除某列
df.drop(labels = ['price'], axis = 1) # 删除指定列
df.drop(labels = [0,1,5],axis = 0) # 删除指定行
# 4、函数filter使用,过滤器,删除
df = pd.DataFrame(np.array(([3,7,1], [2, 8, 256])),
index=['dog', 'cat'],
columns=['China', 'America', 'France'])
df.filter(items=['China', 'France'])
# 根据正则表达式删选列标签
df.filter(regex='a$', axis=1)
# 选择行中包含og
df.filter(like='og', axis=0)
# 5、异常值过滤
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randn(10000,3)) # 正态分布数据
# 3σ过滤异常值,σ即是标准差
cond = (df2 > 3*df2.std()).any(axis = 1)
index = df2[cond].index # 不满足条件的行索引
df2.drop(labels=index,axis = 0) # 根据行索引,进行数据删除第八部分 数据转换
第一节 轴和元素替换
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,10,size = (10,3)),
index = list('ABCDEFHIJK'),
columns=['Python','Tensorflow','Keras'])
df.iloc[4,2] = None # 空数据
''' 1、重命名轴索引 '''
df.rename(index = {'A':'AA','B':'BB'},columns = {'Python':'人工智能'})
# 2、替换值
df.replace(3,1024) # 将3替换为1024
df.replace([0,7],2048) # 将0和7替换为2048
df.replace({0:512,np.nan:998}) # 根据字典键值对进行替换
df.replace({'Python':2},-1024) # 将Python这一列中等于2的,替换为-1024第二节 map Series元素改变
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,10,size = (10,3)),
index = list('ABCDEFHIJK'),
columns=['Python','Tensorflow','Keras'])
df.iloc[4,2] = None # 空数据
# 1、map批量元素改变,Series专有
df['Keras'].map({1:'Hello',5:'World',7:'AI'}) # 字典映射
df['Python'].map(lambda x:True if x >=5 else False) # 隐式函数映射
def convert(x): # 显示函数映射
if x%3 == 0:
return True
elif x%3 == 1:
return False
df['Tensorflow'].map(convert)第三节 apply元素改变 (既支持 Series,也支持 DataFrame)
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,10,size = (10,3)),
index = list('ABCDEFHIJK'),
columns=['Python','Tensorflow','Keras'])
df.iloc[4,2] = None # 空数据
# 1、apply 应用方法数据转换,通用
# Series,其中x是Series中元素
df['Keras'].apply(lambda x:True if x >5 else False)
# DataFrame,其中的x是DataFrame中列或者行,是Series
df.apply(lambda x : x.median(),axis = 0) # 列的中位数
def convert(x): # 自定义方法
return (x.mean().round(1), x.count())
df.apply(convert,axis = 1) # 行平均值,计数
# 2、applymap DataFrame专有
df.applymap(lambda x : x + 100) # 计算DataFrame中每个元素第四节 transform变形金刚
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,10,size = (10,3)),
index = list('ABCDEFHIJK'),
columns=['Python','Tensorflow','Keras'])
df.iloc[4,2] = None # 空数据
# 1、一列执行多项计算
df['Python'].transform([np.sqrt,np.exp]) # Series处理
def convert(x):
if x.mean() > 5:
x *= 10
else:
x *= -10
return x
# 2、多列执行不同计算
df.transform({'Python':convert,'Tensorflow':np.max,'Keras':np.min}) # DataFrame处理
第五节 重排随机抽样哑变量
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,10,size = (10,3)),
index = list('ABCDEFHIJK'),
columns=['Python','Tensorflow','Keras'])
ran = np.random.permutation(10) # 随机重排
df.take(ran) # 重排DataFrame
df.take(np.random.randint(0,10,size = 15)) # 随机抽样
# 哑变量,独热编码,1表示有,0表示没有
df = pd.DataFrame({'key':['b','b','a','c','a','b']})
pd.get_dummies(df,prefix='',prefix_sep='')
第九部分 数据重塑
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,100,size = (10,3)),
index = list('ABCDEFHIJK'),
columns=['Python','Tensorflow','Keras'])
df.T # 转置
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,100,size = (20,3)),
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_product([list('ABCDEFHIJK'),
['期中','期末']]),#多层索引
columns=['Python','Tensorflow','Keras'])
df2.unstack(level = -1) # 行旋转成列,level指定哪一层,进行变换
df2.stack() # 列旋转成行
df2.stack().unstack(level = 1) # 行列互换
# 多层索引DataFrame数学计算
df2.mean() # 各学科平均分
df2.mean(level=0) # 各学科,每个人期中期末平均分
df2.mean(level = 1) # 各学科,期中期末所有人平均分第十部分 数学和统计方法
第一节 简单统计指标
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,100,size = (20,3)),
index = list('ABCDEFHIJKLMNOPQRSTU'),
columns=['Python','Tensorflow','Keras'])
# 1、简单统计指标
df.count() # 非NA值的数量
df.max(axis = 0) #轴0最大值,即每一列最大值
df.min() #默认计算轴0最小值
df.median() # 中位数
df.sum() # 求和
df.mean(axis = 1) #轴1平均值,即每一行的平均值
df.quantile(q = [0.2,0.4,0.8]) # 分位数
df.describe() # 查看数值型列的汇总统计,计数、平均值、标准差、最小值、四分位数、最大值
第二节 索引标签、位置获取
# 2、索引位置
df['Python'].argmin() # 计算最小值位置
df['Keras'].argmax() # 最大值位置
df.idxmax() # 最大值索引标签
df.idxmin() # 最小值索引标签
第三节 更多统计指标
# 3、更多统计指标
df['Python'].value_counts() # 统计元素出现次数
df['Keras'].unique() # 去重
df.cumsum() # 累加
df.cumprod() # 累乘
df.std() # 标准差
df.var() # 方差
df.cummin() # 累计最小值
df.cummax() # 累计最大值
df.diff() # 计算差分
df.pct_change() # 计算百分比变化
# 4、高级统计指标
df.cov() # 属性的协方差
df['Python'].cov(df['Keras']) # Python和Keras的协方差
df.corr() # 所有属性相关性系数
df.corrwith(df['Tensorflow']) # 单一属性相关性系数
第十一部分 数据排序
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,30,size = (30,3)),
index = list('qwertyuioijhgfcasdcvbnerfghjcf'),
columns = ['Python','Keras','Pytorch'])
# 1、索引列名排序
df.sort_index(axis = 0,ascending=True) # 按索引排序,降序
df.sort_index(axis = 1,ascending=False) #按列名排序,升序
# 2、属性值排序
df.sort_values(by = ['Python']) #按Python属性值排序
df.sort_values(by = ['Python','Keras'])#先按Python,再按Keras排序
# 3、返回属性n大或者n小的值
df.nlargest(10, columns='Keras') # 根据属性Keras排序,返回最大10个数据
df.nsmallest(5, columns='Python') # 根据属性Python排序,返回最小5个数据
第十二部分 分箱操作
- 分箱操作就是将连续数据转换为分类对应物的过程。比如将连续的身高数据划分为:矮中高。
- 分箱操作分为等距分箱和等频分箱。
- 分箱操作也叫面元划分或者离散化。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(data = np.random.randint(0,150,size = (100,3)),
columns=['Python','Tensorflow','Keras'])
# 1、等宽分箱
pd.cut(df.Python,bins = 3)
# 指定宽度分箱
pd.cut(df.Keras, # 分箱数据
bins = [0,60,90,120,150], # 分箱断点
right = False, # 左闭右开
labels=['不及格','中等','良好','优秀']) # 分箱后分类
# 2、等频分箱
pd.qcut(df.Python,q = 4,# 4等分
labels=['差','中','良','优']) # 分箱后分类
第十三部分 分组聚合
第一节 分组
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# 准备数据
df = pd.DataFrame(data = {'sex':np.random.randint(0,2,size = 300), # 0男,1女
'class':np.random.randint(1,9,size = 300),#1~8八个班
'Python':np.random.randint(0,151,size = 300),#Python成绩
'Keras':np.random.randint(0,151,size =300),#Keras成绩
'Tensorflow':np.random.randint(0,151,size=300),
'Java':np.random.randint(0,151,size = 300),
'C++':np.random.randint(0,151,size = 300)})
df['sex'] = df['sex'].map({0:'男',1:'女'}) # 将0,1映射成男女
# 1、分组->可迭代对象
# 1.1 先分组再获取数据
g = df.groupby(by = 'sex')[['Python','Java']] # 单分组
for name,data in g:
print('组名:',name)
print('数据:',data)
df.groupby(by = ['class','sex'])[['Python']] # 多分组
# 1.2 对一列值进行分组
df['Python'].groupby(df['class']) # 单分组
df['Keras'].groupby([df['class'],df['sex']]) # 多分组
# 1.3 按数据类型分组
df.groupby(df.dtypes,axis = 1)
# 1.4 通过字典进行分组
m = {'sex':'category','class':'category','Python':'IT','Keras':'IT',
'Tensorflow':'IT','Java':'IT','C++':'IT'}
for name,data in df.groupby(m,axis = 1):
print('组名',name)
print('数据',data)
第二节 分组聚合
# 2、分组直接调用函数进行聚合
# 按照性别分组,其他列均值聚合
df.groupby(by = 'sex').mean().round(1) # 保留1位小数
# 按照班级和性别进行分组,Python、Keras的最大值聚合
df.groupby(by = ['class','sex'])[['Python','Keras']].max()
# 按照班级和性别进行分组,计数聚合。统计每个班,男女人数
df.groupby(by = ['class','sex']).size()
# 基本描述性统计聚合
df.groupby(by = ['class','sex']).describe()
第三节 分组聚合apply、transform
# 3、分组后调用apply,transform封装单一函数计算
# 返回分组结果
df.groupby(by = ['class','sex'])[['Python','Keras']].apply(np.mean).round(1)
def normalization(x):
return (x - x.min())/(x.max() - x.min()) # 最大值最小值归一化
# 返回全数据,返回DataFrame.shape和原DataFrame.shape一样。
df.groupby(by = ['class','sex'])[['Python',
'Tensorflow']].transform(normalization).round(3)第四节 分组聚合agg
# 4、agg 多中统计汇总操作
# 分组后调用agg应用多种统计汇总
df.groupby(by = ['class','sex'])[['Tensorflow','Keras']].agg([np.max,np.min,pd.Series.count])
# 分组后不同属性应用多种不同统计汇总
df.groupby(by = ['class','sex'])[['Python','Keras']].agg({'Python':[('最大值',np.max),('最小值',np.min)],
'Keras':[('计数',pd.Series.count),('中位数',np.median)]})
# 5、透视表
# 透视表也是一种分组聚合运算
def count(x):
return len(x)
df.pivot_table(values=['Python','Keras','Tensorflow'],# 要透视分组的值
index=['class','sex'], # 分组透视指标
aggfunc={'Python':[('最大值',np.max)], # 聚合运算
'Keras':[('最小值',np.min),('中位数',np.median)],
'Tensorflow':[('最小值',np.min),('平均值',np.mean),('计数',count)]})
第十四部分 时间序列
第一节 时间戳操作
# 1、创建方法
pd.Timestamp('2020-8-24 12')# 时刻数据
pd.Period('2020-8-24',freq = 'M') # 时期数据
index = pd.date_range('2020.08.24',periods=5,freq = 'M') # 批量时刻数据
pd.period_range('2020.08.24',periods=5,freq='M') # 批量时期数据
ts = pd.Series(np.random.randint(0,10,size = 5),index = index) # 时间戳索引Series
# 2、转换方法
pd.to_datetime(['2020.08.24','2020-08-24','24/08/2020','2020/8/24'])
pd.to_datetime([1598582232],unit='s')
dt = pd.to_datetime([1598582420401],unit = 'ms') # 世界标准时间
dt + pd.DateOffset(hours = 8) # 东八区时间
dt + pd.DateOffset(days = 100) # 100天后日期
第二节 时间戳索引
index = pd.date_range("2020-8-24", periods=200, freq="D")
ts = pd.Series(range(len(index)), index=index)
# str类型索引
ts['2020-08-30'] # 日期访问数据
ts['2020-08-24':'2020-09-3'] # 日期切片
ts['2020-08'] # 传入年月
ts['2020'] # 传入年
# 时间戳索引
ts[pd.Timestamp('2020-08-30')]
ts[pd.Timestamp('2020-08-24'):pd.Timestamp('2020-08-30')] # 切片
ts[pd.date_range('2020-08-24',periods=10,freq='D')]
# 时间戳索引属性
ts.index.year # 获取年
ts.index.dayofweek # 获取星期几
ts.index.weekofyear # 一年中第几个星期几
第三节 时间序列常用方法
在做时间序列相关的工作时,经常要对时间做一些移动/滞后、频率转换、采样等相关操作,我们来看下这些操作如何使用.
index = pd.date_range('8/1/2020', periods=365, freq='D')
ts = pd.Series(np.random.randint(0, 500, len(index)), index=index)
# 1、移动
ts.shift(periods = 2) # 数据后移
ts.shift(periods = -2) # 数据前移
# 日期移动
ts.shift(periods = 2,freq = pd.tseries.offsets.Day()) # 天移动
ts.tshift(periods = 1,freq = pd.tseries.offsets.MonthOffset()) #月移动
# 2、频率转换
ts.asfreq(pd.tseries.offsets.Week()) # 天变周
ts.asfreq(pd.tseries.offsets.MonthEnd()) # 天变月
ts.asfreq(pd.tseries.offsets.Hour(),fill_value = 0)
#天变小时,又少变多,fill_value为填充值
# 3、重采样
# resample表示根据日期维度进行数据聚合,可以按照分钟、小时、周、月、年等来作为日期维度
ts.resample('2W').sum() # 以2周为单位进行汇总
ts.resample('3M').sum().cumsum() # 以季度为单位进行汇总
# 4、DataFrame重采样
d = dict({'price': [10, 11, 9, 13, 14, 18, 17, 19],
'volume': [50, 60, 40, 100, 50, 100, 40, 50],
'week_starting':pd.date_range('24/08/2020',periods=8,freq='W')})
df1 = pd.DataFrame(d)
df1.resample('M',on = 'week_starting').apply(np.sum)
df1.resample('M',on = 'week_starting').agg({'price':np.mean,'volume':np.sum})
days = pd.date_range('1/8/2020', periods=4, freq='D')
data2 = dict({'price': [10, 11, 9, 13, 14, 18, 17, 19],
'volume': [50, 60, 40, 100, 50, 100, 40, 50]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data2,
index=pd.MultiIndex.from_product([days,['morning',
'afternoon']]))
df2.resample('D', level=0).sum()
第四节 时区表示
index = pd.date_range('8/1/2012 00:00', periods=5, freq='D')
ts = pd.Series(np.random.randn(len(index)), index)
import pytz
pytz.common_timezones # 常用时区
# 时区表示
ts = ts.tz_localize(tz='UTC')
# 转换成其它时区
ts.tz_convert(tz = 'Asia/Shanghai')