5.1配置IBGP和EBGP
5.2.1实验1:配置IBGP和EBGP
- 实验目的
- 熟悉IBGP和EBGP的应用场景
- 掌握IBGP和EBGP的配置方法
- 实验拓扑
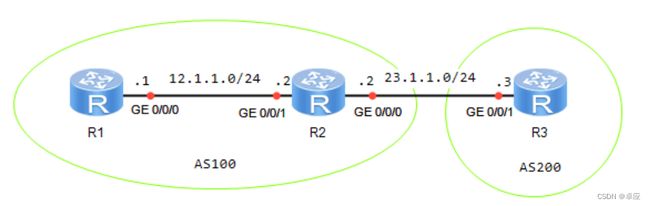
实验拓扑如图5-1所示:
图5-1:配置IBGP和EBGP
- 实验步骤
- IP地址的配置
R1的配置
Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[Huawei]undo info-center enable
[Huawei]sysname R1
[R1]interface g0/0/0
[R1-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip address 12.1.1.1 24
[R1-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]quit
[R1]interface LoopBack 0
[R1-LoopBack0]ip address 1.1.1.1 32
[R1-LoopBack0]quit
R2的配置
Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[Huawei]undo info-center enable
[Huawei]sysname R2
[R2]interface g0/0/1
[R2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]ip address 12.1.1.2 24
[R2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]quit
[R2]interface g0/0/0
[R2-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip address 23.1.1.2 24
[R2-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]quit
[R2]interface LoopBack 0
[R2-LoopBack0]ip address 2.2.2.2 32
[R2-LoopBack0]quit
R3的配置
Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[Huawei]undo info-center enable
[Huawei]sysname R3
[R3]interface g0/0/1
[R3-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]ip address 23.1.1.3 24
[R3-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]quit
[R3]interface LoopBack0
[R3-LoopBack0]ip address 3.3.3.3 32
[R3-LoopBack0]quit
- 配置IGP:R1与R2运行OSPF协议
R1的配置
[R1]ospf router-id 1.1.1.1
[R1-ospf-1]area 0
[R1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]network 12.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[R1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
[R1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]quit
[R1-ospf-1]quit
R2的配置
[R2]ospf router-id 2.2.2.2
[R2-ospf-1]area 0
[R2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]network 12.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[R2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0
[R2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]quit
- 配置IBGP
R1的配置
[R1]bgp 100 //启动BGP进程,进程号为100
[R1-bgp]undo synchronization //关闭同步,默认配置
[R1-bgp]undo summary automatic //关闭自动汇总,默认配置
[R1-bgp]router-id 1.1.1.1 //设置BGP的router-id
[R1-bgp]peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100 //指定邻居和邻居的AS号
[R1-bgp]peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack 0 //用环回口建邻居
[R1-bgp]quit
R2的配置
[R2]bgp 100
[R2-bgp]undo synchronization
[R2-bgp]undo summary automatic
[R2-bgp]bgp
[R2-bgp]router-id 2.2.2.2
[R2-bgp]peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100
[R2-bgp]peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack 0
[R2-bgp]quit
- 配置EBGP
R2的配置
[R2]bgp 100
[R2-bgp]peer 23.1.1.3 as-number 200 //EBGP用直连接口建邻居
R3的配置
[R3]bgp 200
[R3-bgp]undo synchronization
[R3-bgp]undo summary automatic
[R3-bgp]peer 23.1.1.2 as-number 100
[R3-bgp]quit
【技术要点】配置BGP对等体关系的建议
- IBGP用环回口建邻居
- EBGP用直连建邻居
- 如果EBGP用环回口建邻居必须配置peer ebgp-max-hop命令
- 实验调试
- 查看TCP连接
TCPCB Tid/Soid Local Add:port Foreign Add:port VPNID State
1d322414 59 /1 0.0.0.0:23 0.0.0.0:0 -1 Listening
172ede3c 107/2 0.0.0.0:179 2.2.2.2:0 0 Listening
172ed4fc 107/36 1.1.1.1:179 2.2.2.2:65309 0 Established
通过以上可以看到,TCP连接是成功的
- 查看对等体的状态
BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.1 // BGP本地Router ID
Local AS number : 100 //本地AS编号
Total number of peers : 1 Peers in established state : 1
//对等体总个数 //处于建立状态的对等体个数
Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv
2.2.2.2 4 100 146 147 0 02:24:44 Established 0
以上输出邻居表的各个字段的含义如下:
- Peer:对等体的IP地址
- V :对等体使用的BGP版本
- AS:自治系统号
- MsgRcvd:接收的信息统计数
- MsgSent:发送的信息统计数
- OutQ:等待发往指定对等体的消息
- Up/Down:邻居关系建立的时间
- State:邻居的状态
- PrefRcv:本端从对等体上收到路由前缀的数目
(3)在R3上用network宣告的方式产生一条BGP路由、在R1上引入的方式产生一条BGP路由
R3 的配置
[R3]bgp 200
[R3-bgp]network 3.3.3.3 32
[R3-bgp]quit
R1的配置
[R1]bgp 100
[R1-bgp]import-route ospf 1
【技术要点】
BGP路由生成有三种方式:
- Network
- Import-route
- 与IGP协议相同,BGP支持根据已有的路由条目进行聚合,生成聚合路由。
(4)在R1上查看路由表
[R1]display bgp routing-table
BGP Local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped,
h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale
Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Total Number of Routes: 4
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
*> 1.1.1.1/32 0.0.0.0 0 0 ?
*> 2.2.2.2/32 0.0.0.0 1 0 ?
i 3.3.3.3/32 23.1.1.3 0 100 0 200i
*> 12.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 ?
以上输出中,路由条目表项的状态码解析如下:
- *代表路由条目有效
- >代表路由条目最优,可以被传递,只有下一跳可达路由才会最优
- i代表路由是从IBGP学到的
- Networkw:显示BGP路由表中的网络地址
- NextHop:报文发送的下一跳地址
- MED :路由度量值
- LocPrf :本地优先级
- PrefVal : 协议首选值
- Path/Ogn:显示AS路径号及Origin属性
以上输出我们可以发现3.3.3.3不是最优的,如果不优就不会在加载进全局路由表,也不会传给其它路由器,本例不优的原因为下一跳不可达,解决办法如下:
R2的配置
[R2]bgp 100
[R2-bgp]peer 1.1.1.1 next-hop-local //配置下一跳本地
[R2-bgp]quit
(5)再查看R1的路由表
[R1]display bgp routing-table
BGP Local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped,
h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale
Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Total Number of Routes: 4
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
*> 1.1.1.1/32 0.0.0.0 0 0 ?
*> 2.2.2.2/32 0.0.0.0 1 0 ?
*>i 3.3.3.3/32 2.2.2.2 0 100 0 200i
*> 12.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 ?
【技术要点】
什么情况下配置下一跳本地:
对从EBGP邻居收到的路由,在传给IBGP邻居时,修改下一跳地址为本地的connet interface。
(6)查看R2的BGP路由表
BGP Local router ID is 2.2.2.2
Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped,
h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale
Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Total Number of Routes: 4
Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn
i 1.1.1.1/32 1.1.1.1 0 100 0 ?
*>i 2.2.2.2/32 1.1.1.1 1 100 0 ?
*> 3.3.3.3/32 23.1.1.3 0 0 200i
*>i 12.1.1.0/24 1.1.1.1 0 100 0 ?
通过以上输出,我们可以发现1.1.1.1这条路由虽然下一跳可达,但是不是有效和最优的,其原因为:如果IGP表里面宣告了这条路由,然后再在IBGP里面,路由只能本地有效。