浅谈Spring中事务管理器
由于事务部分代码在设计上整体比较简单,我自己觉得它在设计上没有什么特别让我眼前一亮的东西,所以下文更多的是侧重执行流程,能理解事务管理器等一众概念以及相关的变量含义,真正遇到Bug会调试,知道在什么地方打断点就行。
后文更多的是代码+注释的形式呈现(注意,而且根据Spring的不同版本,代码实现上也略有差异),请配合自己项目源码慢慢食用。
文章目录
-
- 一、@EnableTransactionManagement
- 二、TransactionInterceptor
-
- 1、invokeWithinTransaction
- 2、createTransactionIfNecessary
- 3、commitTransactionAfterReturning
- 三、getTransaction
-
- 1、doGetTransaction
- 2、isExistingTransaction
- 3、handleExistingTransaction
- 4、suspend
- 5、doBegin
- 6、prepareSynchronization
一、@EnableTransactionManagement
利用Spring的特性和扩展接口完成Bean的注入,该注入方式也常用于一些分布式中间件的整合
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector.class)
public @interface EnableTransactionManagement {
}
1、使用@EnableTransactionManagement,解析@Import注解上的信息
2、TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector实现了AdviceModeImportSelector扩展类,达到注解Bean的效果
3、如果使用默认形式代理,则会初始化类ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration,在该类的主要作用是初始化一个advisor。熟悉AOP的小伙伴应该都知道,Spring中的事务是基于AOP的,为什么这么说呢,因为Spring在解析AOP相关的逻辑的时候是将所有的切面都解析为一个advisor,然后将所有的advisor串起来,递归调用。而此处事务要做的也就是初始化这个么一个advisor对象,然后添加到AOP的递归调用链中(实例化过程参考下图)
4、所以问题的关键就来到了setAdvice这个属性上(AOP的概念)
二、TransactionInterceptor
@Transactional注解对应的advice切面类为TransactionInterceptor类
- TransactionInterceptor实现了MethodInterceptor(该接口是AOP的接口,执行AOP逻辑的时候会触发相关的回调)
- 常规的afterAdvice、beforeAdvice都是切面的增强逻辑,MethodAdvice是切面逻辑。即TransactionInterceptor类中的invoke方法,就是代理逻辑。,所以我们直接看invoke方法
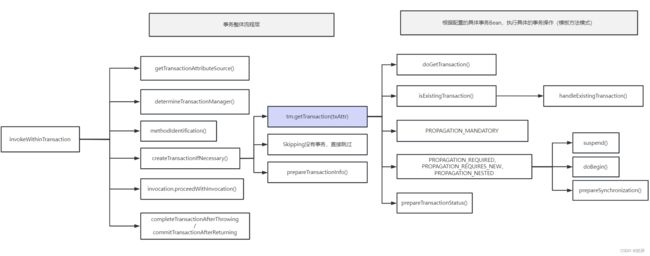
该部分的整体执行流程如下图所示,这里对应的就是代码的创建事务,提交事务,遇到异常回滚事务的逻辑。
1、invokeWithinTransaction
@Nullable
// 方法执行到这了这一步,说明类上有@Transactional注解
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
// 获取@Transactional注解中配置的值
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
// 获取配置的事务管理器对象
final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
// joinpoint的唯一标识,就是当前正在执行的方法名字
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
// 如果有必要就要创建事务,这里涉及到事务的传播机制实现
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
// 具体的业务逻辑
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
// 发生异常,事务回滚
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
// 正常结束,事务提交
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
else {
Object result;
final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder();
// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.
try {
result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) tm).execute(txAttr, status -> {
TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
try {
return invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {
// A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback.
if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
else {
throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);
}
}
else {
// A normal return value: will lead to a commit.
throwableHolder.throwable = ex;
return null;
}
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
});
}
catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) {
throw ex.getCause();
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
ex2.initApplicationException(throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
catch (Throwable ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
// Check result state: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow.
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
throw throwableHolder.throwable;
}
return result;
}
}
2、createTransactionIfNecessary
protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm,
@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) {
// If no name specified, apply method identification as transaction name.
if (txAttr != null && txAttr.getName() == null) {
txAttr = new DelegatingTransactionAttribute(txAttr) {
@Override
public String getName() {
return joinpointIdentification;
}
};
}
// 每个逻辑事务都会创建一个TransactionStatus,但是TransactionStatus中有一个属性代表当前逻辑事务底层的物理事务是不是最新的
TransactionStatus status = null;
if (txAttr != null) {
if (tm != null) {
// 开启事务
// status:含有挂起资源的对象
status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr);
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping transactional joinpoint [" + joinpointIdentification +
"] because no transaction manager has been configured");
}
}
}
return prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
}
3、commitTransactionAfterReturning
以常见的DataSourceTransactionManager为例,进入txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus())方法,核心代码如下
@Override
public final void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
if (status.isCompleted()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Transaction is already completed - do not call commit or rollback more than once per transaction");
}
DefaultTransactionStatus defStatus = (DefaultTransactionStatus) status;
// 可以通过TransactionAspectSupport.currentTransactionStatus().setRollbackOnly() 来设置
// 事务本来是可以要提交的,但是可以强制回滚
// 我们业务逻辑报错,设置事务回滚,设置backOnly就是在这个位置进行判定的
if (defStatus.isLocalRollbackOnly()) {
if (defStatus.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Transactional code has requested rollback");
}
processRollback(defStatus, false);
return;
}
// 判断此事务在之前是否设置了需要回滚,跟globalRollbackOnParticipationFailure有关
if (!shouldCommitOnGlobalRollbackOnly() && defStatus.isGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
if (defStatus.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Global transaction is marked as rollback-only but transactional code requested commit");
}
processRollback(defStatus, true);
return;
}
// 提交
processCommit(defStatus);
}
processCommit
private void processCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
try {
boolean beforeCompletionInvoked = false;
try {
boolean unexpectedRollback = false;
prepareForCommit(status);
// 拿到相关的同步器,完成同步器终得额外的业务逻辑
// 提交前的方法
triggerBeforeCommit(status);
// 完成前的方法(回滚的地方也会调用该方法,回滚也算是完成)
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
beforeCompletionInvoked = true;
if (status.hasSavepoint()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Releasing transaction savepoint");
}
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
status.releaseHeldSavepoint();
}
// 当前事务是自己新建的,才能提交,否则什么都不做
else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Initiating transaction commit");
}
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
// 提交事务
doCommit(status);
}
else if (isFailEarlyOnGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
unexpectedRollback = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
}
// Throw UnexpectedRollbackException if we have a global rollback-only
// marker but still didn't get a corresponding exception from commit.
if (unexpectedRollback) {
throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(
"Transaction silently rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");
}
}
catch (UnexpectedRollbackException ex) {
// can only be caused by doCommit
// 事务同步器,完成后回调接口
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK);
throw ex;
}
catch (TransactionException ex) {
// can only be caused by doCommit
if (isRollbackOnCommitFailure()) {
doRollbackOnCommitException(status, ex);
}
else {
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);
}
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
if (!beforeCompletionInvoked) {
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
}
doRollbackOnCommitException(status, ex);
throw ex;
}
// Trigger afterCommit callbacks, with an exception thrown there
// propagated to callers but the transaction still considered as committed.
try {
// 触发提交后回调接口
triggerAfterCommit(status);
}
finally {
// 事务同步器,完成后回调接口
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_COMMITTED);
}
}
finally {
// 完成后清理,含有挂起前一个事务的,恢复。将之前挂起的对象,又绑定到当前对象
cleanupAfterCompletion(status);
}
}
三、getTransaction
同样还是以DataSourseTransactionManager实现为例。该部分可以理解为spring-tx提供了一个事务的基础模板,用于规范事务的执行框架,但是对于事务具体的一些对象创建,如事务管理器、事务ConnectionHolder则根据项目使用的ORM框架决定,整体骨架是一个典型的模板方法模式。
1、doGetTransaction
@Override
protected Object doGetTransaction() {
// 1、新创建一个dataSourceTransaction对象
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = new DataSourceTransactionObject();
txObject.setSavepointAllowed(isNestedTransactionAllowed());
// 2、根据当前的datasource对象,去我们的ThrealLocalMap中获取对应的ConnextionHolder对象
ConnectionHolder conHolder =
(ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(obtainDataSource());
// 3、把获取到的ConnextionHolder对象,设置到创建出来的DataSourceTransactionObject对象上
// false表示当前的conHolder对象不是新建的,是我们从ThrealLocal中直接拿的
txObject.setConnectionHolder(conHolder, false);
return txObject;
}
2、isExistingTransaction
@Override
protected boolean isExistingTransaction(Object transaction) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
// 判断对应的连接holder上是否存在事务
return (txObject.hasConnectionHolder() && txObject.getConnectionHolder().isTransactionActive());
}
3、handleExistingTransaction
private TransactionStatus handleExistingTransaction(
TransactionDefinition definition, Object transaction, boolean debugEnabled)
throws TransactionException {
// 由于这个方法是在存在事务的判定方法里面,所以如果传播行为是never则会直接抛异常
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NEVER) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never'");
}
// 该注解的形式,数据库连接不会再开一个(因为没有deBegin),但是相关的事物信息会重新设置一遍,这里也会将之前的事务信息进行挂起,然后将新的事务信息完善到新的对象上
// 此时,如果需要执行sql,就会由对应的事务管理器自己去创建数据库连接对象
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Suspending current transaction");
}
// 把当前事务挂起,其中就会把数据库连接对象从ThrealLocal中移除
Object suspendedResources = suspend(transaction);
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
return prepareTransactionStatus(
definition, null, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
}
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Suspending current transaction, creating new transaction with name [" +
definition.getName() + "]");
}
// 把当前事务挂起
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(transaction);
try {
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
// 开启事务
doBegin(transaction, definition);
// 初始化相关的属性
prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
return status;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error beginEx) {
// 发生异常,设置相关参数信息
resumeAfterBeginException(transaction, suspendedResources, beginEx);
throw beginEx;
}
}
// 此时,仅仅保存一个savePoint点
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
if (!isNestedTransactionAllowed()) {
throw new NestedTransactionNotSupportedException(
"Transaction manager does not allow nested transactions by default - " +
"specify 'nestedTransactionAllowed' property with value 'true'");
}
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating nested transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]");
}
if (useSavepointForNestedTransaction()) {
// Create savepoint within existing Spring-managed transaction,
// through the SavepointManager API implemented by TransactionStatus.
// Usually uses JDBC 3.0 savepoints. Never activates Spring synchronization.
DefaultTransactionStatus status =
prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, false, debugEnabled, null);
status.createAndHoldSavepoint();
return status;
}
else {
// Nested transaction through nested begin and commit/rollback calls.
// Usually only for JTA: Spring synchronization might get activated here
// in case of a pre-existing JTA transaction.
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
doBegin(transaction, definition);
prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
return status;
}
}
// Assumably PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS or PROPAGATION_REQUIRED.
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Participating in existing transaction");
}
if (isValidateExistingTransaction()) {
if (definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT) {
Integer currentIsolationLevel = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel();
if (currentIsolationLevel == null || currentIsolationLevel != definition.getIsolationLevel()) {
Constants isoConstants = DefaultTransactionDefinition.constants;
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" +
definition + "] specifies isolation level which is incompatible with existing transaction: " +
(currentIsolationLevel != null ?
isoConstants.toCode(currentIsolationLevel, DefaultTransactionDefinition.PREFIX_ISOLATION) :
"(unknown)"));
}
}
if (!definition.isReadOnly()) {
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" +
definition + "] is not marked as read-only but existing transaction is");
}
}
}
// 默认的传播机制(@Transactional注解的嵌套,相当于什么都没干),仅设置相关的参数状态
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}
4、suspend
@Nullable
protected final SuspendedResourcesHolder suspend(@Nullable Object transaction) throws TransactionException {
// synchronizations是一个ThrealLocal>
// 我们可以在任何地方,通过TransactionSynchronizationManager给当前线程添加TransactionSynchronization
// 这个判断可以理解为,如果创建过事务就不会为null。因为第一次进来的时候就是null,当我们创建过事务后,就会调用init方法
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
// 调用TransactionSynchronization的suspend方法,并清空和返回当前线程中所有的TransactionSynchronization对象
List<TransactionSynchronization> suspendedSynchronizations = doSuspendSynchronization();
try {
Object suspendedResources = null;
if (transaction != null) {
// 挂起事务,把transaction中的connection清空,并把resources中的key-value进行移除,并返回数据库连接connection对象
suspendedResources = doSuspend(transaction);
}
// 获取并清空当前线程中关于TransactionSynchronizationManage的设置
String name = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionName();
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionName(null);
boolean readOnly = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly();
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionReadOnly(false);
Integer isolationLevel = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel();
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel(null);
boolean wasActive = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isActualTransactionActive();
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setActualTransactionActive(false);
// 将当前线程中的数据库连接对象,TransactionSynchronizationManage对象、TransactionSynchronization对象终得设置构造成一个对象
// 表示被挂起的资源持有对象,持有了当前线程中的事务对象、TransactionSynchronization对象
return new SuspendedResourcesHolder(
suspendedResources, suspendedSynchronizations, name, readOnly, isolationLevel, wasActive);
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
// doSuspend failed - original transaction is still active...
doResumeSynchronization(suspendedSynchronizations);
throw ex;
}
}
else if (transaction != null) {
// Transaction active but no synchronization active.
Object suspendedResources = doSuspend(transaction);
return new SuspendedResourcesHolder(suspendedResources);
}
else {
// Neither transaction nor synchronization active.
return null;
}
}
5、doBegin
@Override
protected void doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
Connection con = null;
try {
// 如果当前线程中所使用的DataSource还没有创建过数据库连接,就获取一个新的数据库连接
if (!txObject.hasConnectionHolder() ||
txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) {
Connection newCon = obtainDataSource().getConnection();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Acquired Connection [" + newCon + "] for JDBC transaction");
}
txObject.setConnectionHolder(new ConnectionHolder(newCon), true);
}
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
// 根据@Transactional注解中的设置,设置Connection的readOnly与隔离界别
Integer previousIsolationLevel = DataSourceUtils.prepareConnectionForTransaction(con, definition);
txObject.setPreviousIsolationLevel(previousIsolationLevel);
// Switch to manual commit if necessary. This is very expensive in some JDBC drivers,
// so we don't want to do it unnecessarily (for example if we've explicitly
// configured the connection pool to set it already).
if (con.getAutoCommit()) {
txObject.setMustRestoreAutoCommit(true);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Switching JDBC Connection [" + con + "] to manual commit");
}
con.setAutoCommit(false);
}
prepareTransactionalConnection(con, definition);
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTransactionActive(true);
int timeout = determineTimeout(definition);
if (timeout != TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTimeoutInSeconds(timeout);
}
// Bind the connection holder to the thread.
// 这里判断,我们的这个conHolder是不是新建的(在外层如果是存在事务的情况下, 这个字段是false。当外层没有事务,才会进入该方法的上层方法,继而进入该方法,然后new一个对象,设置相关的参数未true)
// 往resource Map中添加数据
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(obtainDataSource(), txObject.getConnectionHolder());
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, obtainDataSource());
txObject.setConnectionHolder(null, false);
}
throw new CannotCreateTransactionException("Could not open JDBC Connection for transaction", ex);
}
}
6、prepareSynchronization
protected void prepareSynchronization(DefaultTransactionStatus status, TransactionDefinition definition) {
if (status.isNewSynchronization()) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setActualTransactionActive(status.hasTransaction());
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel(
definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT ?
definition.getIsolationLevel() : null);
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionReadOnly(definition.isReadOnly());
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionName(definition.getName());
TransactionSynchronizationManager.initSynchronization();
}
}