操作系统进程调度实验
实验2 进程调度
一、实验目的
进程调度是处理机管理的核心内容。本实验要求用高级程序设计语言编写和调试一个简单的进程调用程序,模拟完成进程控制及进程调度算法。进程控制包括进程的创建、阻塞、唤醒和撤销,进程调度算法包括先来先服务、优先级(包括动态和静态)和论证法。通过本实验可以使学生加深对进程控制块和进程队列的概念的理解,并了解循环轮转调度和优先级调度的实现方法。
二、实验内容
1.设计进程控制块PCB结构,PCB结构包括以下信息:进程ID,用户ID, 进程状态,进程优先数(或轮转时间片),进程创建时间,进程开始执行时间,进程执行完的时间,进程所占用的CPU时间,进程预计执行时间,进程剩余的执行时间等。
2.模拟实现进程调度算法,包括:RoundRobin(轮转法)、PRI(优先级法,包括静态和动态优先级)。
RoundRobin调度算法:其基本思想是让每个进程在就绪队列中的等待时间与享受服务的时间成一定的比例关系。系统给每一个进程分一段CPU时间,这段时间称为进程时间片。运行进程时间片用完后,系统将发生中断,强制该进程退出CPU,并释放相关资源,此进程进入就绪队列尾部等待CPU再次调度。
PRI调度算法:其基本思想是每个进程都有一个优先权,在进程调度时,系统选取优先级最高的进程占有CPU。在dynamicPRI调度算法中,随着运行进程的执行,系统将不断地重新评估其优先级。而在StaticPRI调度算法中,进程优先级初始化后直到进程执行完毕不再发生改变。PRI算法的核心是,一旦就绪进程中有更高优先级的进程时,立即发生高优先级中断。运行进程按优先级序列插入就绪队列等待,高优先级的进程被调度,占有CPU。
三、数据结构设计
进程控制块:系统中PCB块同操作系统中的PCB并不完全相同,考虑到调度算法的可行性问题,将PCB中的部分信息忽略,以简化算法;主要提取了进程描述和控制信息,这些是算法实现所必需的基本信息。
PCBSTRUCT
{
char Name[10];
int Proi;
int Round;
int CpuTime;
int NeedTime;
int Count;
char State; //状态
PCBSTRUCT* Next;
};
四、源码
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "string.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#define NUMBER 5
#define NULL 0
#define PCBSTRUCT struct PCBSTR
typedef PCBSTRUCT* PCB;
enum Algorithm { PR, RR };
char Means[3];
char b;
PCBSTRUCT
{
char Name[10];
int Proi;
int Round;
int CpuTime;
int NeedTime;
int Count;
char State; //状态
PCBSTRUCT* Next;
};
PCB Finish, Ready, Tail, Run;
void FirstIn()
{
Run = Ready;
Run->State = 'R';
Ready = Ready->Next;
}
void Print1()
{
if ((strcmp(Means, "PR") == 0) || (strcmp(Means, "pr") == 0))
printf("\n Name CpuTime NeedTime Pr ioprity State\n");
else
printf("\n Name CpuTime NeedTime Count Round State\n");
}
void Print2(PCB temp)
{
if ((strcmp(Means, "PR") == 0) || (strcmp(Means, "pr") == 0))
printf("%8s %6d %8d %10d %8c\n", temp->Name, temp->CpuTime,
temp->NeedTime, temp->Proi, temp->State);
else
printf("%8s %6d %8d %8d %8d %8c\n", temp->Name, temp->CpuTime,
temp->NeedTime, temp->Count, temp->Round, temp->State);
}
void print()
{
PCB p;
Print1();
printf("It's the Run queue\n");
if (Run != NULL)
Print2(Run);
p = Ready;
printf("It's the Ready queue\n");
while (p != NULL)
{
Print2(p);
p = p->Next;
}
printf("It's the Finished queue\n");
p = Finish;
while (p != NULL)
{
Print2(p);
p = p->Next;
}
printf("\n\n");
}
//按优先级从高到低插入就绪队列
void Insert1(PCB q)
{
PCBSTRUCT* p;
p = Ready;
if (q->Proi > p->Proi)
{
q->Next = p;
Ready = q;
p = q;
}
else {
while (p->Next != NULL)
{
if (q->Proi > p->Next->Proi)
{
q->Next = p->Next;
p->Next = q;
break;
}
else
p = p->Next;
}
if(p->Next==NULL)
p->Next = q;
}
}
void Insert2(PCB p2)
{
Tail->Next = p2;
Tail = p2;
p2->Next = NULL;
}
void Create(enum Algorithm alg)
{
PCB p;
int i, time, pr;
char Na[10];
Ready = NULL;
Finish = NULL;
Run = NULL;
if (alg == PR) //优先级调度
{
Ready = NULL;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
scanf("%s", Na);
scanf("%d", &pr);
scanf("%d", &time);
p = (PCB)malloc(sizeof(PCBSTRUCT));
strcpy(p->Name, Na);
p->CpuTime = 0;
p->NeedTime = time;
p->Proi = pr;
//p->Count = 0;
p->State = 'W';
//p->Round = 2;
if (Ready != NULL)
Insert1(p);
else
{
p->Next = Ready;
Ready = p;
Tail = p;
}
}
}
else //时间片轮转
{
Ready = NULL;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
scanf("%s", Na);
scanf("%d", &time);
p = (PCB)malloc(sizeof(PCBSTRUCT));
strcpy(p->Name, Na);
p->CpuTime = 0;
p->NeedTime = time;
p->Count = 0;
p->State = 'W';
p->Round = 2;
if (Ready != NULL)
Insert2(p);
else
{
p->Next = Ready;
Ready = p;
Tail = p;
}
}
}
if (alg == PR)
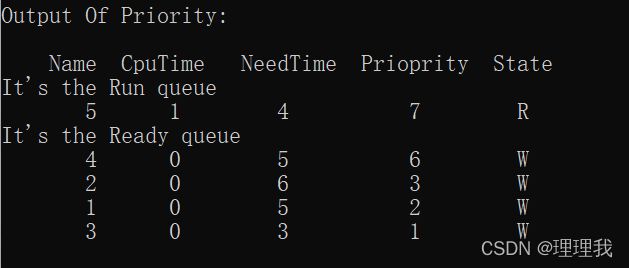
printf("Output Of Priority:\n");
else
printf("Output of RoundRobin:\n");
Run = Ready;
Ready = Ready->Next;
Run->State = 'R';
}
//这是优先级高者优先算法
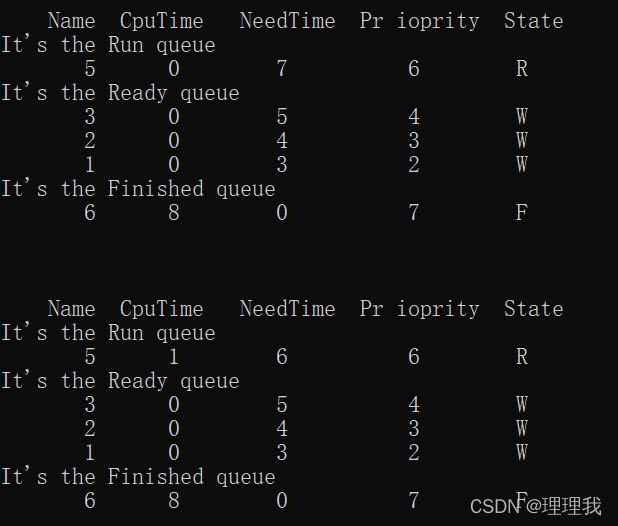
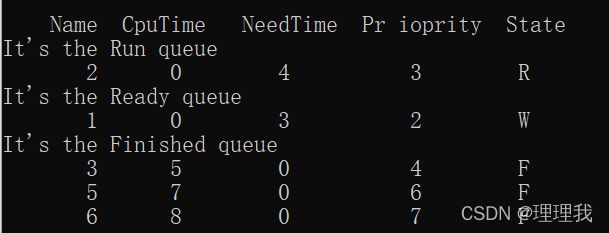
void PriSch()
{
while (Run != NULL)
{
Run->CpuTime = Run->CpuTime + 1;
Run->NeedTime = Run->NeedTime - 1;
//Run->Count = Run->Count + 1;
if (Run->NeedTime == 0)
{
Run->Next = Finish;
Finish = Run;
Run->State = 'F';
Run = NULL;
if (Ready != NULL)
FirstIn();
}
print();
getch();
}
}
void RoundSch()
{
while (Run != NULL)
{
Run->CpuTime = Run->CpuTime + 1;
Run->NeedTime = Run->NeedTime - 1;
Run->Count = Run->Count + 1;
if (Run->NeedTime == 0)
{
Run->Next = Finish;
Finish = Run;
Run->State = 'F';
Run = NULL;
if (Ready != NULL)
FirstIn();
}
else if (Run->Count == Run->Round)
{
Run->Count = 0;
if (Ready != NULL)
{
Run->State = 'W';
Insert2(Run);
FirstIn();
}
}
print();
getch();
}
}
void main()
{
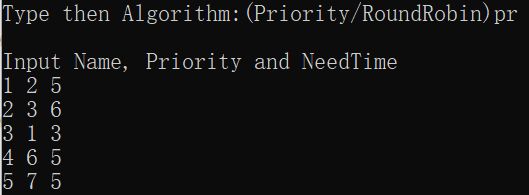
printf("Type then Algorithm:(Priority/RoundRobin)");
scanf("%s", Means);
printf("\nInput Name, Priority and NeedTime\n");
if ((strcmp(Means, "PR") == 0) || (strcmp(Means, "pr") == 0))
{
Create(PR);
PriSch();
}
else if ((strcmp(Means, "RR") == 0) || (strcmp(Means, "rr") == 0))
{
Create(RR);
RoundSch();
}
else
printf("Invalid Input!");
printf("\nIt's Finished!");
getch();
}