vue3源码study
基于尤雨溪手写mini-vue 版
一、整体工作流程
- 将视图模板编译为渲染函数
2、数据响应 模块
- 将数据对象初始化为响应式数据对象
3、视图渲染 模块
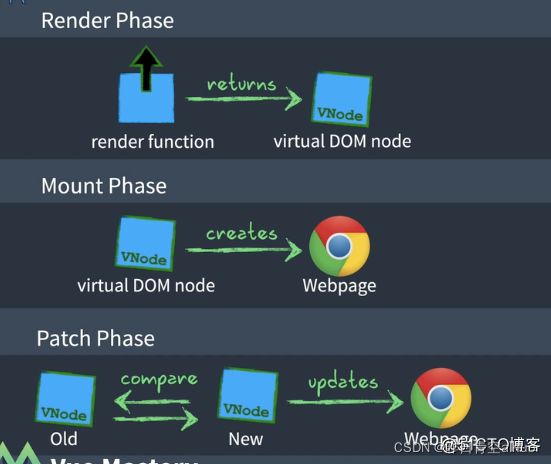
- RenderPhase : 渲染模块使用渲染函数根据初始化数据生成虚拟Dom
- MountPhase : 利用虚拟Dom创建视图页面Html
- PatchPhase:数据模型一旦变化渲染函数将再次被调用生成新的虚拟Dom,然后做Dom Diff更新视图Html
二、三大模块的分工
1、数据响应式模块
提供创建一切数据变化都是可以被监听的响应式对象的方法。
2、编译模块
这个编译过程可以在一下两个时刻执行
- 浏览器运行时 (runtime)
- Vue项目打包编译时 (compile time)
3、渲染函数
- Render Phase
- Mount Phase
- Patch Phase
三、MVVM原型(Mock版)
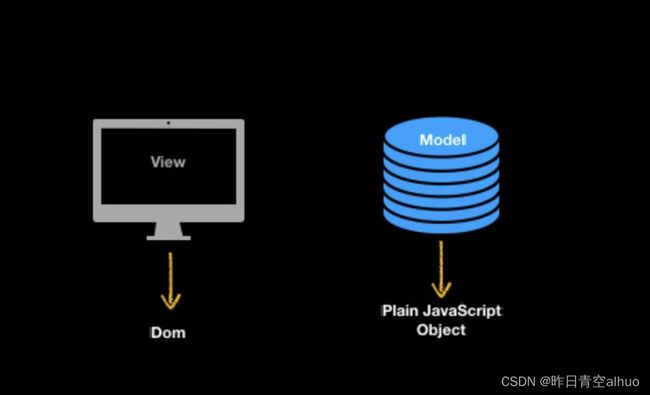
MVVM框架其实就是在原先的View和Model之间增加了一个VM层完成以下工作。完成数据与视图的监听。我们这一步先写一个Mock版本。其实就是先针对固定的视图和数据模型实现监听。
1、接口定义
我们MVVM的框架接口和Vue3一模一样。
初始化需要确定
- 视图模板
- 数据模型
- 模型行为 - 比如我们希望click的时候数据模型的message会会倒序排列。
const App = {
// 视图
template: `
`,
setup() {
// 数据劫持
const state = new Proxy(
{
message: "Hello Vue 3!!",
},
{
set(target, key, value, receiver) {
const ret = Reflect.set(target, key, value, receiver);
// 触发函数响应
// effective();
return ret;
},
}
);
const click = () => {
state.message = state.message.split("").reverse().join("");
};
return { state, click };
},
};
const { createApp } = Vue;
createApp(App).mount("#app");
2、程序骨架
const Vue = {
createApp(config) {
// 编译过程
const compile = (template) => (content, dom) => {
// 重新渲染
dom.innerText = "";
input = document.createElement("input");
input.addEventListener("keyup", function () {
content.state.message = this.value;
});
input.setAttribute("value", content.state.message);
dom.appendChild(input);
let button = dom.querySelector("button");
button = document.createElement("button");
button.addEventListener("click", () => {
return content.click.apply(content.state);
});
button.innerText = content.state.message;
dom.appendChild(button);
};
// 生成渲染函数
const render = compile(config.template);
return {
mount: function (container) {
const dom = document.querySelector(container);
const setupResult = config.setup();
effective = () => render(setupResult, dom);
render(setupResult, dom);
},
};
},
};
3、 编译渲染函数
MVVM框架中的渲染函数是会通过视图模板的编译建立的。
const compile = (template) => (content, dom) => {}
// 生成渲染函数
const render = compile(config.template);
简单的说就是对视图模板进行解析并生成渲染函数。
大概要处理以下三件事
- 确定哪些值需要根据数据模型渲染
- 绑定模型事件
- 确定哪些输入项需要双向绑定
四、数据响应实现
Vue普遍走的就是数据劫持方式。不同的在于使用DefineProperty还是Proxy。也就是一次一个属性劫持还是一次劫持一个对象。当然后者比前者听着就明显有优势。这也就是Vue3的响应式原理。
Proxy/Reflect是在ES2015规范中加入的,Proxy可以更好的拦截对象行为,Reflect可以更优雅的操纵对象。 优势在于
- 针对整个对象定制 而不是对象的某个属性,所以也就不需要对keys进行遍历。
- 支持数组,这个DefineProperty不具备。这样就省去了重载数组方法这样的Hack过程。
- Proxy 的第二个参数可以有 13 种拦截方法,这比起 - Object.defineProperty() 要更加丰富
- Proxy 作为新标准受到浏览器厂商的重点关注和性能优化,相比之下 Object.defineProperty() 是一个已有的老方法
- 可以通过递归方便的进行对象嵌套。
首先制造一个抽象的数据响应函数
/ 定义响应函数let effective
// 数据劫持
const state = new Proxy(
{
message: "Hello Vue 3!!",
},
{
set(target, key, value, receiver) {
const ret = Reflect.set(target, key, value, receiver);
// 触发函数响应
effective();
return ret;
},
}
);
在初始化的时候我们设置响应动作为渲染视图
const dom = document.querySelector(container);
const setupResult = config.setup();
debugger
effective = () => render(setupResult, dom);
视图变化的监听
浏览器视图的变化,主要体现在对输入项变化的监听上,所以只需要通过绑定监听事件就可以了。
input.addEventListener("keyup", function () {
content.state.message = this.value;
});
五、 视图渲染过程
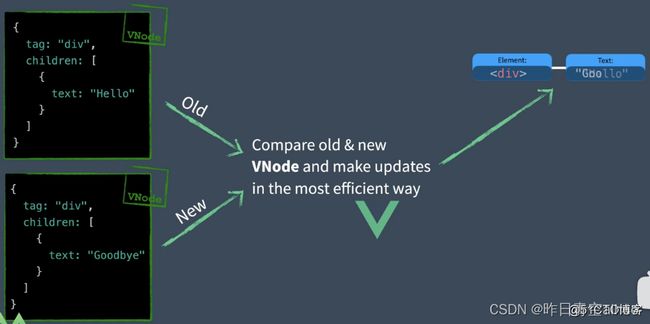
Dom => virtual DOM => render functions
虚拟Dom:用JS对象重新表示实际的Dom
在Vue中我们通过将视图模板(template)编译为渲染函数(render function)再转化为虚拟Dom
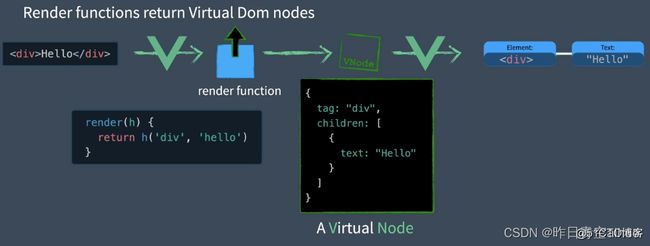
通过DomDiff高效更新视图
六、实现渲染函数
在Vue中我们通过将视图模板(template)编译为渲染函数(render function)再转化为虚拟Dom
渲染流程通常会分为三各部分:
- RenderPhase : 渲染模块使用渲染函数根据初始化数据生成虚拟Dom
- MountPhase : 利用虚拟Dom创建视图页面Html
- PatchPhase:数据模型一旦变化渲染函数将再次被调用生成新的虚拟Dom,然后做Dom Diff更新视图Html
mount: function (container) {
const dom = document.querySelector(container);
// 生成渲染函数
// const render = compile(config.template);
const setupResult = config.setup();
const render = config.render(setupResult);
// 修改
// effective = () => render(setupResult, dom);
// watchEffect(() => render(setupResult, dom));
// render(setupResult, dom);
let isMounted = false;
let prevSubTree;
watchEffect(() => {
if (!isMounted) {
// clear content before mounting
dom.innerHTML = "";
// mount
isMounted = true;
const subTree = config.render(setupResult);
prevSubTree = subTree;
mountElement(subTree, dom);
} else {
// update
const subTree = config.render(setupResult);
diff(prevSubTree, subTree);
prevSubTree = subTree;
}
});
},
1.Render Phase
render(content) { return h("div", null, [
h("div", null, String(content.state.message)),
h( "button",
{onClick: content.click,
}, "click"),
]);
}
2. Mount Phase
利用虚拟Dom创建视图页面Html
function mountElement(vnode, container) {
// 渲染成真实的 dom 节点
const el = (vnode.el = createElement(vnode.tag));
// 处理 props
if (vnode.props) {
for (const key in vnode.props) {
const val = vnode.props[key];
patchProp(vnode.el, key, null, val);
}
}
// 要处理 children
if (Array.isArray(vnode.children)) {
vnode.children.forEach((v) => {
mountElement(v, el);
});
} else {
insert(createText(vnode.children), el);
}
// 插入到视图内
insert(el, container);
}
3. Patch Phase(Dom diff)
function patchProp(el, key, prevValue, nextValue) { // onClick
// 1. 如果前面2个值是 on 的话
// 2. 就认为它是一个事件
// 3. on 后面的就是对应的事件名
if (key.startsWith("on")) {const eventName = key.slice(2).toLocaleLowerCase();
el.addEventListener(eventName, nextValue);
} else {if (nextValue === null) {
el.removeAttribute(key, nextValue);
} else {
el.setAttribute(key, nextValue);
}
}
}
function diff(v1, v2) {
// 1. 如果 tag 都不一样的话,直接替换
// 2. 如果 tag 一样的话
// 1. 要检测 props 哪些有变化
// 2. 要检测 children -》 特别复杂的
const { props: oldProps, children: oldChildren = [] } = v1;
const { props: newProps, children: newChildren = [] } = v2;
if (v1.tag !== v2.tag) {
v1.replaceWith(createElement(v2.tag));
} else {
const el = (v2.el = v1.el);
// 对比 props
// 1. 新的节点不等于老节点的值 -> 直接赋值
// 2. 把老节点里面新节点不存在的 key 都删除掉
if (newProps) {
Object.keys(newProps).forEach((key) => {
if (newProps[key] !== oldProps[key]) {
patchProp(el, key, oldProps[key], newProps[key]);
}
});
// 遍历老节点 -》 新节点里面没有的话,那么都删除掉
Object.keys(oldProps).forEach((key) => {
if (!newProps[key]) {
patchProp(el, key, oldProps[key], null);
}
});
}
// 对比 children
// newChildren -> string
// oldChildren -> string oldChildren -> array
// newChildren -> array
// oldChildren -> string oldChildren -> array
if (typeof newChildren === "string") {
if (typeof oldChildren === "string") {
if (newChildren !== oldChildren) {
setText(el, newChildren);
}
} else if (Array.isArray(oldChildren)) {
// 把之前的元素都替换掉
v1.el.textContent = newChildren;
}
} else if (Array.isArray(newChildren)) {
if (typeof oldChildren === "string") {
// 清空之前的数据
n1.el.innerHTML = "";
// 把所有的 children mount 出来
newChildren.forEach((vnode) => {
mountElement(vnode, el);
});
} else if (Array.isArray(oldChildren)) {
// a, b, c, d, e -> new
// a1,b1,c1,d1 -> old
// 如果 new 的多的话,那么创建一个新的
// a, b, c -> new
// a1,b1,c1,d1 -> old
// 如果 old 的多的话,那么把多的都删除掉
const length = Math.min(newChildren.length, oldChildren.length);
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
const oldVnode = oldChildren[i];
const newVnode = newChildren[i];
// 可以十分复杂
diff(oldVnode, newVnode);
}
if (oldChildren.length > length) {
// 说明老的节点多
// 都删除掉
for (let i = length; i < oldChildren.length; i++) {
remove(oldChildren[i], el);
}
} else if (newChildren.length > length) {
// 说明 new 的节点多
// 那么需要创建对应的节点
for (let i = length; i < newChildren.length; i++) {
mountElement(newChildren[i], el);
}
}
}
}
}
}
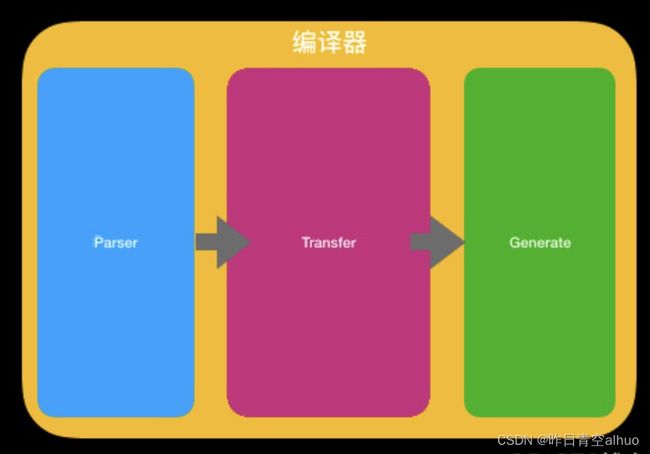
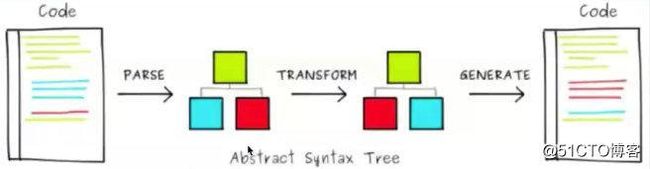
七、编译器原理
-
Parse 模板字符串 -> AST(Abstract Syntax Treee)抽象语法树
-
Transform 转换标记 譬如 v-bind v-if v-for的转换
-
Generate AST -> 渲染函数
1. Parse解析器
解析器的工作原理其实就是一连串的正则匹配。
//
//
// 转换后的AST语法树
const parse = template => (
{
children: [{
tag: 'input',
props: {
name: 'v-model',
exp: {content: 'message'},
},
},
{
tag: 'button',
props: {
name: '@click',
exp: {content: 'message'},
},
content:'{{message}}'
}],
}
)
2. Transform转换处理
在Vue3中会细致的分为两个层级进行处理
const transfer = ast => ({
children: [{
tag: 'input',
props: {
name: 'model',
exp: {content: 'message'},
},
},
{
tag: 'button',
props: {
name: 'click',
exp: {content: 'message'},
},
children: [{
content: {content: 'message'},
}]
}],
})
3. Generate生成渲染器
生成器其实就是根据转换后的AST语法树生成渲染函数。当然针对相同的语法树你可以渲染成不同结果。比如button你希望渲染成 button还是一个svg的方块就看你的喜欢了。这个就叫做自定义渲染器
const generator = ast => (observed, dom) => {
// 重新渲染
let input = dom.querySelector('input')
if (!input) {
input = document.createElement('input')
input.setAttribute('value', observed.message)
input.addEventListener('keyup', function () {
observed.message = this.value
})
dom.appendChild(input)
}
let button = dom.querySelector('button')
if (!button) {console.log('create button')
button = document.createElement('button')
button.addEventListener('click', () => {
return config.methods.click.apply(observed)
})
dom.appendChild(button)
}
button.innerText = observed.message
}