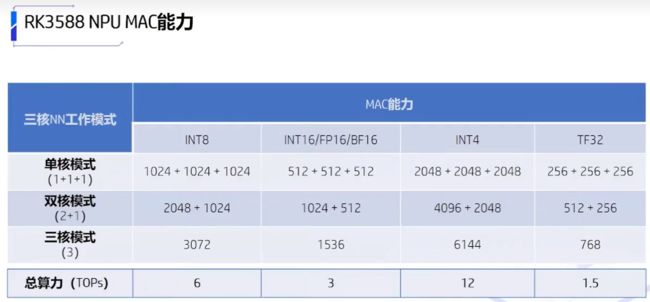
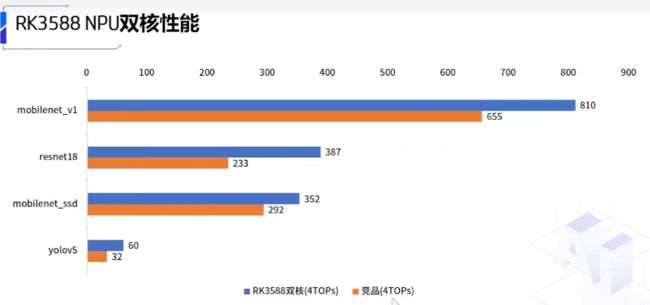
pp-human在rk3588上部署
手把手教你百度飞桨PP-YOLOE部署到瑞芯微RK3588_pp飞桨怎么安装_布衣神棍的博客-CSDN博客手把手教你百度飞桨PP-YOLOE部署到瑞芯微RK3588https://blog.csdn.net/buyishengun/article/details/127653529开发板概况 — TB-RK3588x 0.1 文档![]() https://t.rock-chips.com/wiki/CN/tb-rk3588x/01%E5%BF%AB%E9%80%9F%E4%B8%8A%E6%89%8B.html瑞芯微RK3588等AI硬件NPU部署(paddle)_Vertira的博客-CSDN博客瑞芯微RK3588等AI硬件NPU部署https://blog.csdn.net/Vertira/article/details/127811686yolov5训练pt模型并转换为rknn模型,部署在RK3588开发板上——从训练到部署全过程_rknn yolov5_Billy_zz的博客-CSDN博客本文实现了yolov5模型从训练pt模型,到转换为rknn模型,最终部署在RK3588板子上使用NPU加速推理的过程。https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57315535/article/details/128250096?spm=1001.2101.3001.6650.5&utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-2~default~CTRLIST~Rate-5-128250096-blog-126153227.pc_relevant_3mothn_strategy_and_data_recovery&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-2~default~CTRLIST~Rate-5-128250096-blog-126153227.pc_relevant_3mothn_strategy_and_data_recovery&utm_relevant_index=9rockchip-linux · GitCodeGitCode——开源代码托管平台,独立第三方开源社区,Git/Github/Gitlab
https://t.rock-chips.com/wiki/CN/tb-rk3588x/01%E5%BF%AB%E9%80%9F%E4%B8%8A%E6%89%8B.html瑞芯微RK3588等AI硬件NPU部署(paddle)_Vertira的博客-CSDN博客瑞芯微RK3588等AI硬件NPU部署https://blog.csdn.net/Vertira/article/details/127811686yolov5训练pt模型并转换为rknn模型,部署在RK3588开发板上——从训练到部署全过程_rknn yolov5_Billy_zz的博客-CSDN博客本文实现了yolov5模型从训练pt模型,到转换为rknn模型,最终部署在RK3588板子上使用NPU加速推理的过程。https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57315535/article/details/128250096?spm=1001.2101.3001.6650.5&utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-2~default~CTRLIST~Rate-5-128250096-blog-126153227.pc_relevant_3mothn_strategy_and_data_recovery&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-2~default~CTRLIST~Rate-5-128250096-blog-126153227.pc_relevant_3mothn_strategy_and_data_recovery&utm_relevant_index=9rockchip-linux · GitCodeGitCode——开源代码托管平台,独立第三方开源社区,Git/Github/Gitlab![]() https://gitcode.net/mirrors/rockchip-linuxFirefly | 让科技更简单,让生活更智能Firefly是天启科技旗下的品牌,我们专注于开源智能硬件,物联网,数字音频产品的研发设计、生产和销售,同时提供了智能硬件 产品的整体解决方案。Firefly产品包括行业主板,核心板,开源板等。全系列产品均是芯片原厂瑞芯微(Rockchip)推荐板卡,获得原生SDK支持。核心板与行业主板广泛应用于人工智能,商业显示,广告一体机,智能POS,人脸识别终端,物联网,智慧城市等领域。https://www.t-firefly.com/doc/download/106.html1. NPU使用 — Firefly WikiEC-R3588SPC采用 Rockchip RK3588S新一代旗舰级八核64位处理器,最大可配32GB大内存;支持8K视频编解码;支持千兆网、;支持多种操作系统;可适用于ARM PC、边缘计算、云服务器、智能NVR等领域https://wiki.t-firefly.com/zh_CN/EC-R3588SPC/usage_npu.html【FastDeploy + 瑞芯微】RV1126、RK3588全量化部署详解_哔哩哔哩_bilibili【FastDeploy + 瑞芯微】RV1126、RK3588全量化部署详解, 视频播放量 618、弹幕量 0、点赞数 9、投硬币枚数 4、收藏人数 24、转发人数 6, 视频作者 飞桨PaddlePaddle, 作者简介 后厂村第一炼丹师<( ̄︶ ̄)>,相关视频:【瑞芯微NPU部署】官方YOLOV5+Tengine推理引擎+RV1126嵌入式AI硬件,3588--新一代NPU的介绍及使用,瑞芯微RK3588 ARM PC解决方案,摆脱电脑,直接在RK3588平台上推理,帮用户部署 RKNN 模加速 AI 应用的落地,瑞芯微RK3588高端平板解决方案,开箱首发!瑞芯微旗舰芯RK3588开发板,瑞芯微RK3588边缘计算及AI应用,瑞芯微RK3588智能车载360°全景环视,rv1126板子说明!,香蕉派开源社区完成瑞芯微RK3568/RK3588全国产化开发板硬件验证并运行国产麒麟Linux系统https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Xg411x7MV/?spm_id_from=333.999.top_right_bar_window_history.content.click&vd_source=4aed82e35f26bb600bc5b46e65e25c22examples/vision/detection/paddledetection/rknpu2/README_CN.md · develop · mirrors / paddlepaddle / fastdeploy · GitCode⚡️An Easy-to-use and Fast Deep Learning Model Deployment Toolkit for ☁️Cloud Mobile and
https://gitcode.net/mirrors/rockchip-linuxFirefly | 让科技更简单,让生活更智能Firefly是天启科技旗下的品牌,我们专注于开源智能硬件,物联网,数字音频产品的研发设计、生产和销售,同时提供了智能硬件 产品的整体解决方案。Firefly产品包括行业主板,核心板,开源板等。全系列产品均是芯片原厂瑞芯微(Rockchip)推荐板卡,获得原生SDK支持。核心板与行业主板广泛应用于人工智能,商业显示,广告一体机,智能POS,人脸识别终端,物联网,智慧城市等领域。https://www.t-firefly.com/doc/download/106.html1. NPU使用 — Firefly WikiEC-R3588SPC采用 Rockchip RK3588S新一代旗舰级八核64位处理器,最大可配32GB大内存;支持8K视频编解码;支持千兆网、;支持多种操作系统;可适用于ARM PC、边缘计算、云服务器、智能NVR等领域https://wiki.t-firefly.com/zh_CN/EC-R3588SPC/usage_npu.html【FastDeploy + 瑞芯微】RV1126、RK3588全量化部署详解_哔哩哔哩_bilibili【FastDeploy + 瑞芯微】RV1126、RK3588全量化部署详解, 视频播放量 618、弹幕量 0、点赞数 9、投硬币枚数 4、收藏人数 24、转发人数 6, 视频作者 飞桨PaddlePaddle, 作者简介 后厂村第一炼丹师<( ̄︶ ̄)>,相关视频:【瑞芯微NPU部署】官方YOLOV5+Tengine推理引擎+RV1126嵌入式AI硬件,3588--新一代NPU的介绍及使用,瑞芯微RK3588 ARM PC解决方案,摆脱电脑,直接在RK3588平台上推理,帮用户部署 RKNN 模加速 AI 应用的落地,瑞芯微RK3588高端平板解决方案,开箱首发!瑞芯微旗舰芯RK3588开发板,瑞芯微RK3588边缘计算及AI应用,瑞芯微RK3588智能车载360°全景环视,rv1126板子说明!,香蕉派开源社区完成瑞芯微RK3568/RK3588全国产化开发板硬件验证并运行国产麒麟Linux系统https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Xg411x7MV/?spm_id_from=333.999.top_right_bar_window_history.content.click&vd_source=4aed82e35f26bb600bc5b46e65e25c22examples/vision/detection/paddledetection/rknpu2/README_CN.md · develop · mirrors / paddlepaddle / fastdeploy · GitCode⚡️An Easy-to-use and Fast Deep Learning Model Deployment Toolkit for ☁️Cloud Mobile and![]() https://gitcode.net/mirrors/paddlepaddle/fastdeploy/-/blob/develop/examples/vision/detection/paddledetection/rknpu2/README_CN.mdyolov5训练并生成rknn模型以及3588平台部署_rknn yolov5_新鑫信心的博客-CSDN博客瑞芯微RK3588上yolov5目标检测的部署。https://blog.csdn.net/m0_51714298/article/details/125916417
https://gitcode.net/mirrors/paddlepaddle/fastdeploy/-/blob/develop/examples/vision/detection/paddledetection/rknpu2/README_CN.mdyolov5训练并生成rknn模型以及3588平台部署_rknn yolov5_新鑫信心的博客-CSDN博客瑞芯微RK3588上yolov5目标检测的部署。https://blog.csdn.net/m0_51714298/article/details/125916417
1.bfloat16的安装
使用distutils构建Python扩展模块(Building Python extension module with distutils)_电脑培训使用distutils构建Python扩展模块(Building Python extension module with distutils),我正在使用distutils来构建一个用C ++编写的Python扩展模块。 我遇到的问题是,为了编译![]() https://www.656463.com/wenda/sydistutilsgjPythonkzmk_284https://www.cnblogs.com/goldsunshine/p/8872623.html
https://www.656463.com/wenda/sydistutilsgjPythonkzmk_284https://www.cnblogs.com/goldsunshine/p/8872623.html![]() https://www.cnblogs.com/goldsunshine/p/8872623.html用源码编译,直接sudo pip install 安装有问题,源码python setup.py install --user,有的时候sudo pip install 不好使,就使用--user这种方式,有的时候三方库链接不到,python setup.py install不好使,可以试试python setup.py sdist,记住distutils只是一种打包方式。此外,升级的gcc5.4在源码编译时可能有问题,加上
https://www.cnblogs.com/goldsunshine/p/8872623.html用源码编译,直接sudo pip install 安装有问题,源码python setup.py install --user,有的时候sudo pip install 不好使,就使用--user这种方式,有的时候三方库链接不到,python setup.py install不好使,可以试试python setup.py sdist,记住distutils只是一种打包方式。此外,升级的gcc5.4在源码编译时可能有问题,加上
module.extra_compile_args = ['--std=c++0x']2.rknpu
250帧,640x640
训练框架自带的一些量化操作可以被rknn读取
rknpu即为上面的rknn runtime.
rk3588的cpu比较强,其实在PC或者板子上编译都可以。
dmesg | grep Galcore 查看版本
wget/adb/ssh推送都是可以的
rk3588对输入有优化
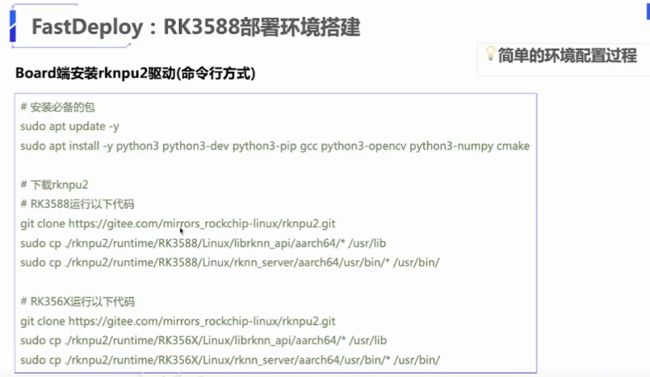
3.paddledetection中的pp-human在rk3588上部署
rknn的部署其实有两部分,第一部分是在linux系统上开发量化和rknn模型,用到的是rknn-toolkit2,在板子上python调用,pc端是必须要装的,因为给的rknn-toolkit2是用来转模型的,如果不用fastdeploy这样的框架的话。可以使用rknn-toolkit2中rknn-lite来部署,可以调用npu接口,如果对速度有更高要求,则需要使用rknpu来进行c++侧的部署,c++优化了预处理等操作,事实上,预处理是很耗时的。
3.1 paddle2rknn
paddle提供的权重已经是export_model之后的模型了,因此在export_model.py之前通过exclude_nms=True不可行。
下面这个链接可行
examples/vision/detection/paddledetection/rknpu2/README_CN.md · develop · mirrors / paddlepaddle / fastdeploy · GitCode⚡️An Easy-to-use and Fast Deep Learning Model Deployment Toolkit for ☁️Cloud Mobile and![]() https://gitcode.net/mirrors/paddlepaddle/fastdeploy/-/blob/develop/examples/vision/detection/paddledetection/rknpu2/README_CN.md
https://gitcode.net/mirrors/paddlepaddle/fastdeploy/-/blob/develop/examples/vision/detection/paddledetection/rknpu2/README_CN.md
代码示例:
paddle2onnx --model_dir /home/sniss/local_disk/rknn-toolkit2-master/examples/onnx/ppyoloe/paddle_ori/mot_ppyoloe_l_36e_pipeline \
--model_filename /home/sniss/local_disk/rknn-toolkit2-master/examples/onnx/ppyoloe/paddle_ori/mot_ppyoloe_l_36e_pipeline/model.pdmodel \
--params_filename /home/sniss/local_disk/rknn-toolkit2-master/examples/onnx/ppyoloe/paddle_ori/mot_ppyoloe_l_36e_pipeline/model.pdiparams \
--save_file /home/sniss/local_disk/rknn-toolkit2-master/examples/onnx/ppyoloe/ppyoloeonnx/mot_ppyoloe_l_36e_pipeline.onnx \
--enable_dev_version True
--opset_version 12
--enable_onnx_checker Truepython -m paddle2onnx.optimize --input_model /home/sniss/local_disk/rknn-toolkit2-master/examples/onnx/ppyoloe/ppyoloeonnx/mot_ppyoloe_l_36e_pipeline.onnx \
--output_model /home/sniss/local_disk/rknn-toolkit2-master/examples/onnx/ppyoloe/ppyoloeonnx/mot_ppyoloe_l_36e_pipeline_opt.onnx \
--input_shape_dict "{'image':[1,3,640,640], 'scale_factor':[1,2]}"python export_rknn.py --config_path /home/sniss/local_disk/rknn-toolkit2-master/examples/onnx/ppyoloe/ppyoloeonnx/mot_ppyoloe_opt.yaml --target_platform rk3588上面这种方式是通过rknn来进行onnx静态图的裁剪,避免了在onnx和paddle上面进行裁剪。
3.2 paddleinference->rknn推理
剪裁完节点之后输出是[(8400,4),8400]的array,第一维是两个点坐标有8400,后面是对应的置信度有8400个,此时解耦头输出的结果。
pphuman部署的是ppyoloe模型,其实是跟踪的模型,但是第一部分还是ppyoloe,后面加上卡尔曼滤波和匈牙利算法,所以核心还是ppyoloe在rk3588的部署。
此处写了两个版本的nms去做后处理,发现都输出的框都有问题,即便是没有量化,输出的框还是有问题。
import os
import urllib
import traceback
import time
import sys
import yaml
import numpy as np
import cv2
from rknn.api import RKNN
ONNX_MODEL = 'yolov5s.onnx'
RKNN_MODEL = '/home/sniss/local_disk/rknn-toolkit2-master/examples/onnx/ppyoloe/ppyoloeonnx/mot_ppyoloe_l_36e_pipeline_opt_rk3588_quantized.rknn'
IMG_PATH = './test.png'
DATASET = './dataset.txt'
QUANTIZE_ON = True
OBJ_THRESH = 0.25
NMS_THRESH = 0.45
IMG_SIZE = 640
CLASSES = ["player"]
def draw_results(result, image, draw_thresh=0.5):
# plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
# im = imread(filename)
# plt.imshow(im)
# currentAxis=plt.gca()
# colors = ['r', 'g', 'b', 'k', 'y', 'pink', 'purple']
for item in result:
top, left, right, bottom= item[2:6]
label = int(item[0])
score = item[1]
name = CLASSES[label]
if item[1] > draw_thresh:
top = int(top)
left = int(left)
right = int(right)
bottom = int(bottom)
cv2.rectangle(image, (top, left), (right, bottom), (255, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(name, score),
(top, left - 6),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.6, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# draw_rectangle(currentAxis, box, edgecolor = colors[label])
# plt.text(box[0], box[1], name, fontsize=12, color=colors[label])
# plt.savefig('/home/aistudio/external-libraries/PaddleDection/outout_img/output_pic.png')
# plt.show()
def draw(image, boxes, scores, classes):
"""Draw the boxes on the image.
# Argument:
image: original image.
boxes: ndarray, boxes of objects.
classes: ndarray, classes of objects.
scores: ndarray, scores of objects.
all_classes: all classes name.
"""
for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):
top, left, right, bottom = box
print('class: {}, score: {}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score))
print('box coordinate left,top,right,down: [{}, {}, {}, {}]'.format(top, left, right, bottom))
top = int(top)
left = int(left)
right = int(right)
bottom = int(bottom)
cv2.rectangle(image, (top, left), (right, bottom), (255, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score),
(top, left - 6),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.6, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# 计算IoU,矩形框的坐标形式为xyxy,这个函数会被保存在box_utils.py文件中
def box_iou_xyxy(box1, box2):
# 获取box1左上角和右下角的坐标
x1min, y1min, x1max, y1max = box1[0], box1[1], box1[2], box1[3]
# 计算box1的面积
s1 = (y1max - y1min + 1.) * (x1max - x1min + 1.)
# 获取box2左上角和右下角的坐标
x2min, y2min, x2max, y2max = box2[0], box2[1], box2[2], box2[3]
# 计算box2的面积
s2 = (y2max - y2min + 1.) * (x2max - x2min + 1.)
# 计算相交矩形框的坐标
xmin = np.maximum(x1min, x2min)
ymin = np.maximum(y1min, y2min)
xmax = np.minimum(x1max, x2max)
ymax = np.minimum(y1max, y2max)
# 计算相交矩形行的高度、宽度、面积
inter_h = np.maximum(ymax - ymin + 1., 0.)
inter_w = np.maximum(xmax - xmin + 1., 0.)
intersection = inter_h * inter_w
# 计算相并面积
union = s1 + s2 - intersection
# 计算交并比
iou = intersection / union
return iou
def nms(bboxes, scores, score_thresh, nms_thresh, pre_nms_topk):
"""
nms
"""
inds = np.argsort(scores)
inds = inds[::-1]
inds = inds[:pre_nms_topk]
keep_inds = []
while(len(inds) > 0):
cur_ind = inds[0]
cur_score = scores[cur_ind]
# if score of the box is less than score_thresh, just drop it
if cur_score < score_thresh:
break
keep = True
for ind in keep_inds:
current_box = bboxes[cur_ind]
remain_box = bboxes[ind]
# import pdb;pdb.set_trace()
iou = box_iou_xyxy(current_box, remain_box)
if iou > nms_thresh:
keep = False
break
if keep:
keep_inds.append(cur_ind)
inds = inds[1:]
return np.array(keep_inds)
def multiclass_nms(bboxes, scores, score_thresh=0.05, nms_thresh=0.5, pre_nms_topk=1000, pos_nms_topk=100):
"""
This is for multiclass_nms
"""
batch_size = bboxes.shape[0]
class_num = scores.shape[1]
rets = []
for i in range(batch_size):
bboxes_i = bboxes[i]
scores_i = scores[i]
ret = []
for c in range(class_num):
scores_i_c = scores_i[c]
keep_inds = nms(bboxes_i, scores_i_c, score_thresh, nms_thresh, pre_nms_topk)
if len(keep_inds) < 1:
continue
keep_bboxes = bboxes_i[keep_inds]
keep_scores = scores_i_c[keep_inds]
keep_results = np.zeros([keep_scores.shape[0], 6])
keep_results[:, 0] = c
keep_results[:, 1] = keep_scores[:]
keep_results[:, 2:6] = keep_bboxes[:, :]
ret.append(keep_results)
if len(ret) < 1:
rets.append(ret)
continue
ret_i = np.concatenate(ret, axis=0)
scores_i = ret_i[:, 1]
if len(scores_i) > pos_nms_topk:
inds = np.argsort(scores_i)[::-1]
inds = inds[:pos_nms_topk]
ret_i = ret_i[inds]
rets.append(ret_i)
return rets
def nms_boxes(boxes, scores):
"""Suppress non-maximal boxes.
# Arguments
boxes: ndarray, boxes of objects.
scores: ndarray, scores of objects.
# Returns
keep: ndarray, index of effective boxes.
"""
x = boxes[:, 0]
y = boxes[:, 1]
w = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]
h = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]
areas = w * h
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x[i], x[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y[i], y[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x[i] + w[i], x[order[1:]] + w[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y[i] + h[i], y[order[1:]] + h[order[1:]])
w1 = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 0.00001)
h1 = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 0.00001)
inter = w1 * h1
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
inds = np.where(ovr <= NMS_THRESH)[0]
order = order[inds + 1]
keep = np.array(keep)
return keep
def ppyolo_nms(pred_bboxes, pred_scores):
# pred_bboxes:(1,8400,1) pred_scores:(1,1,8400)
boxes = pred_bboxes.reshape(-1,4)
box_class_probs = pred_scores.reshape(pred_scores.shape[-1]*pred_scores.shape[0],-1)
box_confidences = np.ones(boxes.shape[0]).reshape(-1,)
_box_pos = np.where(box_confidences >= OBJ_THRESH)
boxes = boxes[_box_pos]
box_confidences = box_confidences[_box_pos]
box_class_probs = box_class_probs[_box_pos]
class_max_score = np.max(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
classes = np.argmax(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
_class_pos = np.where(class_max_score >= OBJ_THRESH)
boxes = boxes[_class_pos]
classes = classes[_class_pos]
scores = (class_max_score* box_confidences)[_class_pos]
# boxes = np.concatenate(boxes)
# classes = np.concatenate(classes)
# scores = np.concatenate(scores)
nboxes, nclasses, nscores = [], [], []
for c in set(classes):
inds = np.where(classes == c)
b = boxes[inds]
c = classes[inds]
s = scores[inds]
keep = nms_boxes(b, s)
nboxes.append(b[keep])
nclasses.append(c[keep])
nscores.append(s[keep])
if not nclasses and not nscores:
return None, None, None
boxes = np.concatenate(nboxes)
classes = np.concatenate(nclasses)
scores = np.concatenate(nscores)
return boxes, classes, scores
def letterbox(im, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(0, 0, 0)):
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
# Compute padding
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return im, ratio, (dw, dh)
if __name__ == '__main__':
with open("/home/sniss/local_disk/rknn-toolkit2-master/examples/onnx/ppyoloe/ppyoloeonnx/mot_ppyoloe_opt.yaml") as file:
file_data = file.read()
yaml_config = yaml.safe_load(file_data)
print(yaml_config)
model = RKNN(True)
# Config
mean_values = yaml_config["mean"]
std_values = yaml_config["std"]
model.config(
mean_values=mean_values,
std_values=std_values,
target_platform="rk3588")
# Load ONNX model
if yaml_config["outputs_nodes"] is None:
ret = model.load_onnx(model=yaml_config["model_path"])
else:
ret = model.load_onnx(
model=yaml_config["model_path"],
outputs=yaml_config["outputs_nodes"])
assert ret == 0, "Load model failed!"
# Build model
ret = model.build(
do_quantization=yaml_config["do_quantization"],
dataset=yaml_config["dataset"])
assert ret == 0, "Build model failed!"
# Init Runtime
ret = model.init_runtime()
assert ret == 0, "Init runtime environment failed!"
# Export
if not os.path.exists(yaml_config["output_folder"]):
os.mkdir(yaml_config["output_folder"])
model_base_name = os.path.basename(yaml_config["model_path"]).split(".")[0]
# model_device_name = config.target_platform.lower()
model_device_name = 'rk3588'
if yaml_config["do_quantization"]:
model_save_name = model_base_name + "_" + model_device_name + "_quantized" + ".rknn"
else:
model_save_name = model_base_name + "_" + model_device_name + "_unquantized" + ".rknn"
ret = model.export_rknn(
os.path.join(yaml_config["output_folder"], model_save_name))
assert ret == 0, "Export rknn model failed!"
print("Export OK!")
# Set inputs
img = cv2.imread(IMG_PATH)
img, ratio, (dw, dh) = letterbox(img, new_shape=(IMG_SIZE, IMG_SIZE))
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img = cv2.resize(img, (IMG_SIZE, IMG_SIZE))
# Inference
print('--> Running model')
outputs = model.inference(inputs=[img])
print('done')
# import pdb;pdb.set_trace()
# pred_bboxes = outputs[0]
# pred_scores = outputs[1]
# bbox_pred = multiclass_nms(pred_bboxes,pred_scores)
# bbox_pred = bbox_pred[0]
# import pdb;pdb.set_trace()
# img_1 = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
# if bbox_pred is not None:
# draw_results(bbox_pred, img_1, draw_thresh=0.1)
# cv2.imwrite("1.png",img_1)
# draw_results(result, image, draw_thresh=0.5):
import pdb;pdb.set_trace()
pred_bboxes = outputs[0]
pred_scores = outputs[1]
# pred_bboxes = pred_bboxes.numpy()
# pred_scores = pred_scores.numpy()
boxes, classes, scores = ppyolo_nms(pred_bboxes,pred_scores)
img_1 = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
if boxes is not None:
draw(img_1, boxes, scores, classes)
cv2.imwrite("1.png",img_1)
rknn.release()
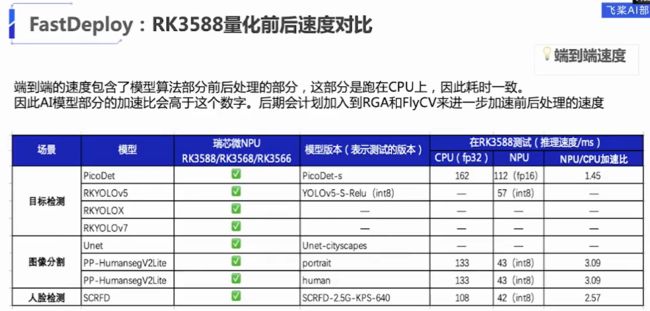
4.fastdeploy部署
fastdeploy可以部署在rk3588上,比较友好的其还有python的接口,可以做快速的尝试,还是用ppyoloe跑检测,后面在加上跟踪的代码,fastdeploy的python接口在rk3588上默认是onnxruntime的推理后端,python似乎是不支持rknpu2,没跑通。
'''
@Time : 2023/2/27 14:37
@Author : [email protected]
'''
import os
import fastdeploy as fd
import cv2
import numpy as np
from ocsort_tracker import OCSORTTracker
from collections import defaultdict
from pathlib import Path
import copy
OBJ_THRESH = 0.25
NMS_THRESH = 0.45
CLASSES = ["player"]
visual = True
def draw(image, boxes, scores, classes):
"""Draw the boxes on the image.
# Argument:
image: original image.
boxes: ndarray, boxes of objects.
classes: ndarray, classes of objects.
scores: ndarray, scores of objects.
all_classes: all classes name.
"""
for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):
top, left, right, bottom = box
print('class: {}, score: {}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score))
print('box coordinate left,top,right,down: [{}, {}, {}, {}]'.format(top, left, right, bottom))
top = int(top)
left = int(left)
right = int(right)
bottom = int(bottom)
cv2.rectangle(image, (top, left), (right, bottom), (255, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score),
(top, left - 6),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.6, (0, 0, 255), 2)
def nms_boxes(boxes, scores):
"""Suppress non-maximal boxes.
# Arguments
boxes: ndarray, boxes of objects.
scores: ndarray, scores of objects.
# Returns
keep: ndarray, index of effective boxes.
"""
x = boxes[:, 0]
y = boxes[:, 1]
w = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]
h = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]
areas = w * h
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x[i], x[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y[i], y[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x[i] + w[i], x[order[1:]] + w[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y[i] + h[i], y[order[1:]] + h[order[1:]])
w1 = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 0.00001)
h1 = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 0.00001)
inter = w1 * h1
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
inds = np.where(ovr <= NMS_THRESH)[0]
order = order[inds + 1]
keep = np.array(keep)
return keep
def ppyolo_nms(pred_bboxes, pred_scores):
boxes = pred_bboxes.reshape(-1, 4)
box_confidences = np.ones(pred_bboxes.shape[0]).reshape(-1, )
box_class_probs = pred_scores.reshape(pred_scores.shape[-1], -1)
_box_pos = np.where(box_confidences >= OBJ_THRESH)
boxes = boxes[_box_pos]
box_confidences = box_confidences[_box_pos]
box_class_probs = box_class_probs[_box_pos]
class_max_score = np.max(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
classes = np.argmax(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
_class_pos = np.where(class_max_score >= OBJ_THRESH)
boxes = boxes[_class_pos]
classes = classes[_class_pos]
scores = (class_max_score * box_confidences)[_class_pos]
nboxes, nclasses, nscores = [], [], []
for c in set(classes):
inds = np.where(classes == c)
b = boxes[inds]
c = classes[inds]
s = scores[inds]
keep = nms_boxes(b, s)
nboxes.append(b[keep])
nclasses.append(c[keep])
nscores.append(s[keep])
if not nclasses and not nscores:
return None, None, None
boxes = np.concatenate(nboxes)
classes = np.concatenate(nclasses)
scores = np.concatenate(nscores)
return boxes, classes, scores
def postprocess(boxes, classes, scores):
nboxes = []
if len(boxes) > 0:
for i, box in enumerate(boxes):
classes_scores = np.append(classes[i], scores[i])
boxes_ = np.append(classes_scores, box)
nboxes.append(boxes_.tolist())
result = {"boxes": np.array([boxes_]), 'boxes_num': np.array([len(boxes)])}
return result
class SDE_Detector(object):
def __init__(self):
use_byte = False
det_thresh = 0.4
max_age = 30
min_hits = 3
iou_threshold = 0.3
delta_t = 3
inertia = 0.2
min_box_area = 0
vertical_ratio = 0
self.tracker = OCSORTTracker(
det_thresh=det_thresh,
max_age=max_age,
min_hits=min_hits,
iou_threshold=iou_threshold,
delta_t=delta_t,
inertia=inertia,
min_box_area=min_box_area,
vertical_ratio=vertical_ratio,
use_byte=use_byte)
def tracking(self, det_results):
pred_dets = det_results['boxes']
pred_embs = det_results.get('embeddings', None)
online_targets = self.tracker.update(pred_dets, pred_embs)
online_tlwhs = defaultdict(list)
online_scores = defaultdict(list)
online_ids = defaultdict(list)
for t in online_targets:
tlwh = [t[0], t[1], t[2] - t[0], t[3] - t[1]] # top,left,w,h
tscore = float(t[4])
tid = int(t[5])
if tlwh[2] * tlwh[3] <= self.tracker.min_box_area: continue
if self.tracker.vertical_ratio > 0 and tlwh[2] / tlwh[
3] > self.tracker.vertical_ratio:
continue
if tlwh[2] * tlwh[3] > 0:
online_tlwhs[0].append(tlwh)
online_ids[0].append(tid)
online_scores[0].append(tscore)
tracking_outs = {
'online_tlwhs': online_tlwhs, # 坐标
'online_scores': online_scores, # >0.4
'online_ids': online_ids, # [10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1]
}
return tracking_outs
def get_color(idx):
idx = idx * 3
color = ((37 * idx) % 255, (17 * idx) % 255, (29 * idx) % 255)
return color
def plot_tracking_dict(image,
num_classes,
tlwhs_dict,
obj_ids_dict,
scores_dict,
frame_id=0,
fps=0.,
ids2names=[]):
im = np.ascontiguousarray(np.copy(image)) # shape:480,854,3
im_h, im_w = im.shape[:2]
text_scale = max(0.5, image.shape[1] / 3000.)
text_thickness = 2
line_thickness = max(1, int(image.shape[1] / 500.))
for cls_id in range(num_classes):
tlwhs = tlwhs_dict[cls_id]
obj_ids = obj_ids_dict[cls_id]
scores = scores_dict[cls_id]
cv2.putText(
im,
'frame: %d fps: %.2f num: %d' % (frame_id, fps, len(tlwhs)),
(0, int(15 * text_scale) + 5),
cv2.FONT_ITALIC,
text_scale, (0, 0, 255),
thickness=text_thickness)
record_id = set()
for i, tlwh in enumerate(tlwhs):
x1, y1, w, h = tlwh
intbox = tuple(map(int, (x1, y1, x1 + w, y1 + h)))
center = tuple(map(int, (x1 + w / 2., y1 + h / 2.)))
obj_id = int(obj_ids[i])
id_text = '{}'.format(int(obj_id))
if ids2names != []:
id_text = '{}_{}'.format(ids2names[cls_id], id_text)
else:
id_text = 'class{}_{}'.format(cls_id, id_text)
_line_thickness = 1 if obj_id <= 0 else line_thickness
in_region = False
color = get_color(abs(obj_id)) if in_region == False else (0, 0,
255)
cv2.rectangle(
im,
intbox[0:2],
intbox[2:4],
color=color,
thickness=line_thickness)
cv2.putText(
im,
id_text, (intbox[0], intbox[1] - 25),
cv2.FONT_ITALIC,
text_scale,
color,
thickness=text_thickness)
return im
option = fd.RuntimeOption()
# option.use_cpu()
# option.use_openvino_backend() # 一行命令切换使用 OpenVINO部署
model = fd.vision.detection.PPYOLOE(
"/home/sniss/local_disk/rknn-toolkit2-master/examples/onnx/ppyoloe/paddle_ori/mot_ppyoloe_l_36e_pipeline/model.pdmodel",
"/home/sniss/local_disk/rknn-toolkit2-master/examples/onnx/ppyoloe/paddle_ori/mot_ppyoloe_l_36e_pipeline/model.pdiparams" ,
"/home/sniss/local_disk/rknn-toolkit2-master/examples/onnx/ppyoloe/paddle_ori/mot_ppyoloe_l_36e_pipeline/infer_cfg.yml")
tracker = SDE_Detector()
mot_results = []
video_file = "kitch.mp4"
output_dir = "results"
capture = cv2.VideoCapture(video_file)
# Get Video info : resolution, fps, frame count
width = int(capture.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
height = int(capture.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
fps = int(capture.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS))
frame_count = int(capture.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
print("video fps: %d, frame_count: %d" % (fps, frame_count))
video_out_name = Path(video_file).stem
if not os.path.exists(output_dir):
os.makedirs(output_dir)
out_path = os.path.join(output_dir, video_out_name + ".mp4")
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v')
writer = cv2.VideoWriter(out_path, fourcc, fps, (width, height))
frame_id = 0
while (1):
# frame_id = 0
if frame_id % 10 == 0:
print('frame id: {}'.format(frame_id))
ret, frame = capture.read()
if not ret:
break
# img = cv2.imread("test.png")
img = frame
result = model.predict(copy.deepcopy(img))
pred_bboxes = np.array(result.boxes)
pred_scores = np.array(result.scores)
boxes, classes, scores = ppyolo_nms(pred_bboxes, pred_scores)
# boxes
# array([[ 618.63458252, 172.54750061, 1023.77459717, 781.89233398]])
# classes
# array([0])
# scores
# array([0.95259225])
det_result = postprocess(boxes, classes, scores)
tracking_outs = tracker.tracking(det_result)
online_tlwhs = tracking_outs['online_tlwhs']
online_scores = tracking_outs['online_scores']
online_ids = tracking_outs['online_ids']
mot_results.append([online_tlwhs, online_scores, online_ids])
if visual:
im = plot_tracking_dict(
frame,
1,
online_tlwhs,
online_ids,
online_scores,
frame_id=frame_id,
ids2names=CLASSES)
cv2.imwrite(
os.path.join(output_dir, '{:05d}.jpg'.format(frame_id)), im)
frame_id += 1
writer.write(im)
# img_1 = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
# if boxes is not None:
# draw(img_1, boxes, scores, classes)
#
# img_2 = cv2.cvtColor(img_1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# cv2.imwrite("fastdeploy_1.png", img_2)
writer.release()fastdeploy的c++版本尝试、
5.rknn-lite2 npu的python接口
用rknn-lite2可以调用rk3588的npu,速度相当不错。
总结:整体来说,在pc端可以使用rknn-toolkit2做rknn模型的转换,这一步最关键的就是.rknn模型的获取,rknpu中虽然也有onnx2rknn,但是想在pc端用python做测试,还是走这个路子,有了rknn模型之后,可以用rknn-lite2在rk3588上推理,或者使用rknpu的c++接口,rknpu的c++接口高效处理了数据预处理,这一步其实很耗时间的,速度会更快点。