第五届传智杯-初赛【B组-题解】
A题
题目背景
在宇宙射线的轰击下,莲子电脑里的一些她自己预定义的函数被损坏了。
对于一名理科生来说,各种软件在学习和研究中是非常重要的。为了尽快恢复她电脑上的软件的正常使用,她需要尽快地重新编写这么一些函数。
你只需输出fun(a,b) 的值。
输入格式
- 共一行两个整数 a,b。
输出格式
- 共一行一个整数 fun(a,b) 的值。
输入输出样例
题解:
签到题:首先用if 语句判断 b 的符号,然后加在 a 的绝对值上即可。
参考代码
版本 1:
#include
#define up(l, r, i) for(int i = l, END##i = r;i <= END##i;++ i)
#define dn(r, l, i) for(int i = r, END##i = l;i >= END##i;-- i)
using namespace std;
typedef long long i64;
const int INF = 2147483647;
int main(){
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
cout << fixed << setprecision(0) << copysignl(a, b) + 1e-9 << endl;
return 0;
} 版本 2:
#include
#define up(l, r, i) for(int i = l, END##i = r;i <= END##i;++ i)
#define dn(r, l, i) for(int i = r, END##i = l;i >= END##i;-- i)
using namespace std;
typedef long long i64;
const int INF = 2147483647;
int main(){
i64 a, b; cin >> a >> b;
cout << (b < 0 ? -llabs(a) : llabs(a));
return 0;
} 版本3:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a,b;
cin >> a >> b;
if (b>0 && a==INT_MIN)
cout << 2147483648ll << endl;
else
{
a=abs(a);
if (b<0)
a*=-1;
cout << a << endl;
}
return 0;
} 版本4:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
long a = scanner.nextLong(), b = scanner.nextLong();
System.out.println((Math.abs(a) * (b > 0 ? 1 : -1)));
}
}B题:
题目背景
【题目背景和题目描述的两个题面是完全等价的,您可以选择阅读其中一部分。】
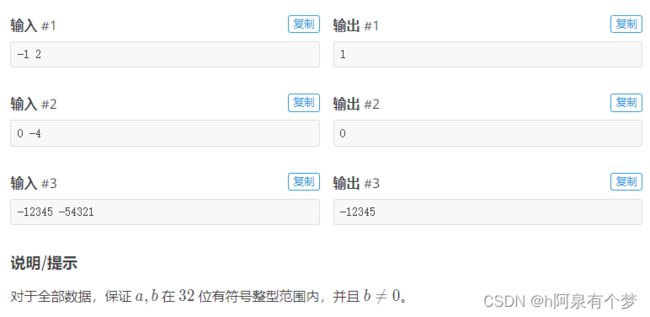
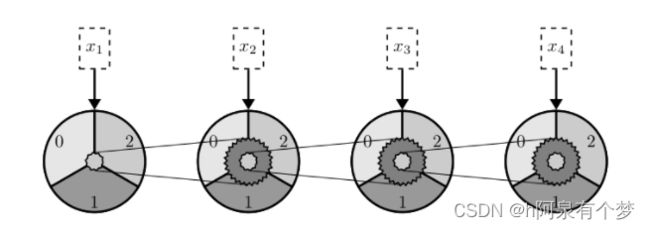
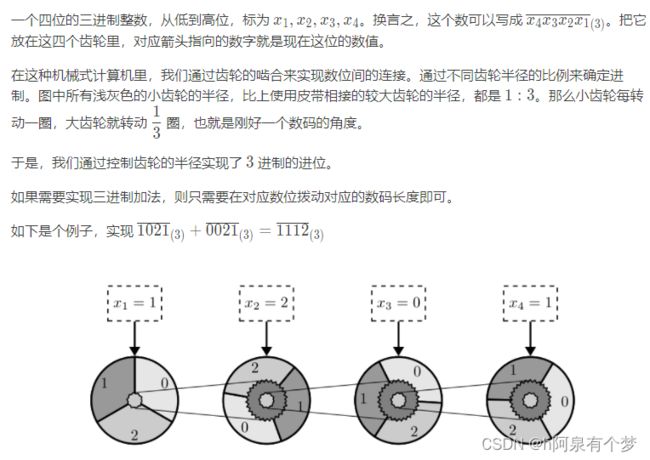
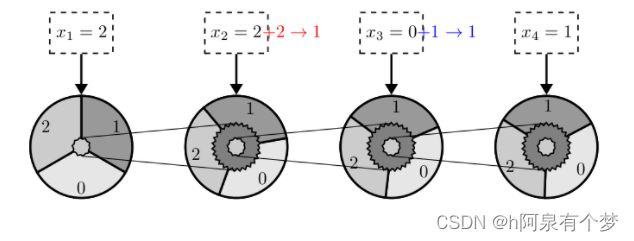
专攻超统一物理学的莲子,对机械结构的运动颇有了解。如下图所示,是一个三进制加法计算器的(超简化)示意图。
初始时齿轮的状态如上。
![]()
![]()
![]()
题解:
模拟题。按照题目要求输入整数 a,b,模拟这个奇怪的进位规则即可。
参考代码
版本 1:
#include
#define up(l, r, i) for(int i = l, END##i = r;i <= END##i;++ i)
#define dn(r, l, i) for(int i = r, END##i = l;i >= END##i;-- i)
using namespace std;
typedef long long i64;
const int INF = 2147483647;
int qread(){
int w=1,c,ret;
while((c = getchar()) > '9' || c < '0') w = (c == '-' ? -1 : 1); ret = c - '0';
while((c = getchar()) >= '0' && c <= '9') ret = ret * 10 + c - '0';
return ret * w;
}
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 3;
int A[MAXN], B[MAXN];
int main(){
int n = qread(), m = qread(), l = max(n, m);
dn(n, 1, i) A[i] = qread();
dn(m, 1, i) B[i] = qread();
up(1, l, i) A[i] += B[i], A[i + 1] += A[i] / (i + 1), A[i] %= i + 1;
if(A[l + 1]) ++ l;
dn(l, 1, i) printf("%d%c", A[i], " \n"[i == 1]);
return 0;
} 版本2:
#include
using namespace std;
int a[200050],b[200050];
int main()
{
auto read=([&]{
int x;cin >> x;
return x;
});
int n=read(),m=read();
int len=max(n,m)+1;
generate_n(a+1,n,read);
generate_n(b+1,m,read);
reverse(a+1,a+n+1);
reverse(b+1,b+m+1);
for (int i=1;i<=len;i++)
{
a[i]+=b[i];
a[i+1]+=(a[i]/(i+1));
a[i]%=(i+1);
}
while (a[len]==0 && len>1)
len--;
reverse(a+1,a+len+1);
for (int i=1;i<=len;i++)
cout << a[i] << " ";
return 0;
} 版本3:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static int[] a = new int[200005];
public static int[] b = new int[200005];
public static int[] c = new int[200005];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt(), m = scanner.nextInt();
int maxLength = Math.max(n, m);
for (int i = (maxLength - n) + 1; i <= maxLength; ++i)
a[i] = scanner.nextInt();
for (int i = (maxLength - m) + 1; i <= maxLength; ++i)
b[i] = scanner.nextInt();
for (int i = maxLength, cnt = 2; i > 0; --i, ++cnt) {
c[i] += a[i] + b[i];
if (c[i] >= cnt) {
c[i] -= cnt;
c[i - 1] += 1;
}
}
if (c[0] > 0) {
System.out.printf("%d ", c[0]);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= maxLength; ++i) {
System.out.printf("%d ", c[i]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}D题:
题目背景
莲子正在研究分子的运动。
每个分子都有一个速度,约定正方向为正,负方向为负。分子的数量极多,速度又并不一致,看上去杂乱无章。于是莲子希望调整部分分子的速度,使得最终分子们看上去整齐。
题解:
参考代码
版本1:
#include
#define up(l, r, i) for(int i = l, END##i = r;i <= END##i;++ i)
#define dn(r, l, i) for(int i = r, END##i = l;i >= END##i;-- i)
using namespace std;
typedef long long i64;
const int INF = 2147483647;
int qread(){
int w=1,c,ret;
while((c = getchar()) > '9' || c < '0') w = (c == '-' ? -1 : 1); ret = c - '0';
while((c = getchar()) >= '0' && c <= '9') ret = ret * 10 + c - '0';
return ret * w;
}
const int MAXN = 1e5 + 3;
int A[MAXN], ans = INF;
int main(){
int n = qread(), m = qread();
up(1, n, i) A[i] = qread();
sort(A + 1, A + 1 + n);
int j = 1;
up(1, min(n, m + 1), i){
j = max(i, j);
while((i - 1) + (n - j) + min(i - 1, n - j) > m) ++ j;
ans = min(ans, A[j] - A[i]);
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
} 版本2:
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
public static int[] a = new int[100005];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt(), m = scanner.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
a[i] = scanner.nextInt();
Arrays.sort(a, 1, n + 1);
int j = 1, ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 1; i <= Math.min(n, m + 1); ++i) {
j = Math.max(j, i);
while((i - 1) + (n - j) + Math.min(i - 1, n - j) > m)
++j;
ans = Math.min(ans, a[j] - a[i]);
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}E题:
题目背景
梅莉这个学期选修了经济学。但是主修心理学的她实在不擅长经济领域的分析,为此她时常抱怨自己学不会,想退课。
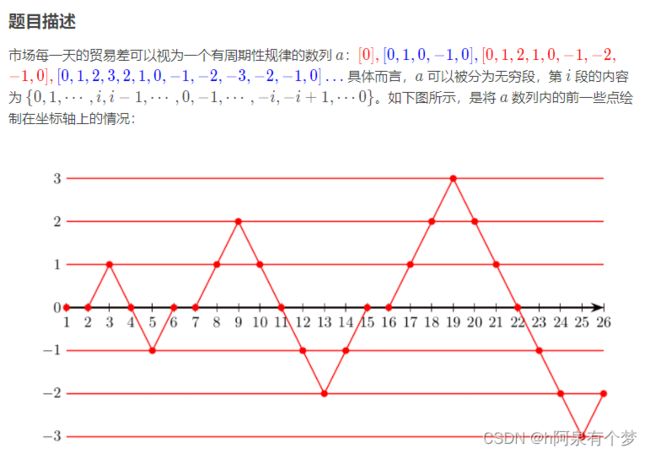
但是如果现在退掉的话这学期的学分就不够啦,因此她根据“梦中”的经历,“胡诌”了一个简单到不现实的市场模型,并依据这个模型编起了 essay。为了方便地编出图表,她需要写一个程序来查询每个时刻的市场贸易差。
题解
参考代码
版本1:
#include
#define up(l, r, i) for(int i = l, END##i = r;i <= END##i;++ i)
#define dn(r, l, i) for(int i = r, END##i = l;i >= END##i;-- i)
using namespace std;
typedef long long i64;
const int INF = 2147483647;
i64 qread(){
i64 w=1,c,ret;
while((c = getchar()) > '9' || c < '0') w = (c == '-' ? -1 : 1); ret = c - '0';
while((c = getchar()) >= '0' && c <= '9') ret = ret * 10 + c - '0';
return ret * w;
}
i64 val(i64 p){return 2 * p * p - p;}
int main(){
up(1, qread(), TTT){
i64 k = qread(), p = 0;
dn(30, 0, i){
if(val(p | 1 << i) < k) p |= 1 << i;
}
int i = p + 1, w = i - 1;
i64 l = val(p) + 1, ll = l + w;
i64 r = val(i), rr = r - w;
if(l <= k && k < ll) printf("%lld\n", k - l ); else
if(ll <= k && k <= rr) printf("%lld\n", w - k + ll); else
printf("%lld\n", k - r);
}
return 0;
}
版本2:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int q;
cin >> q;
while (q--)
{
long long k,l=1,r=2e9,ans=0;
cin >> k;
while (l<=r)
{
long long mid=(l+r)/2;
if ((long long)mid*mid*2-mid>=k)
{
r=mid-1;
ans=mid;
}
else
l=mid+1;
}
ans--;
long long len=ans*ans*2-ans;
k-=len+1;
if (k<=ans)
cout << k << endl;
else if (k<=3*ans)
cout << 2*ans-k << endl;
else
cout << -4*ans+k << endl;
}
return 0;
} 版本3:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
public static long val(long p) {
return p * 2 * p - p;
}
public static class Scanner {
public BufferedReader in;
public StringTokenizer tok;
public String next() { hasNext(); return tok.nextToken(); }
public String nextLine() { try { return in.readLine(); } catch (Exception e) { return null; } }
public long nextLong() { return Long.parseLong(next()); }
public int nextInt() { return Integer.parseInt(next()); }
public PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
public boolean hasNext() {
while (tok == null || !tok.hasMoreTokens()) try { tok = new StringTokenizer(in.readLine()); } catch (Exception e) { return false; }
return true;
}
public Scanner(InputStream inputStream) { in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream)); }
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int q = scanner.nextInt();
while (q-- > 0) {
long k = scanner.nextLong(), p = 0;
for (int i = 30; i >= 0; --i) {
if (val(p | 1 << i) < k)
p |= 1 << i;
}
long i = p + 1, w = i - 1;
long l = val(p) + 1, ll = l + w;
long r = val(i), rr = r - w;
if (l <= k && k < ll)
System.out.println(k - l);
else if (ll <= k && k <= rr)
System.out.println(w - k + ll);
else
System.out.println(k - r);
}
}
}G题
题目背景
梅莉买到了一张特殊的带有花纹的纸。整张纸的图案可以视为,由一个较小的图案,沿着横向与纵向无限循环而成。同时,这个基本图案部分透明,部分不透明。
于是,如果将这张纸覆盖在书本上,那么一些字可以被看见,另一些字看不见。
莲子突发奇想:假使她制作一张很大很大的数表,将花纹纸覆盖在上面,那么就会有很多数字被遮挡。那些没有被遮挡的数字的和是多少呢?
题目描述
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
题解:
 参考代码:
参考代码:
#include
#define up(l, r, i) for(int i = l, END##i = r;i <= END##i;++ i)
#define dn(r, l, i) for(int i = r, END##i = l;i >= END##i;-- i)
using namespace std;
typedef long long i64;
const int INF = 2147483647;
int n, m, r, c, q;
int qread(){
int w=1,c,ret;
while((c = getchar()) > '9' || c < '0') w = (c == '-' ? -1 : 1); ret = c - '0';
while((c = getchar()) >= '0' && c <= '9') ret = ret * 10 + c - '0';
return ret * w;
}
const int MAXN = 2e3 + 3;
const int MAXM = 50 + 3;
const int MOD = 998244353;
int A[MAXN][MAXN], S[MAXN][MAXN]; bool B[MAXN][MAXN];
int calc(int a1, int b1, int a2, int b2){
int ret = S[a2][b2];
if(a1 > r) ret = (ret - S[a1 - r][b2] + MOD) % MOD;
if(b1 > c) ret = (ret - S[a2][b1 - c] + MOD) % MOD;
if(a1 > r && b1 > c) ret = (ret + S[a1 - r][b1 - c]) % MOD;
return ret;
}
int main(){
n = qread(), m = qread();
up(1, n, i) up(1, m, j) A[i][j] = qread();
r = qread(), c = qread();
up(1, r, i) up(1, c, j) B[i][j] = qread();
up(1, n, i) up(1, m, j){
S[i][j] = A[i][j];
if(i > r) S[i][j] = (S[i][j] + S[i - r][j]) % MOD;
if(j > c) S[i][j] = (S[i][j] + S[i][j - c]) % MOD;
if(i > r && j > c)
S[i][j] = (S[i][j] - S[i - r][j - c] + MOD) % MOD;
}
q = qread();
up(1, q, i){
int _x1 = qread(), _y1 = qread();
int _x2 = qread(), _y2 = qread();
int ans = 0;
up(1, min(r, _x2 - _x1 + 1), a)
up(1, min(c, _y2 - _y1 + 1), b) if(B[a][b] == 0){
int a1 = _x1 + a - 1, a2 = a1 + (_x2 - a1) / r * r;
int b1 = _y1 + b - 1, b2 = b1 + (_y2 - b1) / c * c;
ans = (ans + calc(a1, b1, a2, b2)) % MOD;
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
return 0;
} H题
题目背景
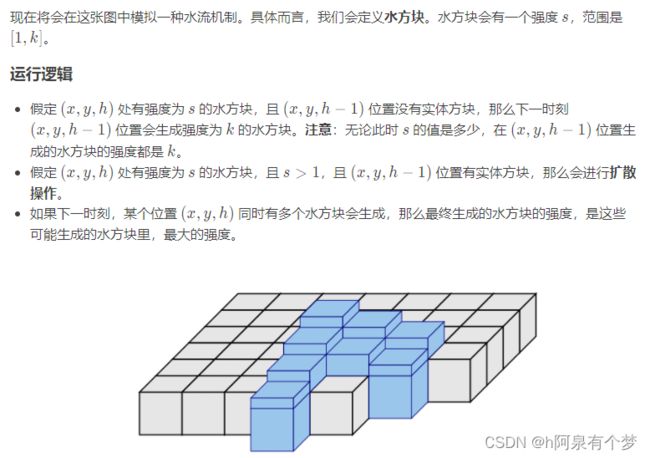
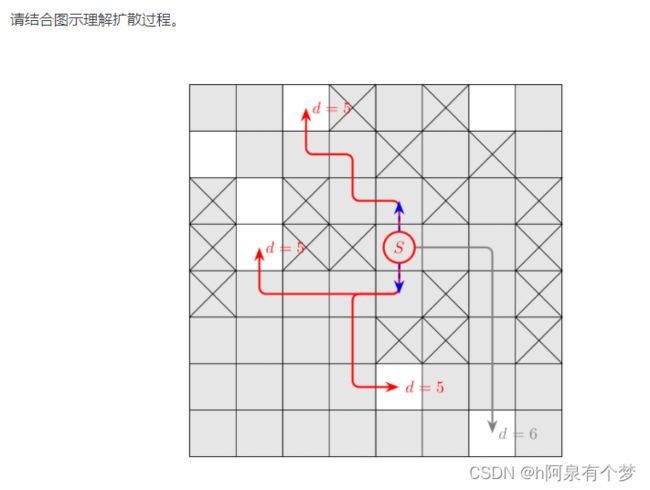
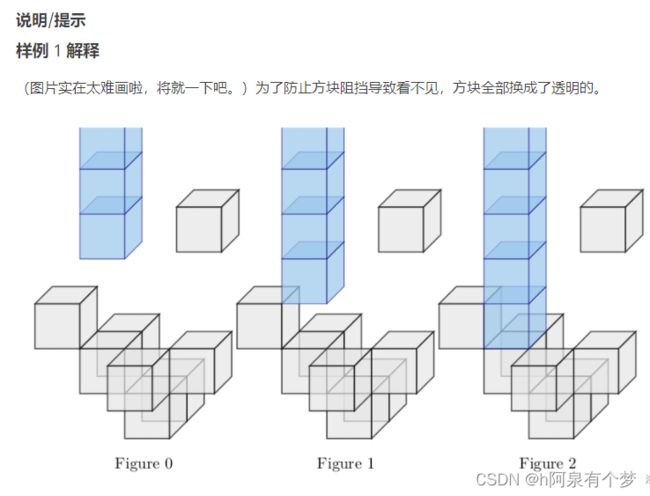
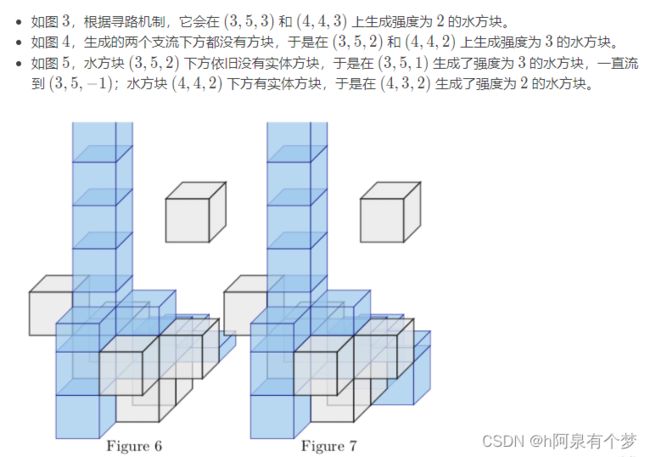
莲子设计了一个三维立体空间软件。这个软件可以模拟真实的物理引擎,包括实体方块和水流方块。然而,同时计算大量水流会对软件造成不小的负荷。
于是,莲子希望找到这样一种算法,快速计算这些水流模拟后的结果。
题解:
搜索题。
注意一个重要性质:水流之间可视为互不干扰的。虽然确实有强度更大的水流可以覆盖强度更小的水流这样的设定,但容易发现强度更大的水流,可以流到的空间,包含了强度更小的水流。
(感性理解一下)
参考代码
代码1:
#include
#define up(l,r,i) for(int i=l,END##i=r;i<=END##i;++i)
#define dn(r,l,i) for(int i=r,END##i=l;i>=END##i;--i)
using namespace std;
typedef long long i64;
const int INF =2147483647;
struct Pos2{
int x, y;
Pos2(int _x = 0, int _y = 0):x(_x), y(_y){}
const bool operator < (const Pos2 &t) const {
if(x != t.x) return x < t.x;
return y < t.y;
}
const bool operator > (const Pos2 &t) const {
if(x != t.x) return x > t.x;
return y > t.y;
}
const bool operator ==(const Pos2 &t) const {
return x == t.x && y == t.y;
}
};
struct Pos3{
int x, y, z;
Pos3(int _x = 0, int _y = 0, int _z = 0):
x(_x), y(_y), z(_z){}
const bool operator < (const Pos3 &t) const {
if(x != t.x) return x < t.x;
if(y != t.y) return y < t.y;
return z < t.z;
}
const bool operator > (const Pos3 &t) const {
if(x != t.x) return x > t.x;
if(y != t.y) return y > t.y;
return z > t.z;
}
const bool operator ==(const Pos3 &t) const {
return x == t.x && y == t.y && z == t.z;
}
};
const int BASE = 13331;
struct Hash{
unsigned operator ()(const Pos2 t) const{
return t.x * BASE + t.y;
}
unsigned operator ()(const Pos3 t) const{
return (t.x * BASE + t.y) * BASE + t.z;
}
};
unordered_map B; // 存 (x, y, z) 是否有方块
unordered_map V; // 存 (x, y, h + 1) 有没有使用过
unordered_map D; // 存 (x, y) 的最短路程
unordered_map W; // 存 (x, y, h + 1) 位置有没有水方块
unordered_map K; // 存 (x, y, h + 1) 位置水方块的强度
const int DIR[4][2] = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 3;
int n, p, X[MAXN], Y[MAXN], Z[MAXN], I[MAXN];
int qread(){
int w = 1, c, ret;
while((c = getchar()) > '9' || c < '0') w = (c == '-' ? -1 : 1); ret = c - '0';
while((c = getchar()) >= '0' && c <= '9') ret = ret * 10 + c - '0';
return ret * w;
}
bool cmp(int a, int b){ return Z[a] > Z[b]; }
int _x0, _y0;
int main(){
n = qread(), p = qread(), _x0 = qread(), _y0 = qread();
W[Pos2(_x0, _y0)] = true;
up(1, n, i){
X[i] = qread(), Y[i] = qread(), Z[i] = qread(), I[i] = i;
B[Pos3(X[i], Y[i], Z[i])] = true;
}
sort(I + 1, I + 1 + n, cmp);
up(1, n, i){
int h = Z[I[i]], j;
queue P, Q;
for(j = i;j <= n && Z[I[j]] == h;++ j){
int o = I[j], x = X[o], y = Y[o];
Pos2 u(x, y);
if(W.count(u))
P.push(u), K[u] = p, W.erase(u);
up(0, 3, k){
int nx = x + DIR[k][0];
int ny = y + DIR[k][1];
Pos2 v(nx, ny);
if(!V.count(v) && !B.count(Pos3(nx, ny, h))
&& !B.count(Pos3(nx, ny, h + 1)))
V[v] = true, D[v] = 0, Q.push(v);
}
}
while(!Q.empty()){
Pos2 u = Q.front(); Q.pop(); int x = u.x, y = u.y;
up(0, 3, k){
int nx = x + DIR[k][0];
int ny = y + DIR[k][1];
Pos2 v(nx, ny);
if(!D.count(v) && B.count(Pos3(nx, ny, h))
&& !B.count(Pos3(nx, ny, h + 1)))
D[v] = D[u] + 1, Q.push(v);
}
}
while(!P.empty()){
Pos2 u = P.front(); P.pop(); int x = u.x, y = u.y;
int d = D[u], s = K[u];
if(!B.count(Pos3{x, y, h})){
W[u] = true; continue;
}
if(s == 1) continue;
up(0, 3, k){
int nx = x + DIR[k][0];
int ny = y + DIR[k][1];
Pos2 v(nx, ny);
if( D[v] == d - 1)
if(!K.count(v) && !B.count(Pos3(nx, ny, h + 1)))
K[v] = s - 1, P.push(v);
}
}
i = j - 1, D.clear(), K.clear(), V.clear();
}
printf("%u\n", W.size());
return 0;
} 代码2:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static class Vec2d {
public int x, y;
public Vec2d(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Arrays.hashCode(new int[] {x, y});
}
public boolean equals(Vec2d vec2d) {
return this.x == vec2d.x && this.y == vec2d.y;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object vec2d) {
if (!(vec2d instanceof Vec2d))
return false;
return this.x == ((Vec2d) vec2d).x && this.y == ((Vec2d) vec2d).y;
}
}
public static class Vec3d {
public int x, y, z;
public Vec3d(int x, int y, int z) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.z = z;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Arrays.hashCode(new int[] {x, y, z});
}
public boolean equals(Vec3d vec2d) {
return this.x == vec2d.x && this.y == vec2d.y && this.z == vec2d.z;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object vec2d) {
if (!(vec2d instanceof Vec3d))
return false;
return this.x == ((Vec3d) vec2d).x && this.y == ((Vec3d) vec2d).y && this.z == ((Vec3d) vec2d).z;
}
}
public static class Scanner {
public BufferedReader in;
public StringTokenizer tok;
public String next() {
hasNext();
return tok.nextToken();
}
public String nextLine() {
try {
return in.readLine();
} catch (Exception e) {
return null;
}
}
public long nextLong() {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
public int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
public PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
public boolean hasNext() {
while (tok == null || !tok.hasMoreTokens()) try {
tok = new StringTokenizer(in.readLine());
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
public Scanner(InputStream inputStream) {
in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
}
}
public static Map isblock = new HashMap<>();
public static Map isused = new HashMap<>();
public static Map dist = new HashMap<>();
public static Map iswater = new HashMap<>();
public static Map strwater = new HashMap<>();
public static final int[] dx = {1, -1, 0, 0}, dy = {0, 0, 1, -1};
public static int n, k, _x0, _y0;
public static int[] x = new int[100050], y = new int[100050], z = new int[100050];
public static List var_id = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
n = scanner.nextInt();
k = scanner.nextInt();
_x0 = scanner.nextInt();
_y0 = scanner.nextInt();
iswater.put(new Vec2d(_x0, _y0), true);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
x[i] = scanner.nextInt();
y[i] = scanner.nextInt();
z[i] = scanner.nextInt();
isblock.put(new Vec3d(x[i], y[i], z[i]), true);
var_id.add(i);
}
var_id.sort((x, y) -> z[y] - z[x]);
List id = new ArrayList<>();
id.add(0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
id.add(var_id.get(i));
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
id.add(0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int height = z[id.get(i)];
Queue p = new LinkedList<>(), q = new LinkedList<>();
// spread at the same height
for (int nid = id.get(i); i <= n && z[nid] == height; ) {
int nx = x[nid], ny = y[nid];
Vec2d u = new Vec2d(nx, ny);
if (iswater.getOrDefault(u, false)) {
iswater.put(u, false);
p.add(u);
strwater.put(u, k);
}
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
int nx1 = nx + dx[j], ny1 = ny + dy[j];
Vec2d v = new Vec2d(nx1, ny1);
Vec3d v1 = new Vec3d(nx1, ny1, height);
Vec3d v2 = new Vec3d(nx1, ny1, height + 1);
if (!isused.getOrDefault(v, false) && !isblock.getOrDefault(v1, false) && !isblock.getOrDefault(v2, false)) {
isused.put(v, true);
dist.put(v, 0);
q.add(v);
}
}
i++;
nid = id.get(i);
}
i--;
// spread water in Q
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Vec2d var1 = q.element();
q.remove();
int x = var1.x, y = var1.y;
Vec2d u = new Vec2d(x, y);
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
int nx = x + dx[j], ny = y + dy[j];
Vec2d v = new Vec2d(nx, ny);
Vec3d v1 = new Vec3d(nx, ny, height);
Vec3d v2 = new Vec3d(nx, ny, height + 1);
if (dist.getOrDefault(v, 0) == 0 && isblock.getOrDefault(v1, false) && !isblock.getOrDefault(v2, false)) {
dist.put(v, dist.get(u) + 1);
q.add(v);
}
}
}
//spread water in P
while (!p.isEmpty()) {
Vec2d var1 = p.element();
p.remove();
int x = var1.x, y = var1.y;
Vec2d u = new Vec2d(x, y);
Vec3d u1 = new Vec3d(x, y, height);
int d = dist.getOrDefault(u, 0), s = strwater.getOrDefault(u, 0);
if (!isblock.getOrDefault(u1, false)) {
iswater.put(u, true);
continue;
}
if (s == 1)
continue;
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
int nx = x + dx[j], ny = y + dy[j];
Vec2d v = new Vec2d(nx, ny);
Vec3d v1 = new Vec3d(nx, ny, height + 1);
if (dist.getOrDefault(v, 0) == d - 1 && strwater.getOrDefault(v, 0) == 0 && !isblock.getOrDefault(v1, false)) {
strwater.put(v, s - 1);
p.add(v);
}
}
}
isused.clear();
dist.clear();
strwater.clear();
}
int cnt = 0;
for (boolean i : iswater.values()) {
cnt += i ? 1 : 0;
}
System.out.println(cnt);
}
}