【Linux 线程同步】互斥锁,信号量,条件变量,读写锁
线程同步
- 互斥锁
-
- API
- 互斥锁的案例
- 5个线程同时对一个全局变量加1000次
- 信号量
-
- API
- 信号量的案例
- 条件变量
-
- API
- 案例
- 读写锁
-
- API
- 案例
互斥锁
API
int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *mutex,pthread_mutexattr_t*attr);
mutex 参数表示要初始化的互斥锁;attr 参数用于自定义新建互斥锁的属性,attr 的值为 NULL 时表示以默认属性创建互斥锁。
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);对互斥锁进行加锁
int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);对互斥锁进行解锁
int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);摧毁互斥锁
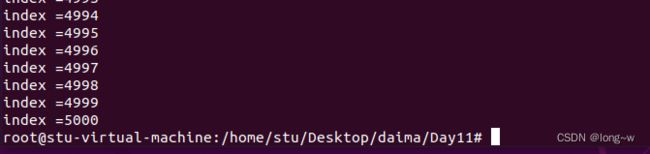
互斥锁的案例
5个线程同时对一个全局变量加1000次
#include信号量
API
int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value);创建信号量
要创建的信号量
pshared 控制信号量的类型,值为 0 代表该信号量用于多线程间的同步,值如果大于 0 表示可以共享,用于多个相关进程间的同步
value为给该信号量的初始值
int sem_wait(sem_t*sem);对该信号量减1
int sem_post(sem_t*sem);对该信号量加1
int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem);摧毁该信号量
信号量的案例
当创建1个信号量且它的值为1时,可以实现和互斥锁一样的功能
下面为5个线程同时对一个全局变量加1000次
#include条件变量
API
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_condattr_t*attr);
cond: 用于指明要初始化的条件变量;
attr :用于自定义条件变量的属性,通常我们将它赋值为 NULL,表示以系统默认的属性完成初始化操作。
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
cond :表示已初始化好的条件变量;
mutex:表示与条件变量配合使用的互斥锁;
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);唤醒单个线程
cond :表示初始化好的条件变量
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);唤醒所有等待的线程
cond :表示初始化好的条件变量
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t*cond);销毁条件变量
cond :表示初始化好的条件变量
案例
获得键盘输入,并通知一个线程打印
#include读写锁
写的时候不能读,可以多个线程同时读,但是只能有一个线程一个时刻写
API
int pthread_rwlock_init(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock, pthread_rwlockattr_t *attr); 初始化锁
rwlock:要初始化的锁
attr:表示读写锁属性,通常传NULL,表示使用默认属性;
int pthread_rwlock_rdlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);以读方式请求锁
rwlock:要请求的锁
int pthread_rwlock_wrlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);以写的方式请求锁
rwlock:要请求的锁
int pthread_rwlock_unlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);解锁
rwlock:要解锁的锁
int pthread_rwlock_destroy(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);销毁锁
rwlock:要销毁的锁
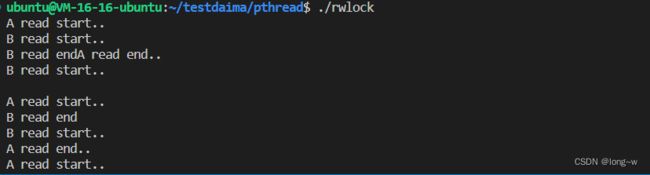
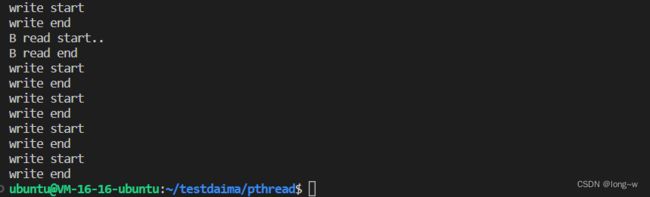
案例
用两个线程模仿读,一个线程模仿写
#include