ubus 介绍
转载https://www.cnblogs.com/gr-nick/p/10805608.html
一、 介绍
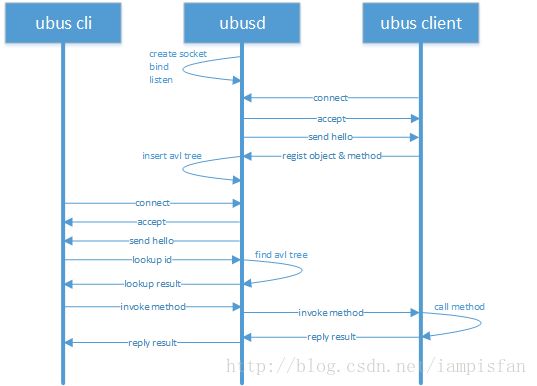
ubus提供了一种多进程通信的机制。存在一个守护进程ubusd,所以进程都注册到ubusd,ubusd进行消息的接收、分发管理。
- ubus依赖于ubox
- ubus启动后会在后台运行ubusd进程,该进程监听一个unix套接字用于与其他应用程序通信。其他应用程序可基于libubox提供的接口(或自己实现)与其通信。
- ubus是为发送消息而设计的,不合适传输大量数据。
ubusd
二、三种实现方式:
1. invoke的方式实现端对端通信
server端:ubus_send_reply(ctx, req, b.head);
uloop_init();
ctx = ubus_connect(NULL);
ubus_add_uloop(ctx);
static struct ubus_method scan_methods[] =
{
UBUS_METHOD("scan", ubus_start_scan, scan_policy),
};
static struct ubus_object scan_obj =
{
.name = "scan_prog", /* 对象的名字 */
.type = &scan_obj_type,
.methods = scan_methods,
.n_methods = ARRAY_SIZE(scan_methods),
};
ubus_add_object(ctx, scan_obj);
ubus_send_reply(ctx, req, b.head);
uloop_run();
ubus_free(ctx);
client端:ubus_invoke(ctx, id, "scan", b.head, scanreq_prog_cb, NULL, timeout * 1000);
uloop_init();
ctx = ubus_connect(path);
struct blob_buf b;
blob_buf_init(&b, 0);
ubus_lookup_id(ctx, "scan_prog", &id);
ubus_invoke(ctx, id, "scan", b.head, scanreq_prog_cb, NULL, timeout * 1000);
ubus_free(ctx);
2. subscribe/notify的方式实现订阅
server端:ubus_notify(ctx, &test_object, "say Hi!", NULL, -1);
static struct ubus_object test_object = {
.name = "test", /* object的名字 */
.type = &test_obj_type,
.subscribe_cb = test_client_subscribe_cb,
};
static void test_client_subscribe_cb(struct ubus_context *ctx, struct ubus_object *obj)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Subscribers active: %d\n", obj->has_subscribers);
}
uloop_init();
ctx = ubus_connect(NULL);
ubus_add_uloop(ctx);
ret = ubus_add_object(ctx, &test_object);
while (1) {
sleep(2);
/* step2: 广播notification消息。 */
ubus_notify(ctx, &test_object, "say Hi!", NULL, -1);
}
uloop_run();
ubus_free(ctx);
uloop_done();
client端:ret = ubus_register_subscriber(ctx, &test_event);
static int test_notify(struct ubus_context *ctx, struct ubus_object *obj, struct ubus_request_data *req, const char *method, struct blob_attr *msg)
{
printf("notify handler...\n");
}
static void test_handle_remove(struct ubus_context *ctx,
struct ubus_subscriber *obj, uint32_t id)
{
printf("remove handler...\n");
}
uloop_init();
ctx = ubus_connect(NULL);
ubus_add_uloop(ctx);
struct ubus_subscriber test_event;
/* 通知到来时的处理函数。 */
test_event.cb = test_notify;
test_event.remove_cb = test_handle_remove; //server主动发起删除该client的订阅的cb函数(如server退出的时候)
/* 注册test_event */
ret = ubus_register_subscriber(ctx, &test_event);
uint32_t obj_id;
ret = ubus_lookup_id(ctx, "test", &obj_id);
ret = ubus_subscribe(ctx, &test_event, obj_id);
uloop_run();
ubus_free(ctx);
uloop_done();
3. 广播事件
server端:发送事件广播消息, ubus_send_event(ctx, "add_device", b.head);
uloop_init();
ctx = ubus_connect(NULL);
blob_buf_init(&b, 0);
/* 需要传递的参数 */
blobmsg_add_u32(&b, "major", 3);
blobmsg_add_u32(&b, "minor", 56);
blobmsg_add_string(&b, "name", "mmc01");
/* 广播名为"add_device"的事件 */
return ubus_send_event(ctx, "add_device", b.head);
ubus_free(ctx);
client端:ret = ubus_register_event_handler(ctx, &listener, "add_device");
#define UBUS_EVENT_ADD_DEVICE "add_device"
#define UBUS_EVENT_REMOVE_DEVICE "rm_device"
static void ubus_probe_device_event(struct ubus_context *ctx, struct ubus_event_handler *ev,
const char *type, struct blob_attr *msg)
{
char *str;
if (!msg)
return;
str = blobmsg_format_json(msg, true);
printf("{ \"%s\": %s }\n", type, str);
free(str);
}
uloop_init();
ctx = ubus_connect(NULL);
ubus_add_fd();
ubus_add_uloop(ctx);
static struct ubus_event_handler listener;
memset(&listener, 0, sizeof(listener));
listener.cb = ubus_probe_device_event;
ret = ubus_register_event_handler(ctx, &listener, UBUS_EVENT_ADD_DEVICE);
ret = ubus_register_event_handler(ctx, &listener, UBUS_EVENT_REMOVE_DEVICE);
uloop_run();
ubus_free(ctx);
三、uloop源码
1. uloop_init
/**
*初始化事件循环
*主要工作是poll_fd = epoll_create(32);/* 创建一个epoll的文件描述符监控句柄。最多监控32个文件描述符
**/
int uloop_init(void)
{
if (poll_fd >= 0)
return 0;
poll_fd = epoll_create(32);/* 创建一个epoll的句柄。最多监控32个文件描述符 */
if (poll_fd < 0)
return -1;
fcntl(poll_fd, F_SETFD, fcntl(poll_fd, F_GETFD) | FD_CLOEXEC); /* fd_cloexecs */
return 0;
}
2. uloop_run
/**
* 事件循环主处理入口
*1.当某一个进程第一次调用uloop_run时,注册sigchld和sigint信号
*2.循环获取当前时间,把超时的timeout处理掉,有一条timeout链表在维护
*3.循环检测是否收到一个sigchld信号,如果收到,删除对应的子进程,有一条process子进程链表在维护
*4.循环调用epoll_wait 监相应的触发事件文件描述符fd
**/
void uloop_run(void)
{
static int recursive_calls = 0; /* static value */
struct timeval tv;
/*
* Handlers are only updated for the first call to uloop_run() (and restored
* when this call is done).
*/
if (!recursive_calls++) /* 第一次运行uloop_run时调用, 注册信号处理函数 */
uloop_setup_signals(true);
uloop_cancelled = false;
while(!uloop_cancelled)
{
uloop_gettime(&tv); /* 获取当前时间 */
uloop_process_timeouts(&tv); /* 把超时的timeout清理掉 */
if (uloop_cancelled)
break;
if (do_sigchld) /* 收到一个sigchld的信号 */
uloop_handle_processes(); /* 销毁该进程的uloop_process */
uloop_gettime(&tv);
uloop_run_events(uloop_get_next_timeout(&tv));/* 处理相应的触发事件fd */
}
if (!--recursive_calls)
uloop_setup_signals(false);
}
3. uloop_done
/**
* 销毁事件循环
* 关闭epoll描述符
* 销毁子进程链表
* 销毁timeout链表
**/
void uloop_done(void)
{
if (poll_fd < 0)
return;
close(poll_fd);
poll_fd = -1;
uloop_clear_timeouts();
uloop_clear_processes();
}
四、uloop三种使用
1. socket使用
uloop_fd_add(uloop_fd, ULOOP_READ);
#include ""
struct uloop_fd ufd; //创建uloop_fd全局变量
static void fd_handler(struct uloop_fd *u, unsigned int ev)
{
if(recvfrom(u->fd, ...)) == -1) {
} else {
//do your work
}
}
int main()
{
//
int socket = socket(....);
ufd.fd = socket;
uloop_init(); //使用库初始化
ufd.cb = fd_handler;
uloop_fd_add(&ufd, ULOOP_READ));
uloop_run();
}
2. 定时器使用
uloop_timeout_set(uloop_timeout, freq);
#include ""
struct uloop_timeout timeout; //创建uloop_timeout全局变量
int frequency = 5; //每隔5秒超时一次
static void timeout_cb(struct uloop_timeout *t)
{
//do your work
uloop_timeout_set(t, frequency * 1000);//设置下次的超时时间
}
int main()
{
uloop_init(); //使用库初始化
timeout.cb = timeout_cb;
uloop_timeout_set(&timeout, frequency * 1000);//设置下次的超时时间
uloop_run();
}
3. 子进程使用
uloop_process_add(uloop_process);
#include ""
static struct uloop_process rsync; //创建rsync全局变量
static void rsync_complete(struct uloop_process *proc, int ret)
{
//do something where child exit;
printf("rsync work is complete\n");
}
function fun()
{
char *argv[]={"rsync", "-az", "rsync://[email protected]/www","/root/www/","--password-file=/root/rsync.secrets", NULL};
rsync.cb = rsync_complete;
rsync.pid = fork();
if (!rsync.pid) {
/* This is child process*/
execvp(argv[0], argv);
fprintf(stderr, "fork failed\n");
exit(-1);
}
if (rsync.pid <=0) {
fprintf(stderr, "fork failed2\n");
return -1;
}
uloop_process_add(&rsync);
}
int main()
{
.....
uloop_init(); //使用库前进行初始化
fun();
uloop_run();
}
五、数据传输
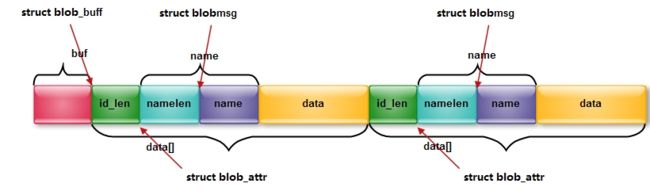
1. blobmsg
enter description here
初始化:
json_uri = blobmsg_open_array(&b, "prog_list");
for (idx = 0; idx < PROG_MAX; idx++)
{
if ('\0' != uri_list[idx].name[0])
{
json_list = blobmsg_open_table(&b, NULL);
blobmsg_add_string(&b, "name", uri_list[idx].name);
blobmsg_add_u32(&b, "channel", uri_list[idx].chn_id);
blobmsg_close_table(&b, json_list);
}
}
blobmsg_close_array(&b, json_uri);
解析:
获取索引: hdr = blob_data(attr); char *name = (char *)hdr->name;
获取数据: blobmsg_get_u32(attr);
获取长度: int len = blobmsg_data_len(tb[RSP_GET_STREAMINFO_ABILITY]);
struct blob_attr *tb[SCAN_POLICY_MAX];
blobmsg_parse(scan_policy, SCAN_POLICY_MAX, tb, blob_data(msg), blob_len(msg));
struct blob_attr *head = blobmsg_data(tb[RSP_GET_STREAMINFO_ABILITY]);
int len = blobmsg_data_len(tb[RSP_GET_STREAMINFO_ABILITY]);
struct blob_attr *attr;
struct blobmsg_hdr *hdr;
__blob_for_each_attr(attr, head, len) {
hdr = blob_data(attr);
struct blob_attr *head_temp;
struct blob_attr *attr_temp;
int len_temp;
char *name = (char *)hdr->name;
if (!strcmp(name, "fmt_number"))
rsp->ability.fmt_number = blobmsg_get_u32(attr);
else if (!strcmp(name, "frmival_num"))
rsp->ability.frmival_num = blobmsg_get_u32(attr);
}
六、Problem
现在使用中遇到了多线程的问题,由于ubus许多变量都是全局变量,对多线程的支持并不好。比如同时在两个线程中监听广播和发送消息,就会出现segment错误:
解决方法,最好能把两个操作放到一个线程中,比如在监听的回调函数中发送消息,不好的就是要根据发送消息的频率去设置回调函数的timeout。
Reference
https://blog.csdn.net/xiaoxiaozhu2010/article/details/78645339
https://www.cnblogs.com/embedded-linux/p/6791560.html