SpringSecurity学习(六)CORS跨域、异常处理
CORS跨域
一. 跨域简介
跨域问题是实际应用开发中一个常见的问题,在Spring框架中对于跨域问题的处理方案由好几种,引入了SpringSecurity后,新增了跨域问题的处理方案。
1. 什么是跨域
CORS是W3C的一种跨域资源共享技术标准,目的是为了解决前端跨域请求(浏览器同源策略会对跨域请求进行拦截)。早期方案由JSONP(仅支持GET),而CORS支持多种http请求,目前主流方案。
cors中新增了一组 http请求头字段,通过这些字段告诉浏览器,那些网站通过浏览器有权限访问那些资源。同时规定,对哪些可能修改服务器数据的http请求方法,浏览器必须首先使用options方法发起一个预检请求(prenightst),预检的目的是为了查看服务端是否支持跨域,如果服务端允许,才发送实际http请求。在预检请求的返回中,服务器也可以告诉客户端,是否需要携带认证信息(cookie、http认证等)。
同源策略:协议(Http/Https)://主机Host:端口Port
简单请求
GET请求为例:如果需要发起一个跨域请求,则请求头如下
Host: localhost:8888
Origin: http://localhost:9999
Referer: http://localhost:9999/index.html
如果服务端支持跨域请求,则返回的乡音头中包含以下字段:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin:http://localhost:9999
Access-Control-Allow-Origin字段用来告诉可以访问该资源的域,当浏览器接受到此类响应头信息后,提取Access-Control-Allow-Origin字段的值,如果该值包含当前域,则允许跨域,不再对前端跨域进行限制。这属于简单请求,即不需要进行预检请求的跨域。
非简单请求
对于一些非简单请求,会先发送一个预检请求,预检请求格式如下:
OPTIONS /put HTTP/1.1 // 请求方法
Host: localhost:8888 //
Connection: keep-alive
Accept: */* /*接受*/
Access-Control-Request-Method: PUT // 将发起的跨域请求使用方式
Origin: http://localhost:9999 // 服务器当前页面所在域
Referer: http://localhost:9999/index.html //当前页面
服务端对此进行判断,如果允许跨域,则响应如下:
HTTP/1.1 200
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://localhost:9999 // 允许跨域的域
Access-Control-Request-Methods: PUT // 允许跨域的方法
Access-Control-Max-Age: 3600 // 预检请求的有效期,单位秒
在预检请求结束后,就会发起一个真正的跨域请求,跨域请求和前面的简单跨域请求类似。
二. Spring的跨域解决方案
1. @CrossOrigin注解(类、方法)
通过注解@CrossOrigin来标记支持跨域,该注解可以添加在方法上,或者Controller类上。
属性:
- allowCredentials:浏览器是否应当发送凭证信息
- allowedFeaders:请求被允许的请求头字段,
*表所有字段 - exposedHeaders:哪些响应头可以作为响应的一部分暴露出来(需要一一列举,
*通配符无效)。 - maxAge:预检请求有效期,默认1800秒
- methods:允许请求的方法,
*表所有方法 - origins:允许的域,
*表所有
2. @addCrosMapping
需要添加在不同的Controller上。还有一种全局的配置方法,通过重写WebMvcConfigure的addCrosMapping方法来实现。

3. CrosFilter
CorsFilter是springweb提供的一个处理跨域的过滤器,开发者可以通过该处理器处理跨域问题。
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfig {
@Bean
FilterRegistrationBean<CorsFilter> corsFilter() {
FilterRegistrationBean<CorsFilter> registrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean<>();
CorsConfiguration corsConfiguration = new CorsConfiguration();
corsConfiguration.setAllowedHeaders(Collections.singletonList("*"));
corsConfiguration.setAllowedMethods(Collections.singletonList("*"));
corsConfiguration.setAllowedOrigins(Collections.singletonList("*"));
corsConfiguration.setMaxAge(3600L);
UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource source = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();
source.registerCorsConfiguration("/**", corsConfiguration);
registrationBean.setFilter(new CorsFilter(source));
registrationBean.setOrder(-1); //设置优先级为最高 正常的 0、1等
return registrationBean;
}
}
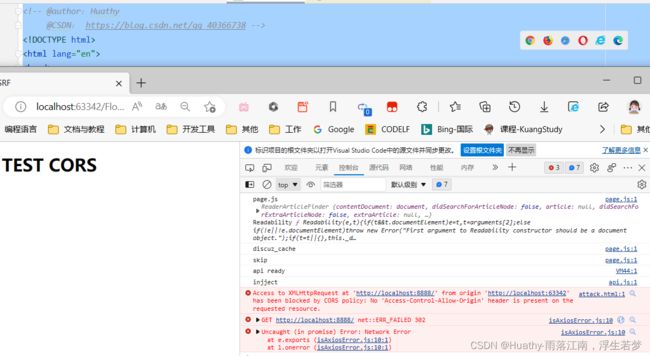 可见在引入SpringSecurity后第三种方式也同样失效了。
可见在引入SpringSecurity后第三种方式也同样失效了。
三、SpringSecurity的跨域解决方
1. 原理分析
当我们对项目添加SpringSecurity依赖后,发现上面三种跨域方式有的失效了,有的可以继续使用。
通过@CrossOrigin注解或者重写addCorsMappings方法配置跨域都失效了,通过CorsFilter配置的跨域是否失效则要看过滤器的优先级,如果过滤器的优先级高于SpringSecurity过滤器(咸鱼SpringSecurity过滤器执行)则CorsFilter所配置的跨域处理器依然有效。
为了清除这个问题,需要了解Filter、DispatcherServlet、Interceptor执行顺序。
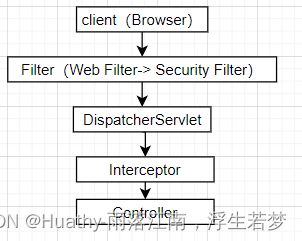
了解了执行顺序,再来看跨域请求过程。由于非简单跨域请求都要先发送 一个预检请求,而预检请求不会携带认证信息,所以预检请求就有可能被SpringSecurity拦截。所以通过@CrossOrigin注解或者重写addCorsMappings方法配置的跨域就会失效。如果使用CorsFilter配置跨域,只有当该过滤器优先于SpringSecurity过滤器加载就不会有问题。但是经过上面的测试最终也是失效的。
2. 实现:SecurityConfig中配置CorsConfigurationSource
@EnableWebSecurity
@Slf4j
public class SecurityConfig1 {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeHttpRequests(req -> {
req.anyRequest().authenticated();
});
http.formLogin();
// 禁用/开启csrf跨站请求伪造攻击防御
http.csrf().disable();
http.cors().configurationSource(corsConfigSource());
return http.build();
}
private CorsConfigurationSource corsConfigSource() {
CorsConfiguration configuration = new CorsConfiguration();
configuration.setAllowedHeaders(Collections.singletonList("*"));
configuration.setAllowedOrigins(Collections.singletonList("*"));
configuration.setAllowedMethods(Collections.singletonList("*"));
configuration.setMaxAge(3600L);
UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource source = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();
source.registerCorsConfiguration("/**", configuration);
return source;
}
}
异常处理
一、SpringSecurity异常体系
SpringSecurity中异常主要分为俩大类:
- AuthenticationException:认证异常
- AccessDeniedException:授权异常
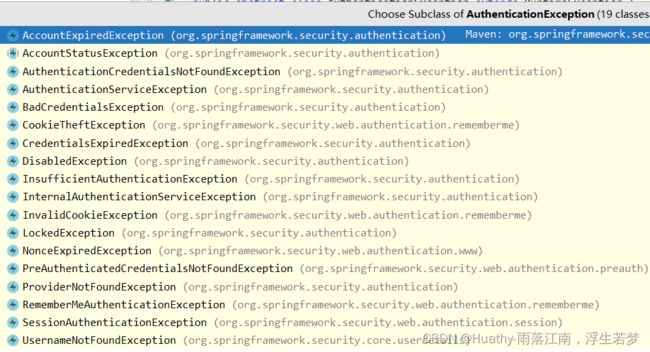
其中认证所涉及异常类型比较多,默认提供以下异常类型:
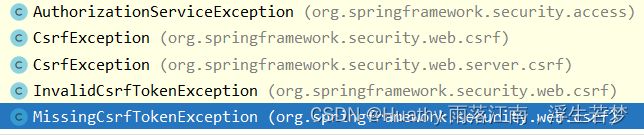
 权限异常类较少,默认提供以下异常类型:
权限异常类较少,默认提供以下异常类型:
 在实际项目开发中,如果默认提供异常类型无法满足业务需求,则需要根据实际来自定义异常类。
在实际项目开发中,如果默认提供异常类型无法满足业务需求,则需要根据实际来自定义异常类。
二、自定义异常配置
@EnableWebSecurity
@Slf4j
public class SecurityCfg3_ExceptionDemo {
@Autowired
private AuthenticationConfiguration authenticationConfiguration;
@Bean
public LoginFilter loginFilter() throws Exception {
log.info(" === loginFilter init ===");
LoginFilter loginFilter = new LoginFilter();
// 指定接受json的用户名密码参数名称
loginFilter.setFilterProcessesUrl("/dologin");
loginFilter.setUsernameParameter("uname");
loginFilter.setPasswordParameter("pwd");
loginFilter.setAuthenticationManager(authenticationConfiguration.getAuthenticationManager());
loginFilter.setAuthenticationSuccessHandler((req, resp, authentication) -> {
Map<String, Object> resMap = new HashMap<>();
resMap.put("用户信息", authentication.getPrincipal());
resMap.put("authentication", authentication);
Result result = Result.success(resMap);
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8");
String jsonData = new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(result);
resp.setStatus(HttpStatus.OK.value());
resp.getWriter().write(jsonData);
});
loginFilter.setAuthenticationFailureHandler((req, resp, exception) -> {
Result result = Result.fail("登录失败", exception.getMessage());
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8");
String jsonData = new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(result);
resp.getWriter().write(jsonData);
});
return loginFilter;
}
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeHttpRequests()
.mvcMatchers("/hi").hasAnyRole("admin")
.anyRequest().authenticated().and().formLogin();
http.exceptionHandling().authenticationEntryPoint((req, resp, exception) -> {
resp.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
resp.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
resp.setStatus(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.value());
// 精细化的异常处理
// if(exception instanceof LockedException){
// resp.getWriter().println("用户锁定!");
// }
resp.getWriter().println("请求未认证!");
}).accessDeniedHandler((req, resp, exception) -> {
resp.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
resp.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
resp.setStatus(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.value());
resp.getWriter().println("无权访问!");
});
http.csrf().disable();
// at:用当前过滤器来替换过滤器链中的哪个过滤器。before放在哪个过滤器之前,after放在哪个过滤器后
http.addFilterAt(loginFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
log.info(" === 替换了成了LoginFilter === ");
return http.build();
}
}