MySQL基础学习(三)————SQL语句的常用操作
文章目录
- 1、库
-
- 1.1库的创建
- 1.2 库的删除
- 1.3 库的修改
- 1.4 库的查找
- 2、表
-
- 2.1 表的创建
- 2.2 表的删除
- 2.3 表的修改
- 2.4 表的查找
- 3、数据或者记录
-
- 3.1 数据的增加
- 3.2 数据的删除
- 3.3 数据的修改
- 3.4 数据的查找
- 4、常用关键字
-
- 4.1 distinct(这个关键字是过滤重复的数据)
- 4.2 limit(限制结果集,限制输出结果的行数)
- 4.3 order by(排序)
- 4.4 as(别名)
- 4.5 group by(分组查询)
- 4.6 聚合函数(统计函数)
- 4.7 SQL的注释
- 5、执行顺序
- 6、数据完整性
-
- 6.1 实体完整性
- 6.2 域完整性
- 6.3 参照完整性
- 7、三大范式
-
- 7.1 第一范式: 原子性
- 7.2 第二范式: 唯一性
- 7.3 第三范式: 字段不要冗余
- 8、多表查询
-
- 8.1 连接查询
-
- 8.1.1 交叉查询
- 8.1.2 内连接
- 8.1.3 外连接
- 8.2 子查询
- 8.3 联合查询
- 9、数据的备份与恢复
-
- 9.1 命令实现
- 9.2 图形化界面
1、库
1.1库的创建
`create database dbName [character set utf8 collate utf8_bin]`
说明:character set : 字符集
collate : 校对规则
字符集常用的是 utf8,他的校对规则常用的有两种,utf8_bin(区分大小写) utf8_general_ci (不区分大小写的)
还有一种 utf8mb4,这种字符集其实是在utf8的基础之上进行了扩展与补充。
还有一种叫做 latin1,这种字符集是不支持中文的
1.2 库的删除
drop database [if exists] dbName;
1.3 库的修改
注意:我们不能修改数据库的名字,只能修改字符集和校对规则
alter database 31th_sql character set utf8 collate utf8_general_ci ;
1.4 库的查找
- 显示所有的数据库
show databases;
- 显示某一个数据库的建库语句
show create database dbName;
2、表
2.1 表的创建
# 对表操作之前,我们需要让数据库知道我们去操作的表在哪一个数据库里面。
use 31th_sql;
## 表的增删改查
# 增
-- 整数类型
create table t_int (
t1 tinyint,
t2 int,
t3 bigint
)character set utf8 collate utf8_bin;
-- 浮点类型
create table t_float (
t1 FLOAT(4,2),
t2 DOUBLE(6,2),
t3 DECIMAL(8,2)
);
-- 关于浮点类型,有一点需要大家注意
-- DECIMAL这个类型底层是以字符串存储的 BigDecimal
-- 时间
set time_zone='+10:00';
create table time1(t1 year, t2 time, t3 date, t4 datetime, t5 timestamp);
insert into time1 values (now(),now(),now(),now(),now());
-- 我们可以发现,datetime跟着MySQL的时区走的,timestamp跟着系统时间走的,在国内,两个时间是一样,这个时候使用timestamp,在国外,应该跟着当地时间走,一般也是使用timestamp
insert into time1 values ('2022','16:33:29','2022-01-22','2022-01-22 16:33:29','2022-01-22 16:33:29');
-- 我们在插入时间类型的时候,一定要加''
-- 字符类型
create table t_str (
t1 varchar(255),
t2 text
);
create table t_str2 (
t1 varchar(255),
t2 text
)character set latin1;
-- 枚举
create table t_enum(
sex ENUM('male','female')
);
-- 集合
create table t_set(
id int,
name varchar(20),
nickname SET('大头','大佬','神')
)character set utf8;
-- 注意:集合和枚举类型都可以规定一个列的取值范围,并且假如数据不对的时候会去校验有没有在定义的枚举类或者是集合类里面,这个是MySQL给我们去做的,但是我们在使用MySQL的时候,原则上是不应该让MySQL负责逻辑相关的校验, 一般不推荐使用ENUM或者是SET
create table employee (
id int,
name varchar(20),
gender varchar(10),
birthday date,
entry_date date,
job varchar(20),
salary DOUBLE(10,2),
resume text
)character set utf8 collate utf8_bin;
2.2 表的删除
-- 删除表
drop table user;
2.3 表的修改
-- 修改表
-- 修改表的表名
rename table employee to user;
-- 修改表的字符集
alter table user character set utf8 collate utf8_bin;
-- 修改表的字段
-- add modify change drop
-- 字段类型
alter table user modify name text;
-- 字段名字
alter table user change name username varchar(250);
alter table user change username name varchar(250);
-- 新增字段
alter table user add weight float(5,2), add nickname varchar(20);
-- 删除字段
alter table user drop nickname;
2.4 表的查找
-- 查表
-- 查询建表语句
show create table employee;
show create table user;
-- 查询表的结构
describe employee;
desc employee;
desc user;
-- 查询表的数据 后面介绍数据的时候讲
3、数据或者记录
3.1 数据的增加
-- 增
insert into employee values (1,'兰钊','male','1983-10-22','2016-10-22','老板',100000,'老板真的很严格');
insert into employee values
(2,'长风','male','1998-10-22','2020-10-22','打工人',1000,'长风真的很细心'),
(3,'天明','male','1993-10-22','2018-10-22','打工人',100000,'浪里小白龙');
insert into employee (id,name) values (4,'景天');
3.2 数据的删除
-- 删除
delete from employee where id = 4;
3.3 数据的修改
-- 修改
update employee set job = '老板';
update employee set job = '打工人' where name = '长风';
update employee set job = '打工人' where name = '天明' or name = '景天';
3.4 数据的查找
select * from t_students;
-- 计算函数和表达式的值
select 3*2;
select now();
select concat("天明","真美");
select id,name from t_students;
select * from t_students where chinese + english + math > 180;
select * from t_students where math >= 80 and math <= 90;
select * from t_students where chinese >= 60 and math>=60 and english >= 60;
-- or
select * from t_students where class = '一班' or class = '二班';
-- <> !=
select * from t_students where id <> 1;
update t_students set chinese = null where id = 1;
-- is null is not null
select * from t_students where chinese is null;
select * from t_students where chinese is not null;
-- between and
select * from t_students where math BETWEEN 80 and 90;
select * from t_students where id BETWEEN 1 and 5;
-- in
-- not in
select * from t_students where id in (1,2,3);
select * from t_students where id not in (1,2,3);
-- like 模糊查询 %表示通配 _表示占位
select * from t_students where name like '黄__';
select * from t_students where name like '%神%';
-- 我们日常生活中遇到的一些应用,例如淘宝,京东,bilibili等等里面都有一些搜索框,但是这些搜索框的实现并不是采用模糊查询来实现的,模糊查询是可以实现的,但是性能很差,满足不了企业的需要
-- 所以大公司做搜索的时候一般都是采用搜索引擎(ES、Solr)来实现的,不是采用模糊查询来做的
4、常用关键字
4.1 distinct(这个关键字是过滤重复的数据)
select distinct(class) from t_students;
4.2 limit(限制结果集,限制输出结果的行数)
select * from t_students limit 0,3;
-- pageNum 页码, pageSize 每一页的条数
select * from tableName limit (pageNum-1)*pageSize,pageSize;
4.3 order by(排序)
-- 对单列进行排序
select * from t_students order by english desc;
-- 对多列进行排序
select * from t_students order by english desc,chinese asc;
-- 查询总成绩前三名同学的信息
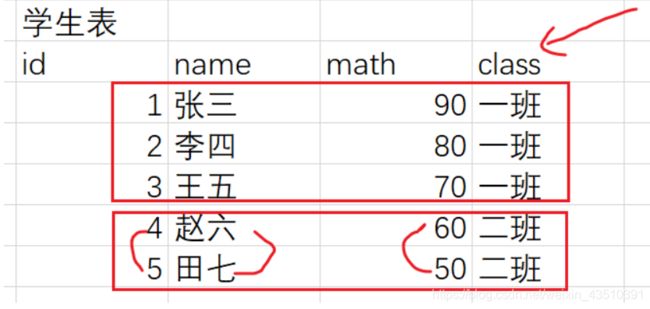
select * from t_students order by chinese + english + math desc limit 3;
4.4 as(别名)
select name as username,(chinese + english + math) as total from t_students order by total desc ;
别名的出现本质上是为了帮助我们简化sql语句的书写的。我们可以对列起别名,也可以对表起别名。
4.5 group by(分组查询)
分组查询其实就是用来合并数据使用的,我们需要配合group_concat(columnName) 这个函数来一起使用。
例如:
SELECT
GROUP_CONCAT( id ) AS id,
GROUP_CONCAT( NAME ) AS NAME,
GROUP_CONCAT( math ) AS math,
class
FROM
USER
GROUP BY
class;
-- 对学生按语文和数学成绩分组
select chinese,math,GROUP_CONCAT(name) from t_students group by chinese,math;
对多个字段进行分组的时候,我们需要保证多个字段的值都保持一致,如果有一个或多个值不一致,那么他们就不是一组。
4.6 聚合函数(统计函数)
-
Max(求各个班级数学分数最高的分数)
-
Min
-
Avg
-
SUM
-
COUNT
-- 求各个班级分数最高的成绩
select class,max(math) from user GROUP BY class;
-- 求各个班级最低的成绩
select class,min(math) from user GROUP BY class;
-- 求各个班级的总成绩
select class,sum(math) as total from user group by class;
-- 求所有人的总成绩
select sum(math) from user;
-- 求各个班学生的平均成绩
select class,avg(math) from user group by class;
-- 统计各个班级的学生人数
select class,count(1) from user group by class;
-- 求表中总的记录
select count(*) from user;
-- 查询人数大于2的班级
select * from t_students;
select class,count(id) as total from t_students group by class having total > 2;
-- 查询各个班级所有科目都及格的学生大于2的班级
SELECT
class,
count( id ) AS count
FROM
t_students
WHERE
chinese >= 60
AND english >= 60
AND math >= 60
GROUP BY
class
HAVING
count > 2;
-- 查询人数少于10的班级,并按人数降序排序。
select class,count(id) as count from t_students GROUP BY class HAVING count < 10 order by count desc;
4.7 SQL的注释
# 注释
-- 注释
/* 注释*/
5、执行顺序
(1) FROM table_name, …
(2) [WHERE …]
(3) [GROUP BY …]
(4) [HAVING …]
(5) SELECT column_name, …
(6) [ORDER BY …];
(7) LIMIT
6、数据完整性
6.1 实体完整性
实体完整性是说数据库中的数据不应该是重复的。主要是通过数据库的主键来保证。
create table stu (
id int PRIMARY key auto_increment,
name varchar(20)
)character set utf8;
- primary key 表示标记该列为主键
- auto_increment 表示该主键是自增的,不用我们自己去维护值
6.2 域完整性
域完整性值的是我们每一个字段都应该是有约束的。我们之前学习的字段的约束的字段的类型,每一个字段都应该有一个具体的数据类型。除了这个数据类型之外,我们还有一些别的约束,例如不为空,例如唯一。
- not null (表示指定某一列的数据不能为空)
create table stu (
id int PRIMARY key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) not null
)character set utf8;
- unique (表示指定某一列的数据是唯一的)
create table stu (
id int PRIMARY key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) unique
)character set utf8;
6.3 参照完整性
create table stu (
id int PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
clazz_id int,
-- 建立外键
constraint FK_clazz_id FOREIGN KEY(clazz_id) REFERENCES clazz(id)
)character set utf8;
作用:
- 在我们对学生表进行数据插入的时候,会去检查班级表有没有对应的id,如果有,那么才可以插入,如果没有,则插入失败
- 在我们对班级表进行修改或者是删除的时候,我们会去检查学生表里面有没有对应的id,如果有,无法删除
副作用:我们发现,我们在插入数据或者是删除数据的时候会做一些额外的操作,这样对性能有一定的影响
总结:一般来说,在公司里面,我们不建议使用外键,使用外键会有一些额外的麻烦,性能也很差。所以,我们在日常的开发中,不一定要满足以上的三条。我们通常来说会满足第一条和第二条,但是第三条基本上不会去满足。也就是说,我们的外键基本上不会去使用。
不使用外键,如何保证插入数据的正确性呢?
如果我们需要保证,我们只能通过我们自己的代码的逻辑来保证。
7、三大范式
7.1 第一范式: 原子性
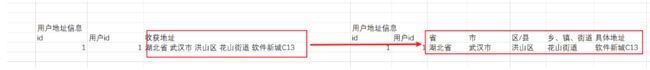
第一范式是指我们在设计数据库的时候,应该保证每一列的原子性。什么意思呢?也就是每一列都是不可以再次分割的数据。
7.2 第二范式: 唯一性
是指记录的唯一性。也就是要求记录必须得有一个唯一标识。具体体现是主键。每一个表都应该具有一个主键,不存在部分依赖。

我们在设计表的时候,应该尽量保持一个原则:一张表只讲述一件事情,不表示多件事情,否则就会存在大量的数据冗余。
7.3 第三范式: 字段不要冗余
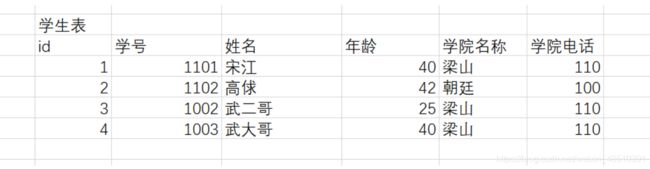
我们一个表去讲述多件事情的时候,会出现一些冗余数据。那么我们在设计数据库表的时候,应该严格遵循这三大范式吗?
我们在设计数据库表的时候,有的时候不去遵循三大范式。为什么不去遵循三大范式呢?一般来说,我们去公司里面偶尔不会去遵循第三范式,因为有的时候适当的冗余信息会方便我们去进行查找。

8、多表查询
8.1 连接查询
8.1.1 交叉查询
select * from A cross join B;
8.1.2 内连接
显示出所有匹配上的数据,不会保留没有匹配上的数据。
-- 显示内连接
select s.* from clazz1 as c INNER JOIN student as s on c.id = s.clazz_id where c.name = '二班';
-- 隐式内连接
select * from clazz1 as c ,student as s where c.id = s.clazz_id and c.name = '二班';
8.1.3 外连接
会显示出所有匹配上的数据,并且会保留左表(左外连接)或者是右表(右外连接)的全部数据。
-- 外连接
-- 左外连接 左外连接可以保留左表的全部数据
select * from clazz1 left join student on clazz1.id = student.clazz_id;
-- 右外连接 右外连接可以保留右表的全部数据
select * from clazz1 right join student on clazz1.id = student.clazz_id;
-- out
8.2 子查询
子查询又称为嵌套查询,是指在where条件语句后面或者是from后面跟上一个sql语句作为查询的条件。
-- 嵌套一层
select cid from s_t where sid = (select id from stu where name = '长风');
-- 嵌套两层
SELECT NAME
FROM
course
WHERE
id IN (
SELECT
cid
FROM
s_t
WHERE
sid = ( SELECT id FROM stu WHERE NAME = '长风' ));
子查询的效率不是很高,并且sql的可读性比较差
8.3 联合查询
select * from stu where name = '长风'
union
select * from stu where name = '张东升';
联合查询在大多数的场景是没啥用的,只有当我们使用or关键字导致索引失效的时候,我们的联合查询才可能会有点作用。
9、数据的备份与恢复
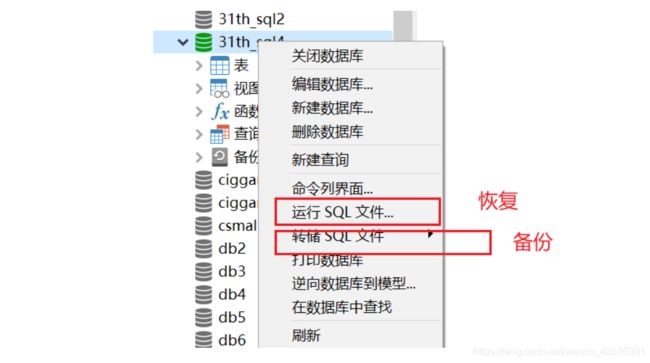
9.1 命令实现
- 备份
mysqldump -uroot -p dbName>路径\文件名字.sql
- 恢复
我们可以注意到的是,我们的数据库备份的时候并不会给你备份数据库的建库语句,只会备份里面的表和数据。
所以我们在恢复的时候,我们要应该新建一个库,然后再去恢复。
source 路径\文件名字.sql