- 如何在 Fork 的 GitHub 项目中保留自己的修改并同步上游更新?github_fork_update
iBaoxing
github
如何在Fork的GitHub项目中保留自己的修改并同步上游更新?在GitHub上Fork了一个项目后,你可能会对项目进行一些修改,同时原作者也在不断更新。如果想要在保留自己修改的基础上,同步原作者的最新更新,很多人会不知所措。本文将详细讲解如何在不丢失自己改动的情况下,将上游仓库的更新合并到自己的仓库中。问题描述假设你在GitHub上Fork了一个项目,并基于该项目做了一些修改,随后你发现原作者对
- git常用命令笔记
咩酱-小羊
git笔记
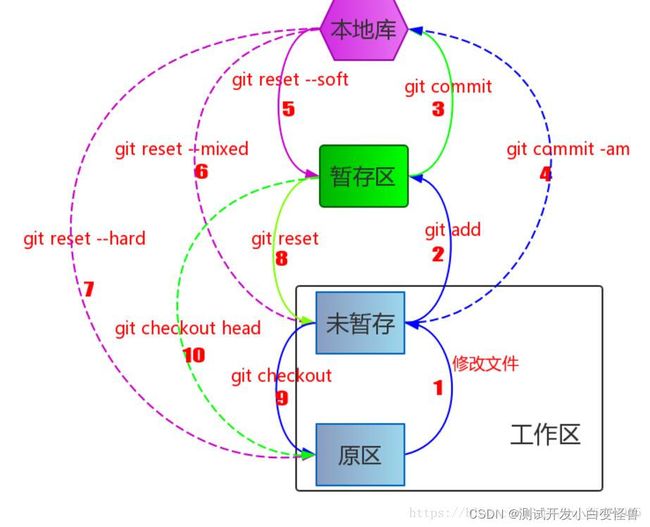
###用习惯了idea总是不记得git的一些常见命令,需要用到的时候总是担心旁边站了人~~~记个笔记@_@,告诉自己看笔记不丢人初始化初始化一个新的Git仓库gitinit配置配置用户信息gitconfig--globaluser.name"YourName"gitconfig--globaluser.email"
[email protected]"基本操作克隆远程仓库gitclone查看
- 下载github patch到本地
小米人er
我的博客gitpatch
以下是几种从GitHub上下载以.patch结尾的补丁文件的方法:通过浏览器直接下载打开包含该.patch文件的GitHub仓库。在仓库的文件列表中找到对应的.patch文件。点击该文件,浏览器会显示文件的内容,在页面的右上角通常会有一个“Raw”按钮,点击它可以获取原始文件内容。然后在浏览器中使用快捷键(如Ctrl+S或者Command+S)将原始文件保存到本地,选择保存的文件名并确保后缀为.p
- 509. 斐波那契数(每日一题)
lzyprime
lzyprime博客(github)创建时间:2021.01.04qq及邮箱:2383518170leetcode笔记题目描述斐波那契数,通常用F(n)表示,形成的序列称为斐波那契数列。该数列由0和1开始,后面的每一项数字都是前面两项数字的和。也就是:F(0)=0,F(1)=1F(n)=F(n-1)+F(n-2),其中n>1给你n,请计算F(n)。示例1:输入:2输出:1解释:F(2)=F(1)+
- Git常用命令-修改远程仓库地址
猿大师
LinuxJavagitjava
查看远程仓库地址gitremote-v返回结果originhttps://git.coding.net/*****.git(fetch)originhttps://git.coding.net/*****.git(push)修改远程仓库地址gitremoteset-urloriginhttps://git.coding.net/*****.git先删除后增加远程仓库地址gitremotermori
- GitHub上克隆项目
bigbig猩猩
github
从GitHub上克隆项目是一个简单且直接的过程,它允许你将远程仓库中的项目复制到你的本地计算机上,以便进行进一步的开发、测试或学习。以下是一个详细的步骤指南,帮助你从GitHub上克隆项目。一、准备工作1.安装Git在克隆GitHub项目之前,你需要在你的计算机上安装Git工具。Git是一个开源的分布式版本控制系统,用于跟踪和管理代码变更。你可以从Git的官方网站(https://git-scm.
- git - Webhook让部署自动化
大猪大猪
我们现在有一个需求,将项目打包上传到gitlab或者github后,程序能自动部署,不用手动地去服务器中进行项目更新并运行,如何做到?这里我们可以使用gitlab与github的挂钩,挂钩的原理就是,每当我们有请求到gitlab与github服务器时,这时他俩会根据我们配置的挂钩地扯进行访问,webhook挂钩程序会一直监听着某个端口请求,一但收到他们发过来的请求,这时就知道用户有请求提交了,这时
- libyuv之linux编译
jaronho
Linuxlinux运维服务器
文章目录一、下载源码二、编译源码三、注意事项1、银河麒麟系统(aarch64)(1)解决armv8-a+dotprod+i8mm指令集支持问题(2)解决armv9-a+sve2指令集支持问题一、下载源码到GitHub网站下载https://github.com/lemenkov/libyuv源码,或者用直接用git克隆到本地,如:gitclonehttps://github.com/lemenko
- Faiss Tips:高效向量搜索与聚类的利器
焦习娜Samantha
FaissTips:高效向量搜索与聚类的利器faiss_tipsSomeusefultipsforfaiss项目地址:https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/fa/faiss_tips项目介绍Faiss是由FacebookAIResearch开发的一个用于高效相似性搜索和密集向量聚类的库。它支持多种硬件平台,包括CPU和GPU,能够在海量数据集上实现快速的近似最近邻搜索(AN
- pyecharts——绘制柱形图折线图
2224070247
信息可视化pythonjava数据可视化
一、pyecharts概述自2013年6月百度EFE(ExcellentFrontEnd)数据可视化团队研发的ECharts1.0发布到GitHub网站以来,ECharts一直备受业界权威的关注并获得广泛好评,成为目前成熟且流行的数据可视化图表工具,被应用到诸多数据可视化的开发领域。Python作为数据分析领域最受欢迎的语言,也加入ECharts的使用行列,并研发出方便Python开发者使用的数据
- node.js学习
小猿L
node.jsnode.js学习vim
node.js学习实操及笔记温故node.js,node.js学习实操过程及笔记~node.js学习视频node.js官网node.js中文网实操笔记githubcsdn笔记为什么学node.js可以让别人访问我们编写的网页为后续的框架学习打下基础,三大框架vuereactangular离不开node.jsnode.js是什么官网:node.js是一个开源的、跨平台的运行JavaScript的运行
- 01-Git初识
Meereen
Gitgit
01-Git初识概念:一个免费开源,分布式的代码版本控制系统,帮助开发团队维护代码作用:记录代码内容。切换代码版本,多人开发时高效合并代码内容如何学:个人本机使用:Git基础命令和概念多人共享使用:团队开发同一个项目的代码版本管理Git配置用户信息配置:用户名和邮箱,应用在每次提交代码版本时表明自己的身份命令:查看git版本号git-v配置用户名gitconfig--globaluser.name
- 【Git】常见命令(仅笔记)
好想有猫猫
GitLinux学习笔记git笔记elasticsearchlinuxc++
文章目录创建/初始化本地仓库添加本地仓库配置项提交文件查看仓库状态回退仓库查看日志分支删除文件暂存工作区代码远程仓库使用`.gitigore`文件让git不追踪一些文件标签创建/初始化本地仓库gitinit添加本地仓库配置项gitconfig-l#以列表形式显示配置项gitconfiguser.name"ljh"#配置user.namegitconfiguser.email"
[email protected]
- 你可能遗漏的一些C#/.NET/.NET Core知识点
追逐时光者
C#.NETDotNetGuide编程指南c#.net.netcoremicrosoft
前言在这个快速发展的技术世界中,时常会有一些重要的知识点、信息或细节被忽略或遗漏。《C#/.NET/.NETCore拾遗补漏》专栏我们将探讨一些可能被忽略或遗漏的重要知识点、信息或细节,以帮助大家更全面地了解这些技术栈的特性和发展方向。拾遗补漏GitHub开源地址https://github.com/YSGStudyHards/DotNetGuide/blob/main/docs/DotNet/D
- Some jenkins settings
SnC_
Jenkins连接到特定gitlabproject的特定branch我采用的方法是在pipeline的script中使用git命令来指定branch。如下:stage('Clonerepository'){steps{gitbranch:'develop',credentialsId:'gitlab-credential-id',url:'http://gitlab.com/repo.git'}}
- python怎么将png转为tif_png转tif
weixin_39977276
发国外的文章要求图片是tif,cmyk色彩空间的。大小尺寸还有要求。比如网上大神多,找到了一段代码,感谢!https://www.jianshu.com/p/ec2af4311f56https://github.com/KevinZc007/image2Tifimportjava.awt.image.BufferedImage;importjava.io.File;importjava.io.Fi
- uniapp map组件自定义markers标记点
以对_
uni-app学习记录uni-appjavascript前端
需求是根据后端返回数据在地图上显示标记点,并且根据数据状态控制标记点颜色,标记点背景通过两张图片实现控制{{item.options.labelName}}exportdefault{data(){return{storeIndex:0,locaInfo:{longitude:120.445172,latitude:36.111387},markers:[//标点列表{id:1,//标记点idin
- windows下python opencv ffmpeg读取摄像头实现rtsp推流 拉流
图像处理大大大大大牛啊
opencv实战代码讲解视觉图像项目windowspythonopencv
windows下pythonopencvffmpeg读取摄像头实现rtsp推流拉流整体流程1.下载所需文件1.1下载rtsp推流服务器1.2下载ffmpeg2.开启RTSP服务器3.opencv读取摄像头并调用ffmpeg进行推流4.opencv进行拉流5.opencv异步拉流整体流程1.下载所需文件1.1下载rtsp推流服务器下载RTSP服务器下载页面https://github.com/blu
- ChatGPT 高效学习套路揭秘:让知识获取事半功倍的秘诀
kkai人工智能
chatgpt人工智能学习媒体ai
最近这段时间,AI热潮因ChatGPT的火爆再次掀起。如今,网上大部分内容都在调侃AI,但很少有人探讨如何正经使用ChatGPT做事情。作为一名靠搜索引擎和GitHub自学编程的开发者,第一次和ChatGPT深度交流后,我就确信:ChatGPT能够极大提高程序员学习新技术的效率。使用ChatGPT一个月后,我越发感受到它的颠覆性。因此,我想从工作和学习的角度,分享它的优势及我的一些使用技巧,而非娱
- LeetCode github集合,附CMU大神整理笔记
Wesley@
LeetCodegithub
GithubLeetCode集合本人所有做过的题目都写在一个java项目中,同步到github中了,算是见证自己的进步。github目前同步的题目是2020-09-17日之后写的题。之前写过的题会陆续跟新到github中。目前大概400个题目Github项目链接:https://github.com/sunliancheng/leetcode_github附上一份优秀的教材整合:这是卡内基梅隆(C
- [Swift]LeetCode943. 最短超级串 | Find the Shortest Superstring
黄小二哥
swift
★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★➤微信公众号:山青咏芝(shanqingyongzhi)➤博客园地址:山青咏芝(https://www.cnblogs.com/strengthen/)➤GitHub地址:https://github.com/strengthen/LeetCode➤原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/streng
- [Swift]LeetCode767. 重构字符串 | Reorganize String
weixin_30591551
swiftruntime
★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★➤微信公众号:山青咏芝(shanqingyongzhi)➤博客园地址:山青咏芝(https://www.cnblogs.com/strengthen/)➤GitHub地址:https://github.com/strengthen/LeetCode➤原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/streng
- RK3229_Android9.0_Box 4G模块EC200A调试
suifen_
网络
0、kernel修改这部分完全可以参考Linux的移植:RK3588EC200A-CN【4G模块】调试_rkec200a-cn-CSDN博客1、修改device/rockchip/rk322xdiff--gita/device.mkb/device.mkindexec6bfaa..e7c32d1100755---a/device.mk+++b/device.mk@@-105,6+105,8@@en
- VUE3 + xterm + nestjs实现web远程终端 或 连接开启SSH登录的路由器和交换机。
焚木灵
node.jsvue
可远程连接系统终端或开启SSH登录的路由器和交换机。相关资料:xtermjs/xterm.js:Aterminalfortheweb(github.com)后端实现(NestJS):1、安装依赖:npminstallnode-ssh@nestjs/websockets@nestjs/platform-socket.io2、我们将创建一个名为RemoteControlModule的NestJS模块,
- 探索ASPICE V3.1:汽车行业软件开发的中文指南
阮懿同
探索ASPICEV3.1:汽车行业软件开发的中文指南ASPICE_V3.1中文版.pdf.zip项目地址:https://gitcode.com/open-source-toolkit/422a2在汽车软件工程领域,高质量的标准对于确保行车安全和提升用户体验至关重要。今天,我们为您介绍一个珍贵的开源宝藏——ASPICEV3.1中文版资源。这是一篇专为国内汽车行业开发者、质量管理者准备的深度解读,旨
- golang实现从服务器下载文件到本地指定目录
余生逆风飞翔
golang服务器开发语言
一、连接服务器,采用sftp连接模式packagemiddlewaresimport("fmt""time""github.com/pkg/sftp""golang.org/x/crypto/ssh")//建立服务器连接funcConnect(user,password,hoststring,portint)(*sftp.Client,error){var(auth[]ssh.AuthMethod
- 入职Java,不会git被开除了.......
不爱洗脚的小滕
javagit开发语言
文章目录前言一、Git是什么?二、Git的核心概念三、Git的常用命令三、总结前言故事的主角是小明,一个充满活力的年轻人,他刚刚入职一家以Java为主导的软件公司。他对Java有深厚的了解,但他有一个致命的缺点——他不会使用git。小明的第一天上班,他的经理给他分配了一个项目,并告诉他需要使用git来管理代码。小明点头表示理解,但实际上他对git一窍不通。他以为git是公司的一个员工,所以他开始在
- Nginx之ngx_http_proxy_connect_module模块
小米bb
Nginxnginxhttp运维
近期由于项目需要使用到https正向代理,而nginx官方模块仅支持做http正向代理,一番百度学习后发现了该模块,故今日记录下此笔记供大家一起学习交流ngx_http_proxy_connect_module模块主要用于隧道SSL请求的代理服务器GitHub地址:http://www.github.com/chobits/ngx_http_proxy_connect_modulenginx配置:
- 史上最全git命令,git回滚,git命令大全
騒周
其他git
git命令大全一、Git整体理解二、由暂存区本地仓库三、由本地仓->远程仓库四、冲突处理五、Git分支操作六、bug的分支七、feature分支八、暂存的使用九、远程仓的操作十、标签的使用十一、Git配置全局信息十二、Linux的一些简单操作和一些符号的解释十三、符号解释十四、显示安装详细信息十五、gitconfig十六、Gitclone十七、Gitinit十八、gitstatus十九、gitre
- Vue3 vant组件库自动导入
不叫虎子
Vuevue.js前端javascript前端框架typescript
实现:完整使用vant组件库文档安装:#Vue3项目,安装最新版Vantnpmivant#通过yarn安装yarnaddvant#通过pnpm安装pnpmaddvant【一】按需引入:https://vant-contrib.gitee.io/vant/#/zh-CN/quickstart#fang-fa-er.-an-xu-yin-ru-zu-jian-yang-shi【二】批量引入在基于vit
- 开发者关心的那些事
圣子足道
ios游戏编程apple支付
我要在app里添加IAP,必须要注册自己的产品标识符(product identifiers)。产品标识符是什么?
产品标识符(Product Identifiers)是一串字符串,它用来识别你在应用内贩卖的每件商品。App Store用产品标识符来检索产品信息,标识符只能包含大小写字母(A-Z)、数字(0-9)、下划线(-)、以及圆点(.)。你可以任意排列这些元素,但我们建议你创建标识符时使用
- 负载均衡器技术Nginx和F5的优缺点对比
bijian1013
nginxF5
对于数据流量过大的网络中,往往单一设备无法承担,需要多台设备进行数据分流,而负载均衡器就是用来将数据分流到多台设备的一个转发器。
目前有许多不同的负载均衡技术用以满足不同的应用需求,如软/硬件负载均衡、本地/全局负载均衡、更高
- LeetCode[Math] - #9 Palindrome Number
Cwind
javaAlgorithm题解LeetCodeMath
原题链接:#9 Palindrome Number
要求:
判断一个整数是否是回文数,不要使用额外的存储空间
难度:简单
分析:
题目限制不允许使用额外的存储空间应指不允许使用O(n)的内存空间,O(1)的内存用于存储中间结果是可以接受的。于是考虑将该整型数反转,然后与原数字进行比较。
注:没有看到有关负数是否可以是回文数的明确结论,例如
- 画图板的基本实现
15700786134
画图板
要实现画图板的基本功能,除了在qq登陆界面中用到的组件和方法外,还需要添加鼠标监听器,和接口实现。
首先,需要显示一个JFrame界面:
public class DrameFrame extends JFrame { //显示
- linux的ps命令
被触发
linux
Linux中的ps命令是Process Status的缩写。ps命令用来列出系统中当前运行的那些进程。ps命令列出的是当前那些进程的快照,就是执行ps命令的那个时刻的那些进程,如果想要动态的显示进程信息,就可以使用top命令。
要对进程进行监测和控制,首先必须要了解当前进程的情况,也就是需要查看当前进程,而 ps 命令就是最基本同时也是非常强大的进程查看命令。使用该命令可以确定有哪些进程正在运行
- Android 音乐播放器 下一曲 连续跳几首歌
肆无忌惮_
android
最近在写安卓音乐播放器的时候遇到个问题。在MediaPlayer播放结束时会回调
player.setOnCompletionListener(new OnCompletionListener() {
@Override
public void onCompletion(MediaPlayer mp) {
mp.reset();
Log.i("H
- java导出txt文件的例子
知了ing
javaservlet
代码很简单就一个servlet,如下:
package com.eastcom.servlet;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URLEncoder;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Resu
- Scala stack试玩, 提高第三方依赖下载速度
矮蛋蛋
scalasbt
原文地址:
http://segmentfault.com/a/1190000002894524
sbt下载速度实在是惨不忍睹, 需要做些配置优化
下载typesafe离线包, 保存为ivy本地库
wget http://downloads.typesafe.com/typesafe-activator/1.3.4/typesafe-activator-1.3.4.zip
解压r
- phantomjs安装(linux,附带环境变量设置) ,以及casperjs安装。
alleni123
linuxspider
1. 首先从官网
http://phantomjs.org/下载phantomjs压缩包,解压缩到/root/phantomjs文件夹。
2. 安装依赖
sudo yum install fontconfig freetype libfreetype.so.6 libfontconfig.so.1 libstdc++.so.6
3. 配置环境变量
vi /etc/profil
- JAVA IO FileInputStream和FileOutputStream,字节流的打包输出
百合不是茶
java核心思想JAVA IO操作字节流
在程序设计语言中,数据的保存是基本,如果某程序语言不能保存数据那么该语言是不可能存在的,JAVA是当今最流行的面向对象设计语言之一,在保存数据中也有自己独特的一面,字节流和字符流
1,字节流是由字节构成的,字符流是由字符构成的 字节流和字符流都是继承的InputStream和OutPutStream ,java中两种最基本的就是字节流和字符流
类 FileInputStream
- Spring基础实例(依赖注入和控制反转)
bijian1013
spring
前提条件:在http://www.springsource.org/download网站上下载Spring框架,并将spring.jar、log4j-1.2.15.jar、commons-logging.jar加载至工程1.武器接口
package com.bijian.spring.base3;
public interface Weapon {
void kil
- HR看重的十大技能
bijian1013
提升能力HR成长
一个人掌握何种技能取决于他的兴趣、能力和聪明程度,也取决于他所能支配的资源以及制定的事业目标,拥有过硬技能的人有更多的工作机会。但是,由于经济发展前景不确定,掌握对你的事业有所帮助的技能显得尤为重要。以下是最受雇主欢迎的十种技能。 一、解决问题的能力 每天,我们都要在生活和工作中解决一些综合性的问题。那些能够发现问题、解决问题并迅速作出有效决
- 【Thrift一】Thrift编译安装
bit1129
thrift
什么是Thrift
The Apache Thrift software framework, for scalable cross-language services development, combines a software stack with a code generation engine to build services that work efficiently and s
- 【Avro三】Hadoop MapReduce读写Avro文件
bit1129
mapreduce
Avro是Doug Cutting(此人绝对是神一般的存在)牵头开发的。 开发之初就是围绕着完善Hadoop生态系统的数据处理而开展的(使用Avro作为Hadoop MapReduce需要处理数据序列化和反序列化的场景),因此Hadoop MapReduce集成Avro也就是自然而然的事情。
这个例子是一个简单的Hadoop MapReduce读取Avro格式的源文件进行计数统计,然后将计算结果
- nginx定制500,502,503,504页面
ronin47
nginx 错误显示
server {
listen 80;
error_page 500/500.html;
error_page 502/502.html;
error_page 503/503.html;
error_page 504/504.html;
location /test {return502;}}
配置很简单,和配
- java-1.二叉查找树转为双向链表
bylijinnan
二叉查找树
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class BSTreeToLinkedList {
/*
把二元查找树转变成排序的双向链表
题目:
输入一棵二元查找树,将该二元查找树转换成一个排序的双向链表。
要求不能创建任何新的结点,只调整指针的指向。
10
/ \
6 14
/ \
- Netty源码学习-HTTP-tunnel
bylijinnan
javanetty
Netty关于HTTP tunnel的说明:
http://docs.jboss.org/netty/3.2/api/org/jboss/netty/channel/socket/http/package-summary.html#package_description
这个说明有点太简略了
一个完整的例子在这里:
https://github.com/bylijinnan
- JSONUtil.serialize(map)和JSON.toJSONString(map)的区别
coder_xpf
jqueryjsonmapval()
JSONUtil.serialize(map)和JSON.toJSONString(map)的区别
数据库查询出来的map有一个字段为空
通过System.out.println()输出 JSONUtil.serialize(map): {"one":"1","two":"nul
- Hibernate缓存总结
cuishikuan
开源sshjavawebhibernate缓存三大框架
一、为什么要用Hibernate缓存?
Hibernate是一个持久层框架,经常访问物理数据库。
为了降低应用程序对物理数据源访问的频次,从而提高应用程序的运行性能。
缓存内的数据是对物理数据源中的数据的复制,应用程序在运行时从缓存读写数据,在特定的时刻或事件会同步缓存和物理数据源的数据。
二、Hibernate缓存原理是怎样的?
Hibernate缓存包括两大类:Hib
- CentOs6
dalan_123
centos
首先su - 切换到root下面1、首先要先安装GCC GCC-C++ Openssl等以来模块:yum -y install make gcc gcc-c++ kernel-devel m4 ncurses-devel openssl-devel2、再安装ncurses模块yum -y install ncurses-develyum install ncurses-devel3、下载Erang
- 10款用 jquery 实现滚动条至页面底端自动加载数据效果
dcj3sjt126com
JavaScript
无限滚动自动翻页可以说是web2.0时代的一项堪称伟大的技术,它让我们在浏览页面的时候只需要把滚动条拉到网页底部就能自动显示下一页的结果,改变了一直以来只能通过点击下一页来翻页这种常规做法。
无限滚动自动翻页技术的鼻祖是微博的先驱:推特(twitter),后来必应图片搜索、谷歌图片搜索、google reader、箱包批发网等纷纷抄袭了这一项技术,于是靠滚动浏览器滚动条
- ImageButton去边框&Button或者ImageButton的背景透明
dcj3sjt126com
imagebutton
在ImageButton中载入图片后,很多人会觉得有图片周围的白边会影响到美观,其实解决这个问题有两种方法
一种方法是将ImageButton的背景改为所需要的图片。如:android:background="@drawable/XXX"
第二种方法就是将ImageButton背景改为透明,这个方法更常用
在XML里;
<ImageBut
- JSP之c:foreach
eksliang
jspforearch
原文出自:http://www.cnblogs.com/draem0507/archive/2012/09/24/2699745.html
<c:forEach>标签用于通用数据循环,它有以下属性 属 性 描 述 是否必须 缺省值 items 进行循环的项目 否 无 begin 开始条件 否 0 end 结束条件 否 集合中的最后一个项目 step 步长 否 1
- Android实现主动连接蓝牙耳机
gqdy365
android
在Android程序中可以实现自动扫描蓝牙、配对蓝牙、建立数据通道。蓝牙分不同类型,这篇文字只讨论如何与蓝牙耳机连接。
大致可以分三步:
一、扫描蓝牙设备:
1、注册并监听广播:
BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_DISCOVERY_STARTED
BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND
BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_DIS
- android学习轨迹之四:org.json.JSONException: No value for
hyz301
json
org.json.JSONException: No value for items
在JSON解析中会遇到一种错误,很常见的错误
06-21 12:19:08.714 2098-2127/com.jikexueyuan.secret I/System.out﹕ Result:{"status":1,"page":1,&
- 干货分享:从零开始学编程 系列汇总
justjavac
编程
程序员总爱重新发明轮子,于是做了要给轮子汇总。
从零开始写个编译器吧系列 (知乎专栏)
从零开始写一个简单的操作系统 (伯乐在线)
从零开始写JavaScript框架 (图灵社区)
从零开始写jQuery框架 (蓝色理想 )
从零开始nodejs系列文章 (粉丝日志)
从零开始编写网络游戏
- jquery-autocomplete 使用手册
macroli
jqueryAjax脚本
jquery-autocomplete学习
一、用前必备
官方网站:http://bassistance.de/jquery-plugins/jquery-plugin-autocomplete/
当前版本:1.1
需要JQuery版本:1.2.6
二、使用
<script src="./jquery-1.3.2.js" type="text/ja
- PLSQL-Developer或者Navicat等工具连接远程oracle数据库的详细配置以及数据库编码的修改
超声波
oracleplsql
在服务器上将Oracle安装好之后接下来要做的就是通过本地机器来远程连接服务器端的oracle数据库,常用的客户端连接工具就是PLSQL-Developer或者Navicat这些工具了。刚开始也是各种报错,什么TNS:no listener;TNS:lost connection;TNS:target hosts...花了一天的时间终于让PLSQL-Developer和Navicat等这些客户
- 数据仓库数据模型之:极限存储--历史拉链表
superlxw1234
极限存储数据仓库数据模型拉链历史表
在数据仓库的数据模型设计过程中,经常会遇到这样的需求:
1. 数据量比较大; 2. 表中的部分字段会被update,如用户的地址,产品的描述信息,订单的状态等等; 3. 需要查看某一个时间点或者时间段的历史快照信息,比如,查看某一个订单在历史某一个时间点的状态, 比如,查看某一个用户在过去某一段时间内,更新过几次等等; 4. 变化的比例和频率不是很大,比如,总共有10
- 10点睛Spring MVC4.1-全局异常处理
wiselyman
spring mvc
10.1 全局异常处理
使用@ControllerAdvice注解来实现全局异常处理;
使用@ControllerAdvice的属性缩小处理范围
10.2 演示
演示控制器
package com.wisely.web;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.spring