大数据技术之Hadoop(Yarn)
第1章 Yarn资源调度器
Yarn是一个资源调度平台,负责为运算程序提供服务器运算资源,相当于一个分布式的操作系统平台,而MapReduce等运算程序则相当于运行于操作系统之上的应用程序。
1.1 Yarn基础架构
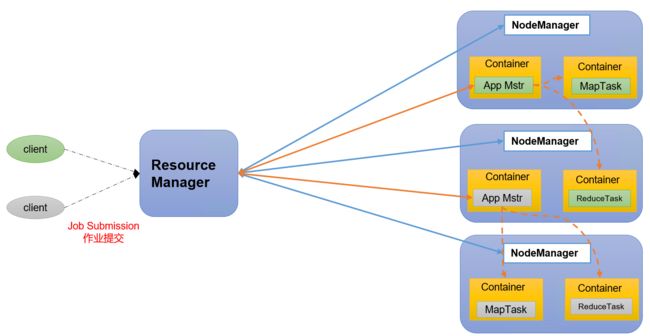
YARN主要由ResourceManager、NodeManager、ApplicationMaster和Container等组件构成。
ResourceManager(RM) 主要作用如下:
处理客户端请求
监控NodeManager
启动或监控ApplicationMaster
资源的分配与调度
NodeManager(NM)主要作用如下:
管理单个节点上的资源
处理来自ResourceManager的命令
处理来自ApplicationMaster的命令
ApplicationMaster(AM)作用如下:
为应用程序申请资源并分配给内部的任务
任务的监控与容错
Container
Container是YARN中的资源抽象,它封装了某个节点上的多维度资源,如内存、CPU、磁盘网络等。
1.2 Yarn工作机制
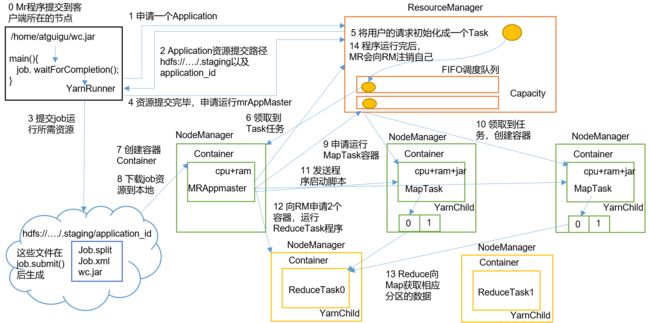
(1)MR程序提交到客户端所在的节点。
(2)YarnRunner向ResourceManager申请一个Application。
(3)RM将该应用程序的资源路径返回给YarnRunner。
(4)该程序将运行所需资源提交到HDFS上。
(5)程序资源提交完毕后,申请运行mrAppMaster。
(6)RM将用户的请求初始化成一个Task。
(7)其中一个NodeManager领取到Task任务。
(8)该NodeManager创建容器Container,并产生MRAppmaster。
(9)Container从HDFS上拷贝资源到本地。
(10)MRAppmaster向RM 申请运行MapTask资源。
(11)RM将运行MapTask任务分配给另外两个NodeManager,另两个NodeManager分别领取任务并创建容器。
(12)MR向两个接收到任务的NodeManager发送程序启动脚本,这两个NodeManager分别启动MapTask,MapTask对数据分区排序。
(13)MrAppMaster等待所有MapTask运行完毕后,向RM申请容器,运行ReduceTask。
(14)ReduceTask向MapTask获取相应分区的数据。
(15)程序运行完毕后,MR会向RM申请注销自己。
1.3 作业提交全过程
作业提交全过程详解
(1)作业提交
第1步:Client调用job.waitForCompletion方法,向整个集群提交MapReduce作业。
第2步:Client向RM申请一个作业id。
第3步:RM给Client返回该job资源的提交路径和作业id。
第4步:Client提交jar包、切片信息和配置文件到指定的资源提交路径。
第5步:Client提交完资源后,向RM申请运行MrAppMaster。
(2)作业初始化
第6步:当RM收到Client的请求后,将该job添加到容量调度器中。
第7步:某一个空闲的NM领取到该Job。
第8步:该NM创建Container,并产生MRAppmaster。
第9步:下载Client提交的资源到本地。
(3)任务分配
第10步:MrAppMaster向RM申请运行多个MapTask任务资源。
第11步:RM将运行MapTask任务分配给另外两个NodeManager,另两个NodeManager分别领取任务并创建容器。
(4)任务运行
第12步:MR向两个接收到任务的NodeManager发送程序启动脚本,这两个NodeManager分别启动MapTask,MapTask对数据分区排序。
第13步:MrAppMaster等待所有MapTask运行完毕后,向RM申请容器,运行ReduceTask。
第14步:ReduceTask向MapTask获取相应分区的数据。
第15步:程序运行完毕后,MR会向RM申请注销自己。
(5)进度和状态更新
YARN中的任务将其进度和状态(包括counter)返回给应用管理器, 客户端每秒(通过mapreduce.client.progressmonitor.pollinterval设置)向应用管理器请求进度更新, 展示给用户。
(6)作业完成
除了向应用管理器请求作业进度外, 客户端每5秒都会通过调用waitForCompletion()来检查作业是否完成。时间间隔可以通过mapreduce.client.completion.pollinterval来设置。作业完成之后, 应用管理器和Container会清理工作状态。作业的信息会被作业历史服务器存储以备之后用户核查。
1.4 Yarn调度器和调度算法
目前,Hadoop作业调度器主要有三种:
FIFO
容量(Capacity Scheduler)
公平(Fair Scheduler)。
Apache Hadoop3.1.3默认的资源调度器是Capacity Scheduler。
CDH框架默认调度器是Fair Scheduler。
具体设置详见:yarn-default.xml文件
The class to use as the resource scheduler.
yarn.resourcemanager.scheduler.class
org.apache.hadoop.yarn.server.resourcemanager.scheduler.capacity.CapacityScheduler
1.4.1 先进先出调度器(FIFO)
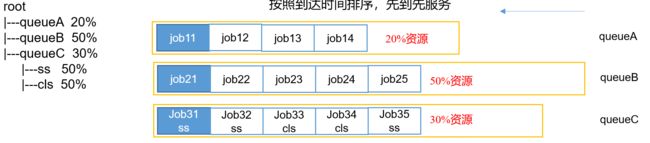
FIFO调度器(First In First Out):单队列,根据提交作业的先后顺序,先来先服务。
优点:简单易懂。
缺点:不支持多队列,生产环境很少使用。
1.4.2 容量调度器(Capacity Scheduler)
Capacity Scheduler是Yahoo开发的多用户调度器。
容器调度器特点
多队列: 每个队列可配置一定的资源量,每个队列采用FIFO调度策略;
容量保证:管理员可为每个队列设置资源最低保证和资源使用上限;
灵活性:如果一个队列中的资源有剩余,可以暂时共享给那些需要资源的队列,而一旦该队列有新的应用程序提交,则其他队列借调的资源会归还给该队列。
多租户:支持多用户共享集群和多应用程序同时运行;
为了防止同一个用户的作业独占队列中的资源,该调度器会对同一用户提交的作业所占资源量进行限定;
容量调度器资源分配算法
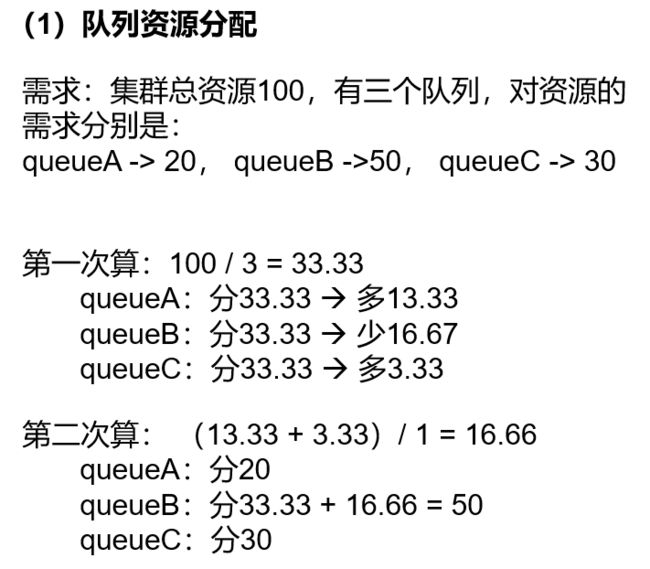
队列资源分配
从root开始,使用深度优先算法,优先选择资原占用率最低的队列分配资源。
作业资源分配
默认按照提交作业的 优先级和提交时间顺序分配资原。
容器资源分配
按照容器的优先级分配资原
如果优先级相同,按照数据本地性原则:
任务和数据在同一节点;
任务和数据在同一机架;
任务和数据不在同一节点,也不在同一机架。
1.4.3 公平调度器(Fair Scheduler)
Fair Schedulere是Facebook开发的多用户调度器。
与容量调度器相同点:
(1)多队列:支持多队列多作业
(2)容量保证:管理员可为每个队列设置资源最低保证和资源使用上限
(3)灵活性:如果一个队列中的资源有剩余,可以暂时共享给那些需要资源的队列,而一旦该队列有新的应用程序提交,则其他队列借调的资源会归还给该队列。
(4)多租户:支持多用户共享集群和多应用程序同时运行,为了防止同一个用户的作业独占队列中的资源,该调度器会对同一用户提交的作业所占资源量进行限定。
与容量调度器不同点:
(1)核心调度策略不同
容量调度器:优先选择资源利用率低的队列
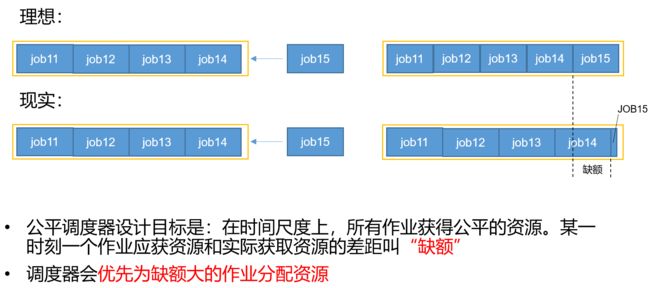
公平调度器:优先选择对资源的缺额比例大的
(2)每个队列可以单独设置资源分配方式
容量调度器: FIFO、DRF
公平调度器: FIFO、FAIR、DRF
公平调度器队列资源分配方式
FIFO策略:
公平调度器每个队列资源分配策略如果选择FIFO的话,此时公平调度器相当于上面进过的容量调度器。
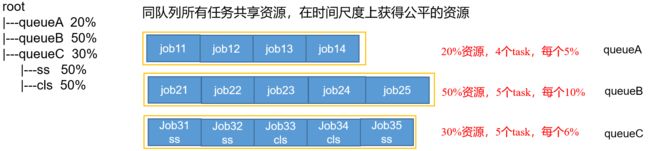
Fair策略:
Fair 策略(默认)是一种基于最大最小公平算法实现的资源多路复用方式,默认情况下,每个队列内部采用该方式分配资源。这意味着,如果一个队列中有两个应用程序同时运行,则每个应用程序可得到1/2的资源;如果三个应用程序同时运行,则每个应用程序可得到1/3的资源。
举例:
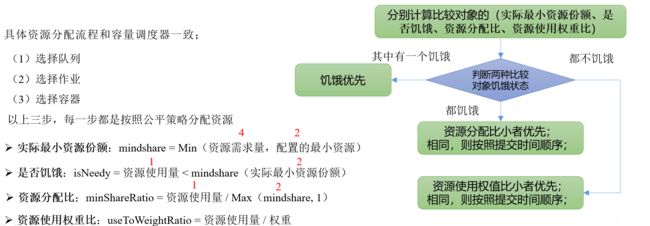
公平调度器资源分配算法
队列资源分配
作业资源分配
不加权(关注点是Job的个数)
加权(关注点是Job的权重)
DRF策略
DRF (Dominant Resource Fairness),我们之前说的资源,都是单一标准,例如只考虑内存(也是Yarn默认的情况)。但是很多时候我们资源有很多种,例如内存,CPU,网络带宽等,这样我们很难衡量两个应用应该分配的资源比例。
那么在YARN中,我们用DRF来决定如何调度:
假设集群一共有100 CPU和10T 内存,而应用A需要(2 CPU,300GB),应用B需要(6 CPU,100GB)则两个应用分别需要A(2%CPU.3%内存)和B(6%CPU1%内存)的资源,这就意味着A是内存主导的,B是CPU主导的,针对这种情况,我们可以选择DRF策略对不同应用进行不同资源(CPU和内存)的一个不同比例的限制。
第2章 Yarn案例实操
2.1 Yarn生产环境核心参数配置案例
1)需求:从1G数据中,统计每个单词出现次数。服务器3台,每台配置4G内存,4核CPU,4线程。
2)需求分析:
1G / 128m = 8个MapTask;1个ReduceTask;1个mrAppMaster
平均每个节点运行10个 / 3台 ≈ 3个任务(433)
3)修改yarn-site.xml配置参数如下:
The class to use as the resource scheduler.
yarn.resourcemanager.scheduler.class
org.apache.hadoop.yarn.server.resourcemanager.scheduler.capacity.CapacityScheduler
Number of threads to handle scheduler interface.
yarn.resourcemanager.scheduler.client.thread-count
8
Flag to determine if logical processors(such as
hyperthreads) should be counted as cores. Only applicable on Linux
when yarn.nodemanager.resource.cpu-vcores is set to -1 and
yarn.nodemanager.resource.detect-hardware-capabilities is true.
yarn.nodemanager.resource.count-logical-processors-as-cores
false
Enable auto-detection of node capabilities such as
memory and CPU.
yarn.nodemanager.resource.detect-hardware-capabilities
false
Multiplier to determine how to convert phyiscal cores to vcores. This value is used if
yarn.nodemanager.resource.cpu-vcores is set to -1(which implies auto-calculate vcores) and
yarn.nodemanager.resource.detect-hardware-capabilities is set to true. The number of vcores will be calculated as number of CPUs * multiplier.
yarn.nodemanager.resource.pcores-vcores-multiplier
1.0
Amount of physical memory, in MB, that can be allocated
for containers. If set to -1 and
yarn.nodemanager.resource.detect-hardware-capabilities is true, it is
automatically calculated(in case of Windows and Linux).
In other cases, the default is 8192MB.
yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb
4096
Number of vcores that can be allocated
for containers. This is used by the RM scheduler when allocating
resources for containers. This is not used to limit the number of
CPUs used by YARN containers. If it is set to -1 and
yarn.nodemanager.resource.detect-hardware-capabilities is true, it is
automatically determined from the hardware in case of Windows and Linux.
In other cases, number of vcores is 8 by default.
yarn.nodemanager.resource.cpu-vcores
4
The minimum allocation for every container request at the RM in MBs. Memory requests lower than this will be set to the value of this property. Additionally, a node manager that is configured to have less memory than this value will be shut down by the resource manager.
yarn.scheduler.minimum-allocation-mb
1024
The maximum allocation for every container request at the RM in MBs. Memory requests higher than this will throw an InvalidResourceRequestException.
yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-mb
2048
The minimum allocation for every container request at the RM in terms of virtual CPU cores. Requests lower than this will be set to the value of this property. Additionally, a node manager that is configured to have fewer virtual cores than this value will be shut down by the resource manager.
yarn.scheduler.minimum-allocation-vcores
1
The maximum allocation for every container request at the RM in terms of virtual CPU cores. Requests higher than this will throw an
InvalidResourceRequestException.
yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-vcores
2
Whether virtual memory limits will be enforced for
containers.
yarn.nodemanager.vmem-check-enabled
false
Ratio between virtual memory to physical memory when setting memory limits for containers. Container allocations are expressed in terms of physical memory, and virtual memory usage is allowed to exceed this allocation by this ratio.
yarn.nodemanager.vmem-pmem-ratio
2.1
4)分发配置
注意:如果集群的硬件资源不一致,要每个NodeManager单独配置。
5)重启集群
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ sbin/stop-yarn.sh
[atguigu@hadoop103 hadoop-3.1.3]$ sbin/start-yarn.sh6)执行WordCount程序
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ hadoop jar share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-3.1.3.jar wordcount /input /output7)观察Yarn任务执行页面
http://hadoop103:8088/cluster/apps
2.2 容量调度器多队列提交案例
1)在生产环境怎么创建队列?
(1)调度器默认就1个default队列,不能满足生产要求。
(2)按照框架:hive /spark/ flink 每个框架的任务放入指定的队列(企业用的不是特别多)。
(3)按照业务模块:登录注册、购物车、下单、业务部门1、业务部门2。
2)创建多队列的好处?
(1)因为担心员工不小心,写递归死循环代码,把所有资源全部耗尽。
(2)实现任务的降级使用,特殊时期保证重要的任务队列资源充足。11.11 6.18
业务部门1(重要)=》业务部门2(比较重要)=》下单(一般)=》购物车(一般)=》登录注册(次要)。
2.2.1 需求
需求1:default队列占总内存的40%,最大资源容量占总资源60%,hive队列占总内存的60%,最大资源容量占总资源80%。
2.2.2 配置多队列的容量调度器
1)在capacity-scheduler.xml中配置如下:
(1)修改如下配置
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.queues
default,hive
The queues at the this level (root is the root queue).
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.capacity
40
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.default.maximum-capacity
60
(2)为新加队列添加必要属性
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.capacity
60
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.user-limit-factor
1
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.maximum-capacity
80
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.state
RUNNING
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.acl_submit_applications
*
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.acl_administer_queue
*
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.acl_application_max_priority
*
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.maximum-application-lifetime
-1
yarn.scheduler.capacity.root.hive.default-application-lifetime
-1
2)分发配置文件
3)重启Yarn或者执行yarn rmadmin -refreshQueues刷新队列,就可以看到两条队列
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ yarn rmadmin -refreshQueues2.2.3 向Hive队列提交任务
hadoop jar的方式:
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ hadoop jar share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-3.1.3.jar wordcount -D mapreduce.job.queuename=hive /input /output
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-3.1.3]$ hadoop jar share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-3.1.3.jar wordcount -D mapreduce.job.queuename=hive /input /output打jar包的方式
默认的任务提交都是提交到default队列的。
如果希望向其他队列提交任务,需要在Driver中声明:
public class WcDrvier {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
// 配置提交 hive 队列
conf.set("mapreduce.job.queuename","hive");
//1. 获取一个Job实例
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
。。。 。。。
//6. 提交Job
boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(b ? 0 : 1);
}
}