支付宝沙箱设置
Like many data science enthusiasts I dove into this field by filling every spare minute learning the DS eco-system –namely Python, Jupyter, NumPy, Pandas, Scikit-learn, Matplotlib, and a dash of Seaborn. Together with the all powerful Unix tools –vi, less, sort, cut, grep, cat, tail, head, etc.– you have an incredibly productive framework to source, clean and analyze datasets, engineer features, run regression models, and build professional visuals. However, once your curiosity (or job) pulls you towards the “deep learning” end of the “machine learning” world, you will quickly discover –as I did– not even a high-end Macbook Pro will have enough muscle to run even the most basic convolutional neural net models (CNN for short). I figured this out quickly working through the fast.ai course by Jeremy Howard and Rachel Thomas. If you are like me and your data science training funding comes from your own pocket then I have an inexpensive, simple, yet powerful solution for you.
像许多数据科学爱好者一样,我会花很多时间学习DS生态系统,例如Python,Jupyter,NumPy,Pandas,Scikit-learn,Matplotlib和一些Seaborn,从而涉足这一领域。 连同所有强大的Unix工具(vi,更少,排序,剪切,grep,cat,tail,head等)一起,您将拥有一个非常有用的框架,可用于获取,清理和分析数据集,工程师功能,运行回归模型并进行构建专业的视觉效果。 但是,一旦您的好奇心(或工作)将您拉向“机器学习”世界的“深度学习”端,您将很快发现-就像我一样-甚至高端Macbook Pro都没有足够的肌肉来运行最基本的卷积神经网络模型(简称CNN)。 我通过Jeremy Howard和Rachel Thomas的fast.ai课程快速解决了这个问题。 如果您像我一样,并且您自己的数据科学培训经费来自您自己的口袋,那么我为您提供了一种便宜,简单但功能强大的解决方案。
Firstly, I admit I like running everything I can on my laptop. However, for some things my laptop just doesn’t cut it e.g. for my music composition hobby, I have a beefed up Intel i7 box in my basement that runs a music library server. But for training DL models an i7 and lots of RAM won’t do much for you. You need GPUs. And GPUs are expensive. But they’re not expense to rent. With the buffet table of cloud options now available in the marketplace my new MO has become, don’t buy, rent.
首先,我承认我喜欢在笔记本电脑上运行所有可以运行的东西。 但是,对于某些事情,我的笔记本电脑并没有削减它,例如,出于我的音乐创作爱好,我在地下室有一个功能强大的Intel i7盒子,可以运行音乐库服务器。 但是对于训练DL模型而言,i7和大量RAM并不会为您带来太大帮助。 您需要GPU。 而且GPU很昂贵。 但他们不是租金的开支。 随着市场上现在有可用的云计算自助餐表,我的新MO变成了( 不购买,租用) 。
Through a bit of Google’ing, and trial-and-error I setup a Jupyter based client-server sandbox using my Macbook Pro and Visual Studio Code as the client, and Jupyter server running on a high-end Linux instance on Google Cloud. The results? My DL model training now happens in seconds. On my Macbook Pro? Well, after 30 minutes running and the fan blazing away I killed the process. You get the picture?
通过一些Google的尝试和反复试验,我使用Macbook Pro和Visual Studio Code作为客户端,并在Google Cloud的高端Linux实例上运行的Jupyter服务器,设置了一个基于Jupyter的客户端-服务器沙箱。 结果? 我的DL模型训练现在只需几秒钟。 在我的Macbook Pro上? 好吧,经过30分钟的跑步,风扇燃烧了,我杀死了整个过程。 你明白了吗?
Note: This approach uses a full Linux server in the Google cloud. There are other paths that cost less e.g. Google Colab, and Kaggle Kernels. However, with this approach you gain configuration flexibility, a $300 credit (if used sparingly will last a while), and some experience with the Google Cloud Platform and using their command line interface.
注意: 此方法在Google云中使用完整的Linux服务器。 还有其他成本更低的路径,例如Google Colab和Kaggle Kernels。 但是,通过这种方法,您可以获得配置灵活性,300美元的信用额度(如果很少使用,将持续一段时间),以及一些使用Google Cloud Platform和使用其命令行界面的经验。
设定伺服器 (Setup Server)
创建GCP帐户并获得$ 300 (Create GCP account and get $300)
First step is to create an account on the Google Cloud Platform (GCP). I’m going to assume you’ve figured that out and are logged into to the GCP console. Next, check to ensure you got your $300 credit. In the top left corner click on the menu and select Billing → Overview. In the bottom right corner of the Overview you should see the Promotional credits balance. And it should be $300.
第一步是在Google Cloud Platform(GCP)上创建一个帐户。 我假设您已经解决了该问题并登录到GCP控制台。 接下来,检查以确保您获得$ 300的信用额度。 在左上角单击菜单,然后选择开票 → 总览 。 在概述的右下角,您应该看到促销信用余额。 应该是300美元。
创建您的VM服务器 (Create your VM server)
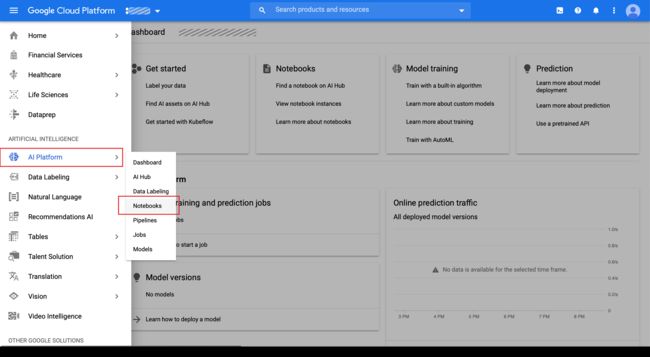
GCP now has a service for provisioning a VM server configured specifically for running Jupyter notebooks. Click on the GCP menu (top left corner) and scroll down to the ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE section. Then select AI Platform → Notebooks.
GCP现在提供了一项服务,用于提供专门配置用于运行Jupyter笔记本的VM服务器。 点击GCP菜单(左上角),然后向下滚动至ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE(人工智慧)部分。 然后选择AI Platform→笔记本 。
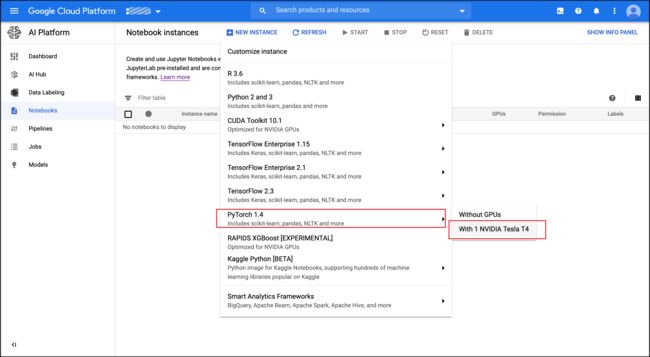
From the Notebook Instances screen select NEW INSTANCE at the top. This menu has many options including some beta and experimental choices. I am going with the PyTorch 1.4 option with one NVIDIA Tesla T4 GPU.
在“笔记本实例”屏幕上,选择顶部的“ 新建实例 ”。 此菜单有许多选项,包括一些beta和实验选项。 我将使用带有一个NVIDIA Tesla T4 GPU的PyTorch 1.4选项。
Next screen presents options. For this exercise I am going with the defaults. The Customize button allows you to add more disk space to your boot drive, add GPUs RAM, etc. The default costs $0.382 per hour. Google E2 instances are billed by the second after the first minute of usage. This default configuration will run 38.2 cents per hour. That’s 785 hours of free usage.
下一个屏幕显示选项。 对于本练习,我将使用默认值。 “ 自定义”按钮允许您向启动驱动器添加更多磁盘空间,添加GPU RAM等。默认每小时收费0.382美元。 Google E2实例在使用后的第一分钟后第二秒计费。 此默认配置将每小时运行38.2美分。 这是785小时的免费使用时间。
Once you click on Create, Google will take a couple minutes to provision your VM instance. When it’s complete you will see a screen like the following.
单击“ 创建”后, Google将需要几分钟来配置您的VM实例。 完成后,您将看到类似以下的屏幕。
You now have a fully functioning Jupyter Notebook with a powerful GPU to support DL model building. Click on OPEN JUPYTERLAB next to your Instance Name. A new tab will open in your browser and a Jupyter notebook will be opened. The interface is very straight forward. You can browse the file system, create a Git repository, or startup up a terminal session.
现在,您将拥有功能齐全的Jupyter Notebook和功能强大的GPU,以支持DL模型构建。 单击您的实例名称旁边的OPEN JUPYTERLAB 。 新的标签页将在您的浏览器中打开,并且Jupyter笔记本将被打开。 界面非常简单。 您可以浏览文件系统,创建Git存储库或启动终端会话。
At this stage you have a fully functioning, powerful DL sandbox. However, this is not a cost effective way to work. Your new VM instance is eating away at that $300 credit every second you have the instance running. I prefer to do all my data gathering, feature engineering, and initial regression work locally on my macbook. Then when I have my dataset cleaned and prepped and I am at the stage to try and fit a DL model I crank up my VM instance, connect, run my model, get my results, then shutdown the instance. To execute this workflow efficiently there’s a few more steps I will now walk through.
在此阶段,您将拥有一个功能全面,功能强大的DL沙箱。 但是,这不是一种经济有效的工作方式。 您的新VM实例每运行一秒钟,就可以得到$ 300的信用额。 我更喜欢在Macbook上本地进行所有数据收集,功能工程和初始回归工作。 然后,当我清理并准备好数据集后,正处于尝试安装DL模型的阶段,我启动了VM实例,连接,运行模型,获取结果,然后关闭实例。 为了有效地执行此工作流程,我现在将执行另外几个步骤。
停止并启动您的VM实例(在继续之前执行此步骤) (Stop and Start your VM Instance (DO THIS STEP BEFORE CONTINUING))
Go back to the Notebooks console and shutdown your instance.
返回Notebooks控制台并关闭实例。
Tip: Go to the Billing section and under Budgets & alerts create a Budget that will email you when you have reached $1 of usage.
提示:转到“结算”部分,在“ 预算和警报”下创建一个预算,当您的使用费达到1美元时,该电子邮件就会通过电子邮件发送给您。
配置VM实例以进行远程HTTP / HTTPS访问 (Configure VM Instance for Remote HTTP/HTTPS Access)
To open up remote access to your VM instance you need to do two things.
要打开对VM实例的远程访问,您需要做两件事。
Step 1. Open up HTTP access to your VM instance. From the main console menu, under the COMPUTE section, select Compute Engine → VM instances.
步骤1 。 打开对您的VM实例的HTTP访问。 在主控制台菜单中的COMPUTE部分下,选择Compute Engine→VM实例 。
Then click on your instance from the list. The details of your instance will be displayed. We need to make two changes here. Click on EDIT at the top, scroll down and check the two HTTP boxes in the Firewalls section, then scroll on to the bottom and click Save.
然后从列表中单击您的实例。 将显示您实例的详细信息。 我们需要在此处进行两项更改。 单击顶部的“ 编辑 ”,向下滚动并选中“防火墙”部分中的两个HTTP框,然后滚动到底部并单击“ 保存” 。
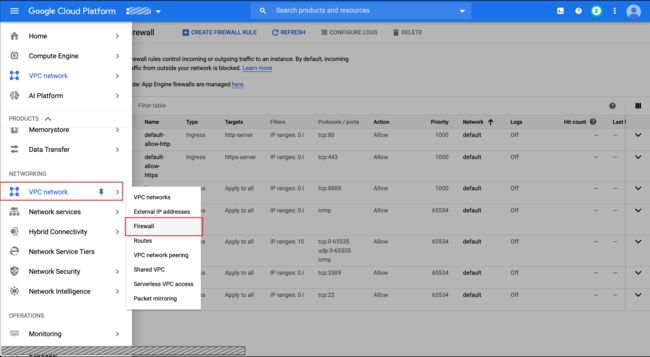
Step 2. Follow the menu below and then click CREATE FIREWALL RULE at the top of the Firewall console.
第二步 。 请遵循下面的菜单,然后单击防火墙控制台顶部的“创建防火墙规则 ”。
Input the noted fields in the following two screens.
在以下两个屏幕中输入注释的字段。
Your firewall rule should now be active. If it isn’t you will know in the next steps.
您的防火墙规则现在应该处于活动状态。 如果不是,您将在接下来的步骤中知道。
Step 3. Stop your VM Instance. Go back to the Notebooks console click the check box next to your instance and click on STOP.
步骤3.停止您的VM实例。 返回Notebooks控制台,单击实例旁边的复选框 ,然后单击STOP 。
使用Google Cloud SDK管理VM实例 (Managing VM Instance with Google Cloud SDK)
Step 1. First step is to install the SDK on you local computer. Here’s the Google instructions for downloading and installing their SDK for MacOS, Windows, and Linux. Make sure you follow all steps including putting the SDK in your PATH.
步骤1.第一步是在本地计算机上安装SDK。 这是 Google针对MacOS,Windows和Linux下载和安装其SDK的说明。 确保遵循所有步骤,包括将SDK放入PATH。
Step 2. Initialize the SDK by running the following command from a terminal.
步骤2.通过从终端运行以下命令来初始化SDK。
> gcloud init
...> You must log in to continue. Would you like to log in (Y/n)?You will be prompted to log in. When you press Y and Return you will be redirected to a Google website to log into your account. Once you successfully log in you should be returned to your terminal session where you will be prompted to select a compute region.
系统将提示您登录。按Y键和Return键后,您将被重定向到Google网站以登录您的帐户。 成功登录后,应返回到终端会话,在该会话中将提示您选择计算区域。
> Do you want to configure a default Compute Region and Zone? (Y/n)?Select Y. In one of the earlier screen shots I suggested noting your instance name and the region in which it was created. Find that region in the list that is presented and enter its index number. Once that completes run the following command.
选择Y。 在较早的屏幕快照之一中,我建议注意您的实例名称和创建实例的区域。 在显示的列表中找到该区域,然后输入其索引号。 完成后,运行以下命令。
> gcloud config listYou should see something like the following in your terminal window.
您应该在终端窗口中看到类似以下的内容。
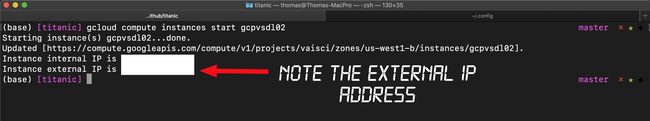
Step 3. Before we left our VM instance we shut it down. Let’s now start it back up using the SDK. Here’s the command. Replace inst_name with the name of your instance.
第三步 。 在离开VM实例之前,我们将其关闭。 现在开始使用SDK备份它。 这是命令。 将inst_name替换为实例的名称。
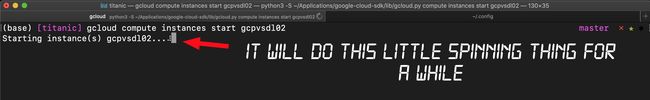
> gcloud compute instances start inst_nameNow let’s practice stopping the instance. Here’s the command.
现在让我们练习停止实例。 这是命令。
> gcloud compute instances stop inst_nameThis can take a couple minutes so just let it run. After the little spinner thing completes you should get this as a result.
这可能需要几分钟,因此只需运行它。 完成微调后,您应该得到此结果。
Once you see the …done then startup your instance again and let’s move on.
看到…完成后,再次启动实例,让我们继续。
Step 4. Time to connect to the instance and finish the server side setup. Enter the following command and replace inst_name with your instance.
步骤4.是时候连接到实例并完成服务器端设置了。 输入以下命令,并将inst_name替换为您的实例。
> gcloud compute ssh inst_nameYou will be prompted for a password. This is the account password you created initially. Next you will see a screen like the following.
系统将提示您输入密码。 这是您最初创建的帐户密码。 接下来,您将看到类似以下的屏幕。
Okay, we are almost there. Just a few configuration changes to Jupyter and then we will be able to connect with Visual Studio Code and run a model. Yeah!
好的,我们快到了。 只需对Jupyter进行一些配置更改,然后我们就可以连接Visual Studio Code并运行模型。 是的
配置Jupyter Notebook服务器 (Configure Jupyter Notebook Server)
Step 1. Create a folder for notebooks. This is where Jupyter will store notebook files. I also recommend creating two subfolder whose purpose will become clear when we run the sample model below.
步骤1.为笔记本创建一个文件夹。 Jupyter将在此处存储笔记本文件。 我还建议创建两个子文件夹,当我们运行下面的示例模型时,其目的将变得清楚。
> mkdir jnotebooks
> mkdir jnotebooks/data
> mkdir jnotebooks/picsStep 2. Create Jupyter configuration. This creates a .jupyter folder off your root directory.
步骤2.创建Jupyter配置。 这将在根目录下创建一个.jupyter文件夹。
> jupyter notebook --generate-configNow for a little tricky part. We need to configure a few Jupyter parameters in the file .jupyter/jupyter_notebook_config.py. I recommend using vim. Before editing the file note your root path by executing pwd. Here’s the parameters. All these parameters are already in the file. However, they are commented out. They need to be uncommented and modified.
现在有一点棘手的部分。 我们需要在文件.jupyter / jupyter_notebook_config.py中配置一些Jupyter参数。 我建议使用vim 。 在编辑文件之前,请通过执行pwd注意您的根路径。 这是参数。 所有这些参数已经在文件中。 但是,它们已被注释掉。 他们需要不加注释和修改。
c.NotebookApp.ip = '*'
c.NotebookApp.port = 8888
c.NotebookApp.notebook_dir = '/home/username/jnotebooks'
c.NotebookApp.open_browser = FalseRemember we created the jnotebooks folder. Enter its full path for the notebook_dir parameter.
记住,我们创建了jnotebooks文件夹。 输入notebook_dir参数的完整路径。
Here’s a short vim cheatsheet of the commands you will need.
这是您需要的简短的vim速查表。
Step 3. Set a Jupyter password. This is optional but highly recommended since we just opened HTTP access. From the command line enter the following and then enter your password. You will have to enter this every time you access this server from VSC so I recommend not going overboard here.
步骤3.设置Jupyter密码。 这是可选的,但由于我们刚刚打开HTTP访问,因此强烈建议使用。 从命令行输入以下内容,然后输入密码。 每次您从VSC访问此服务器时,都必须输入此信息,因此我建议您不要在此过分。
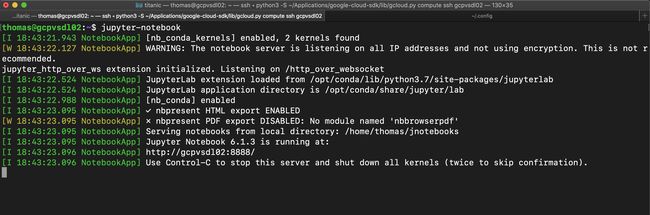
> jupyter notebook passwordStep 4. Final step here. Let’s startup the Jupyter Notebook server. Here’s the command.
步骤4.这里的最后一步。 让我们启动Jupyter Notebook服务器。 这是命令。
> jupyter-notebook而ただ ! 您应该看到类似以下的内容。 (And ta da! You should see something like the following.)
If your screen doesn’t closely resemble this then kill the process by pressing Control-c and go back and check the four parameters in the Jupyter config file.
如果您的屏幕与此不太相似,请按Control-c取消该过程,然后返回并检查Jupyter配置文件中的四个参数。
设置客户端 (Setup Client)
I am a big Visual Studio Code fan. Microsoft open-sourced it some time ago and it has since evolved quickly to become a very user friendly and highly functional editor. And the thing I find really cool is that it now fully supports Jupyter Notebooks. I personally am not in love with running notebooks in a browser when I am in work mode. I prefer a real code editor that I use for Python and Java (and hopefully Swift will be supported soon). In VSC I can build my models in notebooks and then easily export to a Python file and start moving towards production’izing my project, all in the same editor. Enough rambling. Let’s connect to our server and train a model.
我是Visual Studio Code的忠实粉丝。 微软在一段时间前开源了它,此后Swift发展成为一个非常用户友好且功能强大的编辑器。 我觉得很酷的是,它现在完全支持Jupyter Notebooks。 在工作模式下,我个人不喜欢在浏览器中运行笔记本。 我更喜欢用于Python和Java的真实代码编辑器(希望很快会支持Swift) 。 在VSC中,我可以在笔记本中构建模型,然后轻松导出到Python文件,并开始在同一编辑器中对项目进行量产化。 够乱的。 让我们连接到服务器并训练模型。
Step 1. Install and setup Visual Studio Code. If you use an Anaconda distribution then you are all set. Anaconda and VSC work well together. Otherwise click here to get the latest version for your operating system. VSC supports Jupyter natively so there’s nothing extra that needs to be installed.
步骤1 。 安装和设置Visual Studio代码。 如果您使用Anaconda发行版,那么您已经准备就绪 。 Anaconda和VSC可以很好地合作。 否则,请单击此处以获取适用于您的操作系统的最新版本。 VSC本机支持Jupyter,因此无需安装其他组件。
Step 2. Open VSC and create a new Jupyter notebook. The easiest way to do this is by using the command browser. On MacOS the command is shift+command+p. Then type in Python: Create New Blank Jupyter Notebook
步骤2.打开VSC并创建一个新的Jupyter笔记本。 最简单的方法是使用命令浏览器。 在MacOS上,命令为shift + command + p 。 然后键入Python: Create New Blank Jupyter Notebook
Step 3. Connect to your server. Did you note your external IP address when you started up your server? You’ll need it here. Once again access the command browser via shift+command+p. Then enter the command Python: Specify local or remote Jupyter server for connections
第三步 。 连接到您的服务器。 启动服务器时,您是否记下了外部IP地址? 您在这里需要它。 通过shift + command + p再次访问命令浏览器。 然后输入命令Python: Specify local or remote Jupyter server for connections
You see this next.Select Existing.
接下来您将看到此内容。选择“现有”。
Here’s where you need the external IP address of you VM instance.
在这里,您需要VM实例的外部IP地址。
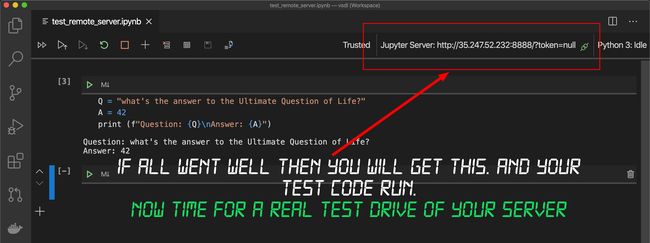
After entering your http address above and pressing return there’s a chance VSC will require a restart. If that does happen then close VSC, start it up again, and then follow this Step 3 back to this point. Type in some test Python code and execute the cell. VSC will send the code to the server and will display the returned result. Then you will see your Jupyter Server address in the top right corner like the highlight below.
在上方输入您的http地址并按回车键后,VSC可能需要重新启动。 如果确实发生这种情况,请关闭VSC,再次启动它,然后按照步骤3的步骤进行操作。 输入一些测试Python代码并执行单元格。 VSC将把代码发送到服务器,并显示返回的结果。 然后,您将在右上角看到您的Jupyter服务器地址,如下图所示。
SUCCESS! Now it’s time for some real fun!
成功! 现在是时候享受一些真正的乐趣了!
欢乐时光—训练DL模型 (FUN TIME — Train a DL Model)
I believe every data science hacker, coder, and professional is familiar with the Titanic data set at Kaggle. It’s like the “Hello World” of data science. I’ve toyed around with this data set as well. I’ve applied just basic reasoning like “assume all men die”. That will get you a mediocre score with just a few lines of code. For fun, I’ve done a lot of feature engineering and then applied all the Scikit-learn models and Xgboost. Then for real fun I thought I would apply a DL model. My model is available on Github. I recommend following along to see the workflow.
我相信所有数据科学黑客,编码人员和专业人员都对Kaggle的Titanic数据集很熟悉。 就像数据科学的“ Hello World”一样。 我也玩弄了这个数据集。 我仅应用了“假设所有人都死了”之类的基本推理。 仅需几行代码,您的评分就会变得平庸。 为了好玩,我做了很多功能设计,然后应用了所有Scikit学习模型和Xgboost。 然后为了真正的乐趣,我想我会应用DL模型。 我的模型在Github上可用。 我建议按照以下步骤查看工作流程。
Step 1. Get model from Github here.
步骤1 。 从GitHub获取模型在这里 。
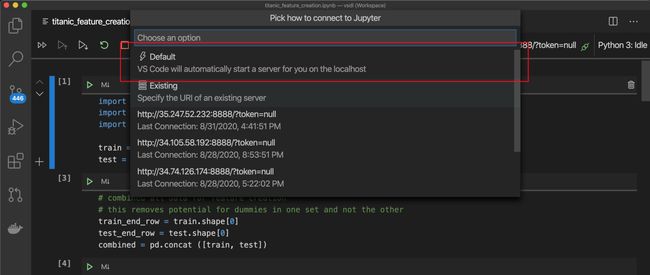
Step 2. Switch VSC to a local Python instance. shift+command+p followed by Python: Specify local or remote Jupyter server for connections then select Default from the menu. This will force a reload of VSC (hopefully this reloading requirement will go away in the future).
步骤2.将 VSC切换到本地Python实例。 shift + command + p后跟Python: Specify local or remote Jupyter server for connections然后从菜单中选择“ 默认 ”。 这将强制重新加载VSC (希望此重新加载要求将来会消失) 。
Step 3. Open the file titanic_feature_creation.ipynb in VSC and execute each cell. The final cell will write out the files titanic_train_wrangled.csv, and titanic_test_wrangled.csv into a subfolder called data. Those two files have to be copied to your VM instance.
步骤3.在VSC中打开文件titanic_feature_creation.ipynb ,然后执行每个单元。 最后一个单元将把文件titanic_train_wrangled.csv和titanic_test_wrangled.csv写出到名为data的子文件夹中。 这两个文件必须复制到您的VM实例。
Step 4. Copy data files to VM instance. From the titanic folder you retrieved from Github execute the following command. Substitute your instance name for inst_name.
步骤4.将数据文件复制到VM实例。 在您从Github检索的titanic文件夹中,执行以下命令。 将您的实例名称替换为inst_name 。
> gcloud compute scp ./data/*.csv inst_name:~/jnotebooks/data/Step 5. Connect VSC to your Server. Shift+command+p followed by Python: Specify local or remote Jupyter server for connections then select your server from the menu. This will force a reload of VSC.
步骤5 。 将VSC连接到服务器。 Sift + command + p,后跟Python: Specify local or remote Jupyter server for connections然后从菜单中选择服务器。 这将强制重新加载VSC。
Step 6. Open the file titanic_model_evaluation_cnn.ipynb. Note, in the first cell the data files that are read. You created these locally and then transferred them to your VM instance.
步骤6.打开文件titanic_model_evaluation_cnn.ipynb 。 请注意,在第一个单元格中读取的数据文件。 您在本地创建了这些,然后将它们转移到您的VM实例。
Step 7. Execute all the cells to generate a submission.csv file.
步骤7.执行所有单元格以生成submitting.csv文件。
注意事项 (Things to Note)
Disclaimer: The cell titled, Convert features to square PNG, is just a simple way to translate each row (or record) of both data files into an image for this exercise. There are many better ways to translate data for DL models. I wanted to keep it bare-bones simple for this demonstration. All created images are stored in a sub folder on the server called images_titanic.
免责声明:标题为“ 将要素转换为方形PNG ”的单元格是将两个数据文件的每一行(或记录)都转换为图像的一种简单方法。 有许多更好的方法可以转换DL模型的数据。 在此演示中,我想让它简单易行。 所有创建的图像都存储在服务器上的子文件夹images_titanic中 。
让我们看看我们如何排名! (Let’s see how we Rank!)
Step1. Now let’s retrieve the file submissions.csv that was created in the last cell shown below.
第1步。 现在,让我们检索在下面显示的最后一个单元中创建的文件submittings.csv 。
Here’s the command. Once again, substitute your instance name for inst_name.
这是命令。 再次用实例名称替换inst_name。
> gcloud compute scp inst_name:~/jnotebooks/data/submission.csv .Step 2. Visit Kaggle’s Titanic site here and submit your work.
步骤2. 在此处访问Kaggle的Titanic网站并提交您的作品。
我们怎么办? (How’d We Do?)
78% percentile is okay. Not bad. However, if you’re a real DS practitioner you would laugh at this. It’s an extreme case of over engineering. But this was not an exercise in optimal deep-learning-model engineering. This was all about how to setup a sandbox so you then go focus on building optimal models.
78%的百分比还可以。 不错。 但是,如果您是一名真正的DS从业人员,您会对此大笑。 这是过度工程的极端情况。 但这不是最佳的深度学习模型工程中的练习。 这是所有关于如何建立一个沙箱,所以你然后再重点打造最佳的车型。
One last thing.
最后一件事。
翻译自: https://medium.com/@tmmorris/setup-your-own-deep-learning-sandbox-quick-guide-9f09e140baef
支付宝沙箱设置