Mac M1芯片安装PyTorch、GPU加速环境
文章目录
- 1. 安装Xcode
- 2. 新建一个conda环境
- 3. 用pip命令安装torch
- 4. 重装Numpy
- 5. Jupyter Lab虚拟环境的配置
- 6. 环境测试代码
-
- 6.1 测试代码1
- 6.2 测试代码2
- 6.3 在Mac M1中指定使用GPU加速
1. 安装Xcode
通过App store安装或者使用命令$ xcode-select --install安装
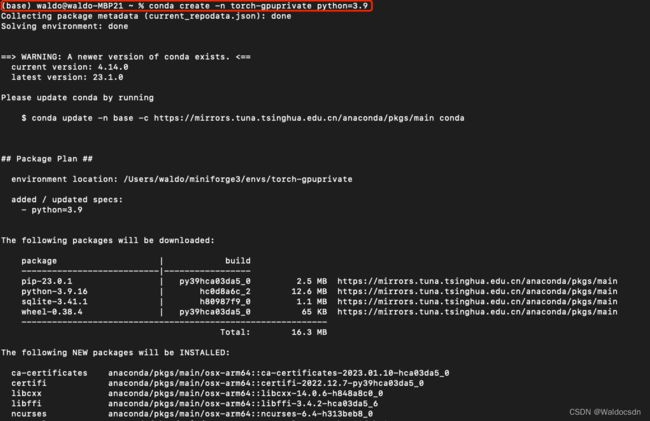
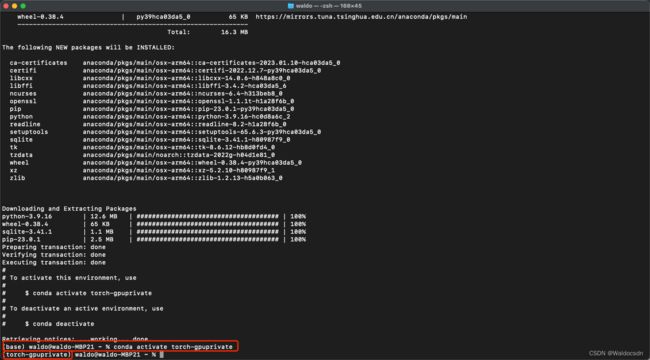
2. 新建一个conda环境
$ conda create -n torch-gpuprivate python=3.9
$ conda activate torch-gpuprivate
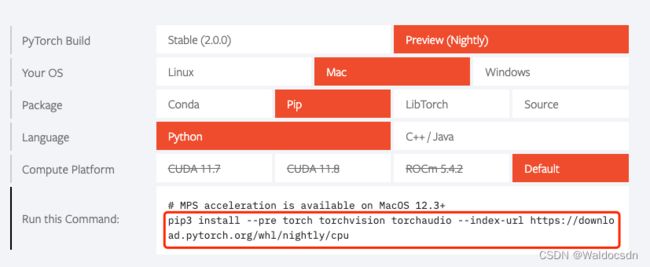
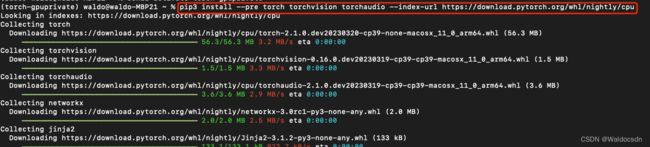
3. 用pip命令安装torch
pip3 install --pre torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/cpu
4. 重装Numpy
通过上述方式安装的PyTorch可能自带的Numpy太低,所以重新安装Numpy:
pip uninstall numpy # 这样会移除刚刚安装的Pytorch以及一些其他的第三方库
pip install numpy
或者
conda uninstall numpy # 这样会移除刚刚安装的Pytorch以及一些其他的第三方库
conda install numpy
使用“conda list”可以查看此conda环境内的包和各个包的版本。使用“conda deactivate”可退出当前conda环境。
5. Jupyter Lab虚拟环境的配置
这一步是要将此conda环境“torch-gpuprivate”,添加进Jupyter Lab的Kernel
conda activate torch-gpuprivate //注意替换成自己的虚拟环境名
conda install ipykernel //安装ipykernel
sudo python -m ipykernel install --name torch-gpuprivate //在ipykernel中安装当前环境
conda deactivate
此时打开Jupyter Lab切换Kernel,已出现刚刚安装的“torch-gpuprivate”conda环境。
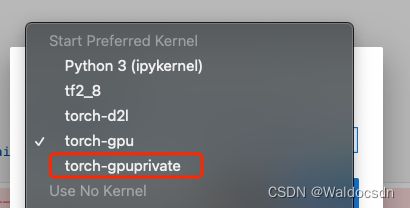
6. 环境测试代码
6.1 测试代码1
import torch
import math
# this ensures that the current MacOS version is at least 12.3+
print(torch.backends.mps.is_available())
# this ensures that the current current PyTorch installation was built with MPS activated.
print(torch.backends.mps.is_built())
6.2 测试代码2
dtype = torch.float
device = torch.device("mps")
# Create random input and output data
x = torch.linspace(-math.pi, math.pi, 2000, device=device, dtype=dtype)
y = torch.sin(x)
# Randomly initialize weights
a = torch.randn((), device=device, dtype=dtype)
b = torch.randn((), device=device, dtype=dtype)
c = torch.randn((), device=device, dtype=dtype)
d = torch.randn((), device=device, dtype=dtype)
learning_rate = 1e-6
for t in range(2000):
# Forward pass: compute predicted y
y_pred = a + b * x + c * x ** 2 + d * x ** 3
# Compute and print loss
loss = (y_pred - y).pow(2).sum().item()
if t % 100 == 99:
print(t, loss)
# Backprop to compute gradients of a, b, c, d with respect to loss
grad_y_pred = 2.0 * (y_pred - y)
grad_a = grad_y_pred.sum()
grad_b = (grad_y_pred * x).sum()
grad_c = (grad_y_pred * x ** 2).sum()
grad_d = (grad_y_pred * x ** 3).sum()
# Update weights using gradient descent
a -= learning_rate * grad_a
b -= learning_rate * grad_b
c -= learning_rate * grad_c
d -= learning_rate * grad_d
print(f'Result: y = {a.item()} + {b.item()} x + {c.item()} x^2 + {d.item()} x^3')
6.3 在Mac M1中指定使用GPU加速
To run PyTorch code on the GPU, use torch.device(“mps”) analogous to torch.device(“cuda”) on an Nvidia GPU. Hence, in this example, we move all computations to the GPU:
要在 Mac M1的GPU 上运行 PyTorch 代码,使用命令 torch.device("mps")来指定。这类似于 Nvidia GPU 上的torch.device("cuda")命令。具体使用方法见下图代码: