jdk1.8 HashMap扩容机制变化
概述
JDK1.8中的HashMap较于前代有了较大的变更,主要变化在于扩容机制的改变。在JDK1.7及之前HashMap在扩容进行数组拷贝的时候采用的是头插法,因此会造成并发情景下形成环状链表造成死循环的问题。JDK1.8中改用了尾插法进行数组拷贝,修复了这个问题。
其次,JDK1.8开始HashMap改用数组+链表/红黑树组合的数据结构来提高查询效率,降低哈希冲突产生的链表过长导致的查询效率减缓现象。
本文的主要内容是对JDK1.8中的扩容机制与前代进行比较。
JDK1.8之前的扩容
由resize()和transfer()两个方法共同完成。
/**
* Rehashes the contents of this map into a new array with a
* larger capacity. This method is called automatically when the
* number of keys in this map reaches its threshold.
*
* If current capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY, this method does not
* resize the map, but sets threshold to Integer.MAX_VALUE.
* This has the effect of preventing future calls.
*
* @param newCapacity the new capacity, MUST be a power of two;
* must be greater than current capacity unless current
* capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY (in which case value
* is irrelevant).
*/
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
// 新建数组
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
// 拷贝原数据
transfer(newTable);
// 得到新数组
table = newTable;
// 更改阈值
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
}
/**
* Transfers all entries from current table to newTable.
*/
void transfer(Entry[] newTable) {
Entry[] src = table;
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (int j = 0; j < src.length; j++) {
// 获取当前node节点 e
Entry e = src[j];
if (e != null) {
// 将原数组该位置置空
src[j] = null;
do {
// 获取下一元素
Entry next = e.next;
// 计算元素在新数组中的索引
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
// 头插法 插入新数组中
e.next = newTable[i];
// 在新索引位置放入元素
newTable[i] = e;
// e 指向下一元素
e = next;
} while (e != null); //直至e为空,即全部复制完毕
}
}
}
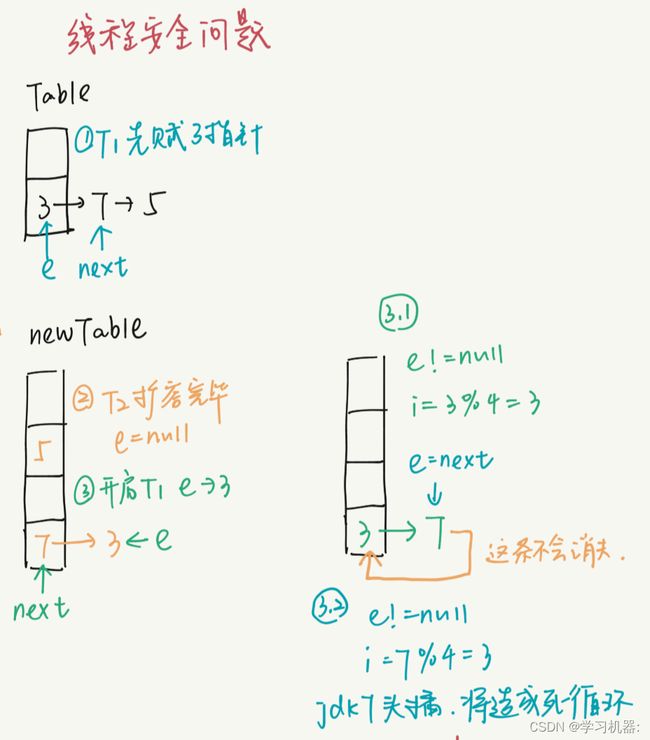
线程不安全问题
拷贝原数据采用的是头插法,在并发场景下,如果两个值在新数组中哈希冲突一样会出现环状链表的情形,最终导致死循环。如下图所示:
JDK1.8中的扩容
JDK1.8中将transfer()方法的操作也放入了resize()方法中,而由于JDK1.8引入了红黑树的结构,扩容的操作看起来也更加复杂。
/**
* Initializes or doubles table size. If null, allocates in
* accord with initial capacity target held in field threshold.
* Otherwise, because we are using power-of-two expansion, the
* elements from each bin must either stay at same index, or move
* with a power of two offset in the new table.
*
* @return the table
*/
final Node[] resize() {
Node[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
// 新建数组
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node[] newTab = (Node[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
// 数据转移操作
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
// 元素没有后续节点,直接放入新数组对应索引位置
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
// 元素是树节点,进行树转移操作(本文暂不考虑)
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order
// 不是树节点并且有后续节点那就只剩下链表形式了
Node loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node next;
// 尾插法转移链表数据
do {
next = e.next;
// 索引不进行变化,放入新数组和原数组一样的位置
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
// 直接放入
loHead = e;
else
// 尾插法
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
// 需要重新计算元素在新数组中的位置
if (hiTail == null)
// 直接放入
hiHead = e;
else
// 尾插法
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
// 重新计算的数组索引位置也就是原索引加上原数组长度
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
这里对 if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) 进行一个解释说明
- 这个结果等于0时,则将该头节点放到新数组时的索引位置等于其在旧数组时的索引位置,记为低位区链表lo开头-low;
- 不等于0时,则将该头节点放到新数组时的索引位置等于其在旧数组时的索引位置再加上旧数组长度,记为高位区链表hi开头high.
具体推演过程见
(2条消息) HashMap扩容时的rehash方法中(e.hash & oldCap) == 0算法推导_Dylanu的博客-CSDN博客_e.hash![]() https://blog.csdn.net/u010425839/article/details/106620440
https://blog.csdn.net/u010425839/article/details/106620440