开源项目gin-vue-admin学习笔记
目录
-
- 开篇
- 克隆报错
- 用到的开源库
-
- cobra
-
- 说明
- 小试牛刀
-
- 1.项目初始化
- 2.生成命令行模板
- 3.编译
- 4.执行
- 开发方式
-
- 初始化子文件
- 修改并增加自定义代码
- 编译运行
- 知识点
- flag
-
- 说明
- 小试牛刀
-
- 1.项目初始化
- 2.编码
- Viper
-
- 说明
- 小试牛刀
- 小知识
-
- 反射
开篇
为了学习go的使用,利用开源项目gin-vue-admin来熟悉go编程的“套路”
克隆报错
解决方式:
在克隆的目标文件夹中执行下方命令
> git init
> git config http.postBuffer 524288000
> git config http.sslVerify "false"
再次克隆成功。
用到的开源库
cobra
说明
cobra 是用于编写命令行工具的一个go语言库,一般用于项目初始化或者修改配置。
cobra有以下几种基本概念,以命令 rm -rf aaa.md为例说明:
- command :具体的命令 如rm
- flag:命令的标志 如 -rf
- args:命令参数 如 aaa.md
小试牛刀
用一个小项目来学习他的使用
1.项目初始化
go mod init todo
安装库
go get -u github.com/spf13/cobra/cobra
2.生成命令行模板
在项目跟目录执行
cobra init --pkg-name todo -a shalk -l mit
执行完成后会在当前文件下生成目录
3.编译
go build
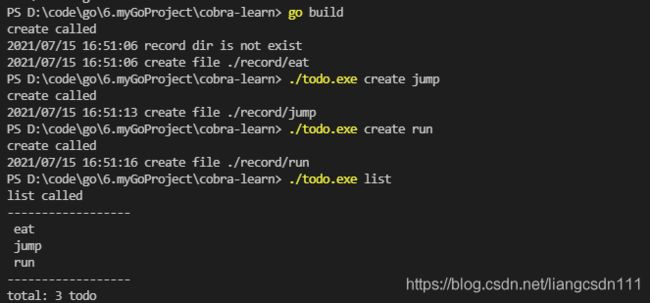
4.执行
./todo -h
输出内容:
开发方式
一般开发使用上述的命令行来配合开发。上节生成的代码中 root,go内容如下
package cmd
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"github.com/spf13/cobra"
"github.com/spf13/viper"
)
var cfgFile string
// rootCmd represents the base command when called without any subcommands
var rootCmd = &cobra.Command{
Use: "todo",
Short: "A brief description of your application",
Long: `A longer description that spans multiple lines and likely contains
examples and usage of using your application. For example:
Cobra is a CLI library for Go that empowers applications.
This application is a tool to generate the needed files
to quickly create a Cobra application.`,
// Uncomment the following line if your bare application
// has an action associated with it:
// Run: func(cmd *cobra.Command, args []string) { },
}
// Execute adds all child commands to the root command and sets flags appropriately.
// This is called by main.main(). It only needs to happen once to the rootCmd.
func Execute() {
cobra.CheckErr(rootCmd.Execute())
}
func init() {
cobra.OnInitialize(initConfig)
// Here you will define your flags and configuration settings.
// Cobra supports persistent flags, which, if defined here,
// will be global for your application.
rootCmd.PersistentFlags().StringVar(&cfgFile, "config", "", "config file (default is $HOME/.todo.yaml)")
// Cobra also supports local flags, which will only run
// when this action is called directly.
rootCmd.Flags().BoolP("toggle", "t", false, "Help message for toggle")
}
// initConfig reads in config file and ENV variables if set.
func initConfig() {
if cfgFile != "" {
// Use config file from the flag.
viper.SetConfigFile(cfgFile)
} else {
// Find home directory.
home, err := os.UserHomeDir()
cobra.CheckErr(err)
// Search config in home directory with name ".todo" (without extension).
viper.AddConfigPath(home)
viper.SetConfigType("yaml")
viper.SetConfigName(".todo")
}
viper.AutomaticEnv() // read in environment variables that match
// If a config file is found, read it in.
if err := viper.ReadInConfig(); err == nil {
fmt.Fprintln(os.Stderr, "Using config file:", viper.ConfigFileUsed())
}
}
一般 todo为命令行名称,我们需要一些动作来完成功能,比如 :
- todo create xxx
- todo list xxx
- todo delete
这些 add list delete被称为子命令。
子命令需要在init函数中利用 rootCmd.AddCommand()注册,而且子命令为单独文件编写,可以利用cora自身来初始化这些子文件。
注意
初始化子文件
cobra add create
cobra add delete
cobra add list
create.go内容如下
package cmd
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/spf13/cobra"
)
// createCmd represents the create command
var createCmd = &cobra.Command{
Use: "create",
Short: "A brief description of your command",
Long: `A longer description that spans multiple lines and likely contains examples
and usage of using your command. For example:
Cobra is a CLI library for Go that empowers applications.
This application is a tool to generate the needed files
to quickly create a Cobra application.`,
Run: func(cmd *cobra.Command, args []string) {
fmt.Println("create called")
},
}
func init() {
rootCmd.AddCommand(createCmd)
// Here you will define your flags and configuration settings.
// Cobra supports Persistent Flags which will work for this command
// and all subcommands, e.g.:
// createCmd.PersistentFlags().String("foo", "", "A help for foo")
// Cobra supports local flags which will only run when this command
// is called directly, e.g.:
// createCmd.Flags().BoolP("toggle", "t", false, "Help message for toggle")
}
修改并增加自定义代码
create.go
package cmd
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"github.com/spf13/cobra"
)
// createCmd represents the create command
var createCmd = &cobra.Command{
Use: "create",
Short: "crate todo ",
Long: `create my todo `,
Run: func(cmd *cobra.Command, args []string) {
fmt.Println("create called")
//新建文件夹
_, err := os.Stat("record")
if os.IsNotExist(err) {
log.Printf("record dir is not exist")
err := os.Mkdir("record", 644)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
//新建文件
fileName := "./record/" + args[0]
_, err = os.Stat(fileName) //检查文件是否存在
if os.IsNotExist(err) {
file, err := os.Create(fileName)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
log.Printf("create file %s", fileName)
defer file.Close()
} else {
}
},
//自定义增加的代码 结束
}
func init() {
rootCmd.AddCommand(createCmd)
}
list.go
package cmd
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"os"
"github.com/spf13/cobra"
)
// listCmd represents the list command
var listCmd = &cobra.Command{
Use: "list",
Short: "list todo",
Long: `list todo`,
Run: func(cmd *cobra.Command, args []string) {
fmt.Println("list called")
_, err := os.Stat("record")
if os.IsNotExist(err) {
log.Fatal("record dir is not exits")
}
dirs, err := ioutil.ReadDir("record")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("read record dir fail")
}
fmt.Println("------------------")
for _, dir := range dirs {
fmt.Printf(" %s\n", dir.Name())
}
fmt.Println("------------------")
fmt.Printf("total: %d todo\n", len(dirs))
},
}
func init() {
rootCmd.AddCommand(listCmd)
}
delete.go
package cmd
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"github.com/spf13/cobra"
)
// deleteCmd represents the delete command
var deleteCmd = &cobra.Command{
Use: "delete todo",
Short: "delete todo",
Long: `delete todo`,
Run: func(cmd *cobra.Command, args []string) {
fmt.Println("delete called")
fileName := "./record/" + args[0]
stat, err := os.Stat(fileName)
if os.IsNotExist(err) {
log.Fatalf("todo %s is not exist", fileName)
}
if stat.IsDir() {
log.Fatalf("%s is dir , can not be deleted", fileName)
}
err2 := os.Remove(fileName)
if err2 != nil {
log.Fatalf("delete %s fail, err%v", fileName, err)
} else {
log.Printf("delete post %s success", fileName)
}
},
}
func init() {
rootCmd.AddCommand(deleteCmd)
}
编译运行
go bulid
知识点
- log.Fatal(“xxxx”)的作用相当于 printf(“xxxx”) os.Exit(0)两句话的含义,无论是Fotal还是 Exit 都执行函数的defer
- panic()会执行函数的defer,并会一直上传传播,类似java的异常机制
- log为go自带包,可以直接使用
- init函数在go中先于 main函数执行,用来进行一些初始化操作
flag
说明
flag库是用于获取命令行选项的一个go库。要想获取命令
docker exec -it -p 8000:8080 /bin/bash中 获取 -p 对应的网络端口,可以使用flag库。
小试牛刀
1.项目初始化
go mod init flag-learn
2.编码
Viper
说明
Viper是一个读取和设置配置的go库。支持以下特性:
Viper能够为你执行下列操作:
- 查找、加载和反序列化
JSON、TOML、YAML、HCL、INI、envfile和Java properties格式的配置文件。- 提供一种机制为你的不同配置选项设置默认值。
- 提供一种机制来通过命令行参数覆盖指定选项的值。
- 提供别名系统,以便在不破坏现有代码的情况下轻松重命名参数。
- 当用户提供了与默认值相同的命令行或配置文件时,可以很容易地分辨出它们之间的区别。
Viper会按照下面的优先级。每个项目的优先级都高于它下面的项目:
- 显示调用
Set设置值- 命令行参数(flag)
- 环境变量
- 配置文件
- key/value存储
小试牛刀
1.项目初始化
go mod init conf
go get github.com/spf13/viper
小知识
反射
javascirpt 在运行时可以访问自己的类型,所以不需要反射,而go不行。类似于java,go也有反射,反射简单来说就是提供了在运行时获取变量类型、以及其他扩展功能的一种操作方法
上代码:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"reflect"
)
type Student struct {
Name string
Age uint8
Sex bool
}
func main() {
fmt.Println("reflect test begin")
zs := Student{Name: "张三", Age: 20, Sex: true}
fmt.Printf("zs is %v\r\n", zs)
//反射测试
//1.获取变量的基本信息
t := reflect.TypeOf(zs)
v := reflect.ValueOf(zs)
k := v.Kind()
fmt.Printf("type is %v\r\n", t) //获取类型 student
fmt.Printf("val is %v\r\n", v) //获取值
fmt.Printf("kind is %v\r\n", k) //获取种类 struct 注意和类型的区别
//遍历变量的key val
fieldNum := v.NumField()
fmt.Printf("zs has %d field\r\n", fieldNum)
//遍历
for i := 0; i < fieldNum; i++ {
key := t.Field(i)
val := v.Field(i)
fmt.Printf("第 %d 个 字段的键为: %v 值为:%v\r\n", i, key.Name, val)
}
}
- TypeOf 用于获取变量类型
- TypeOf 用于获取变量值
- type.Kind() 用于获取变量的种类
- val.NumField() 用于获取类型中的所有字段的总个数
- typ.Field(i) 获取结构体中第i个字段名称
- val.Field(i)获取结构体中第i个字段值
类型和种类的区别是:类型表示了改变量的类型,必须自定义结构体为 type student struct 那么他的类型为student,他的种类为 struct
输出如下: