啊哈C语言 第三章 【代码】【习题答案】
目录
第2节 判断正数
如果a大于0,则显示yes:
如果a大于0显示yes,如果a小于等于0显示no:
判断一个数是否小于或等于100,如果是则输出yes:
输入正数时显示yes,输入负数时显示no,输入0时显示0:
第3节 偶数判断
如果a除以2的余数与0相等,则输出yes;不相等则输出no:
判断一个数是否是7的倍数:
判断一个数的末尾是不是0?如果是则输出yes,不是则输出no:
第4节 神器else
读入一个整数判断它是否为偶数:
判断一个数的末尾是否为7,如果是则打印yes,不是则打印no:
输出正整数,判断这个数是否为1~9,如果是输出yes,否则输出no:
第5节 请告诉我谁大
如何让计算机判断两个数中谁更大:
读入两个整数,判断它们是否相等,如果相等输出yes,否则输出no:
第6节 逻辑挑战2:3个数怎么办
找出3个数中最大的数:
分别比较变量a和b,以及变量a和c的关系:
判断是否为7的倍数或者末尾含7的数,如果是输出yes,否则输出no:
从键盘任意读入3个整数,找出最小的一个:
从键盘任意读入4个整数,找出最大的一个:
输入一个整数年份,判断这个年份是否为闰年,是输出yes否输出no:
第7节 逻辑挑战3:我要排序
把3个数从大到小排序(直接法):
把3个数从大到小排序(换位法):
如果是奇数输出这个数后面3个数,如果是偶数输出这个数前面3个数:
从键盘读入任意4个整数,将其从小到大输出:
第9节 1 > 2 究竟对不对
如果1 > 2成立输出yes,否则输出no:
如果if是1会输出什么?:
如果if是-5会输出什么?:
如果if是0会输出什么?:
如下3个程序都是打印yes:
第10节 讨厌的嵌套
如何在三个数中找出最大的一个数:
第2节 判断正数
如果a大于0,则显示yes:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
if (a > 0)
{
printf("yes\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
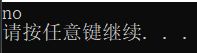
} 调试结果:
如果a大于0显示yes,如果a小于等于0显示no:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
if (a > 0)
{
printf("yes\n");
}
if (a <= 0)
{
printf("no\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
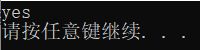
} 调试结果:
判断一个数是否小于或等于100,如果是则输出yes:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
if (a <= 100);
{
printf("yes\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
输入正数时显示yes,输入负数时显示no,输入0时显示0:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
if (a > 0)
{
printf("yes\n");
}
if (a == 0)
{
printf("0\n");
}
if (a < 0)
{
printf("no\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
第3节 偶数判断
如果a除以2的余数与0相等,则输出yes;不相等则输出no:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
if (a % 2 == 0)
{
printf ("yes\n");
}
if (a % 2 != 0)
{
printf("no\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
判断一个数是否是7的倍数:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
if (a % 7 == 0)
{
printf("yes\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
判断一个数的末尾是不是0?如果是则输出yes,不是则输出no:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
if (a % 10 == 0)
{
printf("yes\n");
}
if (a % 10 != 0)
{
printf("no\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
第4节 神器else
读入一个整数判断它是否为偶数:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
if (a % 2 == 0)
{
printf("yes\n");
}
if (a % 2 != 0)
{
printf("no\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
判断一个数的末尾是否为7,如果是则打印yes,不是则打印no:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
if (a % 10 == 7)
{
printf("yes\n");
}
else
{
printf("no\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
输出正整数,判断这个数是否为1~9,如果是输出yes,否则输出no:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
if (a >= 1 && a <= 9)
{
printf("yes\n");
}
else
{
printf("no\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
第5节 请告诉我谁大
如何让计算机判断两个数中谁更大:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
if (a > b)
{
c = a;
}
else
{
c = b;
}
printf("%d\n", c);
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
读入两个整数,判断它们是否相等,如果相等输出yes,否则输出no:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
if (a == b)
{
printf("yes\n");
}
else
{
printf("no\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
第6节 逻辑挑战2:3个数怎么办
找出3个数中最大的数:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a, b, c, d;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
if (a > b)
{
d = a;
}
else
{
d = b;
}
if (d < c)
{
d = c;
}
printf("%d\n", d);
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
分别比较变量a和b,以及变量a和c的关系:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
if (a >= b && a >= c)
{
printf("%d\n", a);
}
if (b > a && b >= c)
{
printf("%d\n", b);
}
if (c > a && c > b)
{
printf("%d\n", c);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
判断是否为7的倍数或者末尾含7的数,如果是输出yes,否则输出no:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
if (a % 7 == 0 || a % 10 == 7)
{
printf("yes\n");
}
else
{
printf("no\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
从键盘任意读入3个整数,找出最小的一个:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a, b, c, d;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
if (a < b)
{
d = a;
}
else
{
d = b;
}
if (d > c)
{
d = c;
}
printf("%d\n", d);
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
从键盘任意读入4个整数,找出最大的一个:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a, b, c, d,e;
scanf("%d %d %d %d", &a, &b, &c, &d);
if (a > b)
{
e = a;
}
else
{
e = b;
}
if (e < c)
{
e = c;
}
if (e < d)
{
e = d;
}
printf("%d\n", e);
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
输入一个整数年份,判断这个年份是否为闰年,是输出yes否输出no:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
if (a % 4 == 0 && a % 100 != 0 || a % 400 == 0 || a % 172800 == 0)
{
printf("yes\n");
}
else
{
printf("no\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
第7节 逻辑挑战3:我要排序
把3个数从大到小排序(直接法):
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
if (a >= b && b >= c)
{
printf("%d %d %d\n", a, b, c);
}
if (a >= c && c > b)
{
printf("%d %d %d\n", a, c, b);
}
if (b > a && a >= c)
{
printf("%d %d %d\n", b, a, c);
}
if (b >= c && c > a)
{
printf("%d %d %d\n", b, c, a);
}
if (c > a && a >= b)
{
printf("%d %d %d\n", c, a, b);
}
if (c > b && b > a)
{
printf("%d %d %d\n", c, b, a);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:
把3个数从大到小排序(换位法):
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a, b, c, t;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
if (a < b)
{
t = a;
a = b;
b = t;
}
if (a < c)
{
t = a;
a = c;
c = t;
}
if (b < c)
{
t = b;
b = c;
c = t;
}
printf("%d %d %d\n", a, b, c);
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
如果是奇数输出这个数后面3个数,如果是偶数输出这个数前面3个数:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
if (a % 2 == 1)
{
printf("%d", a + 1);
printf("%d", a + 2);
printf("%d\n", a + 3);
}
else
{
printf("%d", a - 1);
printf("%d", a - 2);
printf("%d\n", a - 3);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
从键盘读入任意4个整数,将其从小到大输出:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a, b, c, d, t;
scanf("%d %d %d %d", &a, &b, &c, &d);
if (a > b)
{
t = a;
a = b;
b = t;
}
if (a > c)
{
t = a;
a = c;
c = t;
}
if (a > d)
{
t = a;
a = d;
d = t;
}
if (b > c)
{
t = b;
b = c;
c = t;
}
if (b > d)
{
t = b;
b = d;
d = t;
}
if (c > d)
{
t = c;
c = d;
d = t;
}
printf("%d %d %d %d\n", a, b, c, d);
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
第9节 1 > 2 究竟对不对
如果1 > 2成立输出yes,否则输出no:
#include
#include
int main()
{
if (1 > 2)
{
printf("yes\n");
}
else
{
printf("no\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
如果if是1会输出什么?:
#include
#include
int main()
{
if (1)
{
printf("yes\n");
}
else
{
printf("no\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
如果if是-5会输出什么?:
#include
#include
int main()
{
if (-5)
{
printf("yes\n");
}
else
{
printf("no\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
如果if是0会输出什么?:
#include
#include
int main()
{
if (0)
{
printf("yes\n");
}
else
{
printf("no\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
如下3个程序都是打印yes:
#include
#include
int main()
{
if (8)
{
printf("yes\n");
}
else
{
printf("no\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} #include
#include
int main()
{
if (1000)
{
printf("yes\n");
}
else
{
printf("no\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} #include
#include
int main()
{
if (-123)
{
printf("yes\n");
}
else
{
printf("no\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果:
第10节 讨厌的嵌套
如何在三个数中找出最大的一个数:
#include
#include
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
if (a >= b) //a >= b 成立的情况
{
if (a >= c) //进一步讨论a与c的关系
{
printf("%d\n", a);
}
else
{
printf("%d\n", c);
}
}
else //a >= b 不成立的情况
{
if (b >= c) //进一步讨论b与c的关系
{
printf("%d\n", b);
}
else
{
printf("%d\n", c);
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
} 调试结果: